Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. May 15, 2024; 16(5): 1725-1736
Published online May 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.1725
Published online May 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.1725
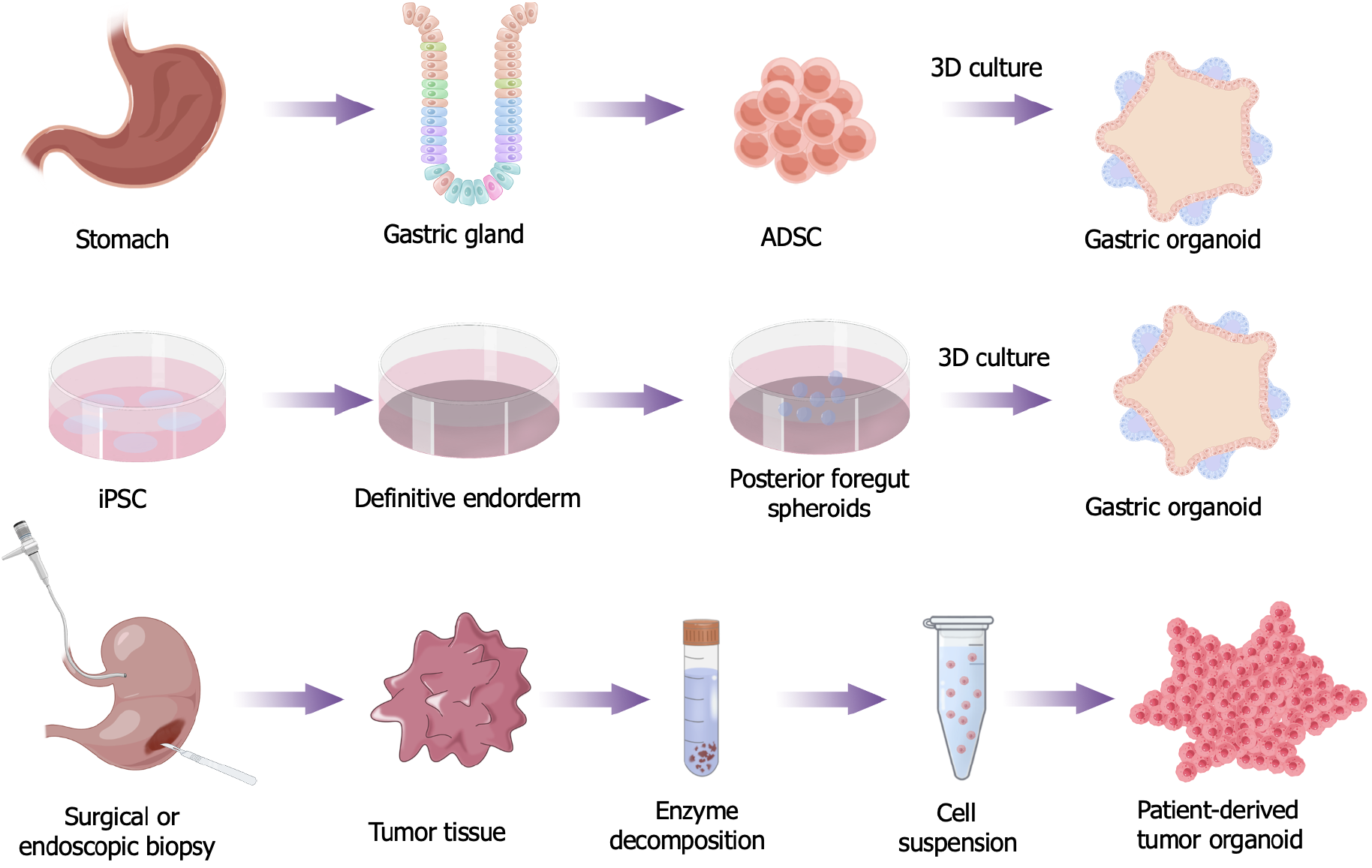
Figure 1 Gastric organoid cultures from different sources.
A: Adipose-derived stem cell-derived gastric organoids: The structures derived from adult stem cells found in the gastric glands, which during 3D cultured to become gastric organoids; B: Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC)-derived gastric organoids: The iPSCs was differentiated into the definitive endoderm, this endoderm was patterned into both anterior and foregut regions then directed the foregut spheroids to differentiate into the posterior foregut, during 3D cultured to become gastric organoids; C: Organoids from gastric tumors: The tumor tissue is obtained by surgical or endoscopic biopsy, then mechanically disrupted and enzymatically digested to obtain a cell suspension. Allowing the cells to grow and form 3D structures, becoming the patient-derived tumor organoid. ADSC: Adipose-derived stem cell; iPSC: Induced pluripotent stem cells.
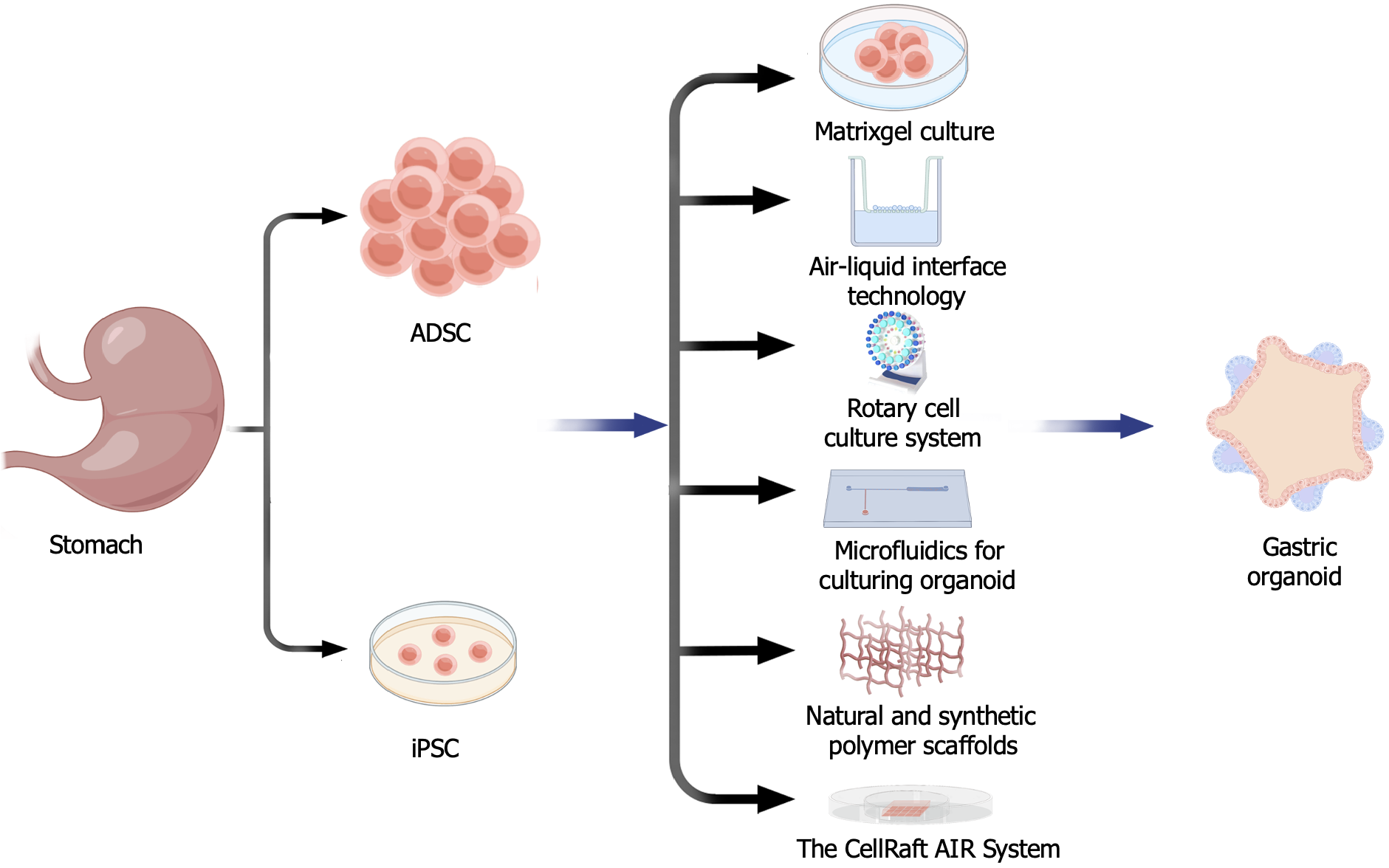
Figure 2 Six organoid culture models.
Matrigel culture, Air-liquid interface organoid culture, Rotary cell culture system, Microfluidics for culturing organoids, Natural and synthetic polymer scaffolds, The CellRaft AIR® System. These six organoid culture models offer a variety of choices, allowing to better culture gastric organoid. ADSC: Adipose-derived stem cell; iPSC: Induced pluripotent stem cells.
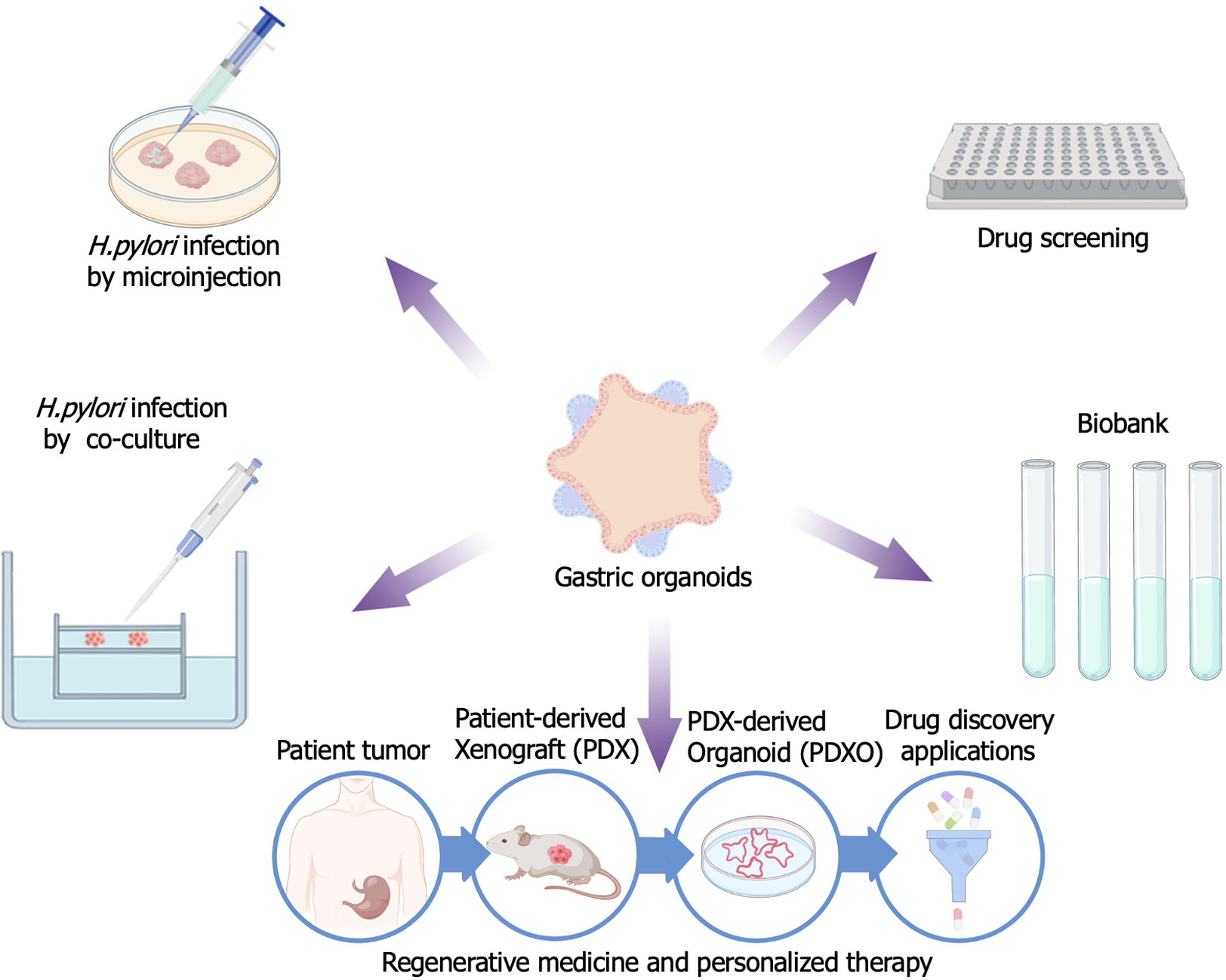
Figure 3 Application of gastric organoid.
The role of gastric organoids in observing the pathogenesis of gastric cancer caused by Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori): Used a microinjection method to inject H. pylori directly into the gastric epithelial organoid sphere. The role of gastric organoids in the study of microbe-host relationships: By co-culturing gastric organ tissues of individuals infected with H. pylori with host immune cells. Drug screening: Effectiveness, toxicity and drug resistance: In the process of drug screening and development, drug testing is necessary, including preclinical experiments and clinical trials. Organoid biobank: Referred to a specialized repository used for the preservation and study of various artificially synthesized organoids. Regenerative medicine and personalized therapy: Patient-derived xenografts organoids offer new possibilities for individualized therapy by culturing patient-derived tumor xenograft models in a way that preserves tumor properties and stem cell properties, representing a new tool for personalized therapy and regenerative medicine research. H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori.
- Citation: Liu YY, Wu DK, Chen JB, Tang YM, Jiang F. Advances in the study of gastric organoids as disease models. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(5): 1725-1736
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i5/1725.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.1725