Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 16, 2023; 11(5): 1009-1018
Published online Feb 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i5.1009
Published online Feb 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i5.1009
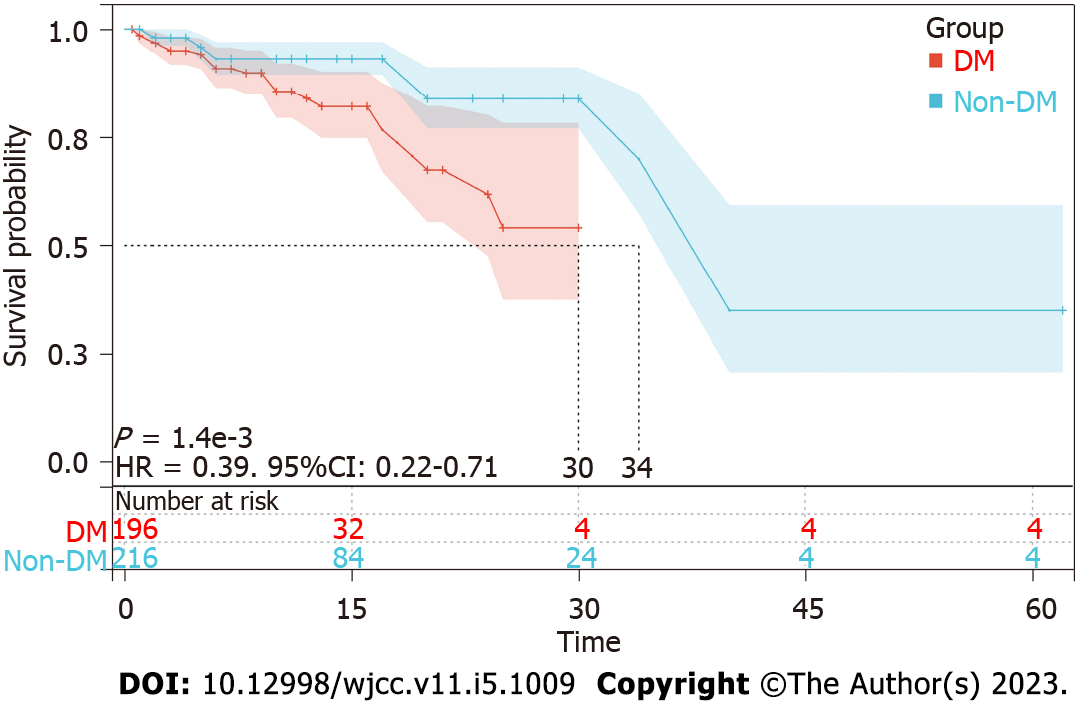
Figure 1 Rates of hepatocellular carcinoma development in patients with or without type 2 diabetes mellitus.
The type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) group had a significantly higher rate of hepatocellular carcinoma development than the non-DM group (P < 0.05). CI: Confidence interval; HR: Hazard ratio; DM: Diabetes mellitus.
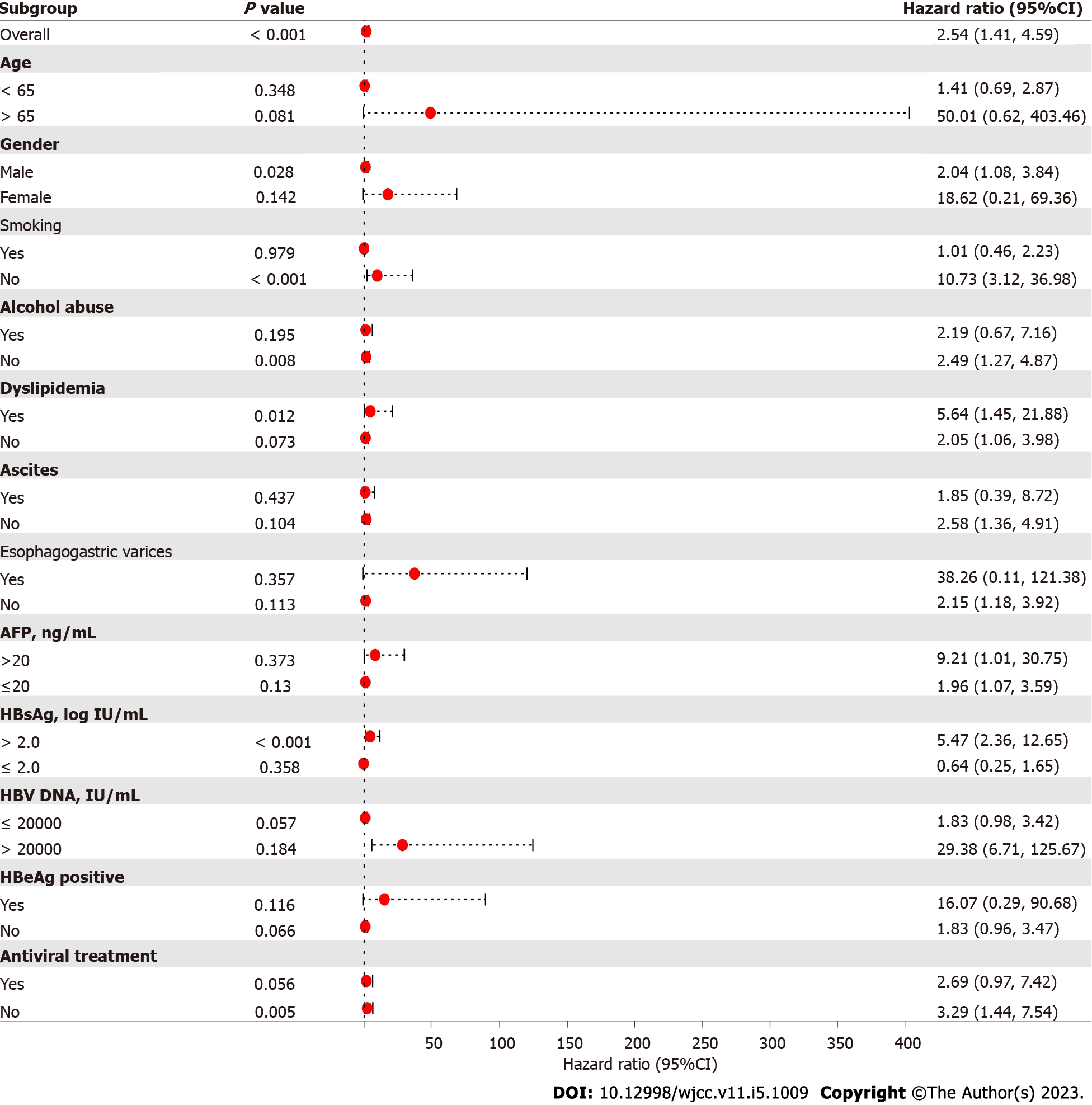
Figure 2 Correlation between type 2 diabetes mellitus and hepatocellular carcinoma development across different subgroups.
The results showed that type 2 diabetes mellitus and hepatocarcinogenesis were significantly correlated in the male subgroup, the non-smoker subgroup, the no alcohol abuse subgroup, the hepatitis B surface antigen > 2.0 log IU/mL subgroup, and the no antiviral treatment subgroup (P < 0.05). AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein; CI: Confidence interval; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HBeAg: Hepatitis B e-antigen.
- Citation: Li MY, Li TT, Li KJ, Zhou C. Type 2 diabetes mellitus characteristics affect hepatocellular carcinoma development in chronic hepatitis B patients with cirrhosis. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(5): 1009-1018
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i5/1009.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i5.1009