Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 16, 2021; 9(20): 5730-5736
Published online Jul 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i20.5730
Published online Jul 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i20.5730
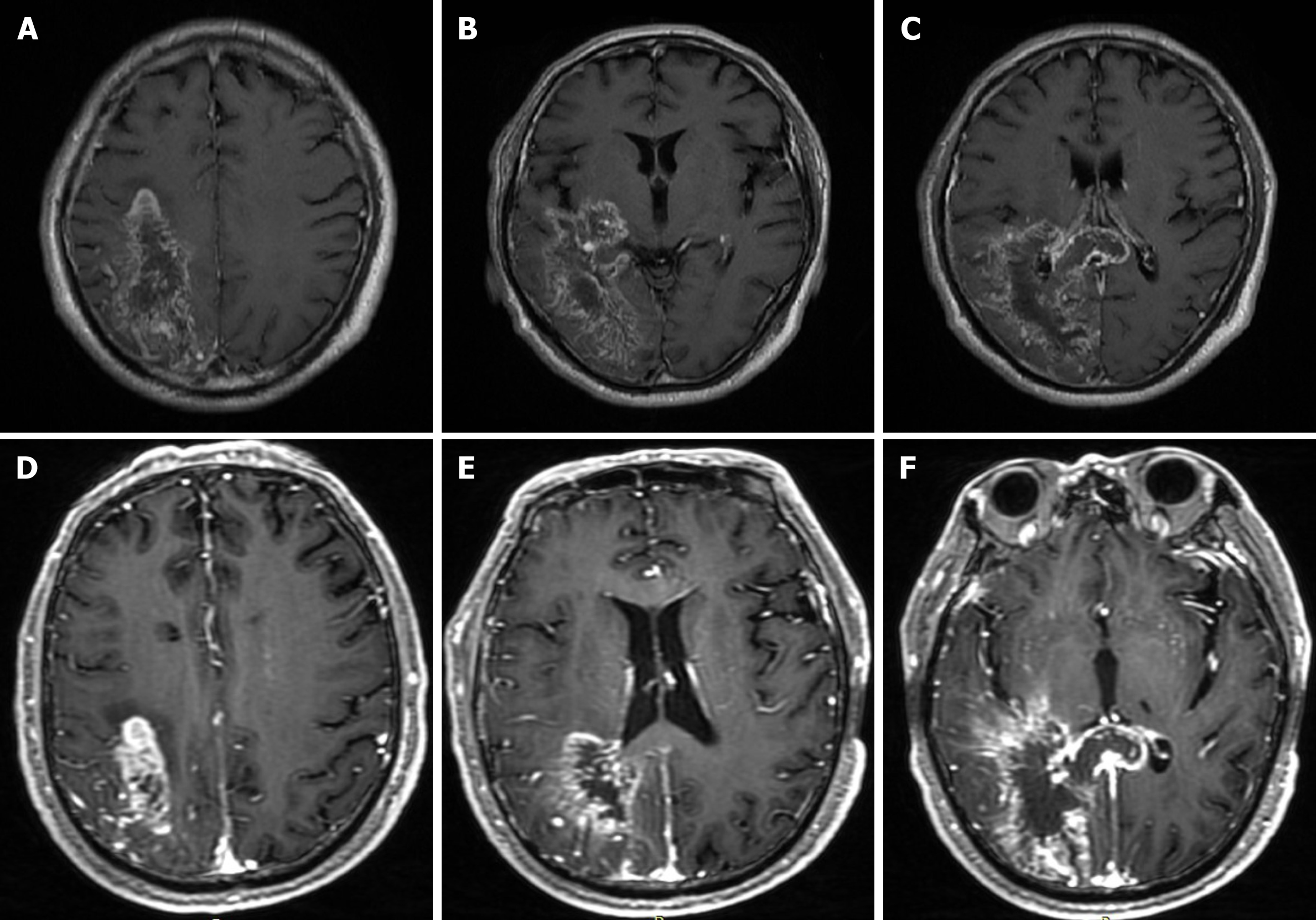
Figure 1 Brain magnetic resonance imaging.
T1-weighted images showed different locations of a massive cerebral infarction accompanied by minor bleeding and gliosis. A: The right parietal lobe; B: The right temporal lobe and the occipital lobe; C: The right temporal lobe, the occipital lobe and the corpus callosum. Enhanced T1-weighted images showed irregular ring enhancement; D: The right parietal lobe; E: the right temporal lobe and the occipital lobe; F: The right temporal lobe, the occipital lobe and the corpus callosum.
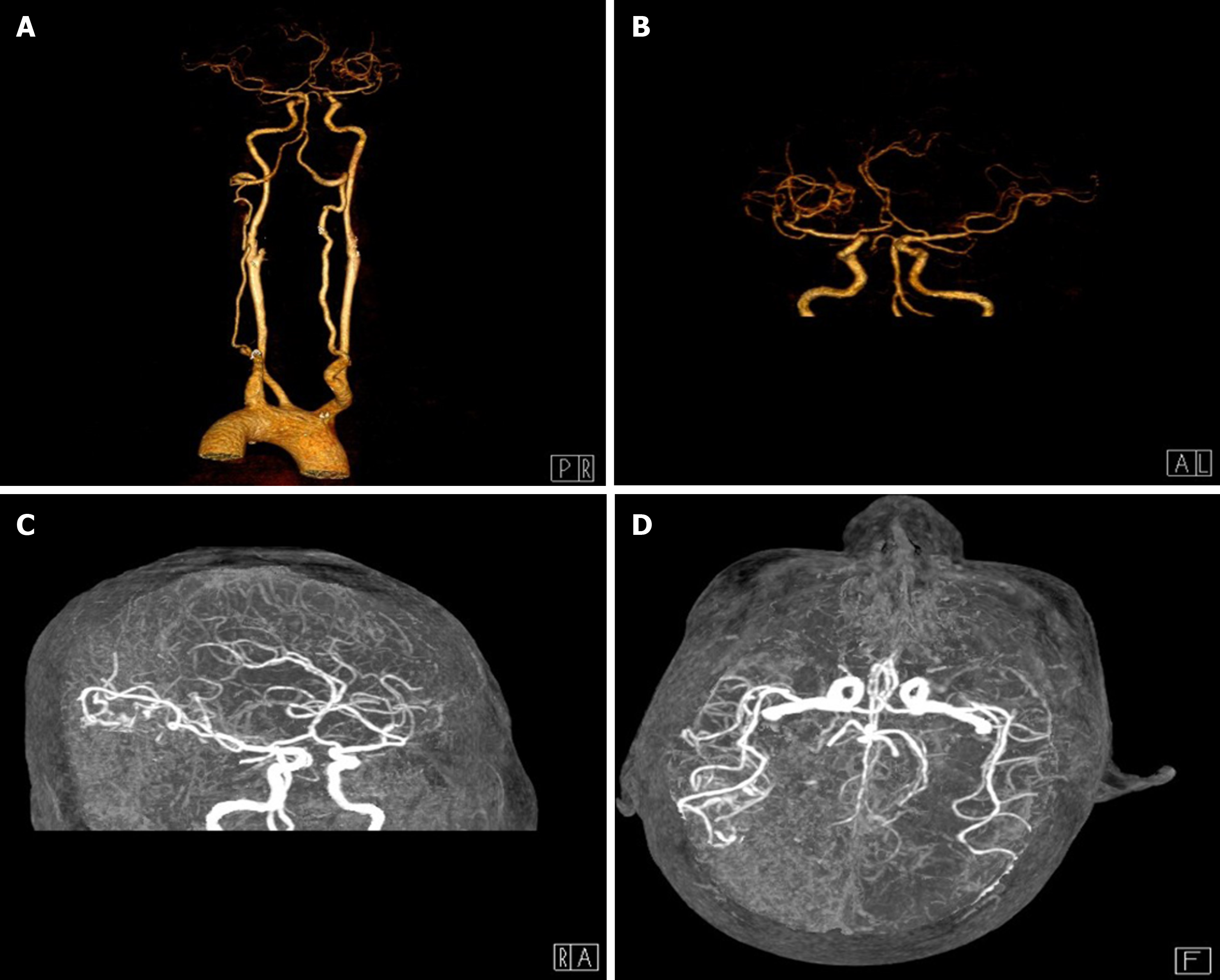
Figure 2 Brain computed tomography angiography.
Computed tomography angiography showed different locations of artery stenosis and hyperplasia. A: Mild stenosis in the internal carotid arteries on both sides at the beginning; B: The right middle cerebral artery with hyperplasia; C: The thickness of the anterior cerebral arteries on both sides was uneven; D: The posterior cerebral artery on the right was slender.
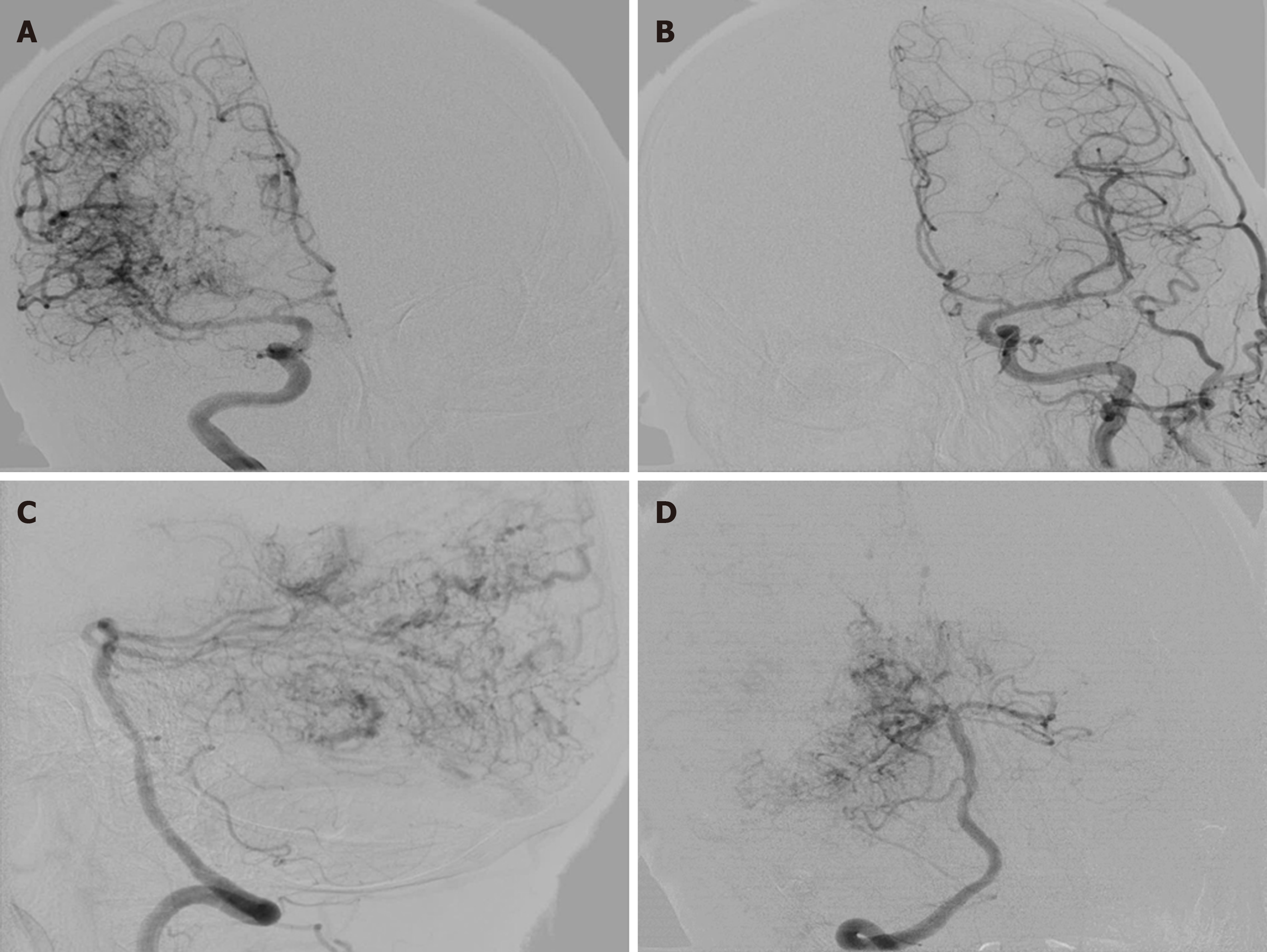
Figure 3 Brain digital subtraction angiography.
Anteroposterior view of a right internal carotid artery (ICA) angiogram. A: Anteroposterior view of a left ICA angiogram; B: Lateral view of a right posterior cerebral artery (PCA) angiogram; C: Anteroposterior view of a right PCA angiogram; D: Diffuse vascular malformation can be seen in the right cerebral hemisphere.
- Citation: Xia Y, Yu XF, Ma ZJ, Sun ZW. Hemorrhagic transformation of ischemic cerebral proliferative angiopathy: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(20): 5730-5736
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i20/5730.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i20.5730