Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 6, 2024; 12(22): 5094-5107
Published online Aug 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i22.5094
Published online Aug 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i22.5094
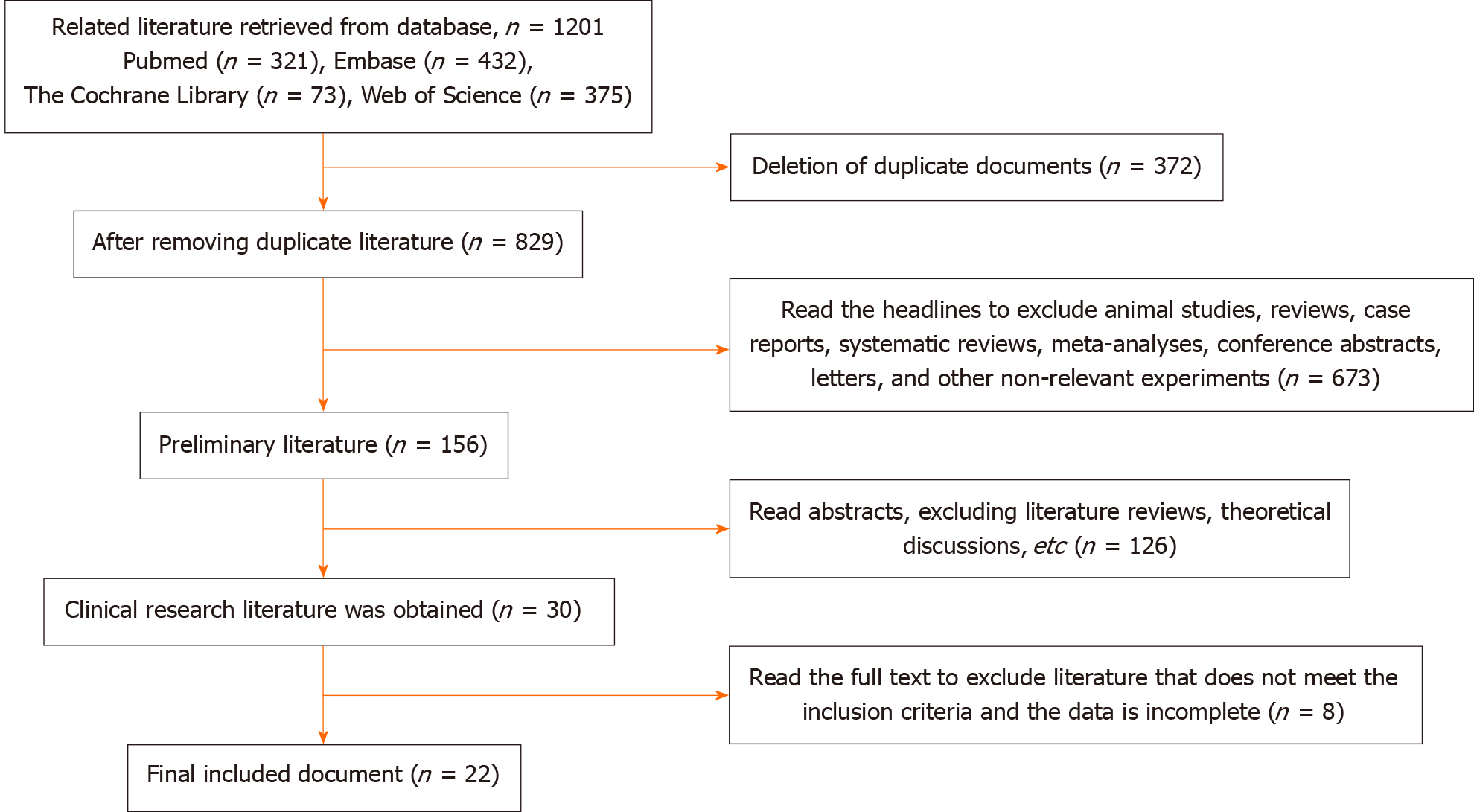
Figure 1 Literature screening process.
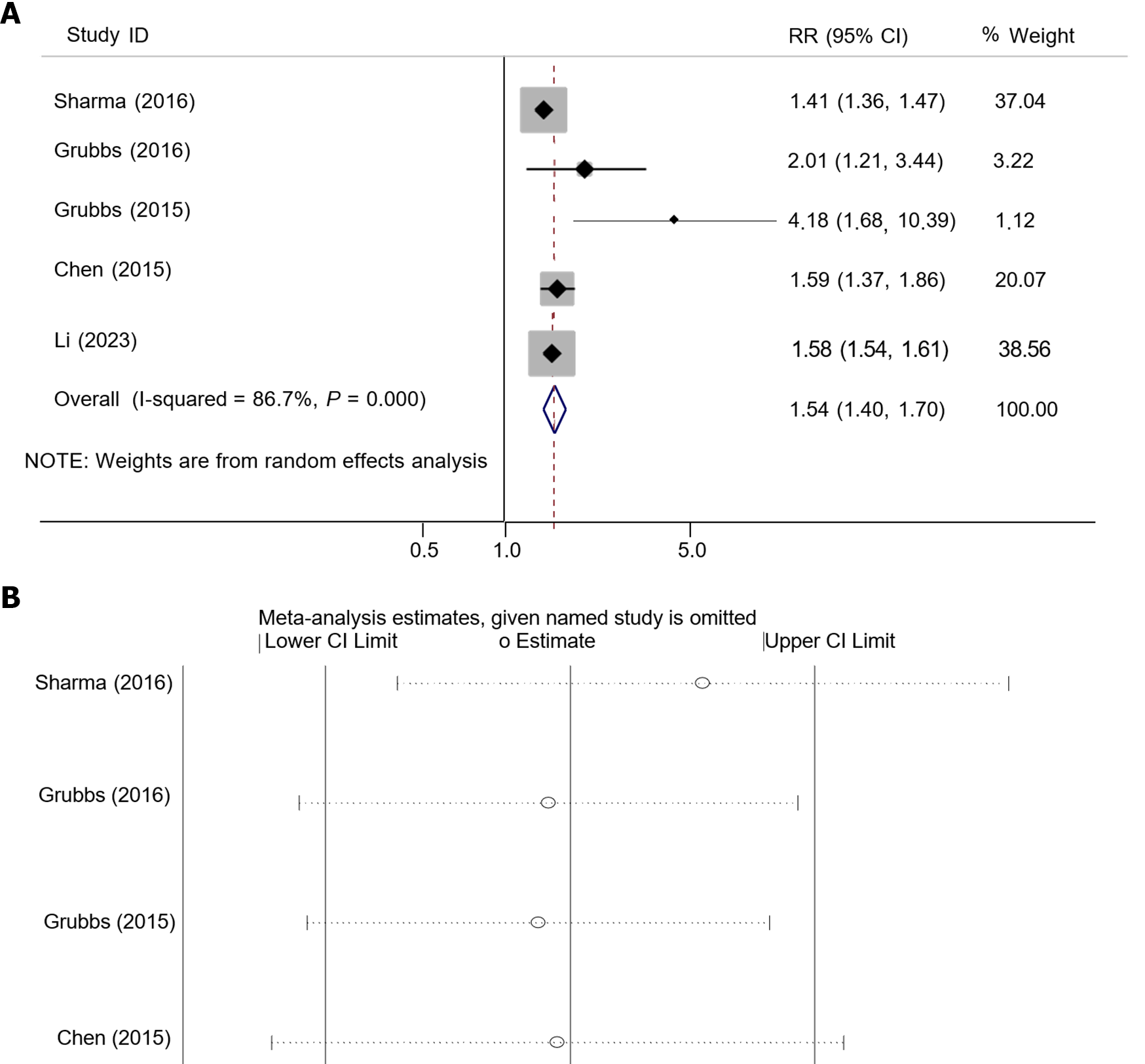
Figure 2 Meta-analysis (A) and sensitivity analysis (B) results of cohort studies on correlation between chronic periodontitis and chronic kidney disease.
RR: Relative risk.
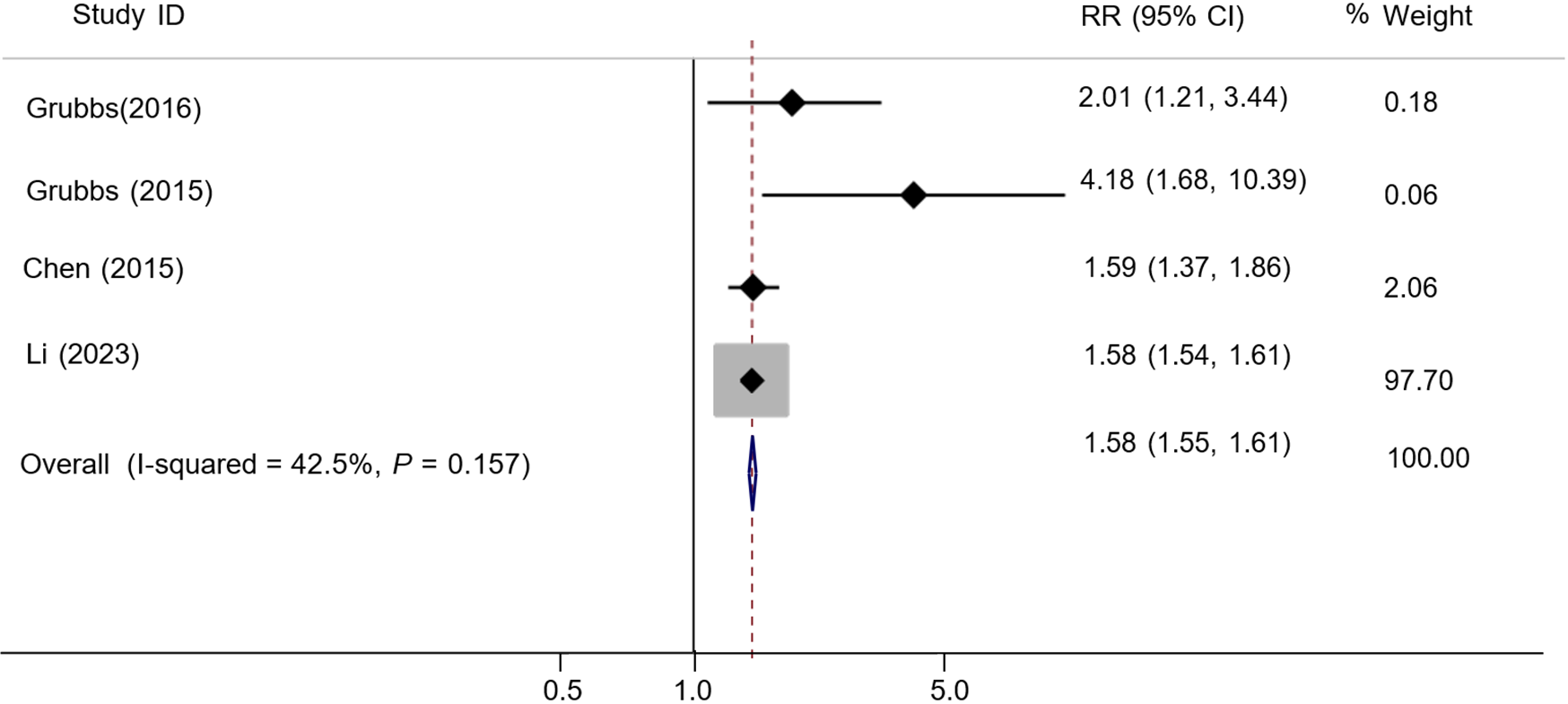
Figure 3 Meta-analysis of the correlation between chronic periodontitis and chronic kidney disease cohort study obtained after the study of Sharma et al[15] was removed.
RR: Relative risk.
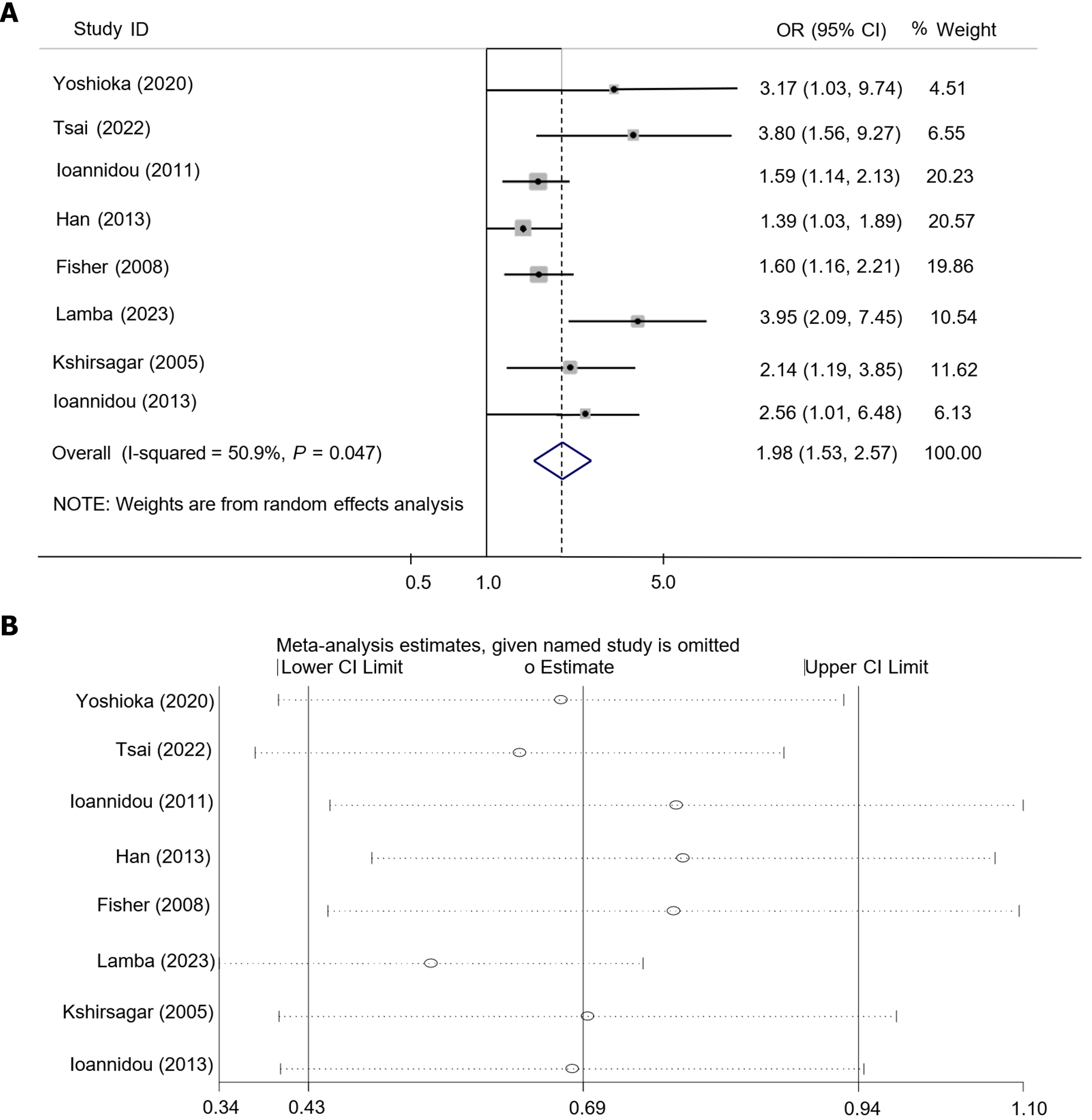
Figure 4 Meta-analysis (A) and sensitivity analysis (B) results of cross-sectional studies on the correlation between chronic periodontitis and chronic kidney disease.
OR: Overall risk.
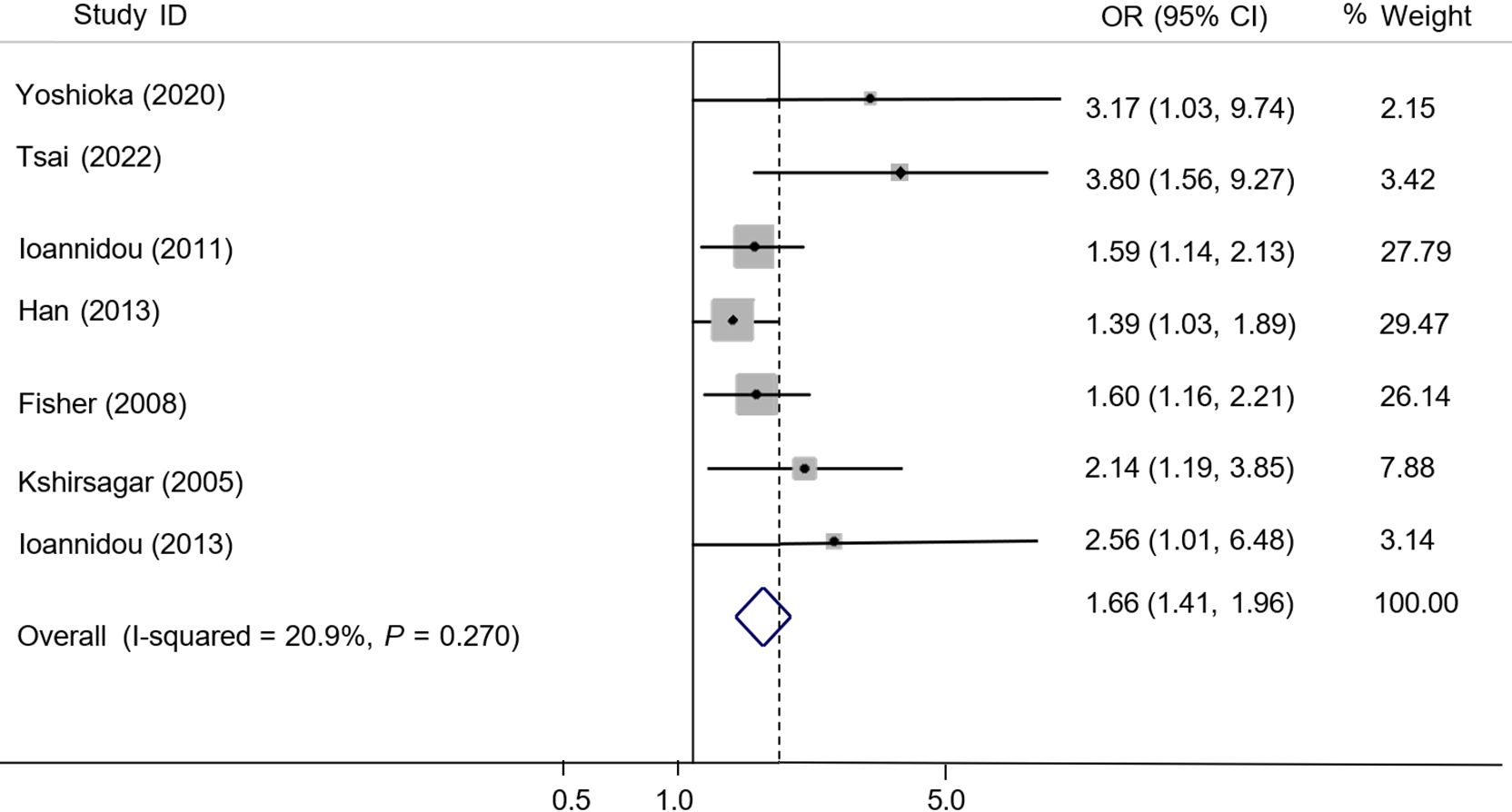
Figure 5 Meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies on the correlation between chronic periodontitis and chronic kidney disease after removing the Lamba et al[13] 2023 study.
OR: Overall risk.
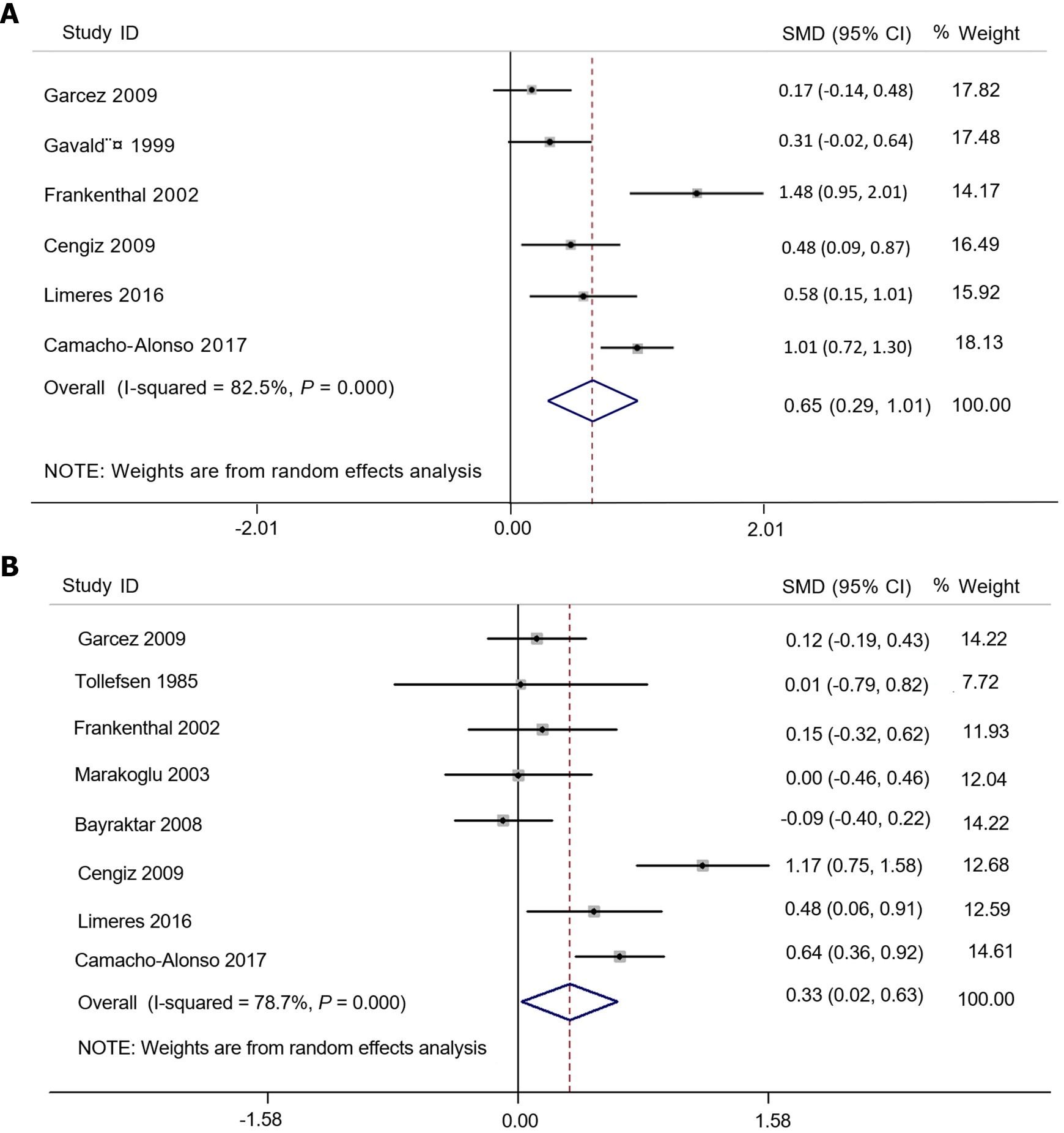
Figure 6 Differences in clinical attachment level depth (A) and Pocket probing depth (B) between chronic kidney disease patients and non-chronic kidney disease groups.
SMD: Standardized mean difference.
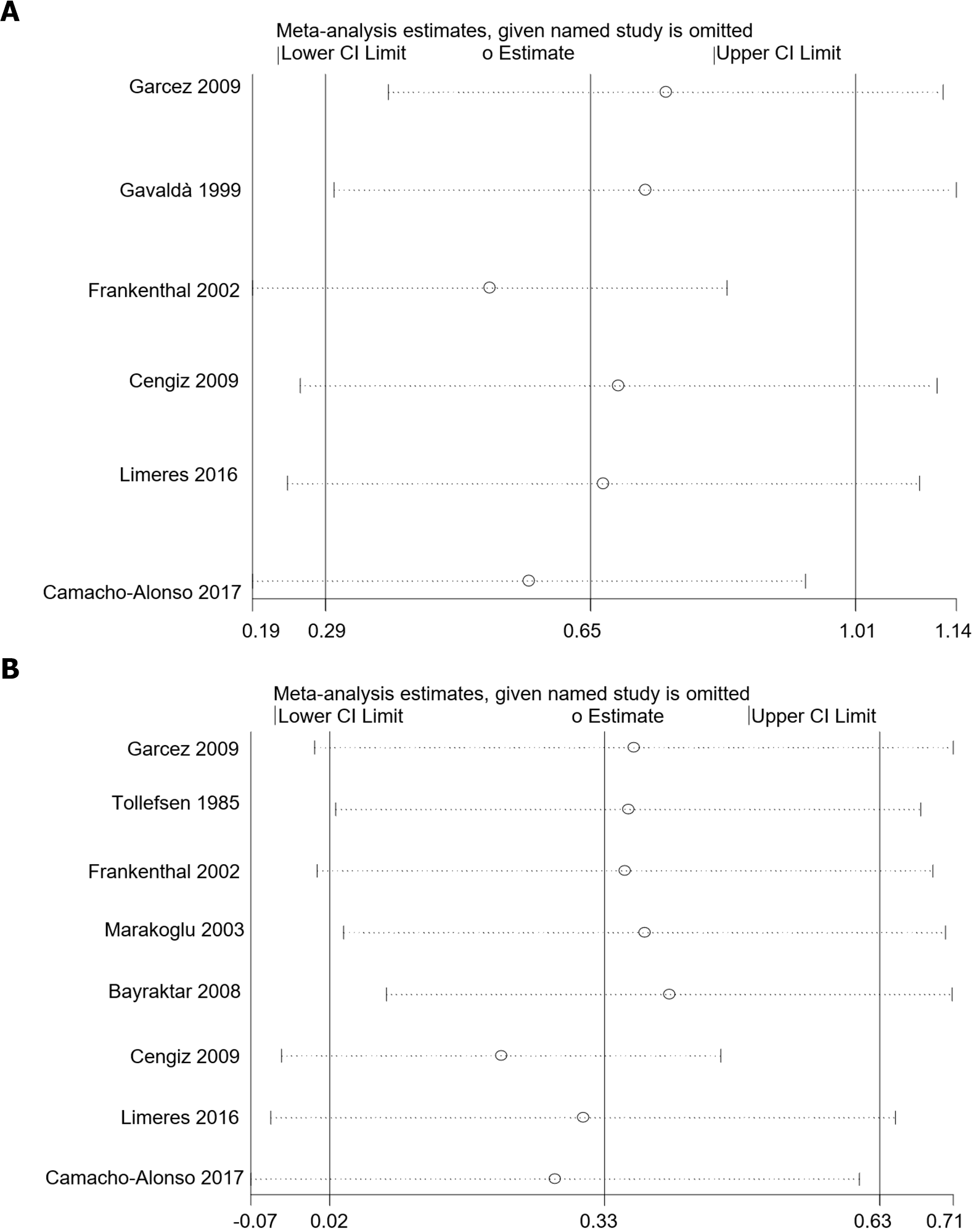
Figure 7 Sensitivity analysis results of chronic kidney disease and clinical attachment level depth (A), and pocket probing depth (B).
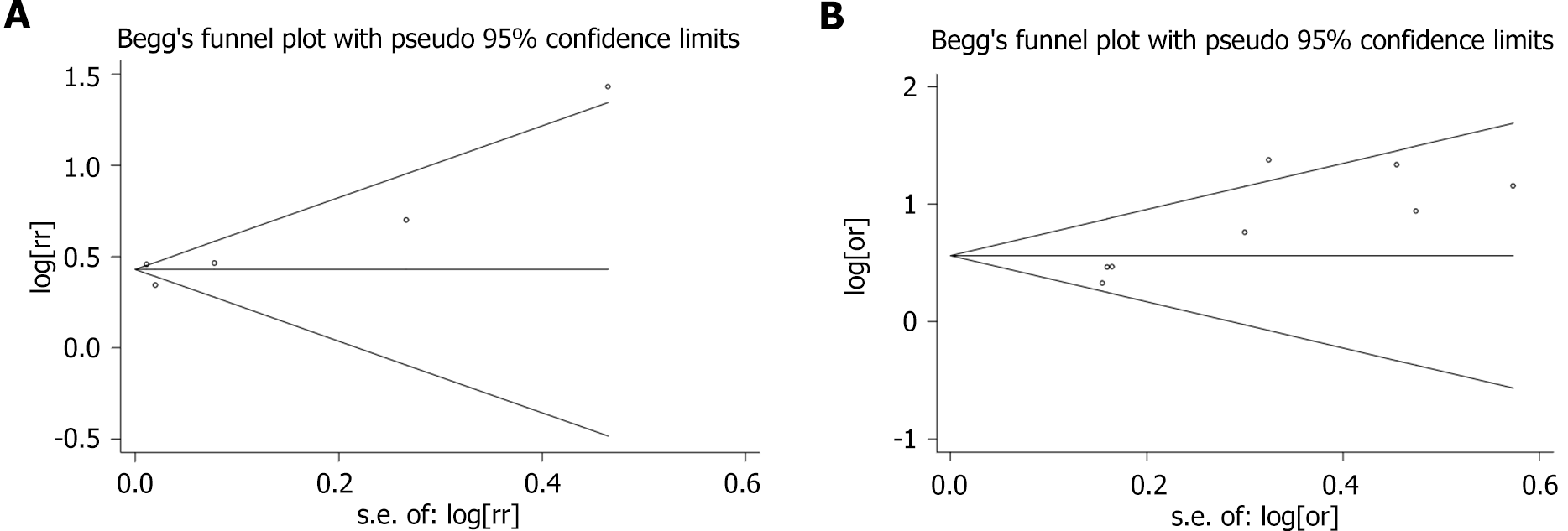
Figure 8 Funnel plot of correlation between chronic periodontitis and chronic kidney disease.
A: Cohort study; B: Cross-sectional study.
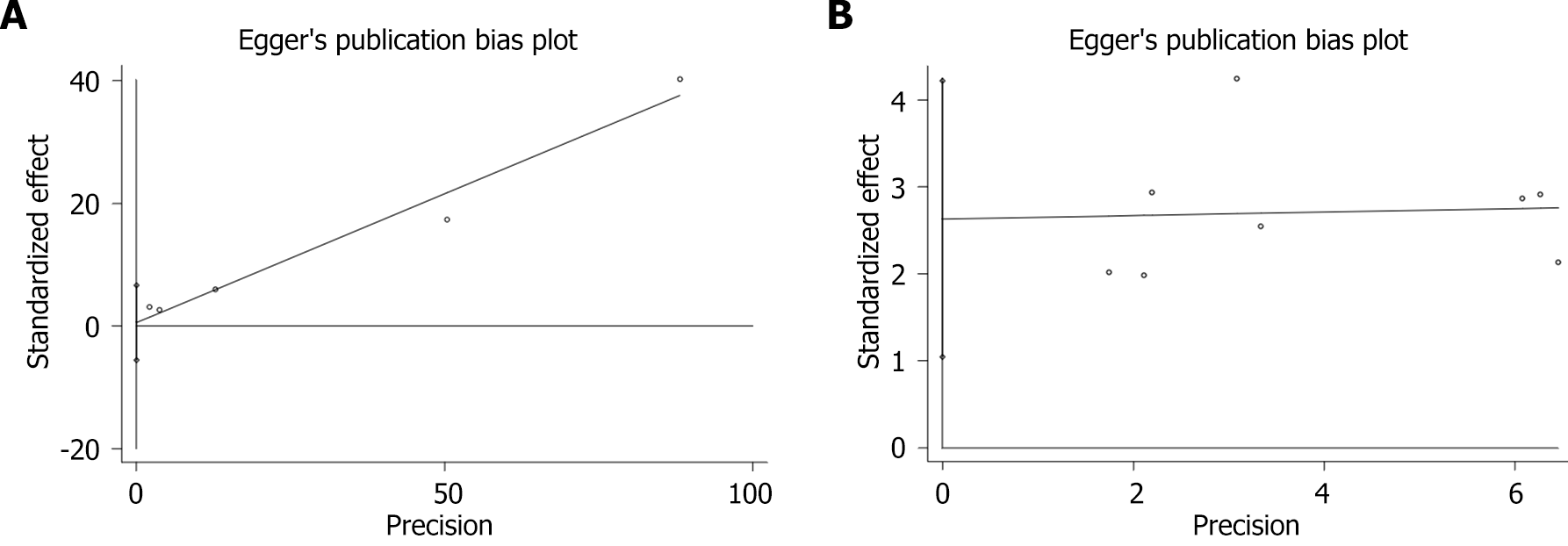
Figure 9 Egger diagram of the correlation between chronic periodontitis and chronic kidney disease.
A: Cohort study; B: Cross-sectional study.
- Citation: Yang F, Shu CJ, Wang CJ, Chen K. Meta-analysis of the association between chronic periodontitis and chronic kidney disease. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(22): 5094-5107
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i22/5094.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i22.5094