Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 6, 2021; 9(16): 4052-4062
Published online Jun 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i16.4052
Published online Jun 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i16.4052
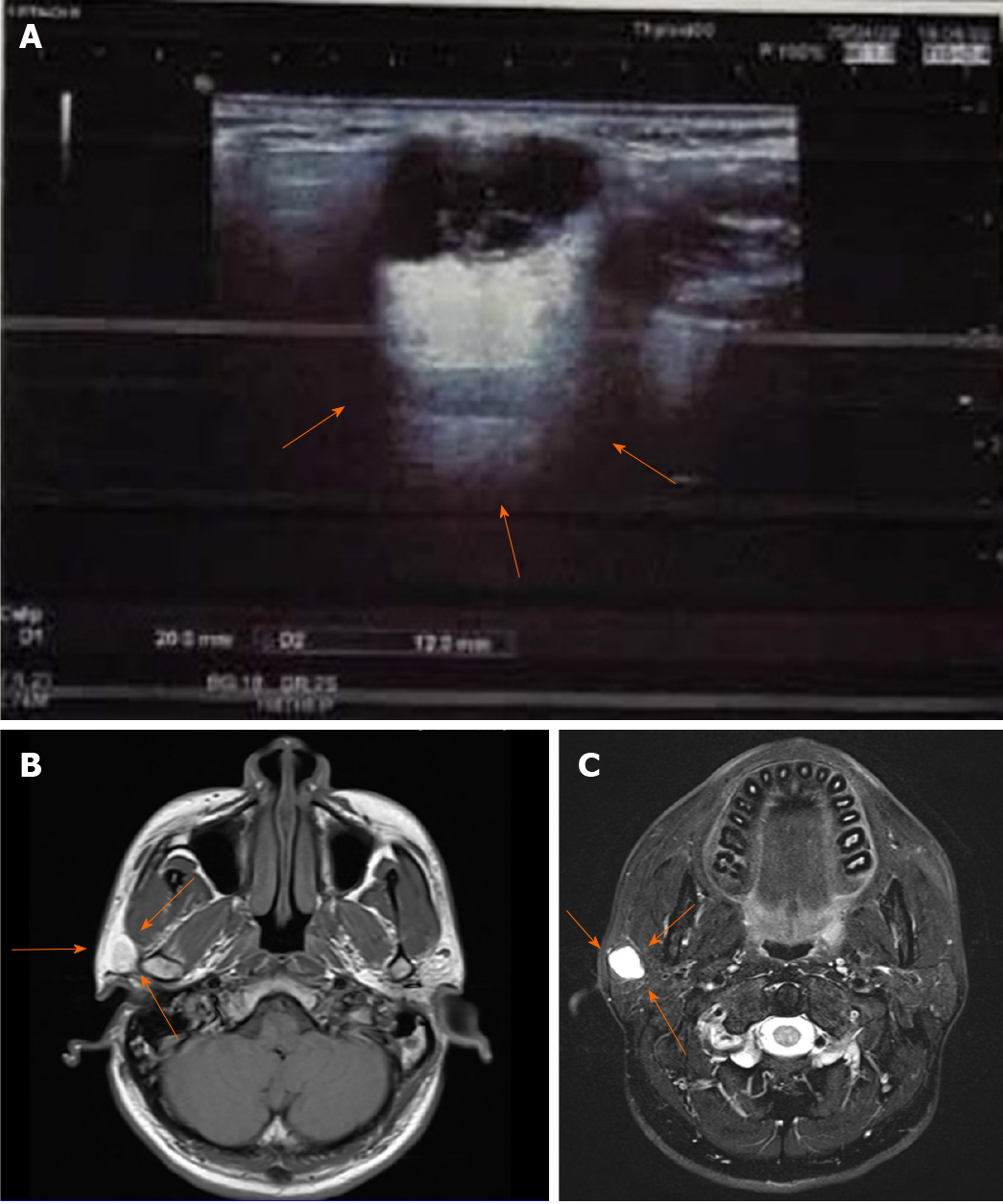
Figure 1 Radiological results for the lesion.
A: Ultrasonic examination showing a clear boundary with strong echoes of strips and dots (arrows); B: Magnetic resonance imaging results for the lesion showing iso-low signals for T1; C: High signals for the T2 fat compression.
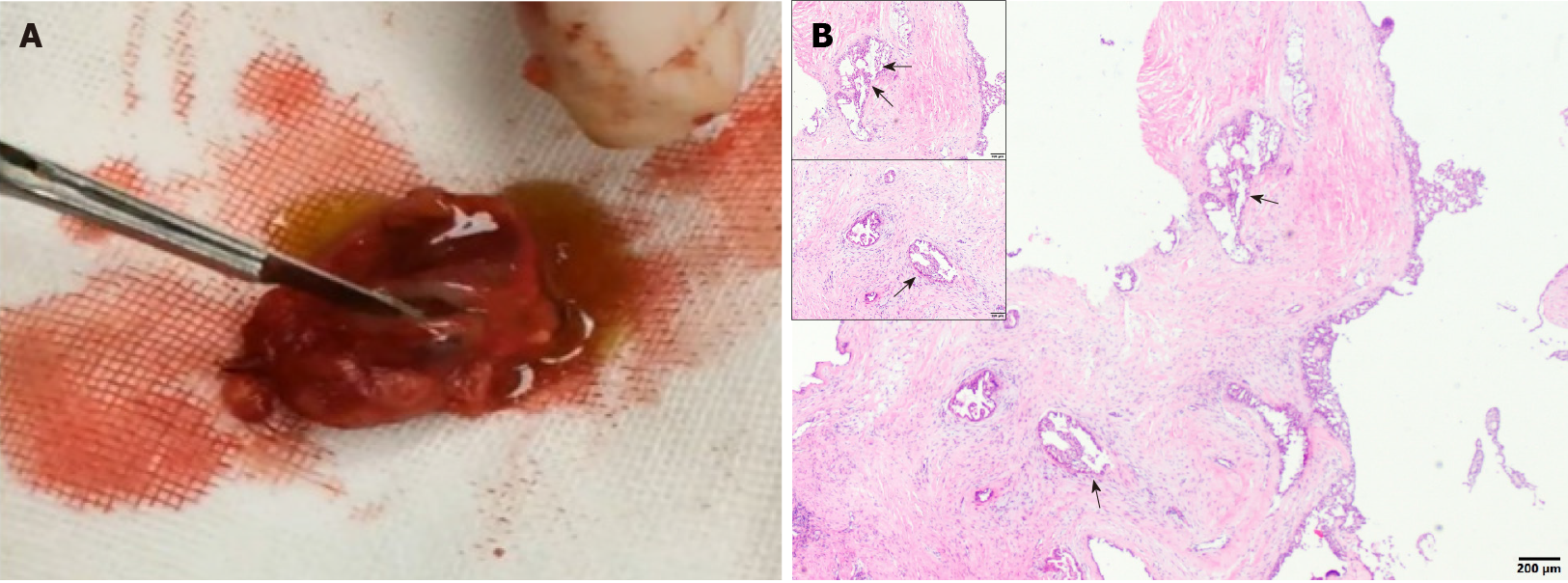
Figure 2 Clinical and histological examinations of the tumor tissues.
A: A section of the tumor, showing a solid, brownish red, cystic, mass with yellowish green liquid; B: The histological examination of the lesion showing the cystic components, areas of the cyst wall epithelium, and papillary hyperplasia to the cyst cavity (indicated using black arrows).
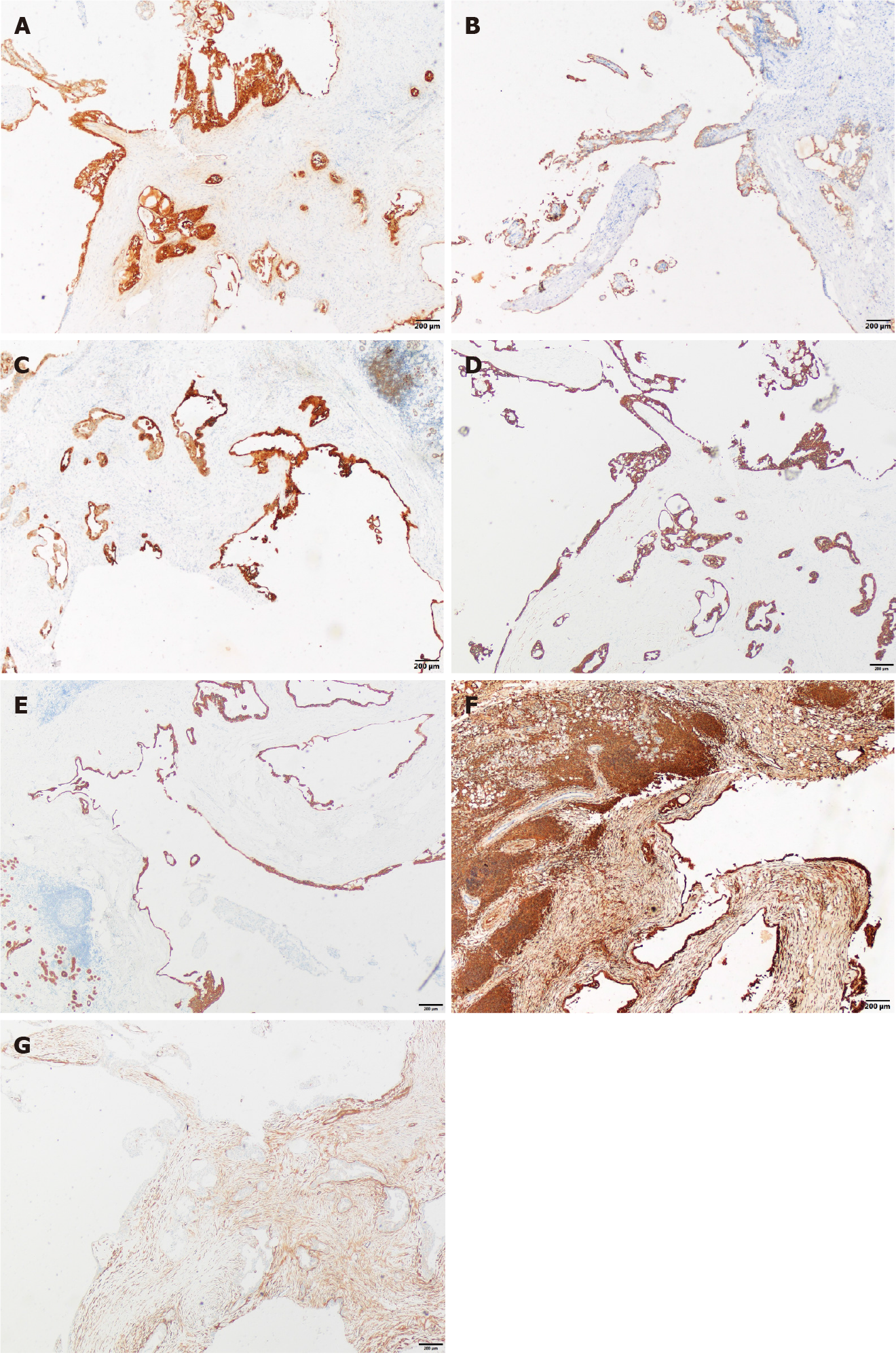
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical staining (×40).
A: Immunostaining for S-100; B: Immunostaining for Mammaglobin; C: Immunostaining for Cytokeratin (CK) 5/6; D: Immunostaining for CK7; E: CK8 (+); F: Vimentin (+); G: Immunostaining for Smooth Muscle Actin.
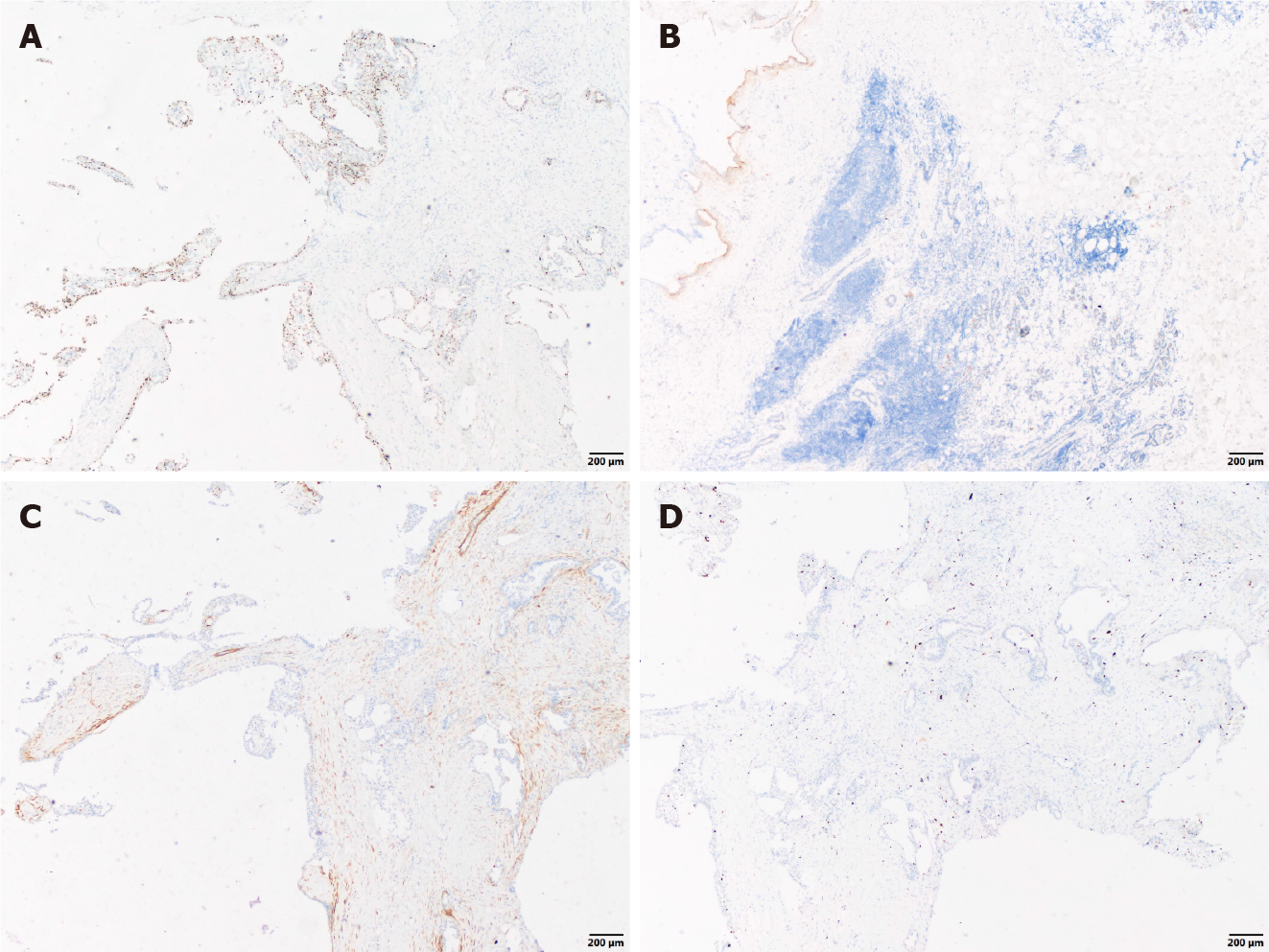
Figure 4 Immunohistochemical staining (×40).
A: Immunostaining for scattered P63; B: Immunostaining for discovered on Gastrointestinal Stromal tumor-1; C: Immunostaining for Calponin; D: Immunostaining for Ki-67.
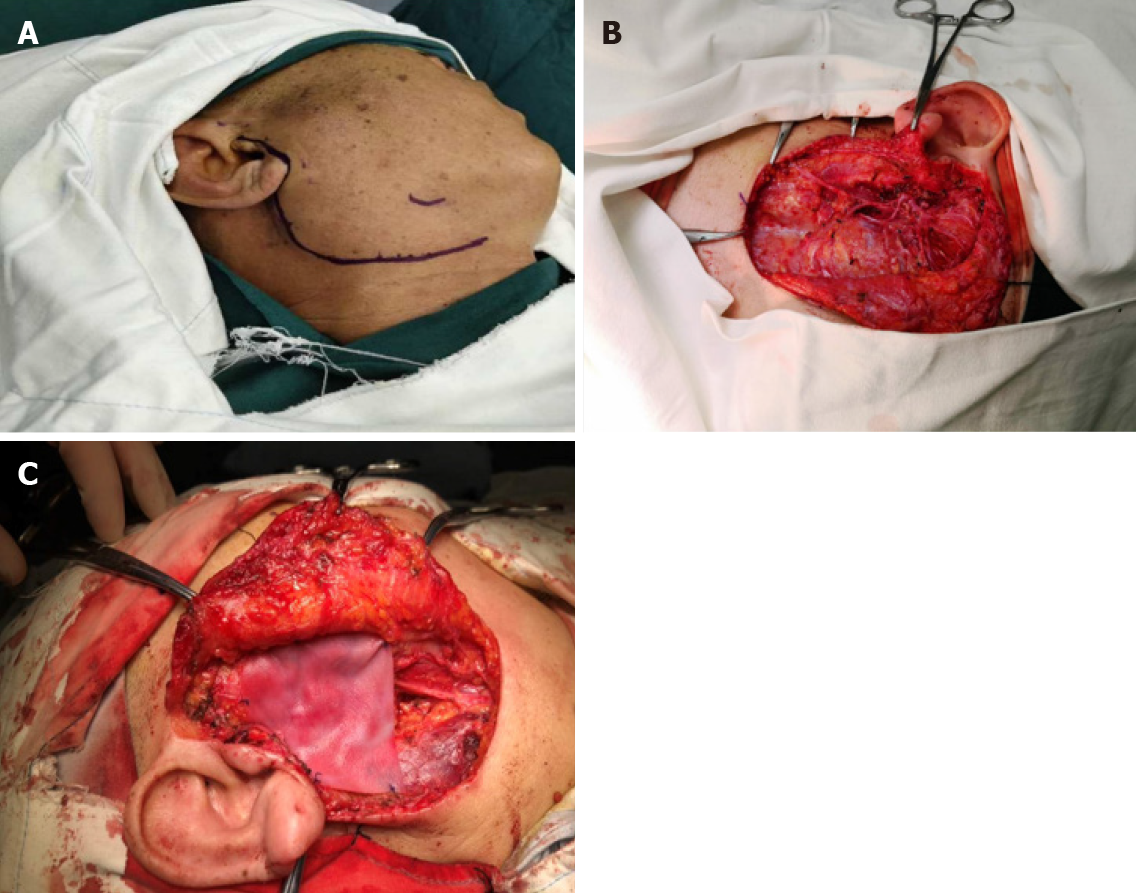
Figure 5 Surgical management of the patient.
A: Design of incision before total lobectomy of the right parotid gland; B: Total lobectomy of the right parotid gland and preservation of facial nerve; C: Implantation of a biological patch to restore the sunken deformity and prevent Frey’s syndrome.
- Citation: Min FH, Li J, Tao BQ, Liu HM, Yang ZJ, Chang L, Li YY, Liu YK, Qin YW, Liu WW. Parotid mammary analogue secretory carcinoma: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(16): 4052-4062
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i16/4052.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i16.4052