Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 26, 2023; 11(27): 6653-6663
Published online Sep 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i27.6653
Published online Sep 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i27.6653
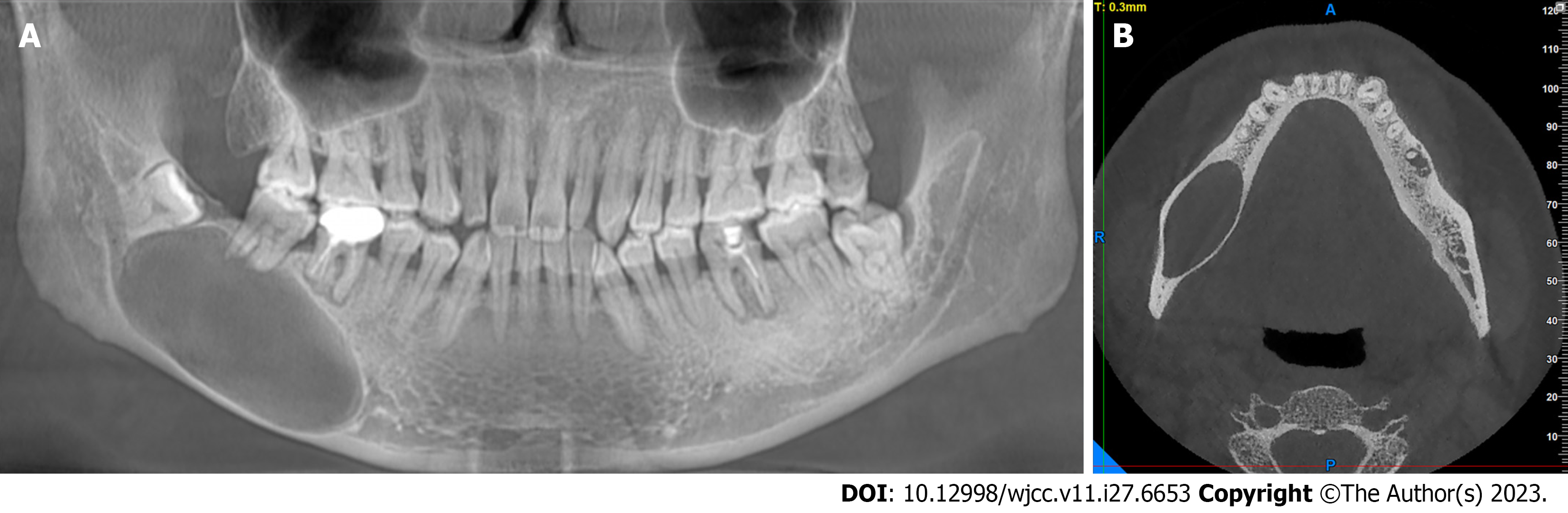
Figure 1 Imaging examination.
A: The oral cone-beam computed tomography (CT) revealed a hypodense image with a size of approximately 4.7 cm × 2.3 cm in the body of the right mandible. A white line is observed around the lesion. The lesion affected the apex of tooth 47 with visible root resorption. The area affected by the inferior alveolar nerve canal was locally dilated without displacement; B: CT (axial section) showing an oval-shaped, low-density area of the right mandible accompanied by cortical bone thinning.
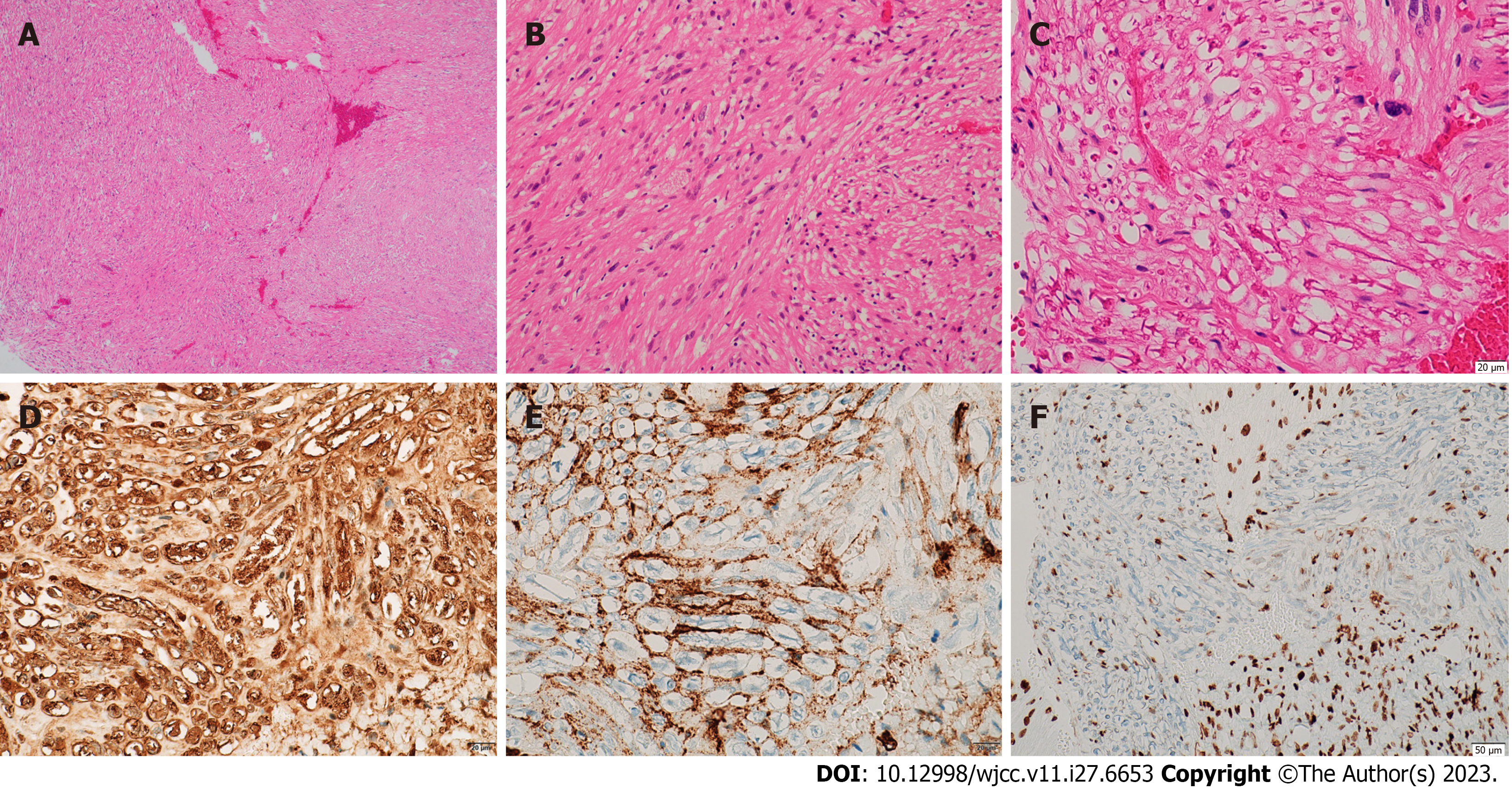
Figure 2 Microscopic features of neurofibroma.
A-C: Histopathological examination with toluidine blue and hematoxylin and eosin staining showing spindle fiber and fibroblast-like cell proliferation with slight nuclear enlargement. The nuclei were short and spindle-shaped, the cytoplasm was richly stained red, and axons were locally visible; D: Immunohistochemistry positive for S-100 protein; E: Immunohistochemistry positive for CD34; F: Immunohistochemistry positive for H3K27ME3.
- Citation: Zhang Z, Hong X, Wang F, Ye X, Yao YD, Yin Y, Yang HY. Solitary intraosseous neurofibroma in the mandible mimicking a cystic lesion: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(27): 6653-6663
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i27/6653.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i27.6653