Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 26, 2020; 8(12): 2448-2463
Published online Jun 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i12.2448
Published online Jun 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i12.2448
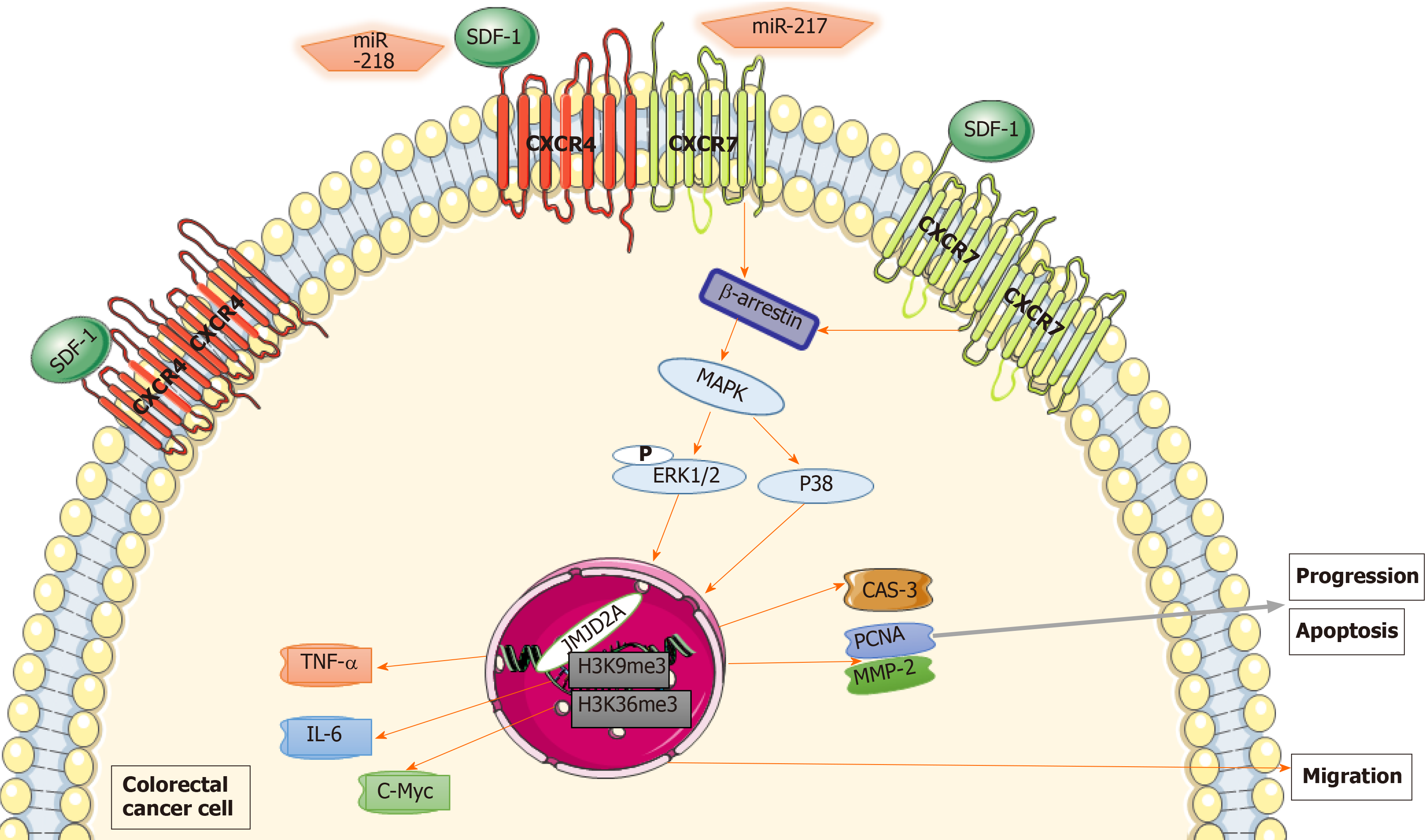
Figure 4 Mechanism of chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 7 promoting colorectal cancer growth and metastasis.
Chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 7 (CXCR7) gene induced cell anti-apoptosis and promoted colorectal cancer progression in colorectal cancer cells through extracellular regulated protein kinases 1/2 and β-arrestin pathway-mediated regulation of proliferating cell nuclear antigen, matrix metalloproteinase 2 and caspase-3 expression. miR-217, miR-218 and their targets may be regulatory molecules of Chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 (CXCR4) or CXCR7. The CXCR7/CXCR4 heterodimer translocated much more β-arrestin 1 to the nucleus and then activated histone lysine demethylase to regulate JMJD2A expression via multiprotein complexes, selectively enriching the promoters of human tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6, and cellular-myelocytomatosis, which might facilitate the recruitment of histone demethylases, resulting in enhanced local histone demethylation and transcription of these genes. The CXCR7/CXCR4 heterodimer induced high levels of JMJD2A, leading to demethylation of histones H3K9me3 and H3K36me3 compared with the CXCR7 monomer and CXCR4 monomer. CXCR7: Chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 7; ERK1/2: Extracellular regulated protein kinases 1/2; PCNA: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen; MMP-2: Matrix metalloproteinase 2; CAS-3: Caspase-3; CXCR4: Chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4; TNFα: Human tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IL-6: Interleukin-6; c-Myc: Cellular-myelocytomatosis.
- Citation: Xin Q, Sun Q, Zhang CS, Zhang Q, Li CJ. Functions and mechanisms of chemokine receptor 7 in tumors of the digestive system. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(12): 2448-2463
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i12/2448.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i12.2448