Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 6, 2021; 9(19): 5203-5210
Published online Jul 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i19.5203
Published online Jul 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i19.5203
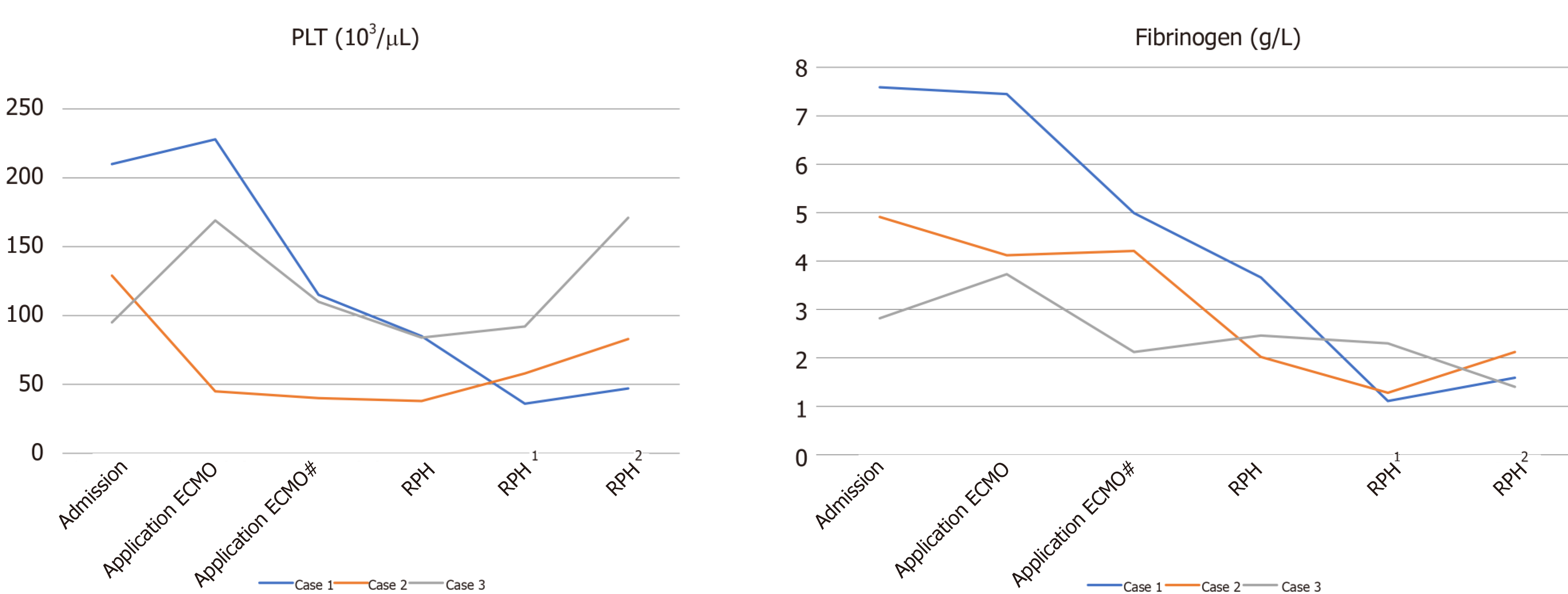
Figure 1 Three patients with delayed retroperitoneal hemorrhage during treatment with veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
Prothrombin time international normalized ratio, platelets, and fibrinogen changed before and after retroperitoneal hemorrhage, consistent with bleeding. Activated partial thromboplastin time did not change because anticoagulation was used during the extracorporeal membrane oxygenation treatment.
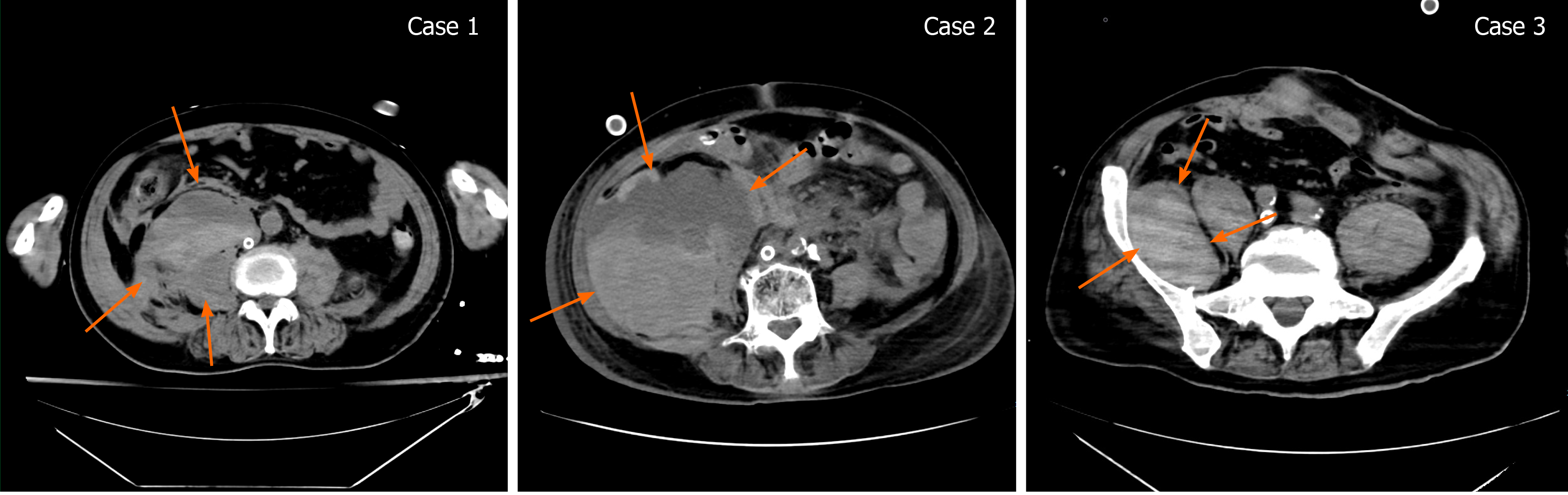
Figure 2 Computed tomography scans show the retroperitoneal hematomas (arrows) that occurred in the three patients.
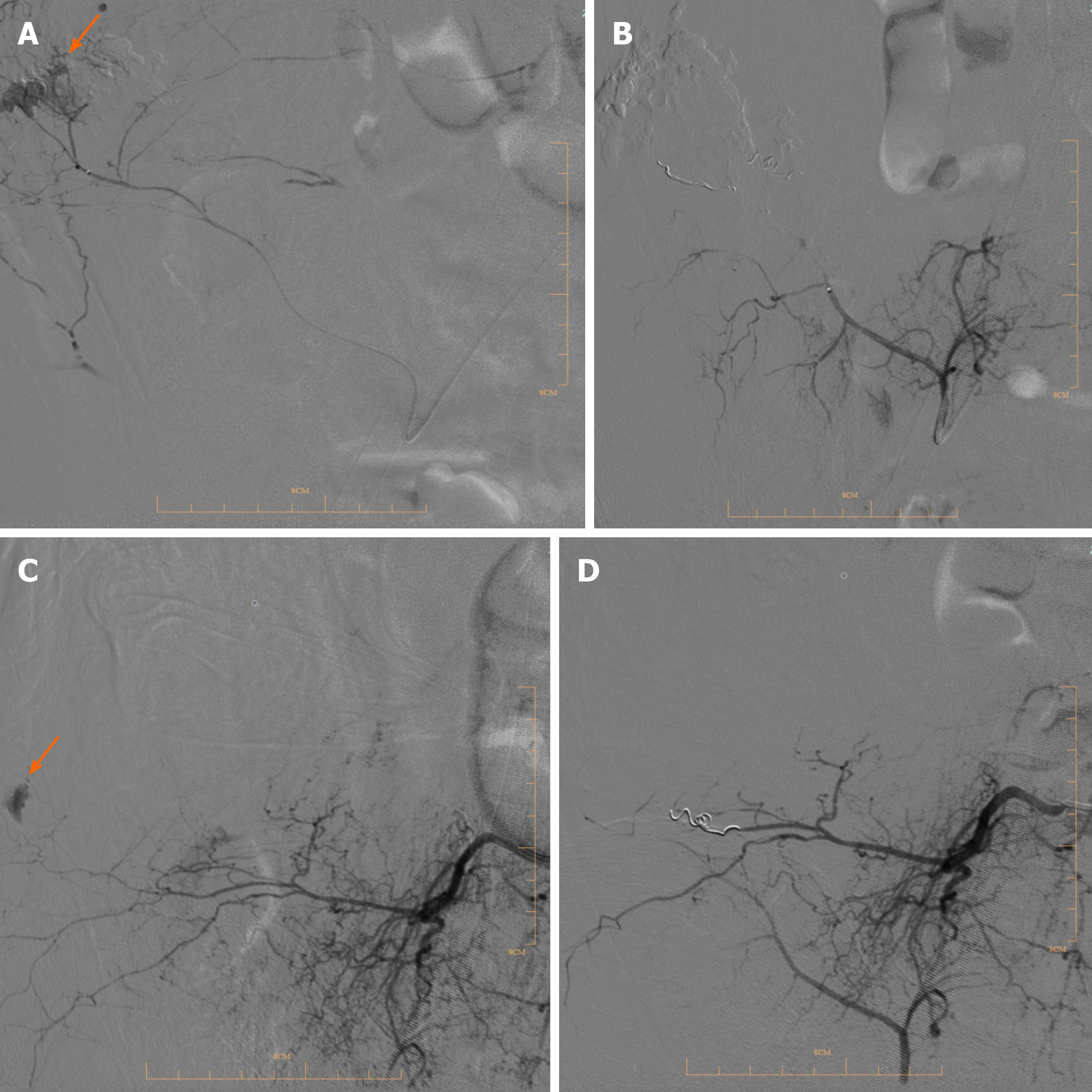
Figure 3 Vascular images of two patients treated by transcatheter arterial embolization.
A: Digital subtraction angiography in case 1 shows the effusion of hematomas (arrow) in arteriae lumbales; B: Vascular image after the transcatheter arterial embolization treatment; C: DSA in case 2 in the effusion of hematomas (arrow) in the internal iliac artery branch; D: Vascular image after transcatheter arterial embolization.
- Citation: Zhang JC, Li T. Delayed retroperitoneal hemorrhage during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in COVID-19 patients: A case report and literature review. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(19): 5203-5210
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i19/5203.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i19.5203