Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 26, 2021; 9(12): 2930-2936
Published online Apr 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i12.2930
Published online Apr 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i12.2930
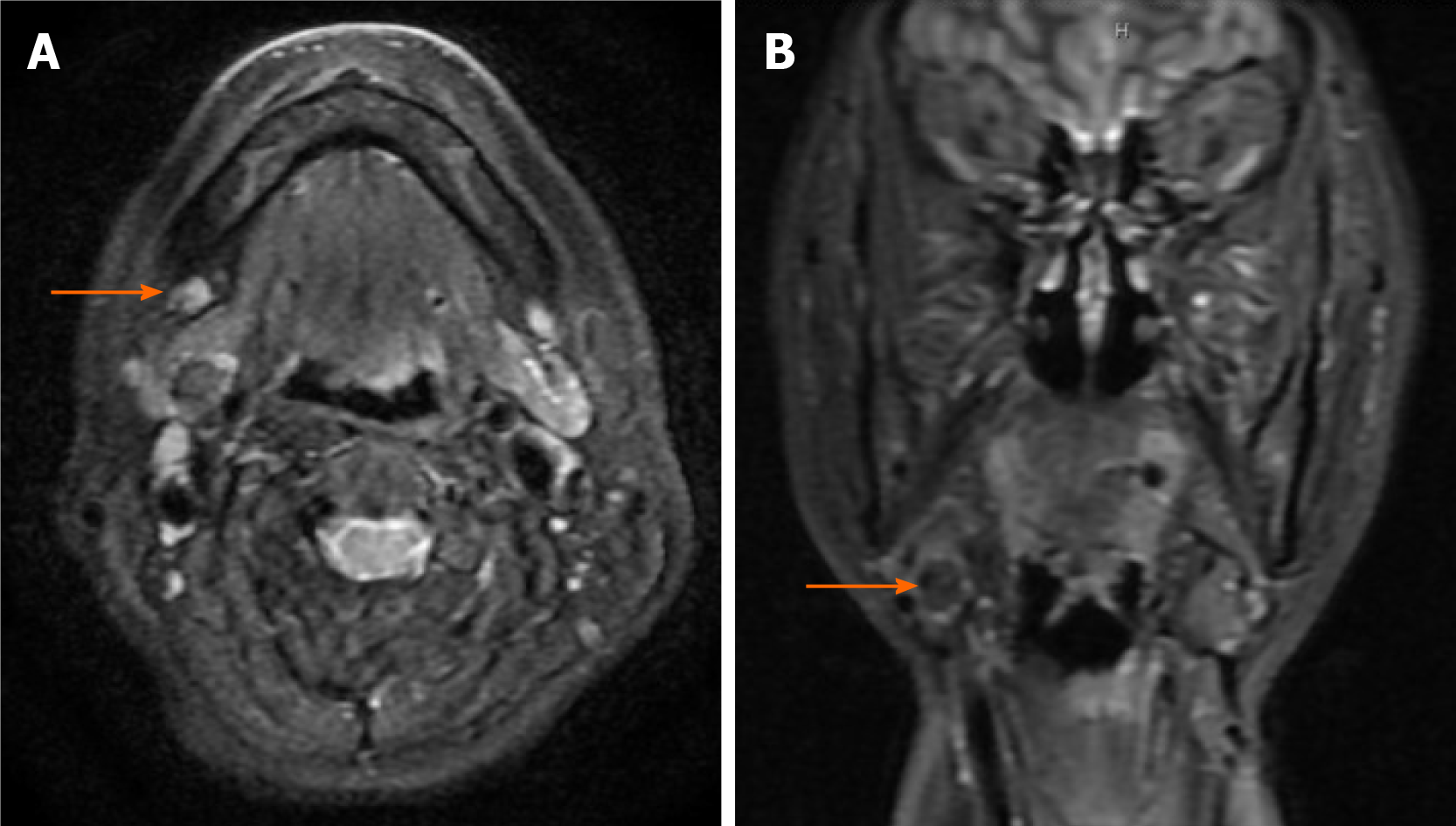
Figure 1 Magnetic resonance images (T2-weighted image).
A: Axial scan revealed a mass in the right submandibular area (orange arrow); B: Coronal scan revealed a mass in the right submandibular area (orange arrow).
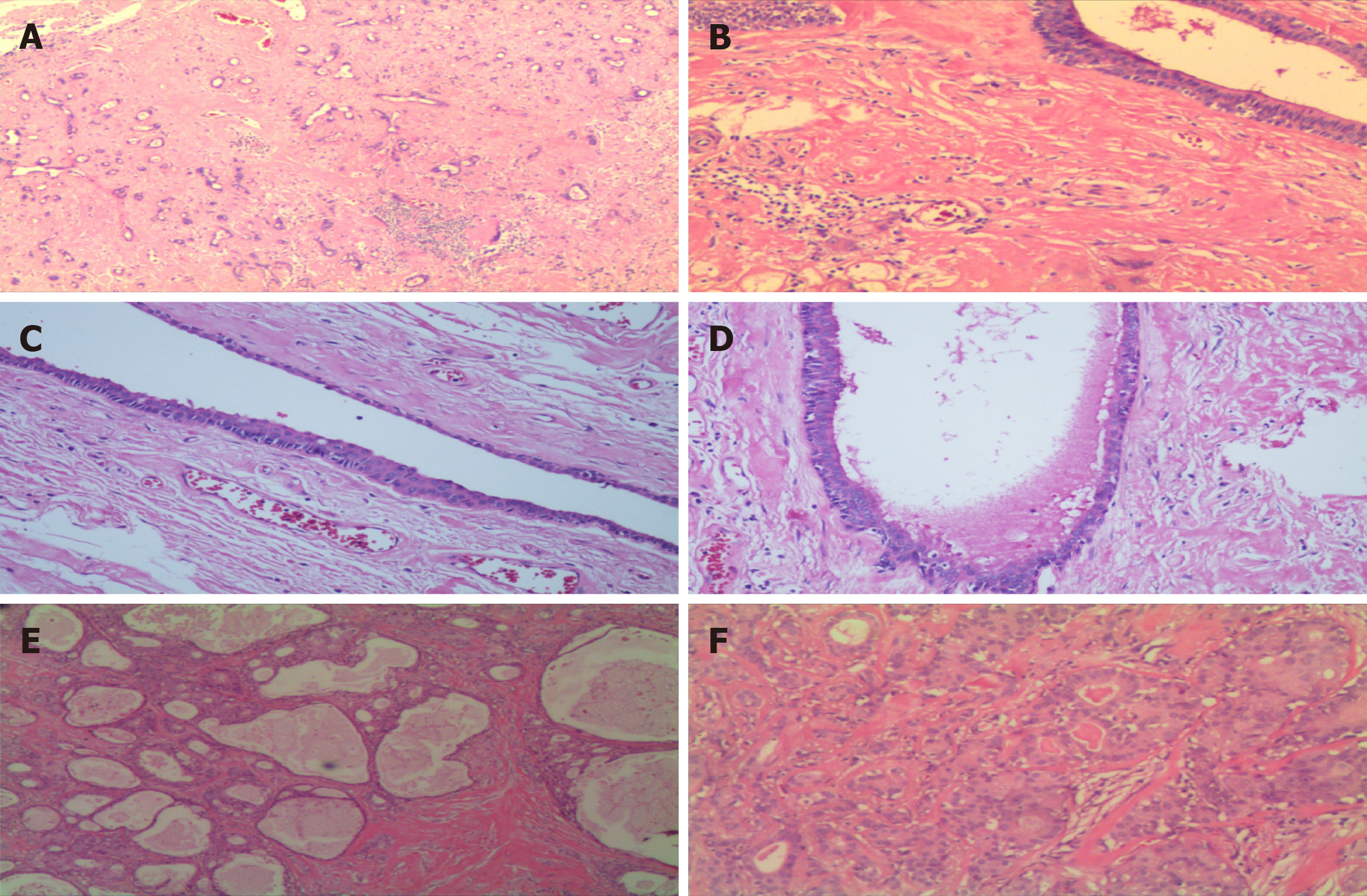
Figure 2 Sclerosing polycystic adenosis.
A: Proliferation of acini and ducts in a dense sclerotic stroma background; B: Dilated duct embedded in a highly sclerotic stroma; C: Flat and cuboidal epithelium and eosinophils are seen in the ductal epithelium; D: The lumen of the cysts containing eosinophilic secretory material; E: Numerous tubular and cystic structures containing variable amounts of intraluminal, eosinophilic material with periductal fibrosis; F: Apocrine and secretory areas with histiocytes are typical.
- Citation: Wu L, Wang Y, Hu CY, Huang CM. Sclerosing polycystic adenosis of the submandibular gland: Two case reports. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(12): 2930-2936
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i12/2930.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i12.2930