Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. May 16, 2022; 10(14): 4654-4660
Published online May 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i14.4654
Published online May 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i14.4654
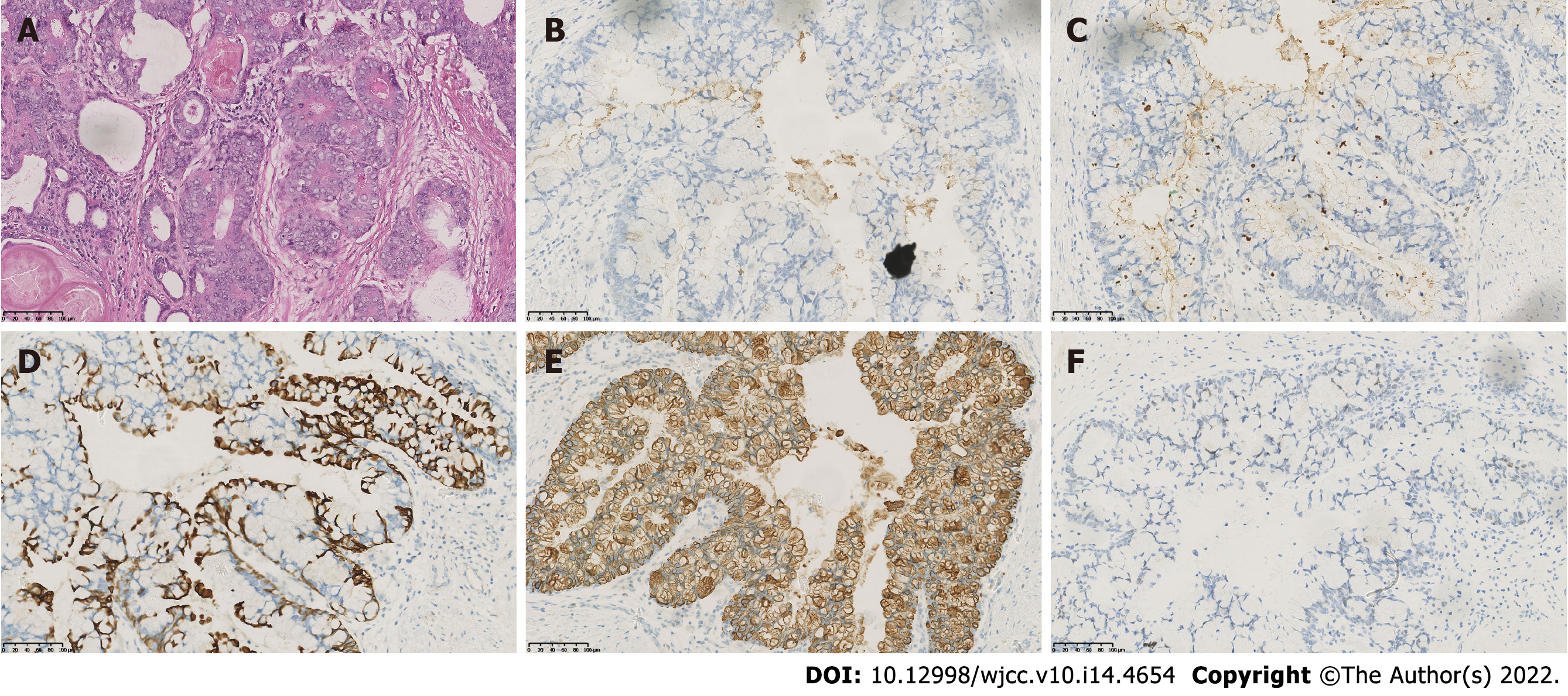
Figure 1 Histological examination of the robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy specimen indicated prostatic mucinous carcinoma.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin staining of the residual prostate tissue indicated lakes of extracellular mucin. B-F: Immunohistochemistry staining of the residual prostate for (B) prostate specific antigen, (C) prostatic serum acid phosphatase, (D) cell keratin 7, (E) cell keratin 20, and (F) caudal-type homeobox transcription factor 2. Magnification × 200.
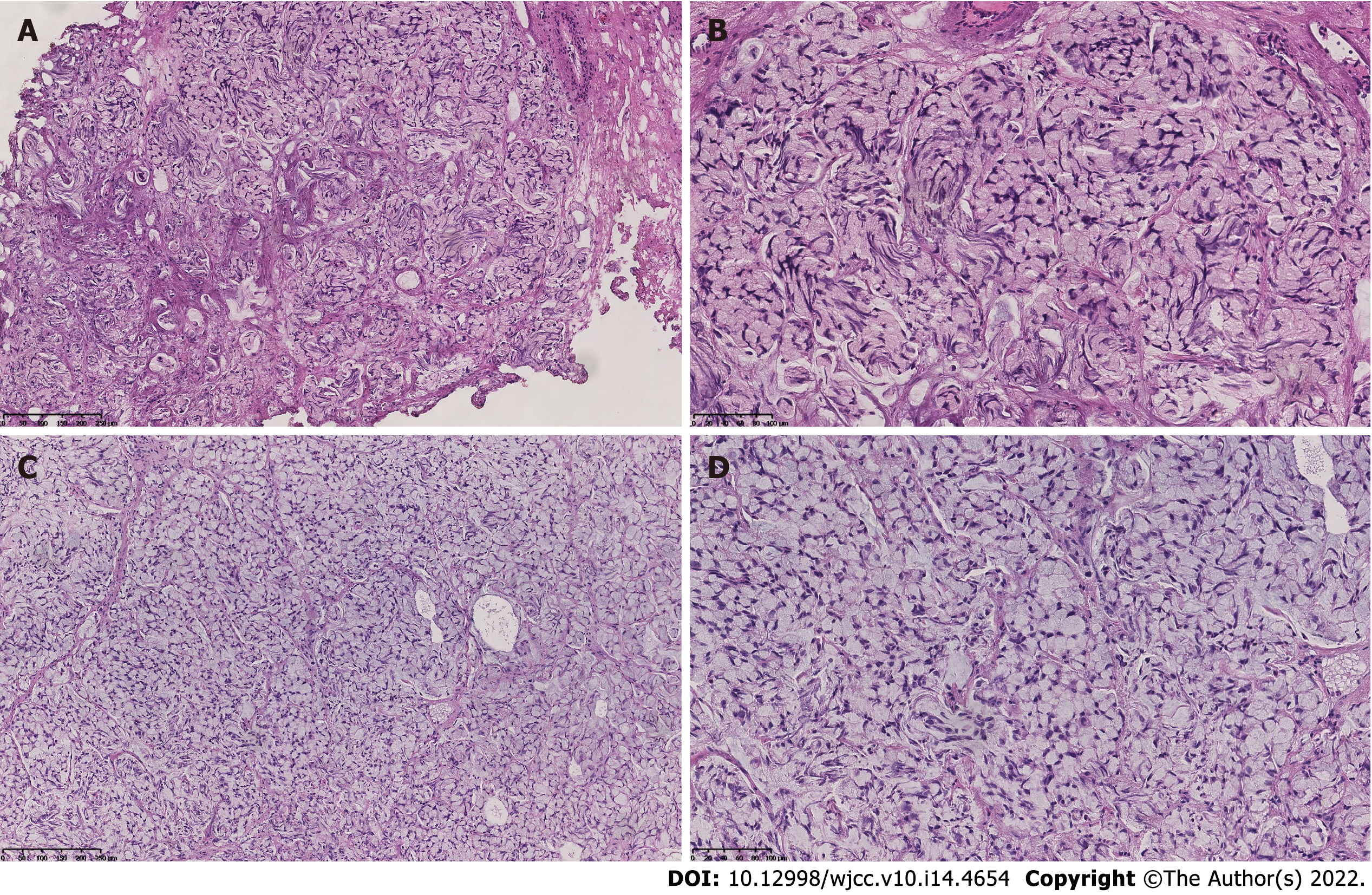
Figure 2 Histological examination of the transurethral resections of bladder tumors specimens showed the extracellular mucin and signet ring cells.
Hematoxylin and eosin staining of the first transurethral resection of bladder tumors specimen (A and B) vs the second transurethral resection of bladder tumors specimen (C and D). Magnification × 100 and × 200, respectively.
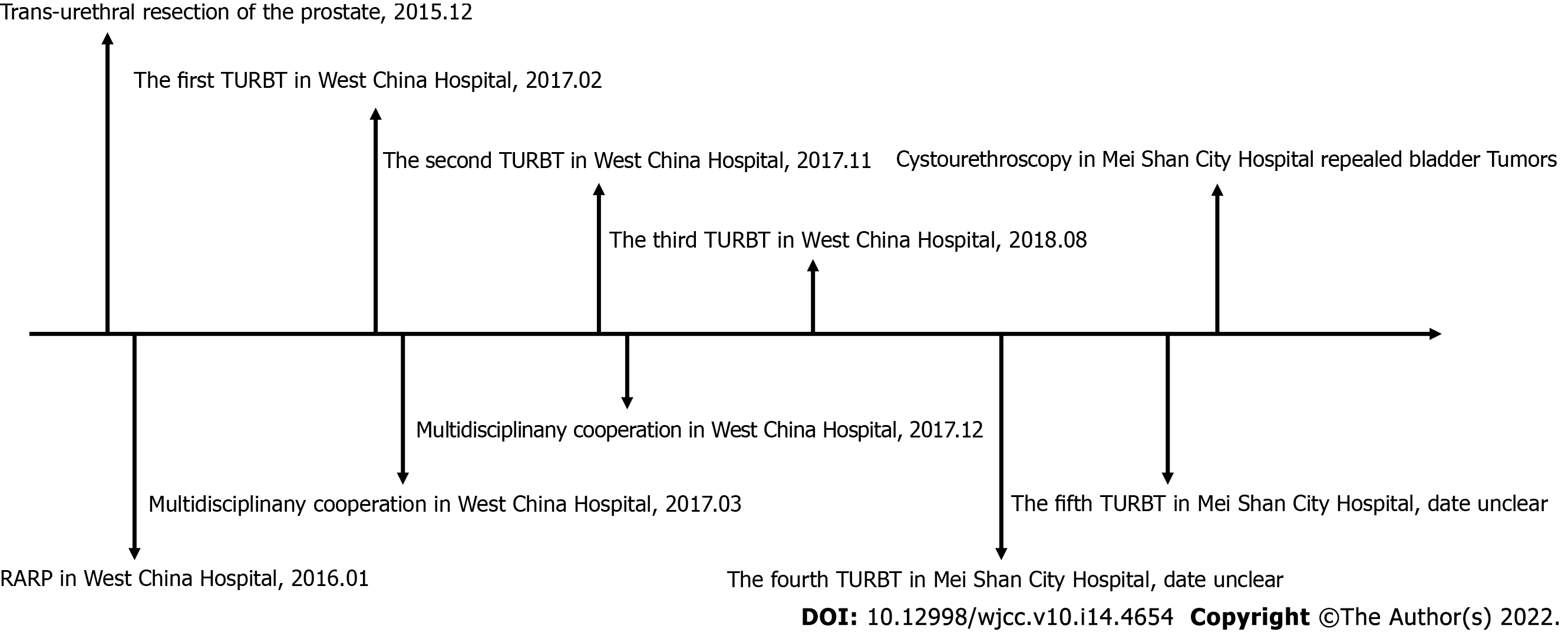
Figure 3 Timeline of the patient’s medical care.
RARP: Robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy; TURBT: Transurethral resection of bladder tumors.
- Citation: Bai SJ, Ma L, Luo M, Xu H, Yang L. Management about intravesical histological transformation of prostatic mucinous carcinoma after radical prostatectomy: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(14): 4654-4660
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i14/4654.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i14.4654