Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 16, 2021; 9(32): 9792-9803
Published online Nov 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i32.9792
Published online Nov 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i32.9792
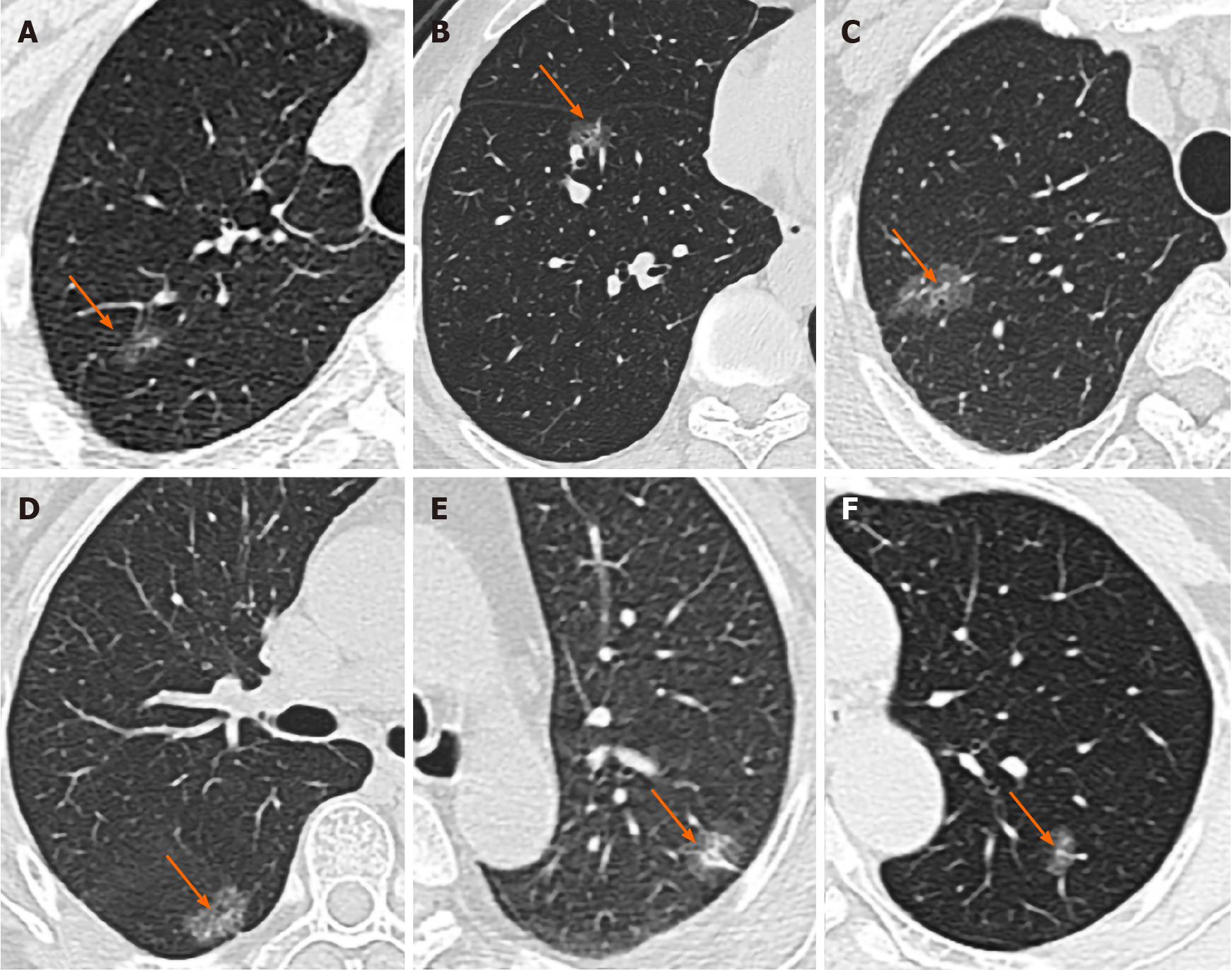
Figure 1 High-resolution computed tomography images.
A: An irregularly shaped pure ground-glass nodule (GGN, arrow) in the right lower lobe. Vacuole sign was seen inside the lesion, and the overall tumor size was about 10 mm, which was consistent with a minimally invasive adenocarcinoma (MIA) that harbored epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 21 L858R compound mutation; B: A round-like GGN (arrow) located in the right upper lobe with a diameter of 14 mm, which strongly suggested an MIA that harbored EGFR exon 21 L858R compound mutation. Visceral pleural invasion with honeycomb signs were also seen; C: An irregularly shaped GGN (arrow) in the right middle lobe with a diameter of approximately 22 mm, which was consistent with invasive pulmonary adenocarcinoma (IPA) that harbored EGFR exon 19 deletion. Vacuole sign was seen inside the lesion; D: An ovoid GGN (arrow) in the right lower lobe with a diameter of about 16 mm, which indicated IPA that harbored EGFR exon 21 L858R compound mutation. Honeycomb sign was seen inside; E: Female, 64 years old. A partially solid circular nodules was seen in the upper lobe of the left lung, about 17 mm in diameter, showing as superficial lobulated nodules. The pleura was locally pulled. The wild type of the IPA and EGFR genes was confirmed by pathology; F: Female, 58 years old. An irregular, partially solid nodule was found in the upper lobe of the left lung, about 11 mm in diameter, showing as superficial lobulated nodules. One vessel extended into the lesion and thickened. The wild type of the IPA and EGFR genes was confirmed by pathology.
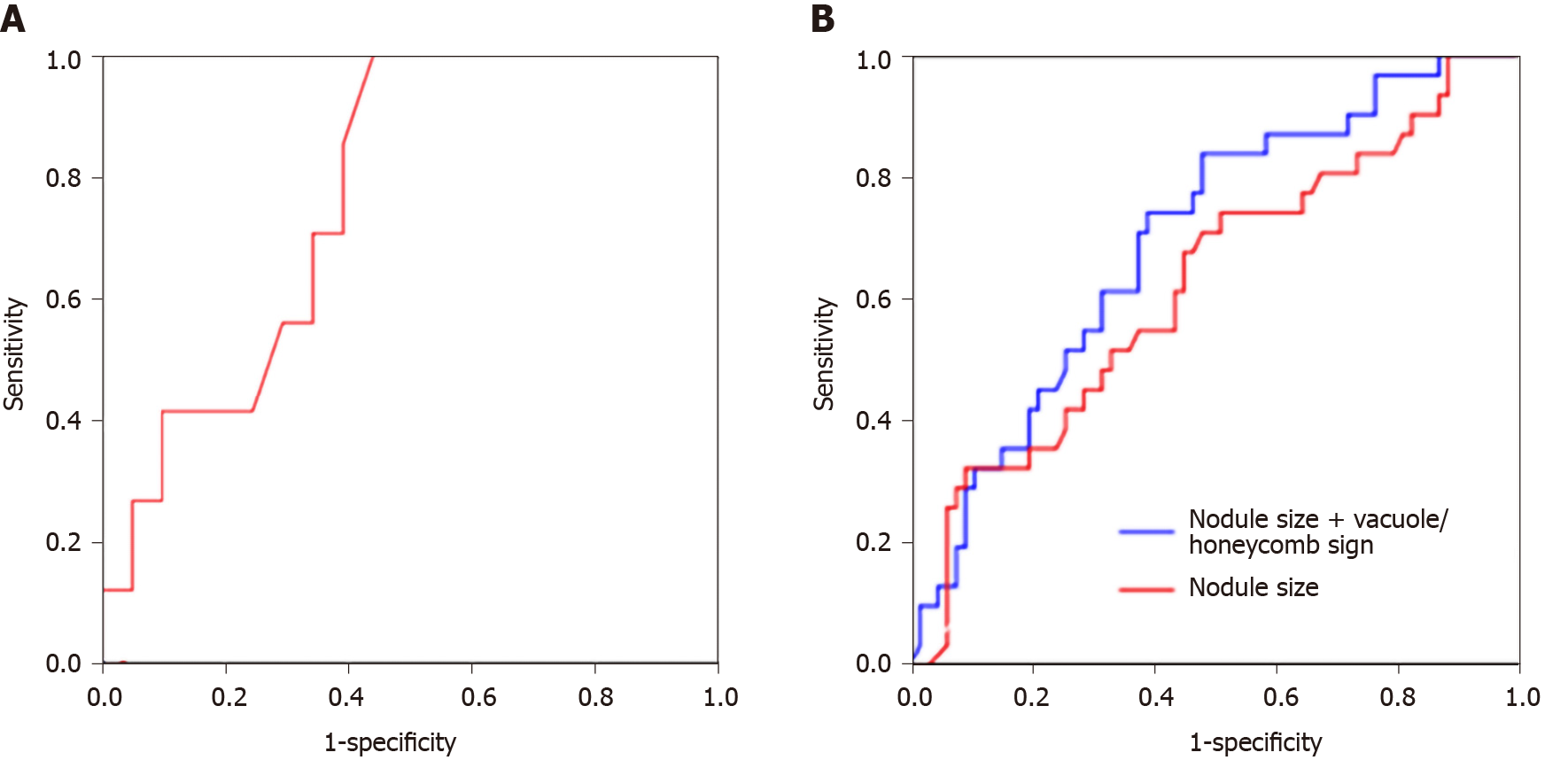
Figure 2 Receiver operating characteristic curves.
A: Receiver operating characteristic curves for assessing the predictive values of nodule size (red). For pure ground-glass nodular adenocarcinomas with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations, the optimal cut-off value was 8.65 mm; the model yielded a sensitivity of 100%, a specificity of 57.1%, and an AUC of 0.782 (95%CI: 0.609–0.956; P = 0.028); B: Nodule size (red) and nodule size in combination with vacuole/honeycomb sign (blue) in ground-glass nodular adenocarcinomas (mixed) with EGFR mutations. The optimal cutoff value was set to 13.38 mm; the sensitivity, specificity and AUC were 74.2%, 50.7%, and 0.625 (95%CI: 0.504-0.745; P = 0.048), respectively. The final model showed an AUC of 0.698 (95%CI: 0.589-0.806; P = 0.002). Its sensitivity was 83.9% and specificity was 52.2%.
- Citation: Zhu P, Xu XJ, Zhang MM, Fan SF. High-resolution computed tomography findings independently predict epidermal growth factor receptor mutation status in ground-glass nodular lung adenocarcinoma. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(32): 9792-9803
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i32/9792.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i32.9792