Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2023; 15(5): 342-353
Published online May 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i5.342
Published online May 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i5.342
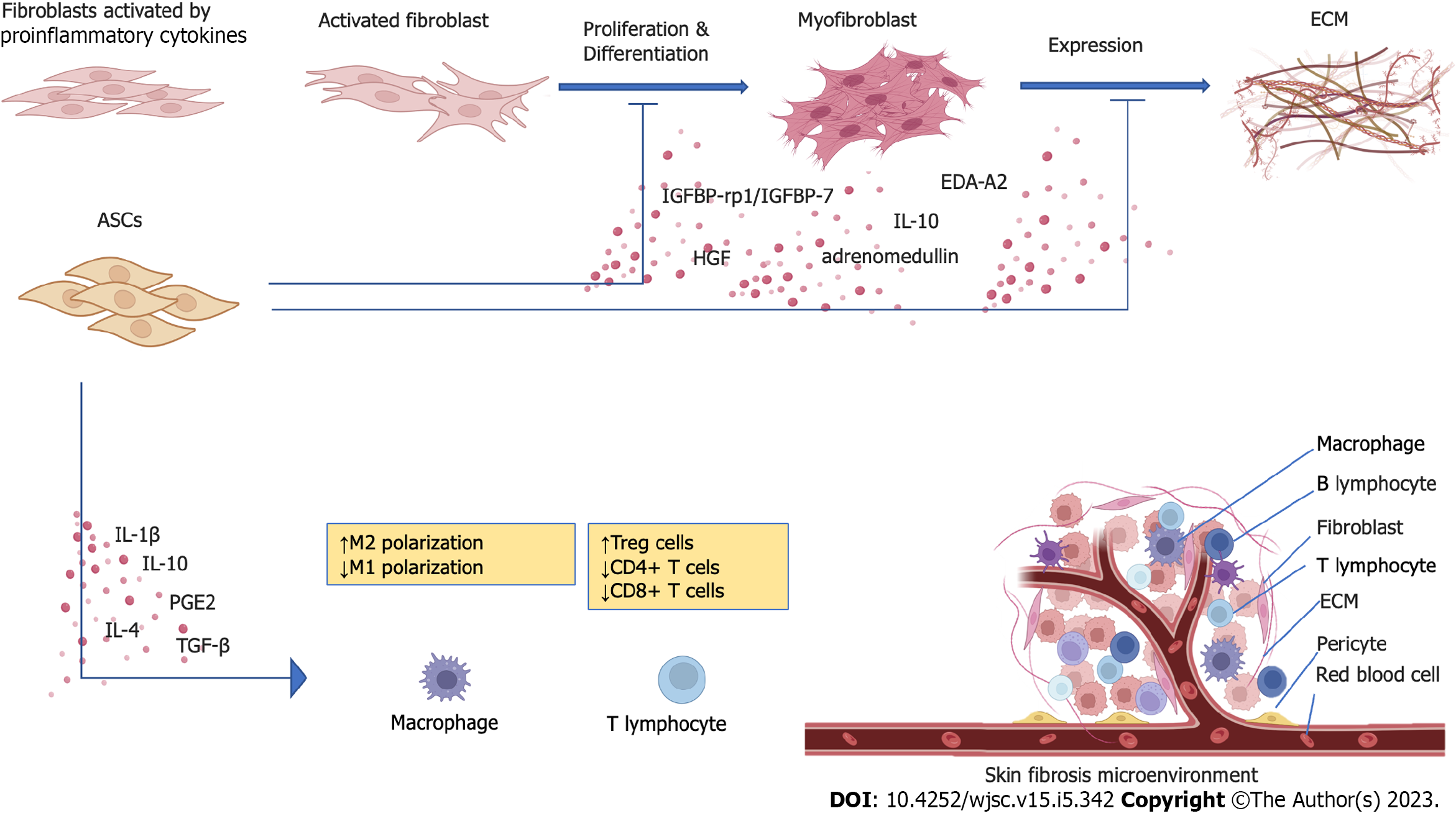
Figure 1 The brief mechanism of adipose-derived stem cell therapy in skin fibrosis.
ECM: Extracellular matrix; ASC: Adipose-derived stem cell; HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; IGFBP-rp1/IGFBP-7: Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related protein-1/Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-7; EDA-A2: Ectodysplasin-A2; IL-10: Interleukin 10; IL-4: Interleukin 4; IL-1β: Interleukin 1β; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor beta; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2. Figure 1 is created with BioRender.com.
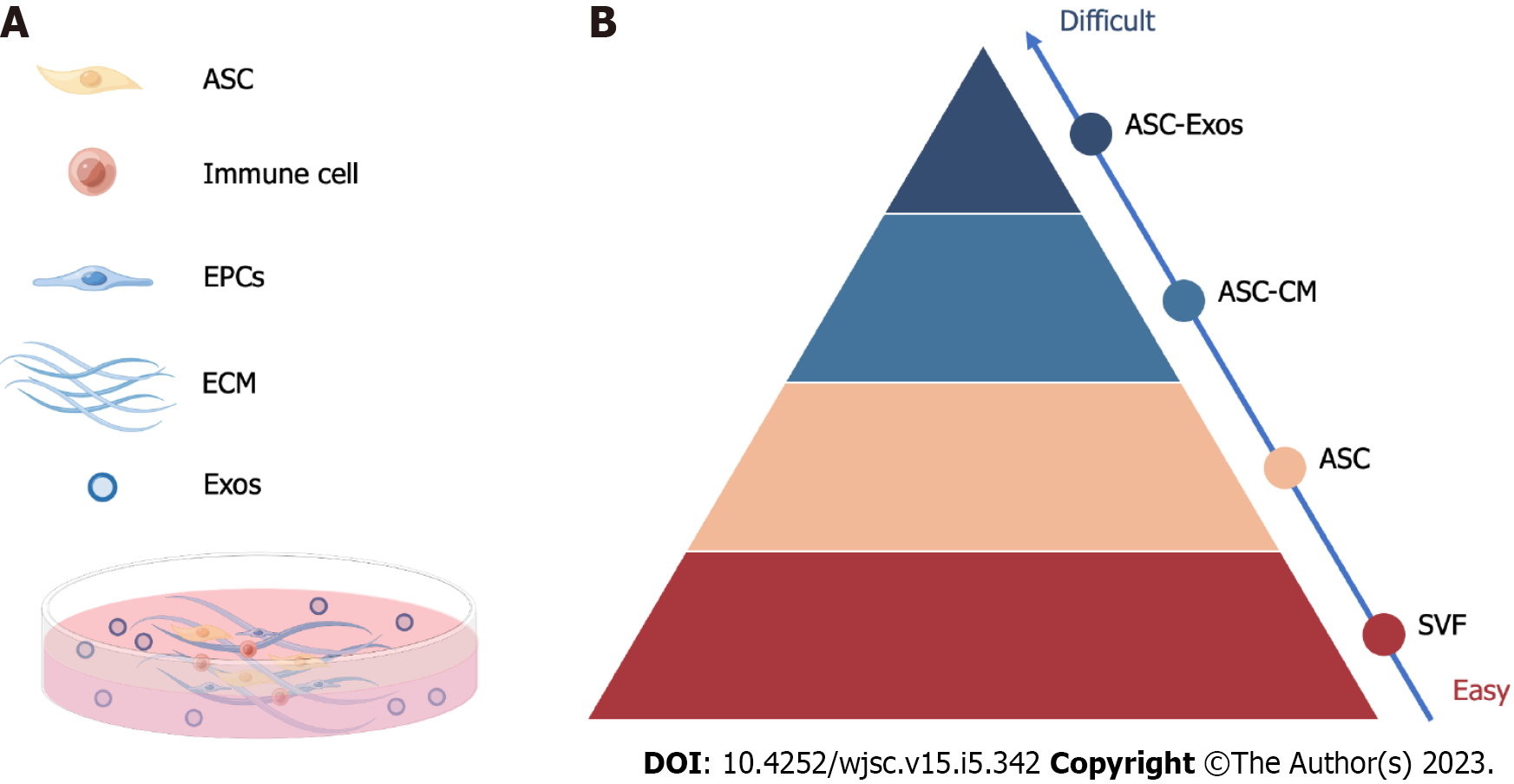
Figure 2 The culture and classification of adipose-derived stem cells and their derivatives.
A: Culture of adipose-derived stem cells (ASC) and their derivatives; B: Classification of ASC and their derivatives. EPCs: Endothelial precursor cells; ECM: extracellular matrix; Exo: Exosomes; ASC: Adipose-derived stem cell; ASC-CM: ASC-conditioned medium; ASC-Exo: ASC exosomes; SVF: Stromal vascular fraction. Figure 2 is created by Figdraw.
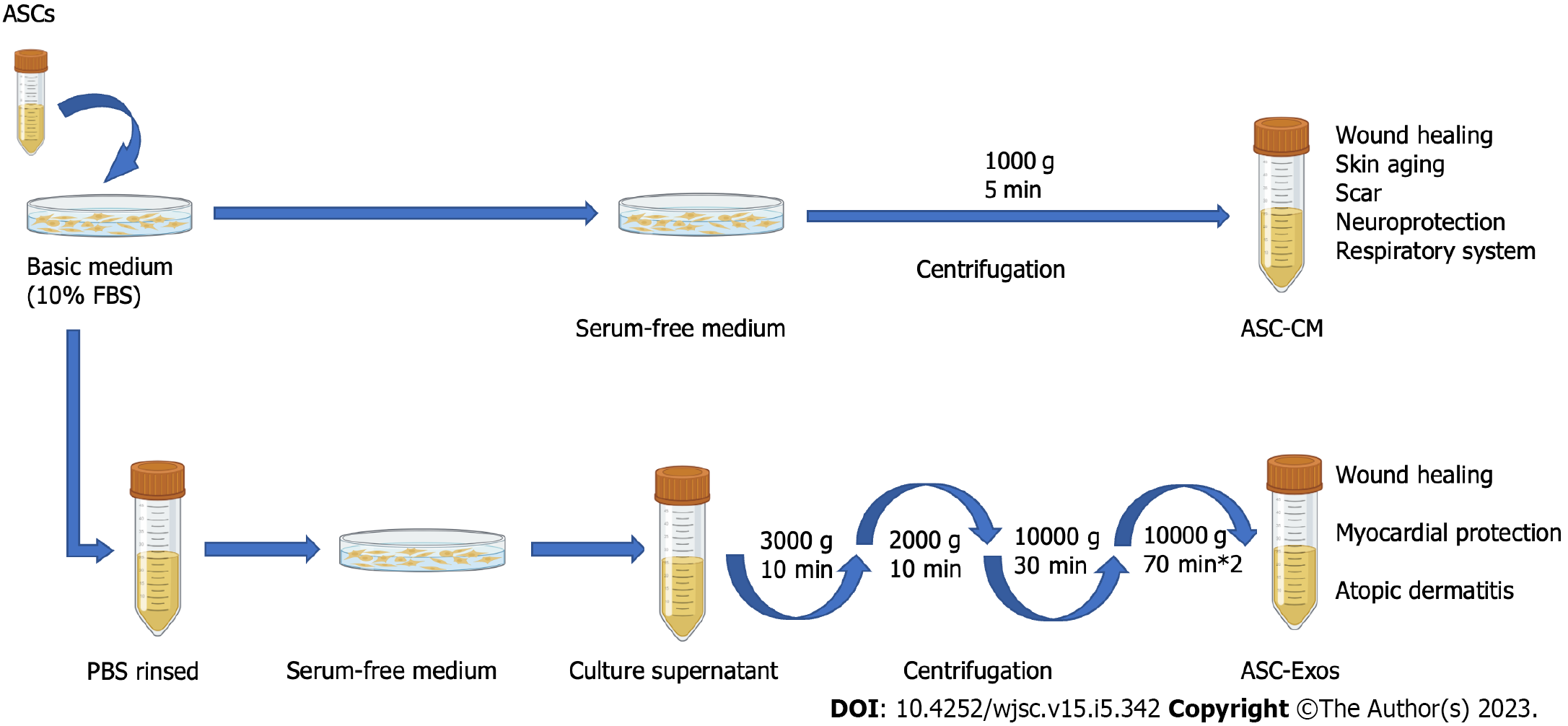
Figure 3 Adipose-derived stem cell conditioned media, exosomes, and adipose tissue extracts synthesis and therapeutic application.
ASC: Adipose-derived stem cell; ASC-CM: ASC-conditioned medium; ASC-Exo: ASC exosomes; FBS: fetal bovine serum; PBS: Phosphate-buffered saline. Figure 3 is created with BioRender.com.
- Citation: Liu YX, Sun JM, Ho CK, Gao Y, Wen DS, Liu YD, Huang L, Zhang YF. Advancements in adipose-derived stem cell therapy for skin fibrosis. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(5): 342-353
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i5/342.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i5.342