Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2023; 15(5): 466-475
Published online May 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i5.466
Published online May 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i5.466
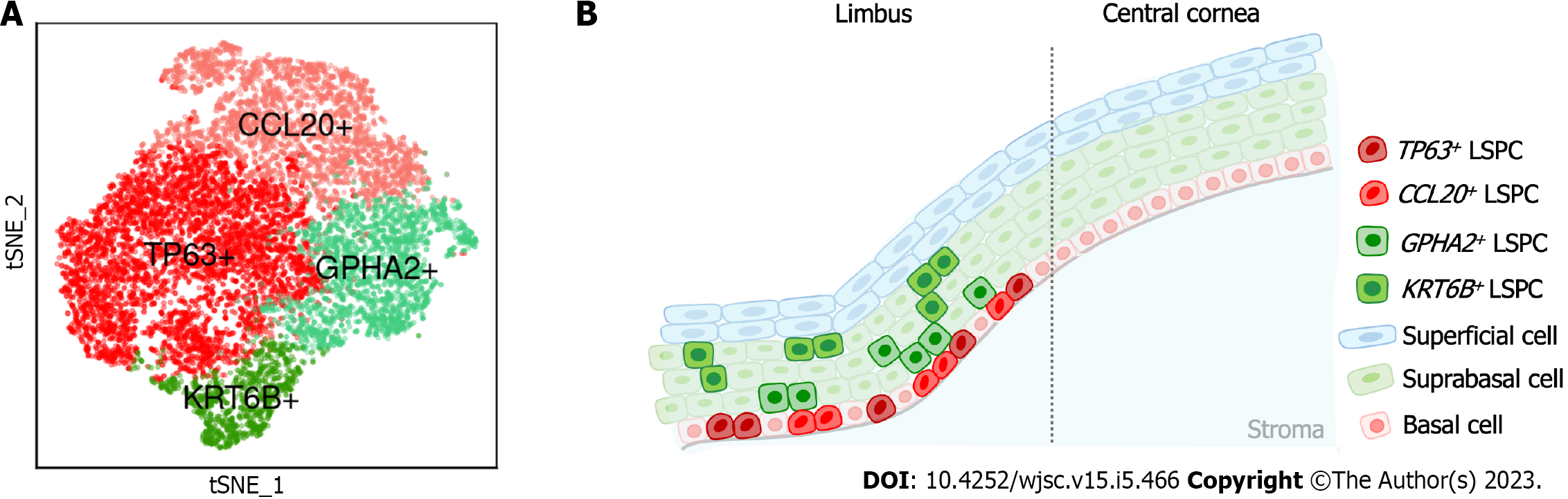
Figure 1 Heterogeneity of limbal stem cells in humans.
A: The t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding plot of four subpopulations of limbal stem cells; B: Schematic diagram of the heterogeneous limbal stem cells in the human limbus. LSPC: Limbal stem/progenitor cell.
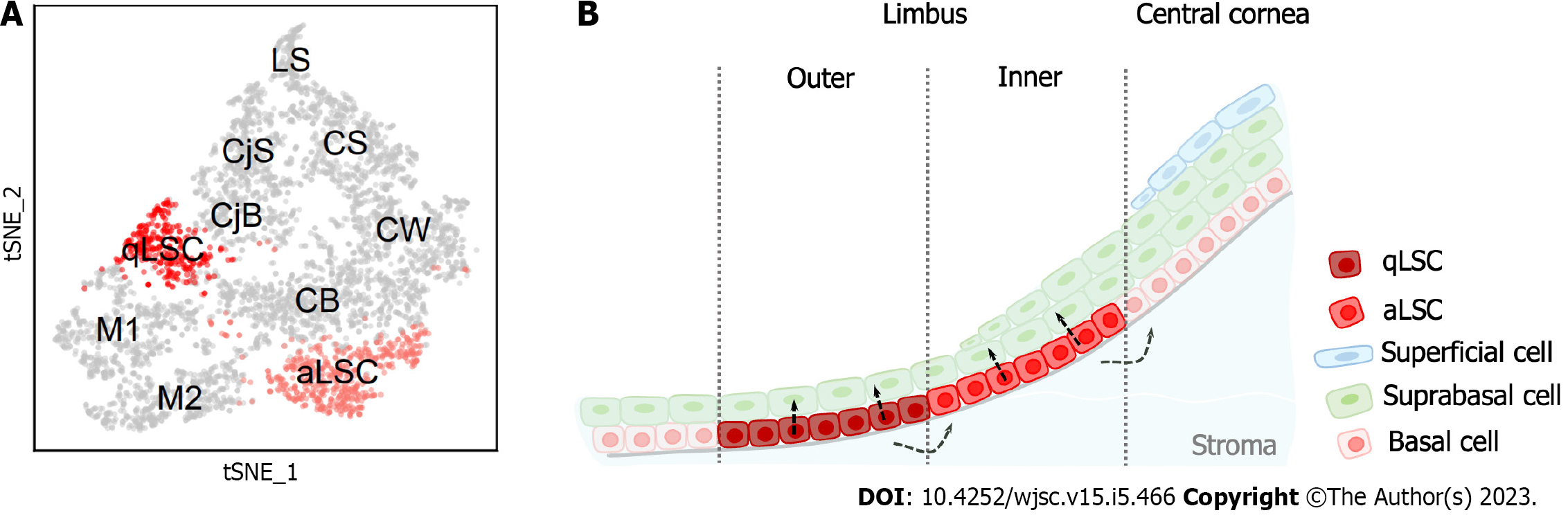
Figure 2 Heterogeneity of limbal stem cells in mice.
A: The t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding plot of the corneal epithelial cell subpopulations in the mouse limbus. The limbal stem cells are highlighted in red; B: Schematic diagram of the heterogenous limbal stem cells in the mouse limbus. aLSC: Active limbal stem cell; CB: Corneal basal cell; CjB: Conjunctival basal cell; CjS: Conjunctival suprabasal cell; CS: Corneal superficial cell; CW: Corneal wing cell; LS: Limbal superficial cell; M1/M2: Cells in mitosis; qLSC: Quiescent limbal stem cell.
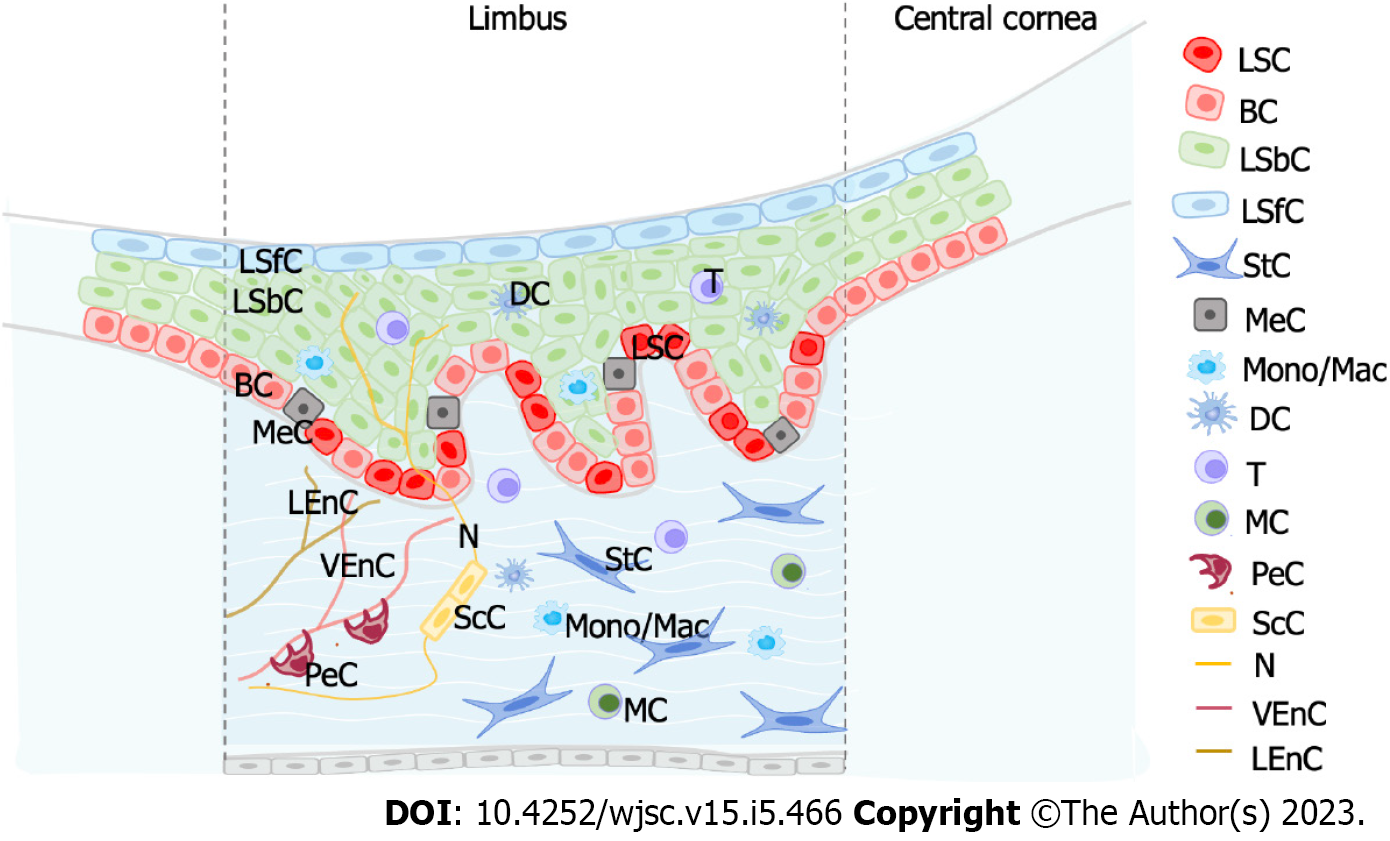
Figure 3 Structure and cellular compositions in the limbal stem cell environment.
Niche cells regulate limbal stem cells. LSCs: Limbal stem cells; BC: Basal cell; DC: Dendritic cell; LEnC, Lymphatic endothelial cell; LSbC: Limbal suprabasal cell; LSfC: Limbal superficial cell; MC: Mast cell; MeC: Melanocyte; Mono/Mac: Monocyte/macrophage; N: Nerve; PeC: Peripheral cell; ScC: Schwann cell; StC: Stromal cell; T: T cell; VEnC: Vascular endothelial cell.
- Citation: Sun D, Shi WY, Dou SQ. Single-cell RNA sequencing in cornea research: Insights into limbal stem cells and their niche regulation. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(5): 466-475
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i5/466.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i5.466