Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Apr 15, 2019; 11(4): 281-294
Published online Apr 15, 2019. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i4.281
Published online Apr 15, 2019. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i4.281
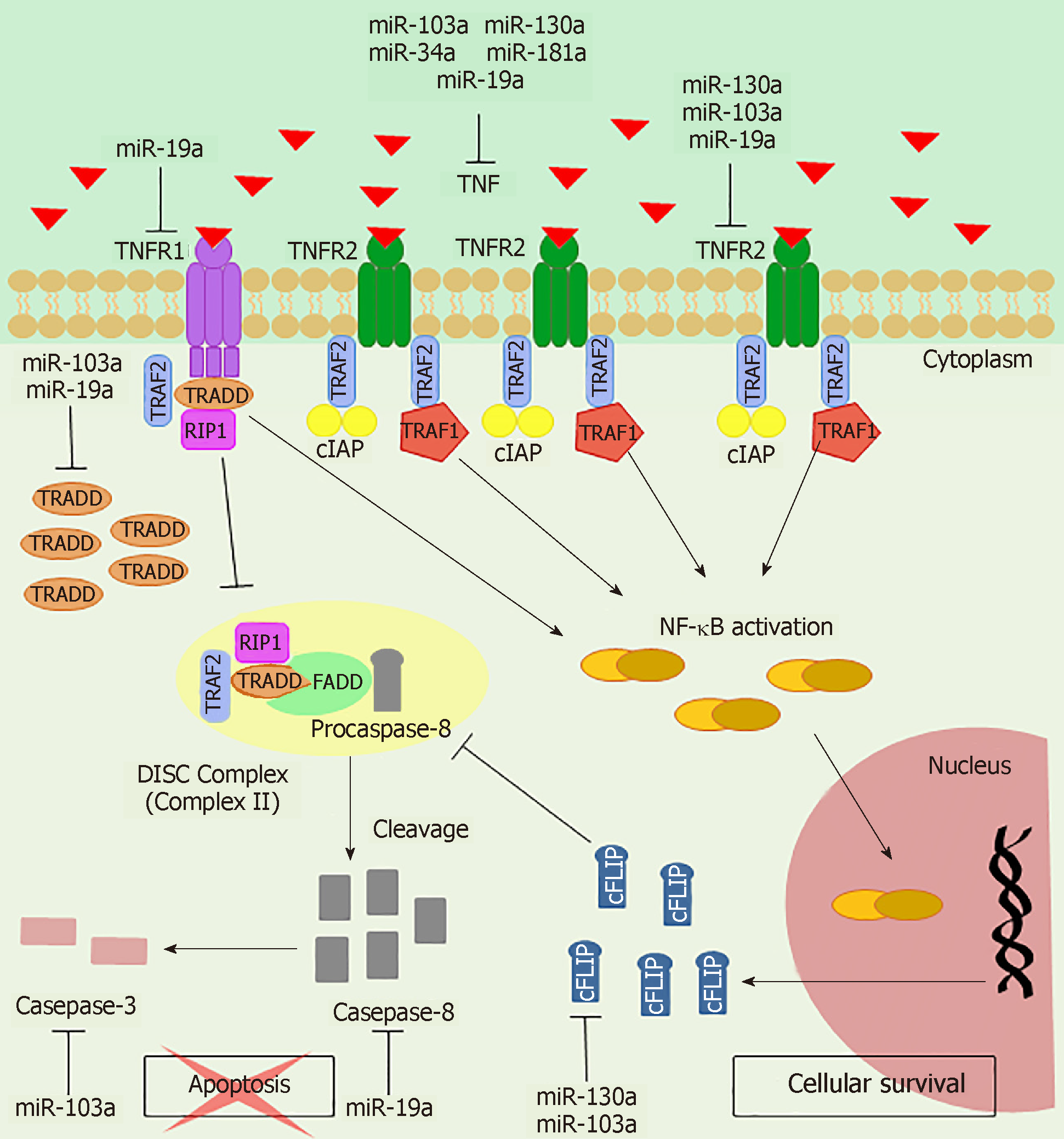
Figure 5 Tumor necrosis factor-α signaling in gastric cancer.
Up-regulation of TNFR2 and anti-apoptotic mediators results in predominance of cell survival pathway gene expression. After tumor necrosis factor (TNF)/TNFR2 interaction, TRAF2, TRAF1 and cellular inhibitor of apoptosis (cIAP) bind to the receptor, which results in NF-κB activation and consequent transcription of anti-apoptotic genes, such as cFLIP. Down-regulation of TNFR1 and CASP3 indicate impairment of the apoptotic pathway. Interaction of TRAF2 with TNFR1 through TRADD disturbs formation of the death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) or also called Complex II, which cleaves and activates caspase-8 and caspase-3. In addition, cFLIP induced by NF-κB inhibits activity of the DISC, rendering cells resistant to apoptosis. miRNAs regulate several genes of this pathway by interfering with cellular processes that contribute to gastric carcinogenesis.
- Citation: Rossi AFT, Contiero JC, Manoel-Caetano FDS, Severino FE, Silva AE. Up-regulation of tumor necrosis factor-α pathway survival genes and of the receptor TNFR2 in gastric cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2019; 11(4): 281-294
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v11/i4/281.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v11.i4.281