Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 16, 2022; 10(5): 1729-1737
Published online Feb 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i5.1729
Published online Feb 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i5.1729
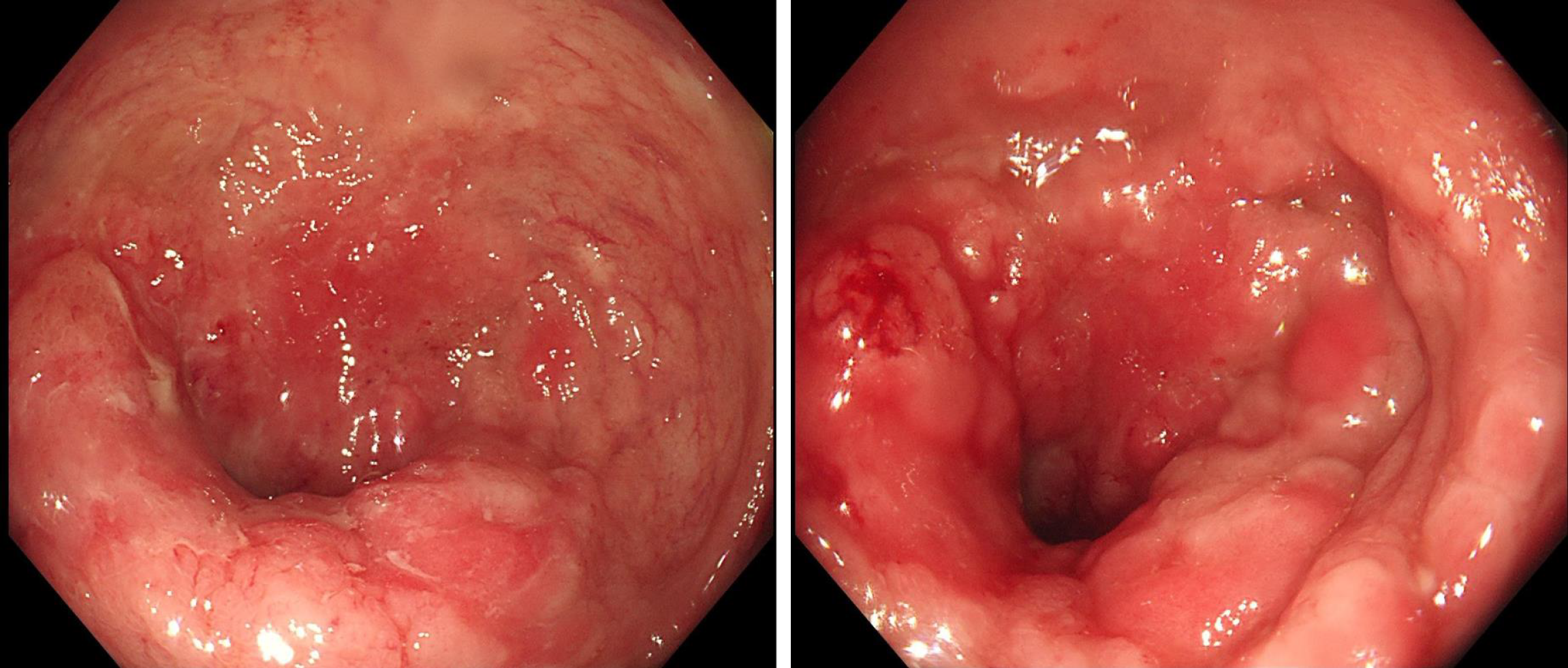
Figure 1 Preoperative colonoscopy.
The surface showed nodular or cauliflower-like changes; the rectal mucosa was congested and showed edema; the surface showed longitudinal changes, with many scattered small ulcers and a little mucus-like white coating on the surface or a small amount of bleeding. The intestinal cavity was so narrow that the endoscope was unable to pass.
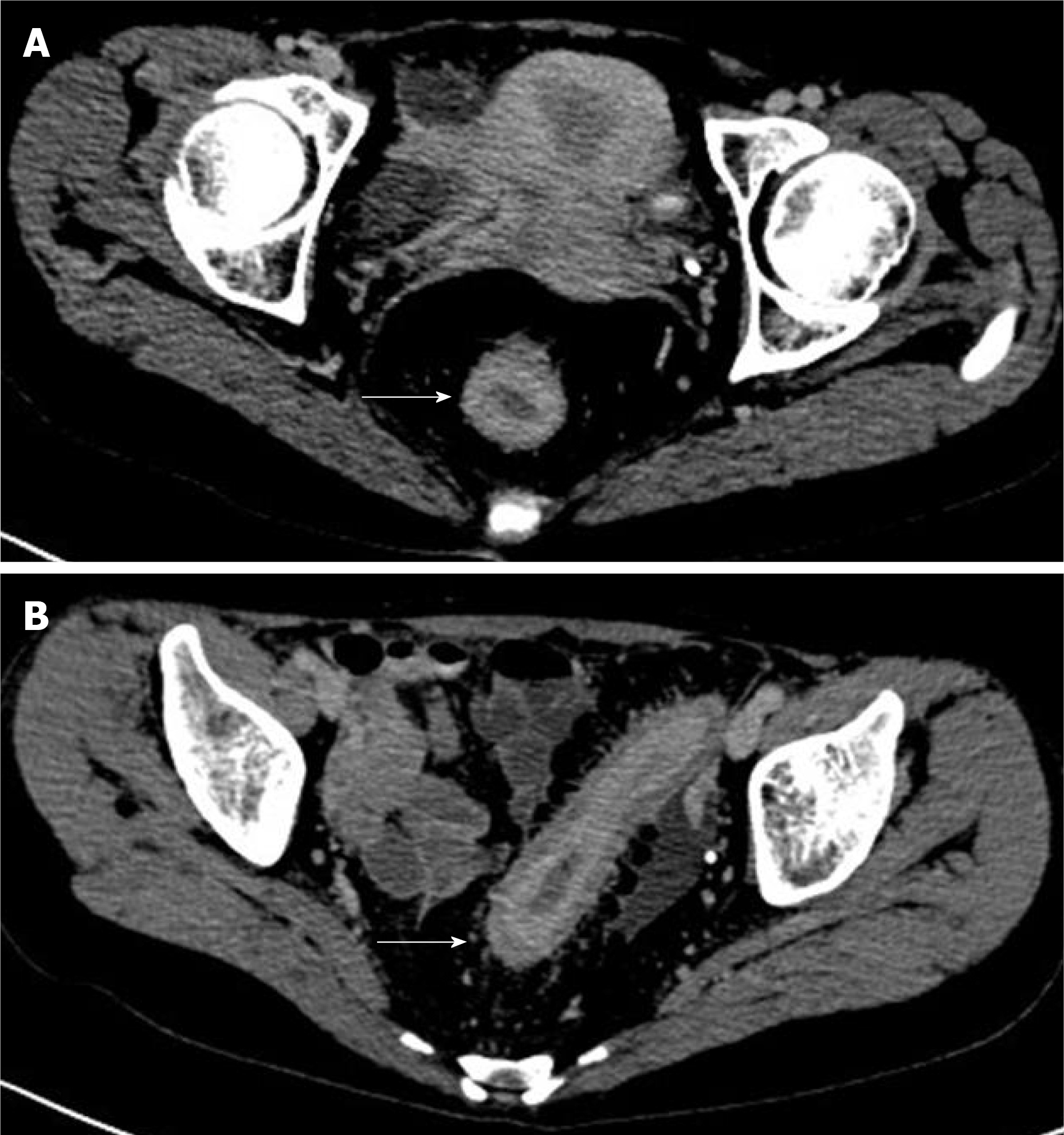
Figure 2 Preoperative computed tomography examination.
A: The rectal wall thickened uniformly in stages, and the intestinal cavity was obviously narrowed; B: The rectal mucosal layer was obviously strengthened (the area indicated by the white arrow, 2019/11/28).
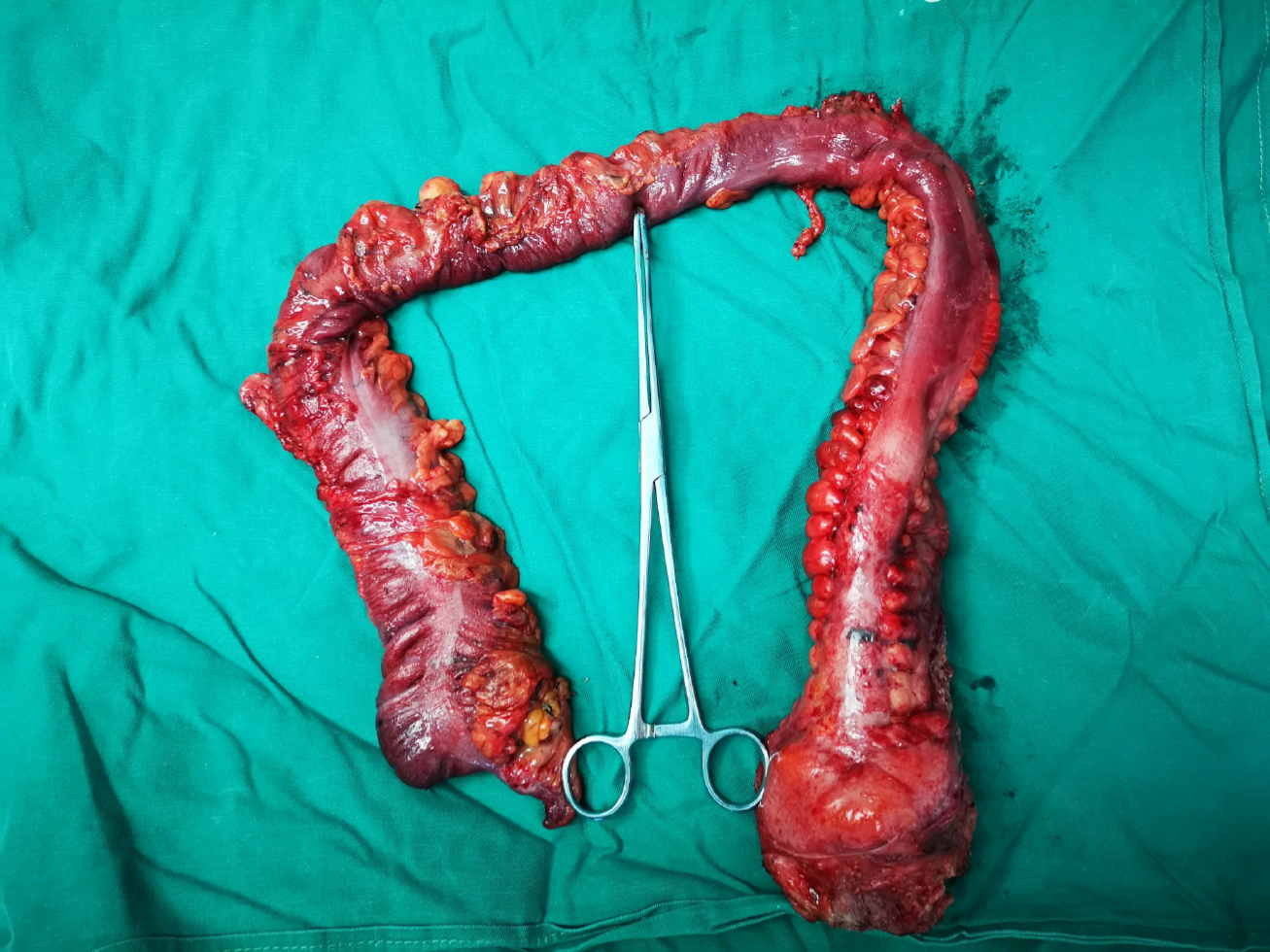
Figure 3 Gross specimen after surgery.
The excised intestine had a length of 67 cm and a diameter of 3.5-7.5 cm. The intestine was cut along the opposite side of the mesentery. There were multiple congestions with superficial ulcers on the mucosal surface of the intestinal canal, with a segmental distribution. The wall of the tube 1-16 cm from the rectal stump was diffusely thickened and stiff, with a wall thickness of about 1.2 cm, and the mucosae were polypoid and fused with each other.
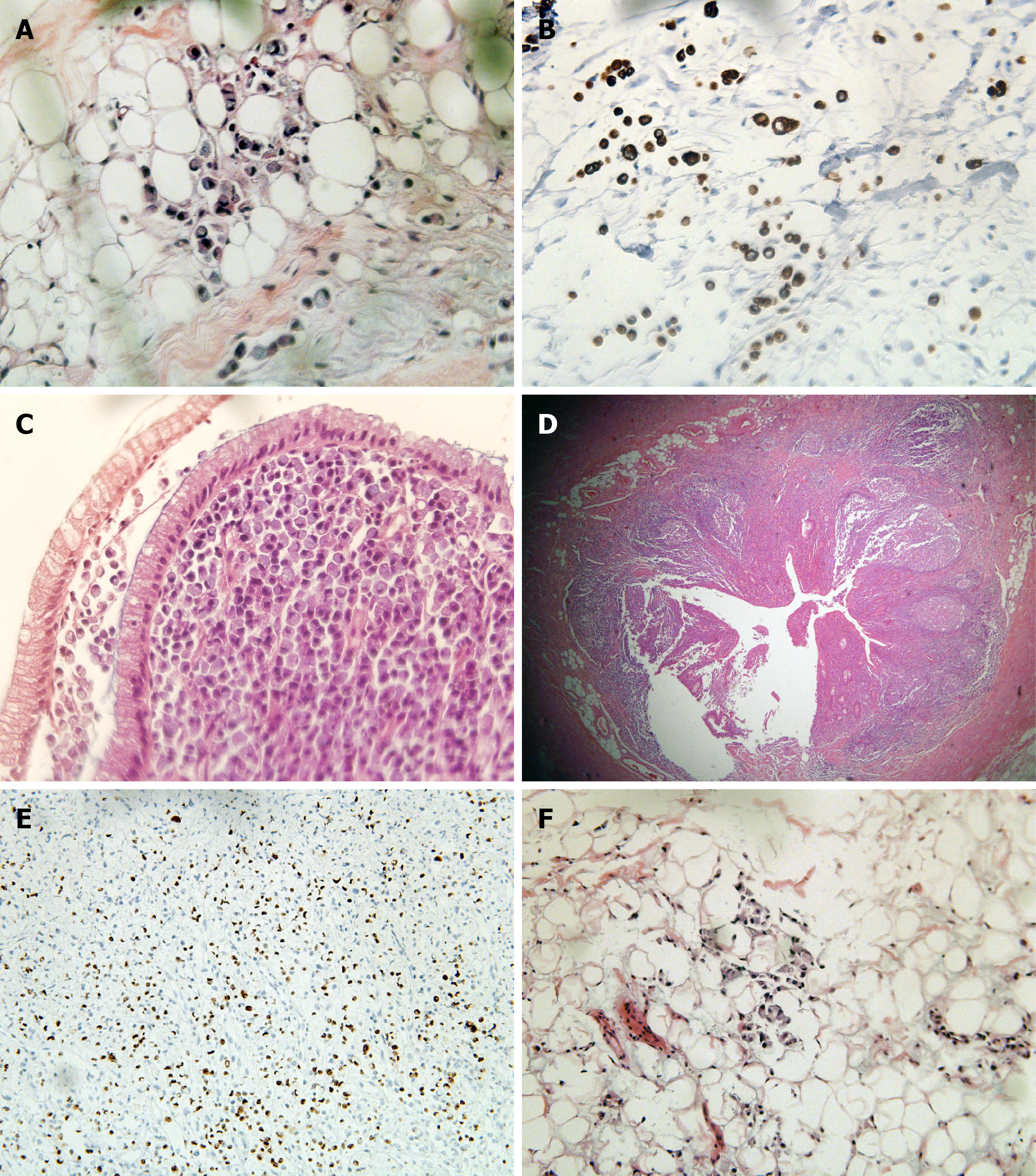
Figure 4 Postoperative pathological section.
A and B: Tumor cells infiltrated the tissue stroma. They were rich in cytoplasm and full of mucus, and the nucleus was squeezed on the side of the cytoplasm, resembling a signet ring (hematoxylin and eosin, 10 ×); C: Tumor cells invaded the colonic mucosa and submucosa, and the polarity of the glandular epithelial cells was still normal; D: Tumor cells invaded the entire thickness of the appendix; E: Ki-67 > 90% in the hotspot area; F: The tissue stroma of the upper rectum near the peritoneum reflex was filled with tumor cells, so an intestinal origin was considered in combination with morphology.
- Citation: Zhang Z, Yu PF, Gu GL, Zhang YH, Wang YM, Dong ZW, Yang HR. Diffuse invasive signet ring cell carcinoma in total colorectum caused by ulcerative colitis: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(5): 1729-1737
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i5/1729.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i5.1729