Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 16, 2023; 11(5): 1188-1197
Published online Feb 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i5.1188
Published online Feb 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i5.1188
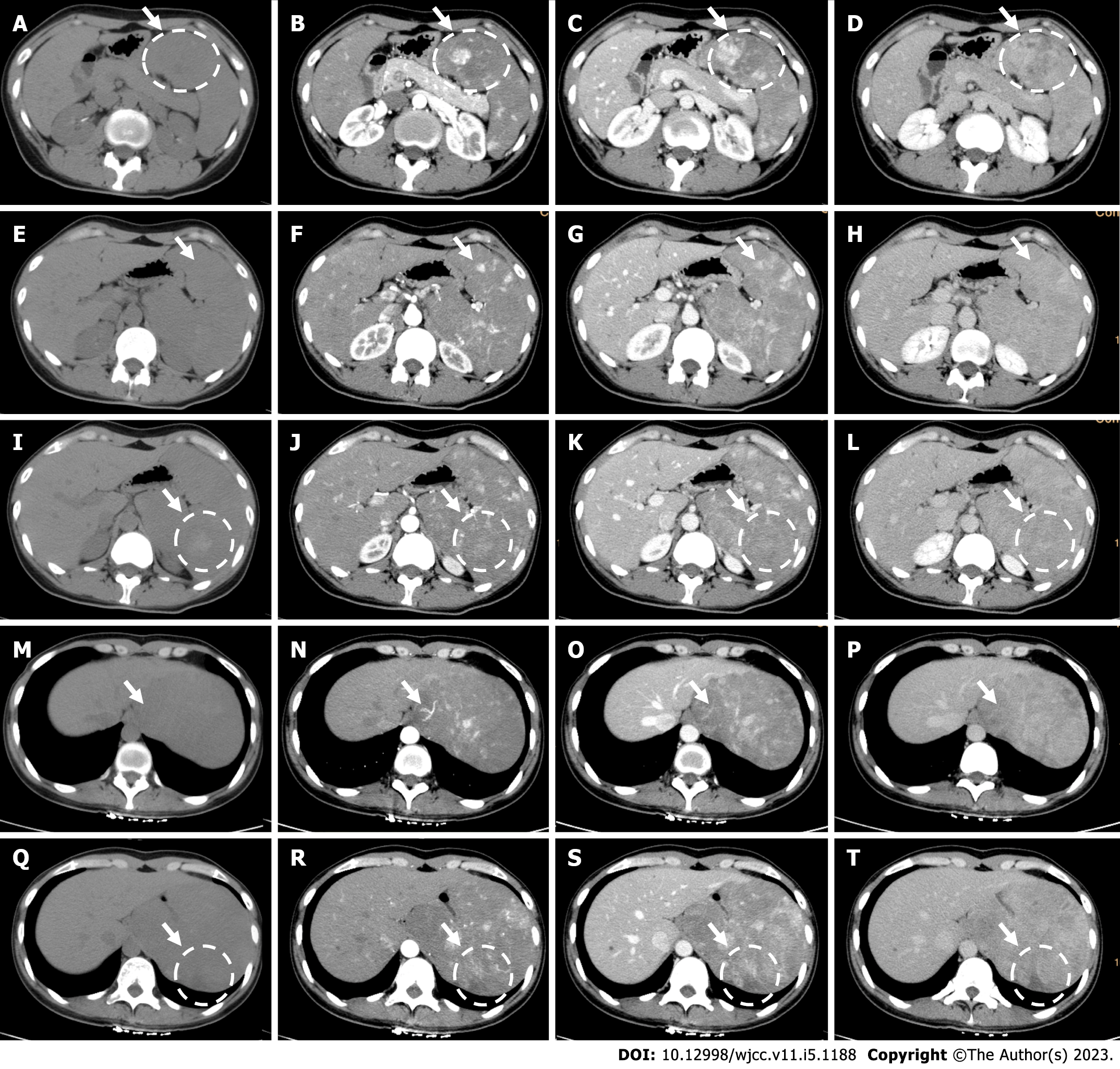
Figure 1 Computed tomography.
A-D: Larger lesions with hypo/iso-density were patchy or nodular enhanced from the peripheral part of the lesions, gradually centripetally full-filled in the venous or delayed phase with decreased degree of enhancement, finally presented with iso-enhancement, and central part of the lesion presented with no enhancement; E-H: Smaller lesions with hypo/iso-density were fully enhanced in the arterial or venous phase presenting hyper-enhancement, then gradually decreased and became iso-enhancement in the delayed phase; I-L: Some lesions showed hyper-density and presented with no obvious enhancement; M-P: Branches of the splenic arteries extending into the larger lesion; Q-T: A peripheral wedge shaped hypo-density area in the spleen showed no obvious enhancement (white arrow).
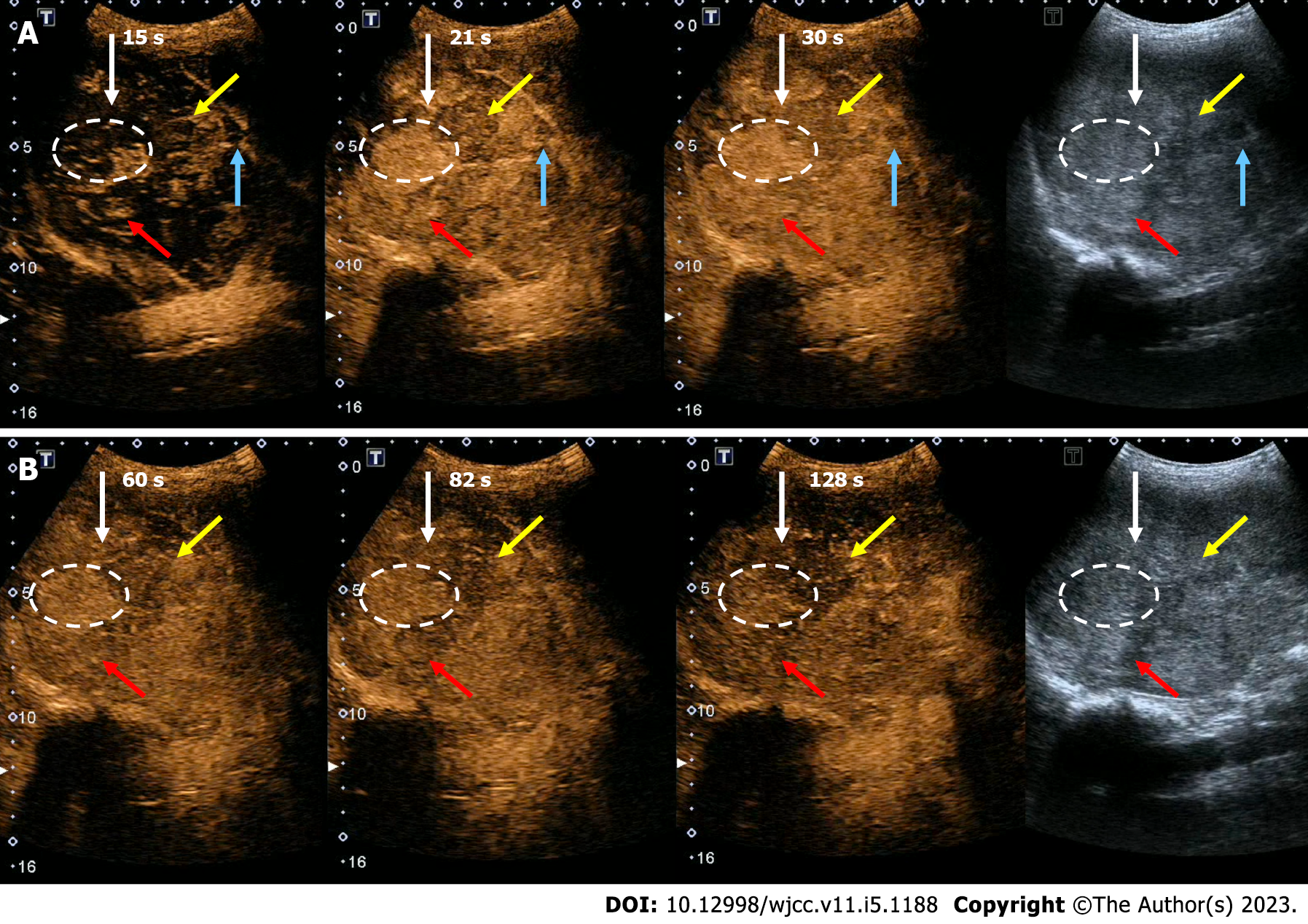
Figure 2 Contrast-enhanced ultrasound.
A and B: White arrow: Contrast-enhanced ultrasound showed some larger lesions, especially hyper-echoic part of the lesion, presented with nodular enhancement in the early arterial phase, then quickly became full-filly enhancement, then gradually decreased in the venous phase with slightly hyper-enhancement; red arrow: Some small hyper-echogenic lesions presented with nodular or completely enhancement in the arterial phase, then fast decreased to iso-enhancement, or just slowly slightly decreased and still presented with hyper-enhancement in the venous phase; blue arrow: Some small lesions with hypo-echoic presented with hypo-enhancement; and yellow arrow: One heterogeneous lesion, with slight posterior acoustic shadow, presented with iso-enhancement during the process.
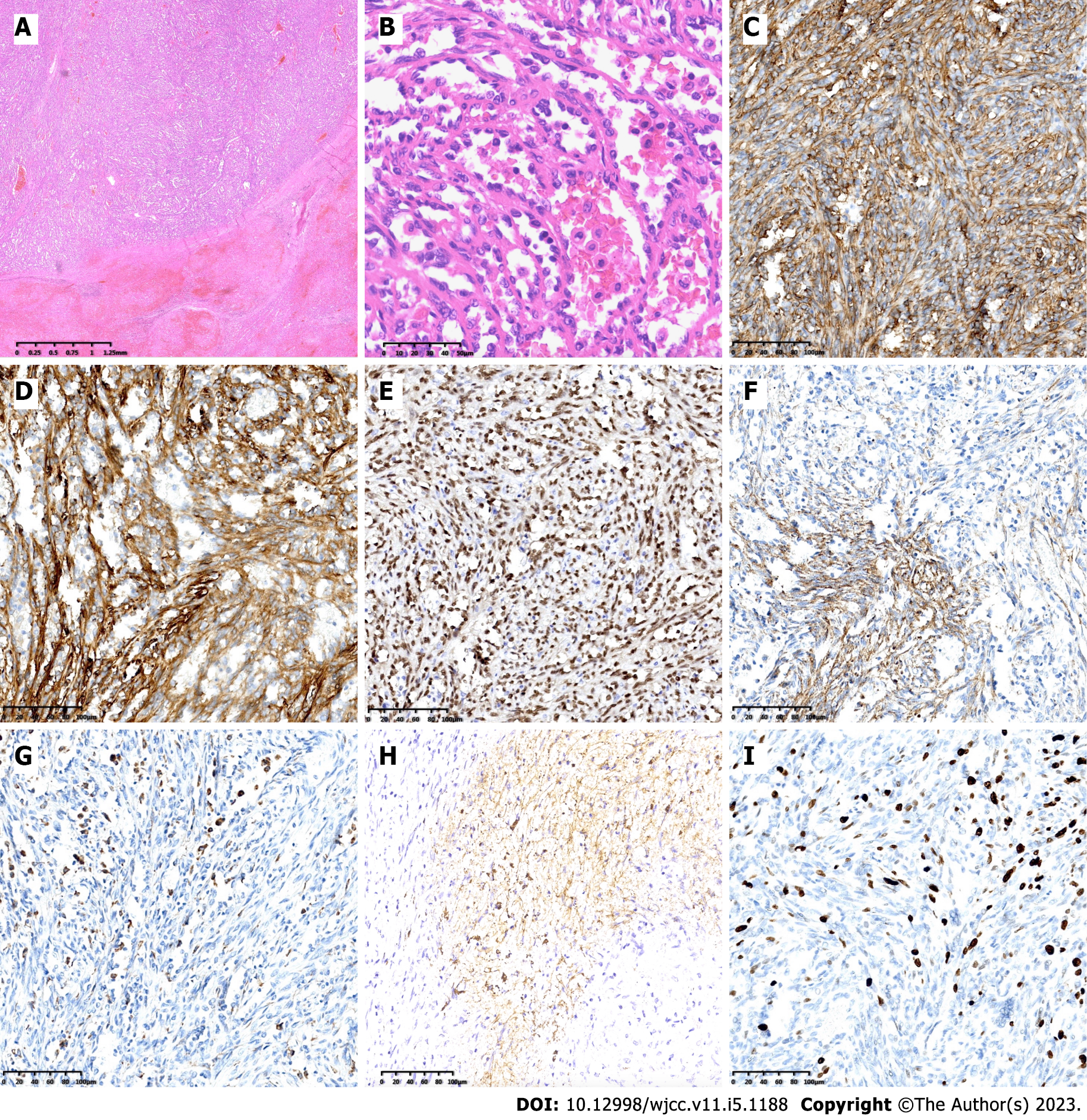
Figure 3 Pathological examination.
A: The lesion was located in the splenic red pulp, nearly all the surrounding tissues were invaded by the tumor cells (H&E magnification × 20); B: The lesion consists of a large amount of variably sized sinuses with anastomosing vascular channels lined by relatively plump round to columnar histiocytic-endothelial littoral cells, some cells with small nucleus with deep chromatin, some columnar cells with large nucleus with vacuolated chromatin, some exfoliated into the expanded sinuses (H&E magnification × 400); C-F: Immunohistochemical staining confirming endothelial differentiation with CD31, CD34, ERG, and FVIII (magnification × 200); G and H: Immunohistochemical staining confirming histiocytic differentiation with CD68 and CD21 (magnification × 200); I: Ki-67 labeling index was no more than 20% (magnification × 200).
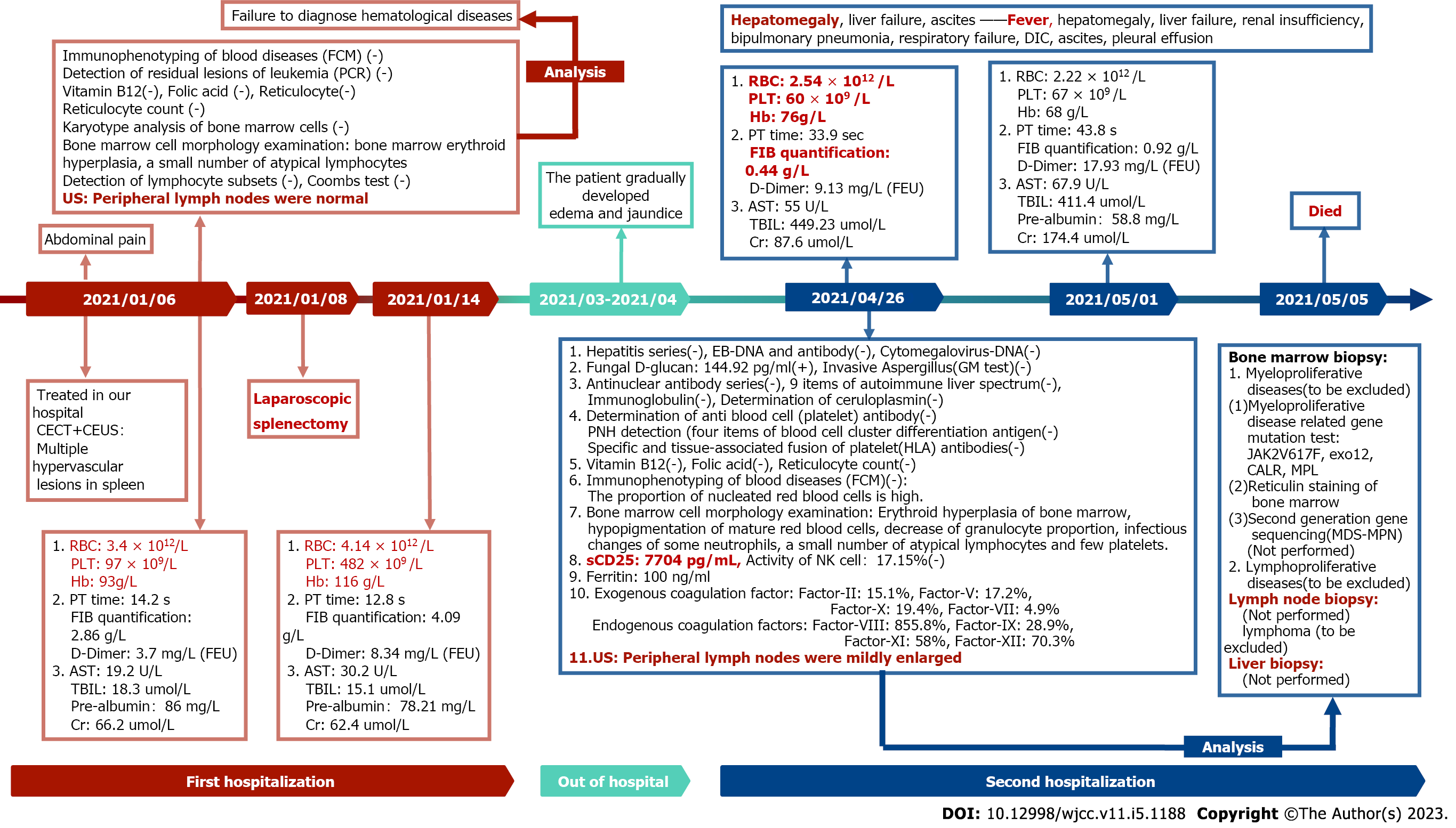
Figure 4 Results of the laboratory examinations and disease progression of the patient.
FCM: Fluorescence confocal microscopy; PCR: Polymerase chain reaction; CEUS: Contrast-enhanced ultrasound; CECT: Contrast-enhanced computed tomography; AST: aspartate aminotransferase; RBC: Red blood cell; PLT: Platelet; Cr: Creatinine; Hb: Hemoglobin; TBIL: Total bilirubin; FIB: Fibrinogen.
- Citation: Jia F, Lin H, Li YL, Zhang JL, Tang L, Lu PT, Wang YQ, Cui YF, Yang XH, Lu ZY. Early postsurgical lethal outcome due to splenic littoral cell angioma: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(5): 1188-1197
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i5/1188.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i5.1188