Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. May 15, 2023; 15(5): 713-730
Published online May 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i5.713
Published online May 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i5.713
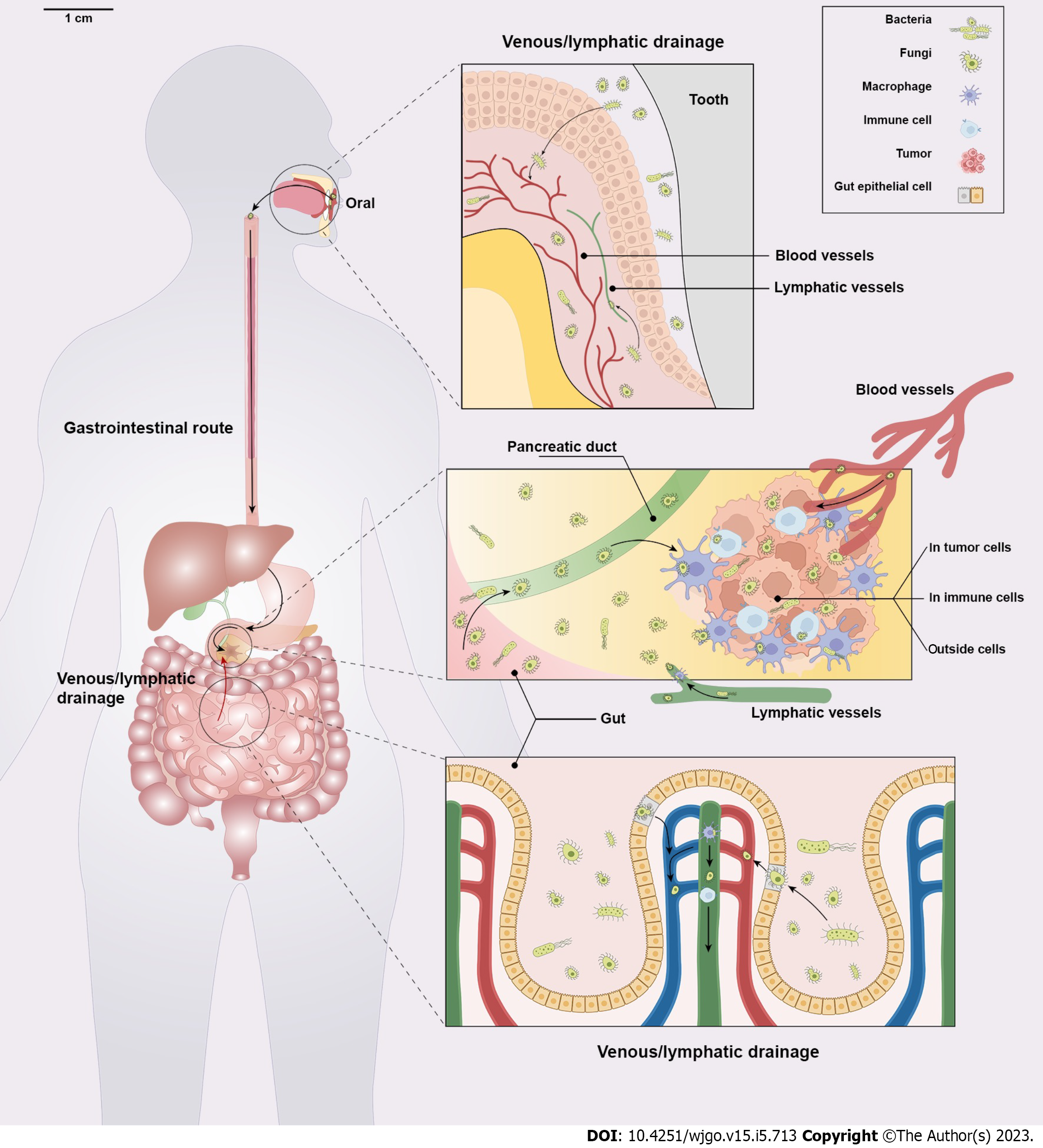
Figure 1 The origin and localization of the intratumour microbiome in pancreatic cancer.
The microbiome in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) may originate from the gut and the oral cavity. The microbiome located in the oral cavity and gut can reach the pancreas via the pancreatic duct. But also exists the possibility of drainage via blood and lymph. The microbiome located in the gut migrates through the damaged intestinal epithelial barrier into the pancreas via venous blood, especially in the inferior gastrointestinal tract. In the case of oral microbiome, it can also enter the pancreas via the venous or lymphatic drainage. And the PDAC intratumour microbiome locates in tumour cells, immune cells and outside cells.
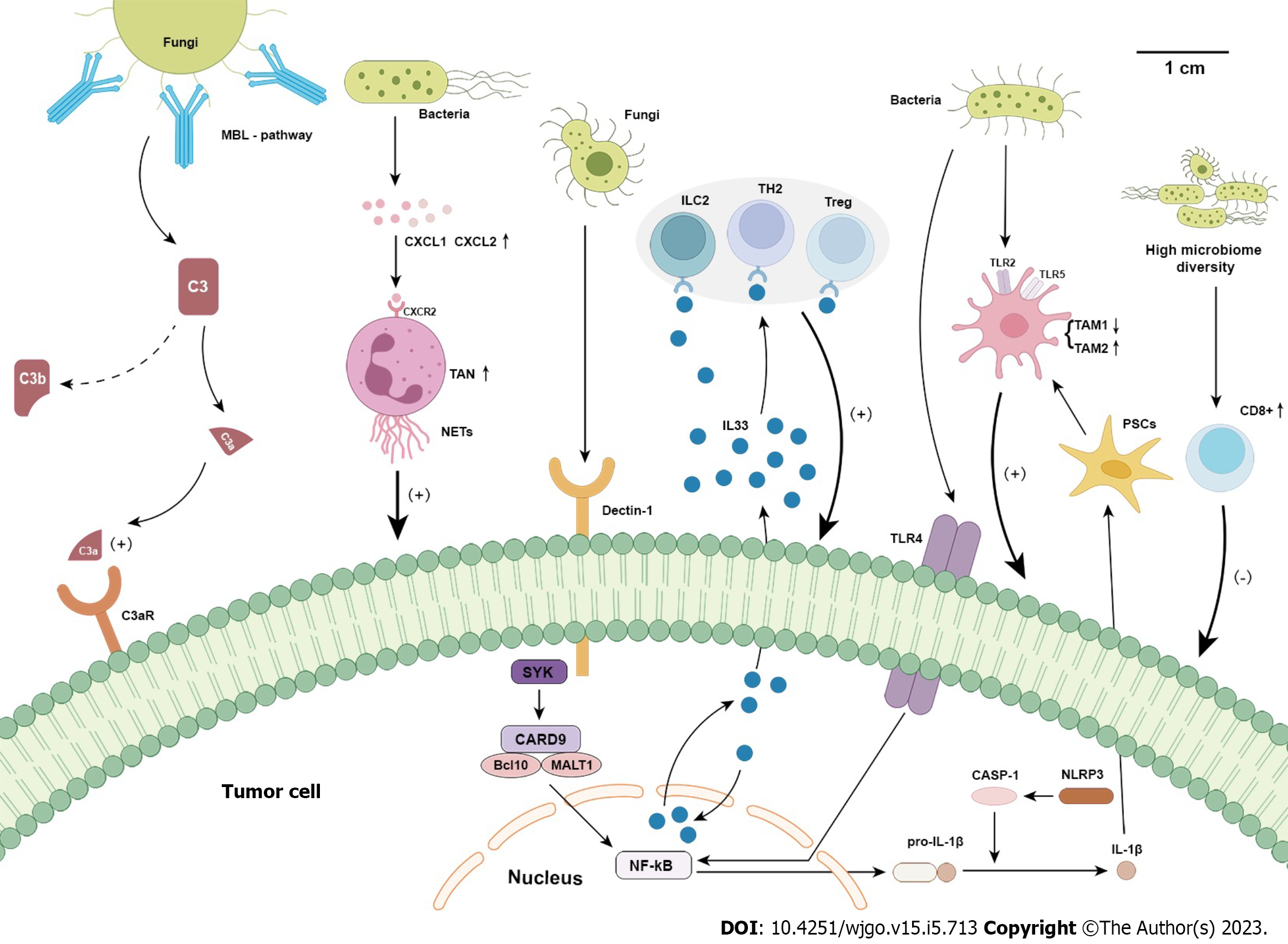
Figure 2 The intratumour microbiome-immune-pancreatic cancer axis.
The intratumour fungi can activate the complement 3 (C3) complement cascade through the "lectin activation pathway". And C3a, as a fragment after C3 complement cascade reaction, promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cells proliferation by binding to C3a receptors on the surface of cancer cells. Moreover, the intratumour fungi (Malassezia globosa or Alternaria alternata) and their cell-free extracts facilitate interleukin (IL)-33 secretion through activation of the dectin-1 receptor-mediated Src-Syk-CARD9 pathway. And IL-33 secretion promotes T helper 2 cell, group 2 innate lymphoid cells and Tregs enrichment in tumour microenvironment (TME), thus promoting PDAC progression. The intratumour bacteria promotes the secretion of neutrophil chemokines in the TME of PDAC thereby promoting tumour-associated neutrophils 2 (TAN2) enrichment in the TME. A portion of the effect of TAN2 may be through neutrophil extracellular traps. The PDAC intratumour bacteria also reduces the TAM1 polarization and decreased the antigen-presenting ability of TAM1 though through activation of toll-like receptors (TLR)2 and TLR4 on the surface of cells. TAM1 inhibition is accompanied by an increase in TAM to TAM2 conversion. It also promotes the secretion of IL-1β through TLR4 on the surface of PDAC cells. And IL-1β secretion promotes TAM2 activation through an indirect pathway that activates pancreatic stellate cells. Finally, the high diversity of intratumour microbiome promotes the activation of CD8+ T cells, which inhibits PDAC. C3: Complement 3; PDAC: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; Th2: T helper 2 cell; ILC2: Group 2 innate lymphoid cells; TME: Tumour microenvironment; TAN2: Tumour-associated neutrophils 2; NETs: Neutrophil extracellular traps; TAM: Tumour-associated macrophages; TLR: Toll-like receptors; PSCs: Pancreatic stellate cells.
- Citation: Guan SW, Lin Q, Yu HB. Intratumour microbiome of pancreatic cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2023; 15(5): 713-730
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v15/i5/713.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v15.i5.713