Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 6, 2022; 10(16): 5208-5216
Published online Jun 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i16.5208
Published online Jun 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i16.5208
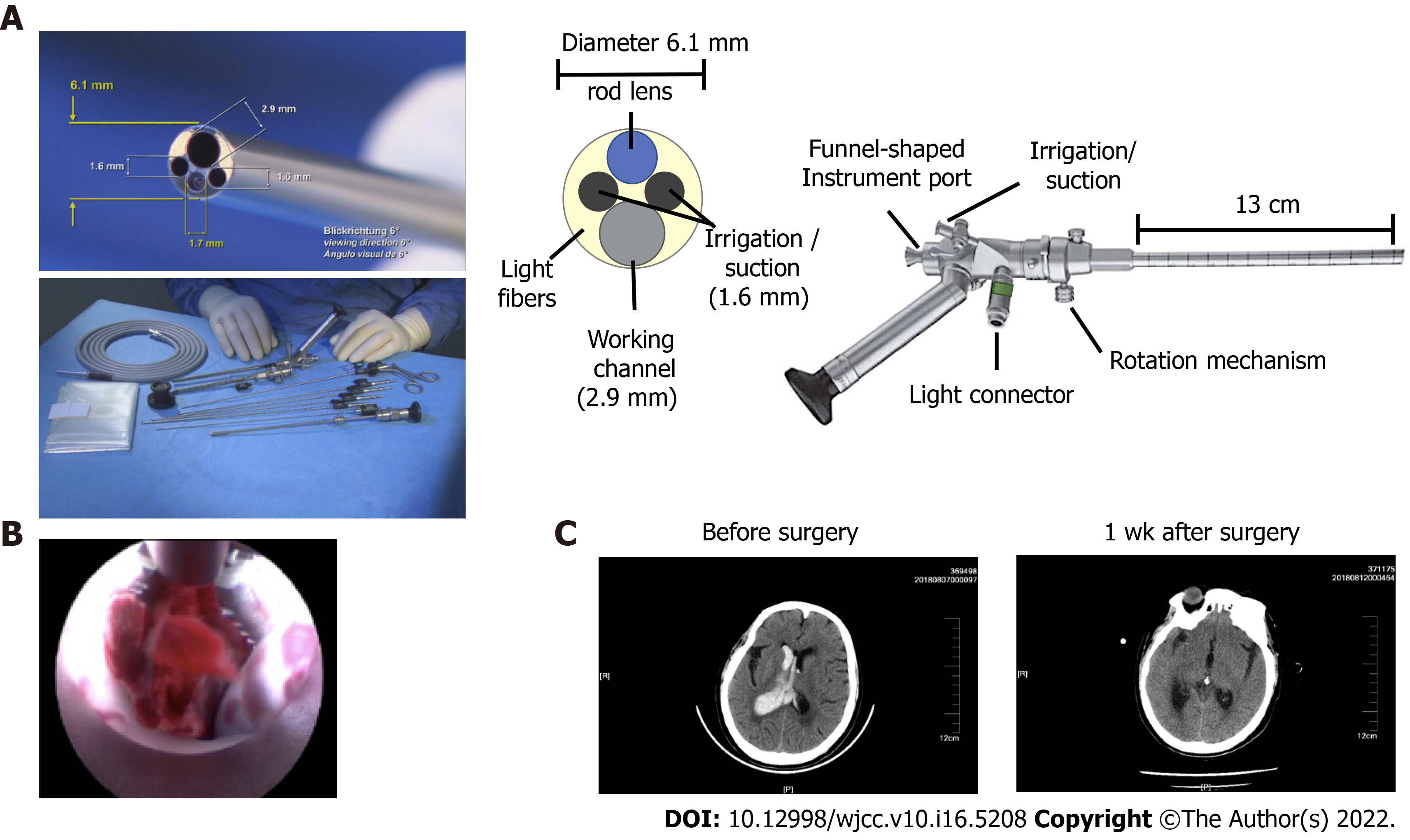
Figure 1 The structure and procedure of endoscopic surgery for intraventricular hemorrhage.
A: The structure of the KARL STORZ high resolution ventriculoscope system (provided by KARL STORZ Co. Ltd.); B: A representative image showing how to pull out the clot by advancing through the working channel using forceps; C: Representative images of head computed tomography in the endoscopic group before and after surgery.
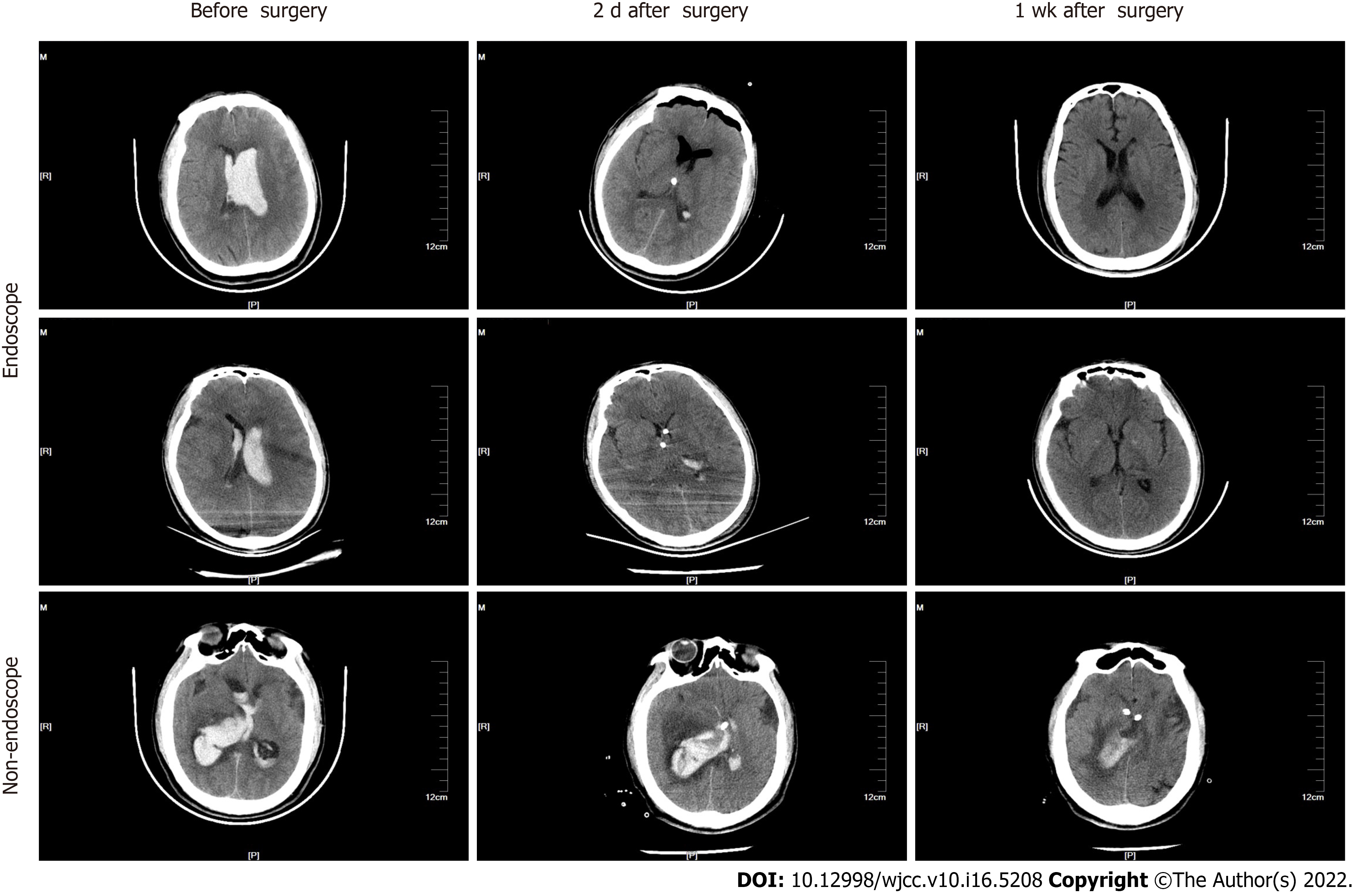
Figure 2 Representative head computed tomography images in the endoscopic and non-endoscopic groups.
The upper and middle panels show images from patients in the endoscopic group. The lower panel shows images from the non-endoscopic group. Three time points are shown, including before surgery, two days after surgery, and one week after surgery.
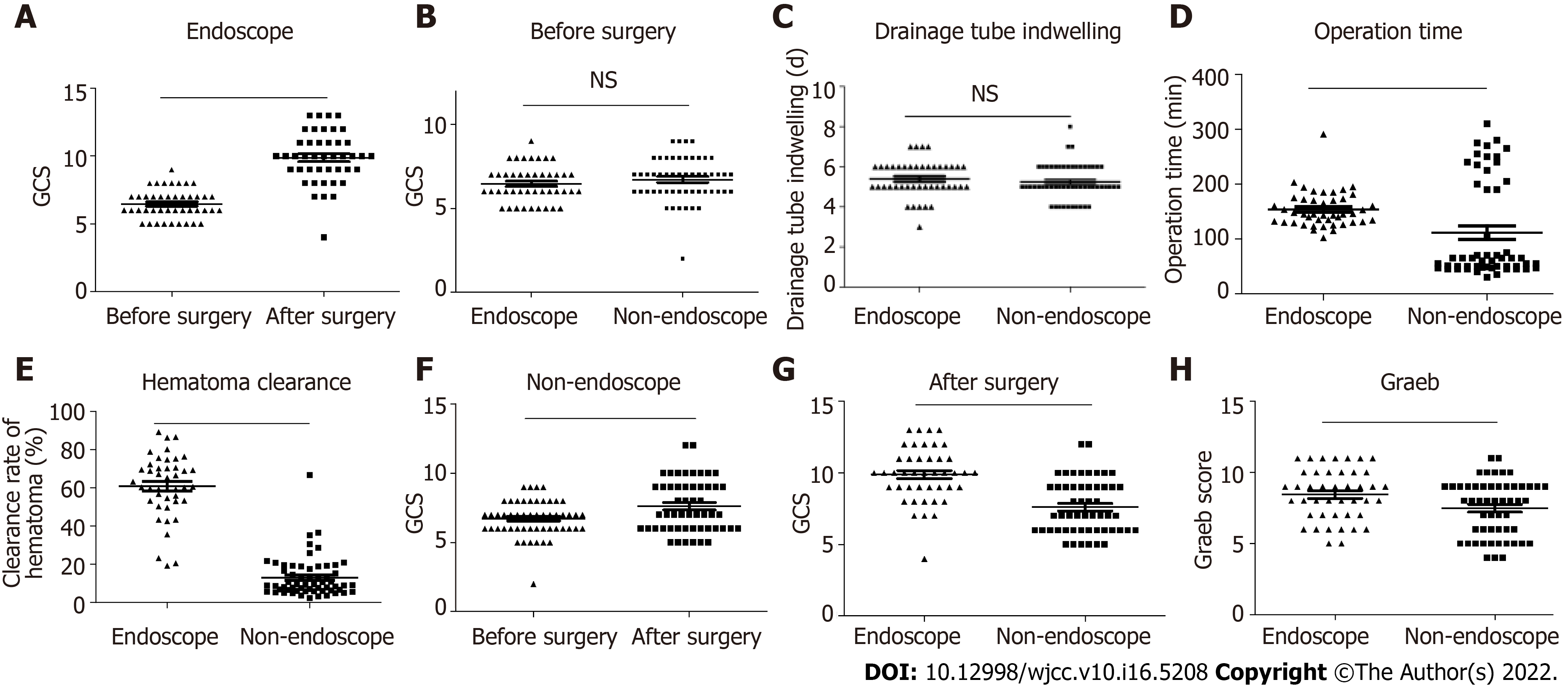
Figure 3 The endoscopic surgery group showed better clinical outcomes than the non-endoscopic group.
A: The change of the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score in the endoscopic group after surgery. n = 43. A two-tailed paired t-test was performed; B: The comparison in the GCS score between the endoscopic group and non-endoscopic group before surgery. Endoscopic group, n = 43; Non-endoscopic group, n = 53. The Kruskal–Wallis test was performed; C: The comparison of the drainage tube indwelling time between the endoscopic group and non-endoscopic group before surgery. Endoscopic group, n = 43; Non-endoscopic group, n = 53. The Kruskal–Wallis test was performed; D: The operation time in the endoscopic and non-endoscopic groups. Endoscopic group, n = 43; Non-endoscopic group, n = 53. The Kruskal–Wallis test was performed; E: The clearance rate of hematoma in the endoscopic and non-endoscopic groups. Endoscopic group, n = 43; Non-endoscopic group, n = 53. The Kruskal–Wallis test was performed; F: The change of the GCS score in the non-endoscopic group after surgery. n = 53. A two-tailed paired t-test was performed; G: The comparison of the GCS score between the endoscopic group and non-endoscopic group after surgery. Endoscopic group, n = 43; Non-endoscopic group, n = 53. The Kruskal–Wallis test was performed; H: The comparison of the Graeb score between the endoscopic group and non-endoscopic group after surgery. Endoscopic group, n = 43; Non-endoscopic group, n = 53. The Kruskal–Wallis test was performed. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001; P < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant. Two-tailed unpaired t-tests were performed.
- Citation: Wang FB, Yuan XW, Li JX, Zhang M, Xiang ZH. Endoscopic surgery for intraventricular hemorrhage: A comparative study and single center surgical experience. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(16): 5208-5216
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i16/5208.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i16.5208