Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 26, 2020; 8(8): 1507-1514
Published online Apr 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i8.1507
Published online Apr 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i8.1507
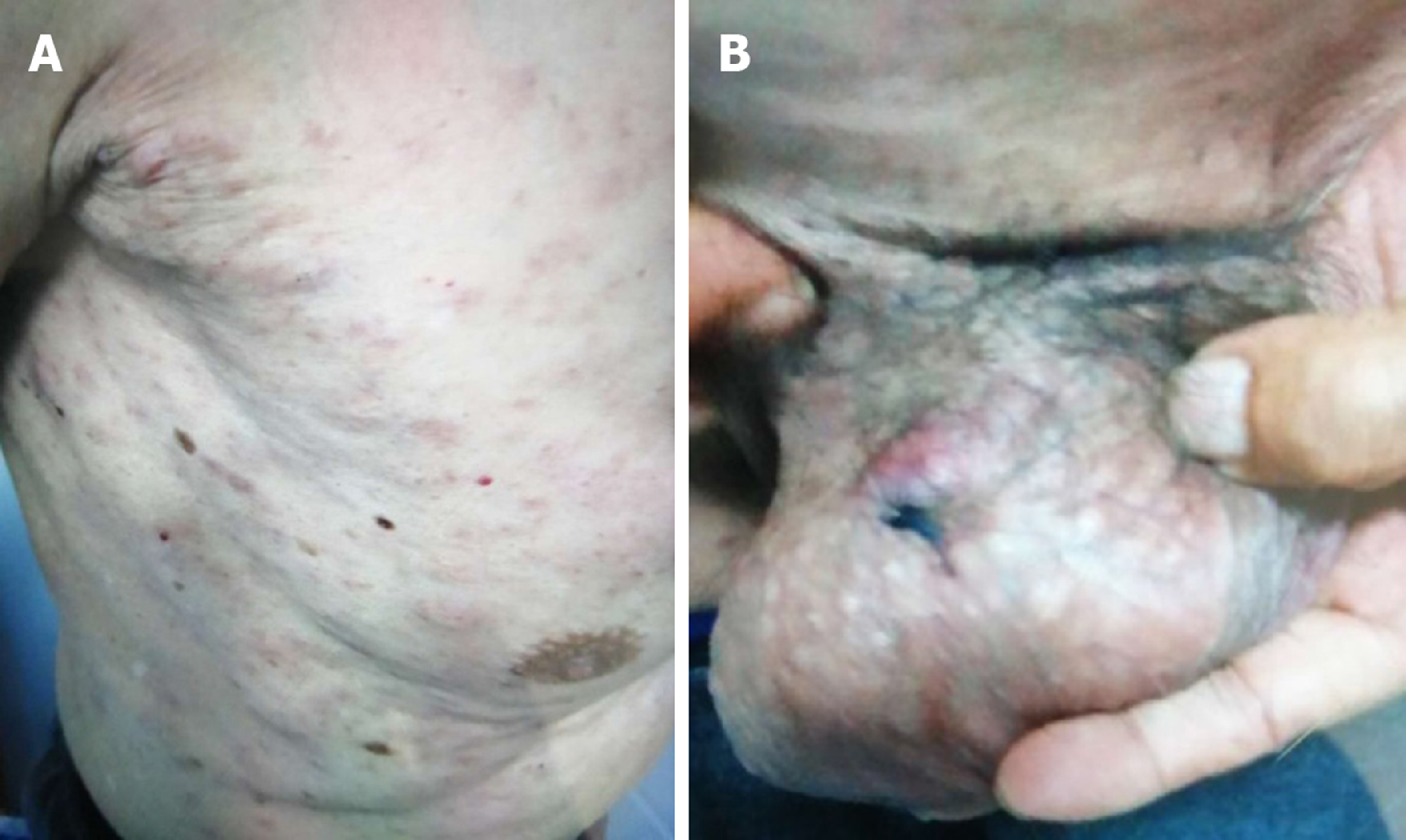
Figure 1 Clinical cutaneous features of this case.
A: Diffuse, irregular cutaneous erythematous nodules and plaques on the trunk; B: Diffuse, irregular cutaneous erythematous nodules and plaques on the scrotum.
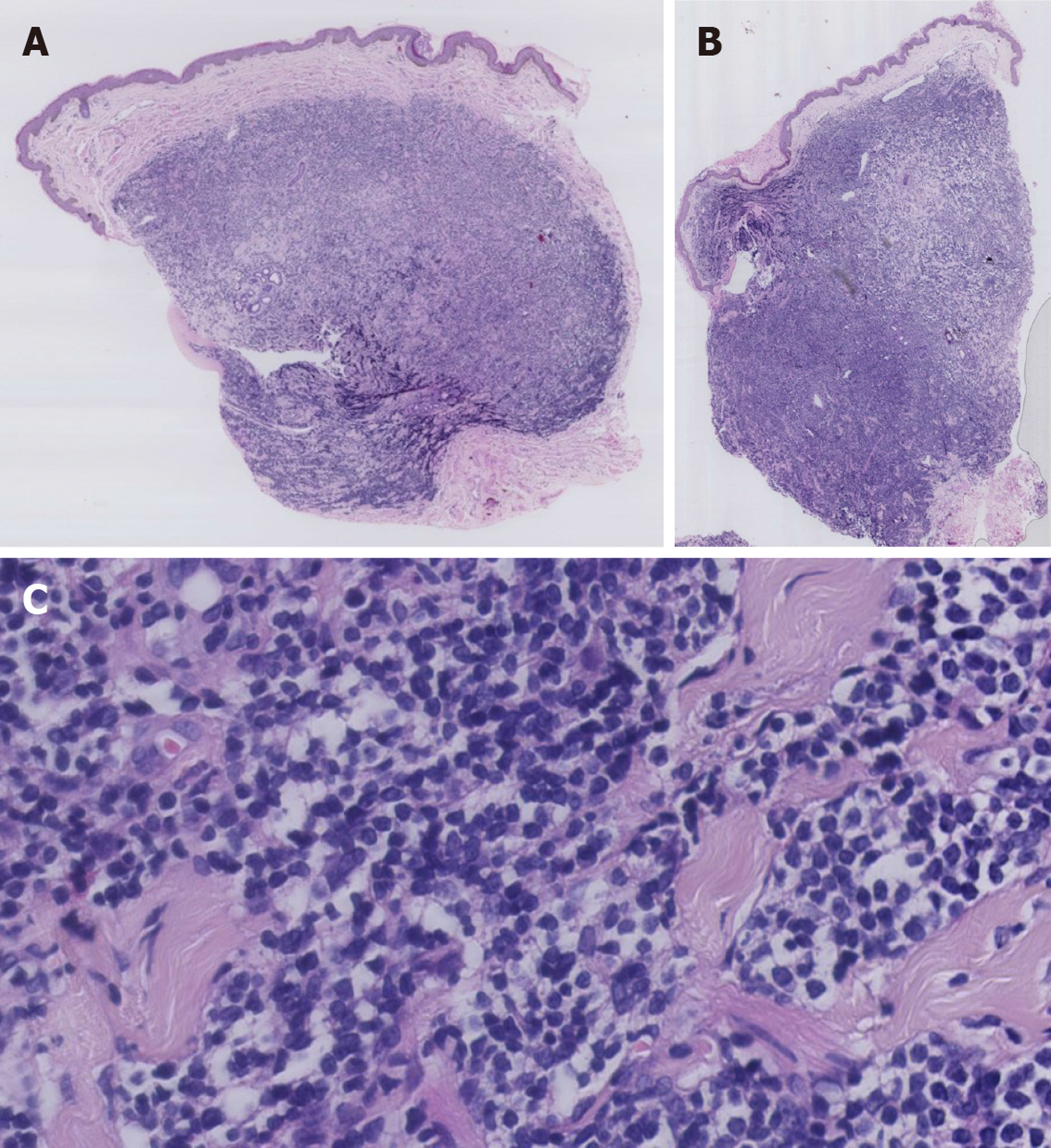
Figure 2 Histopathological changes of this case.
A: A diffuse superficial and deep dermal monomorphic lymphoid infiltrate with a grenz-zone was observed, sparing the epidermis of biopsy of skin lesions on the trunk (HE staining, ×20); B: A diffuse superficial and deep dermal monomorphic lymphoid infiltrate with a grenz-zone was observed, sparing the epidermis of biopsy of skin lesions on the scrotum (HE staining, ×20); C: The lymphoid cells were small to medium-sized with mildly irregular nuclei, interspersed through the collagen fibers (HE staining, ×400).
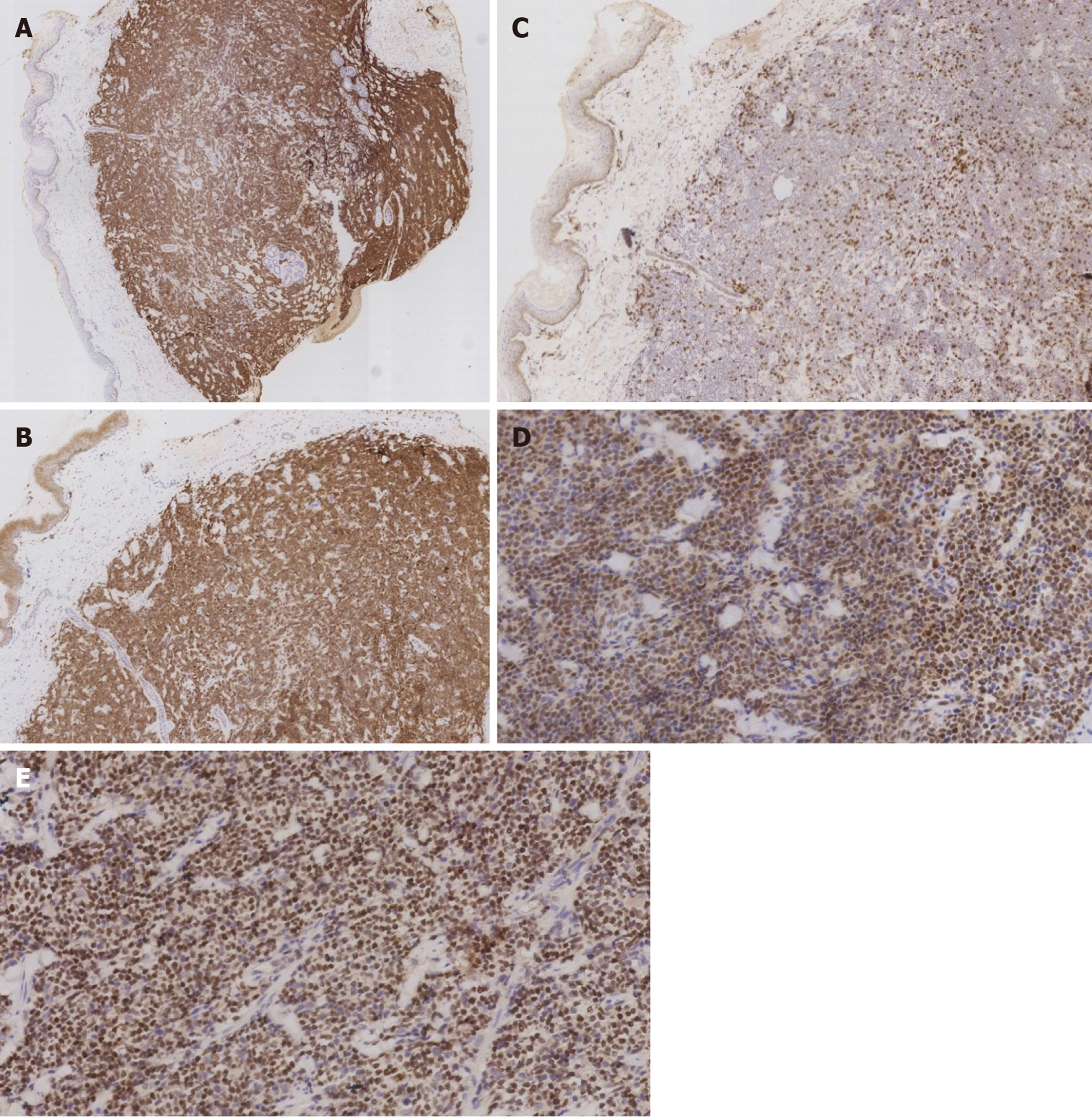
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical features of this case.
A: Positivity for CD20 (×25); B: Positivity for CD5 (×50); C: Negativity for CD3 (×50); D: Positivity for cyclin D1 (×200); E: Positivity for SOX-11 (×200).
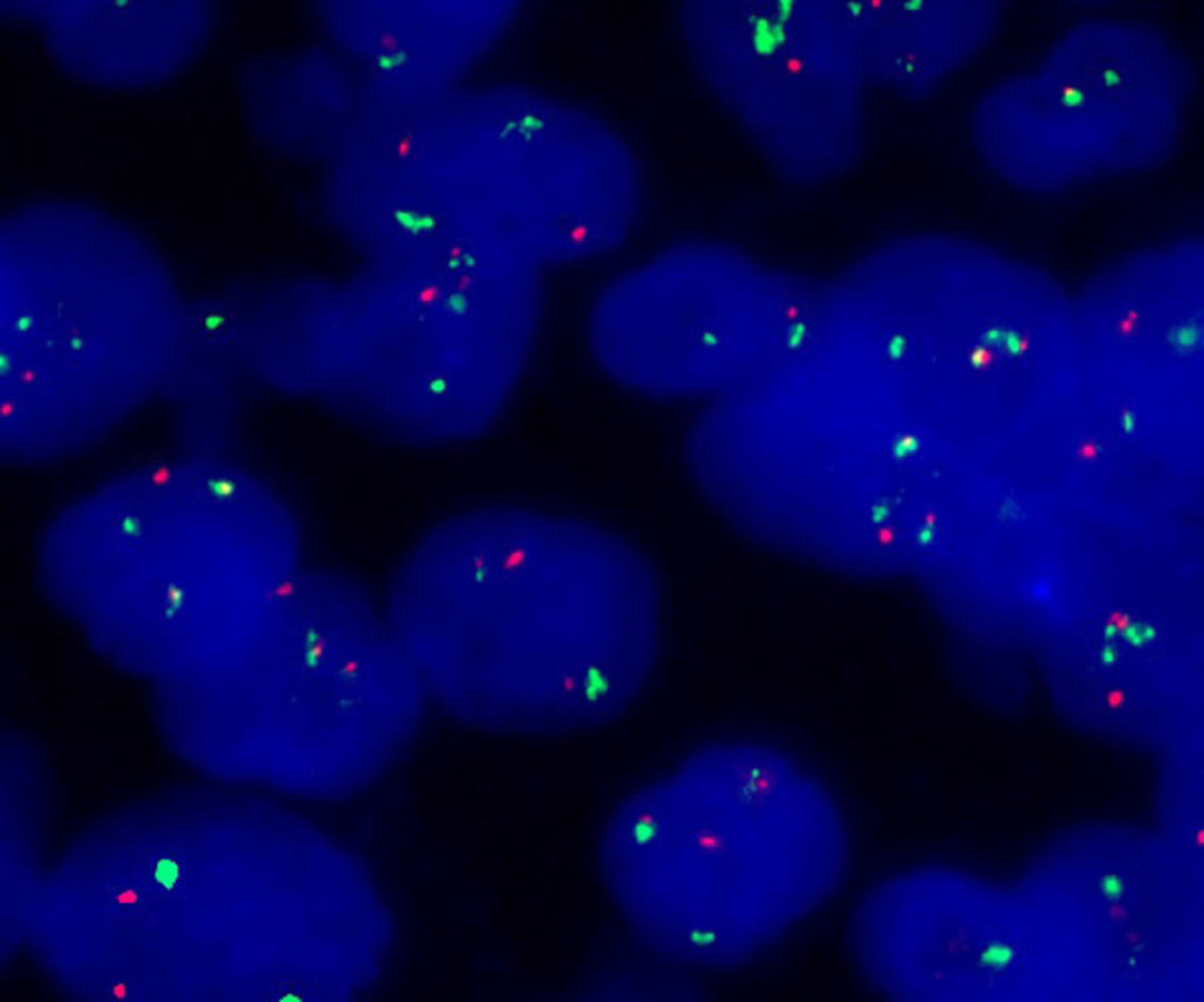
Figure 4 Fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis of this case.
Fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis demonstrated fusion of the CCND1 gene locus (orange) and the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene locus (green).
- Citation: Zheng XD, Zhang YL, Xie JL, Zhou XG. Primary cutaneous mantle cell lymphoma: Report of a rare case. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(8): 1507-1514
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i8/1507.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i8.1507