Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. Nov 26, 2022; 14(11): 777-797
Published online Nov 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i11.777
Published online Nov 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i11.777
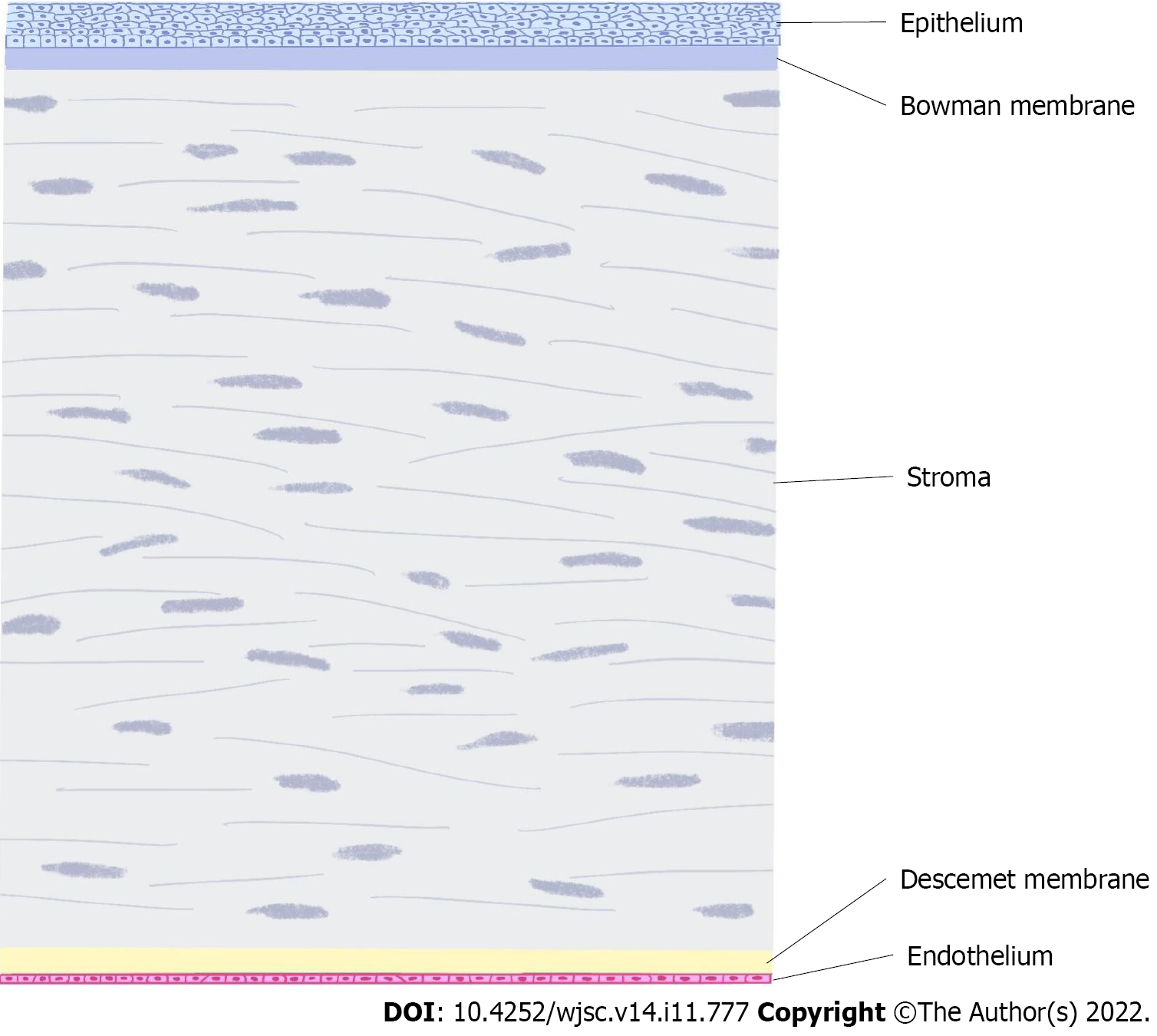
Figure 1 Corneal stratification.
The corneal layer includes the epithelium, bowman membrane, stroma, Descemet membrane and endothelium.
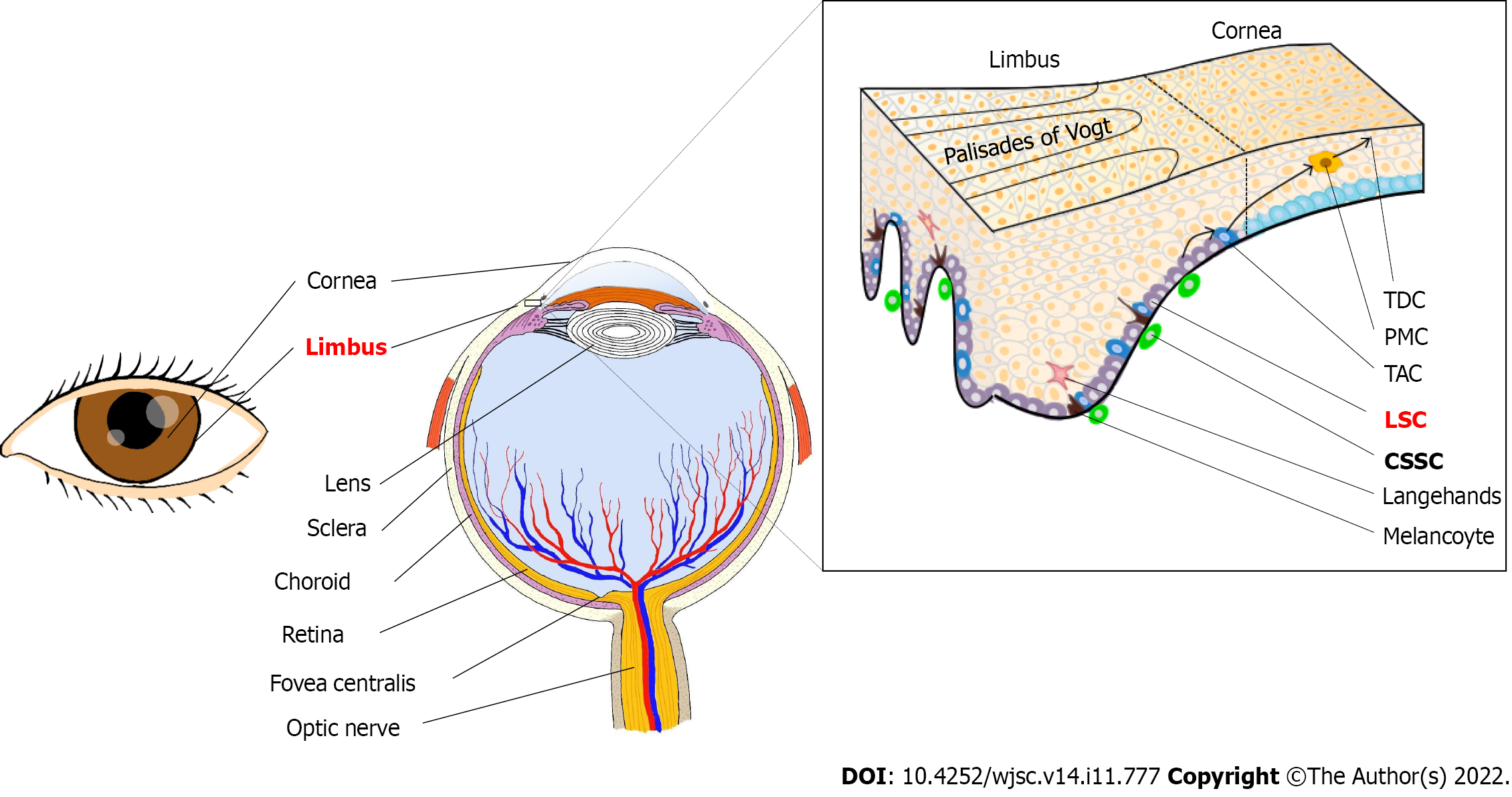
Figure 2 Location of limbal stem cells and corneal stromal stem cells.
Limbal stem cells (LSCs) are located at the base of the limbus and are in close contact with niche cells, including melanocytes. LSCs are symmetrically divided into two identical cells in the horizontal plane or asymmetrically differentiated into another LSC and a transient amplifying cell (TAC) in both vertical and horizontal planes. Then, TACs are divided into postmitotic cells (PMCs) as they migrate centripetally. The PMCs are then differentiated into terminally differentiated cells (TDCs) and shed from the corneal surface. Corneal stromal stem cells are in the anterior stroma subjacent to the epithelial basement membrane, in regions where the basement membrane has muslimah and folds termed the Palisades of Vogt. LSC: Limbal stem cell; TAC: Transient amplifying cell; PMC: Postmitotic cell; TDC: Terminal differentiated cell; CSSC: Corneal stromal stem cell.
- Citation: Ying PX, Fu M, Huang C, Li ZH, Mao QY, Fu S, Jia XH, Cao YC, Hong LB, Cai LY, Guo X, Liu RB, Meng FK, Yi GG. Profile of biological characterizations and clinical application of corneal stem/progenitor cells. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(11): 777-797
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i11/777.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i11.777