Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Aug 26, 2020; 12(8): 776-786
Published online Aug 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i8.776
Published online Aug 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i8.776
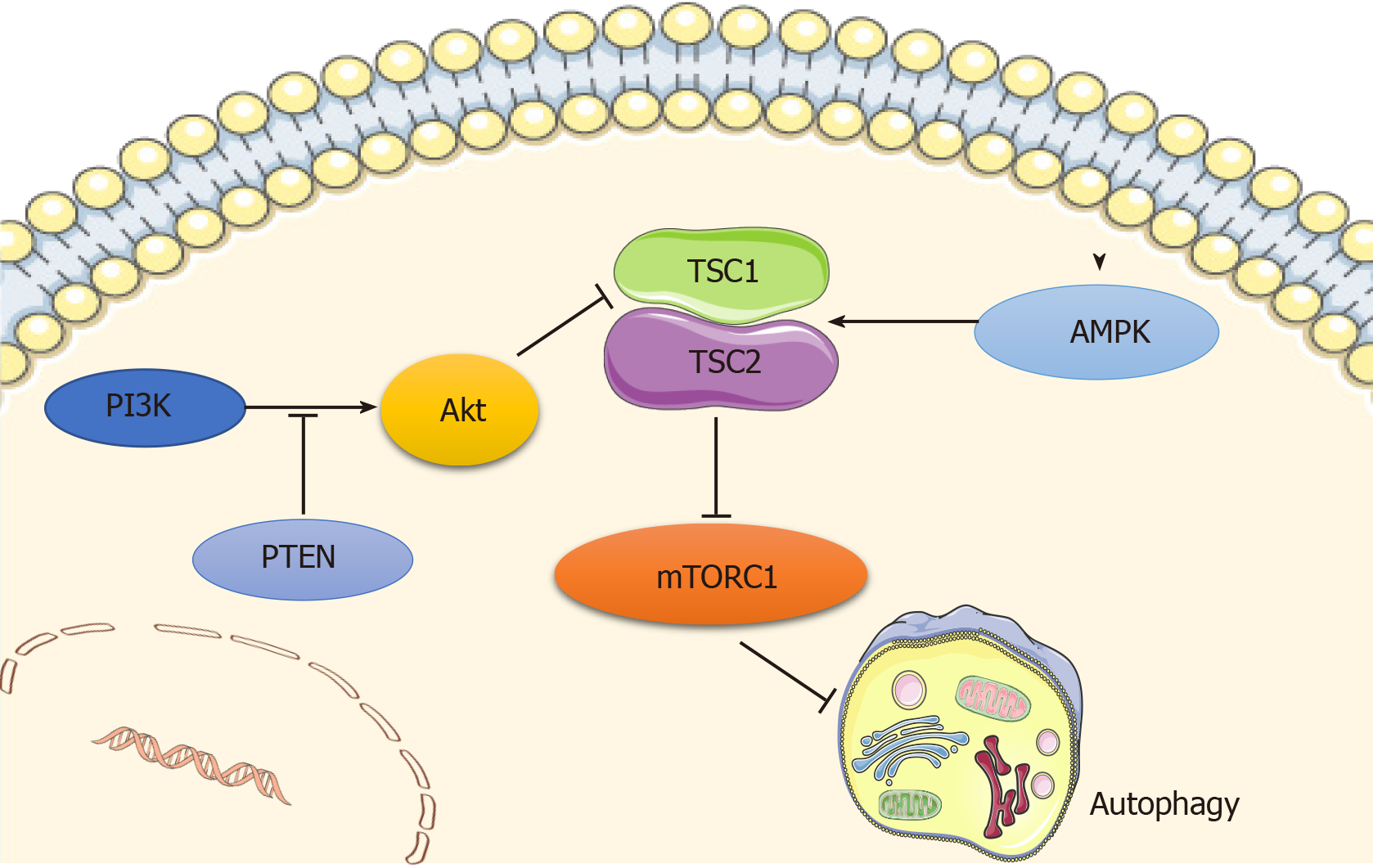
Figure 1 Main signaling pathways regulating autophagy.
Autophagy is regulated by the adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and PI3K/AKT pathways, which converge at mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) that functions as a negative regulator of autophagy. AMPK inhibits mTOR by phosphorylating tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC), and consequently inducing autophagy. PI3K/AKT pathway inactivates TSC, phosphorylates mTOR, and then blocks autophagy activity, while PTEN acts as a brake upstream of Akt. Original elements used in this diagram are from Servier Medical Art (http://smart.servier.com/ ). AMPK: Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; TSC: Tuberous sclerosis complex.
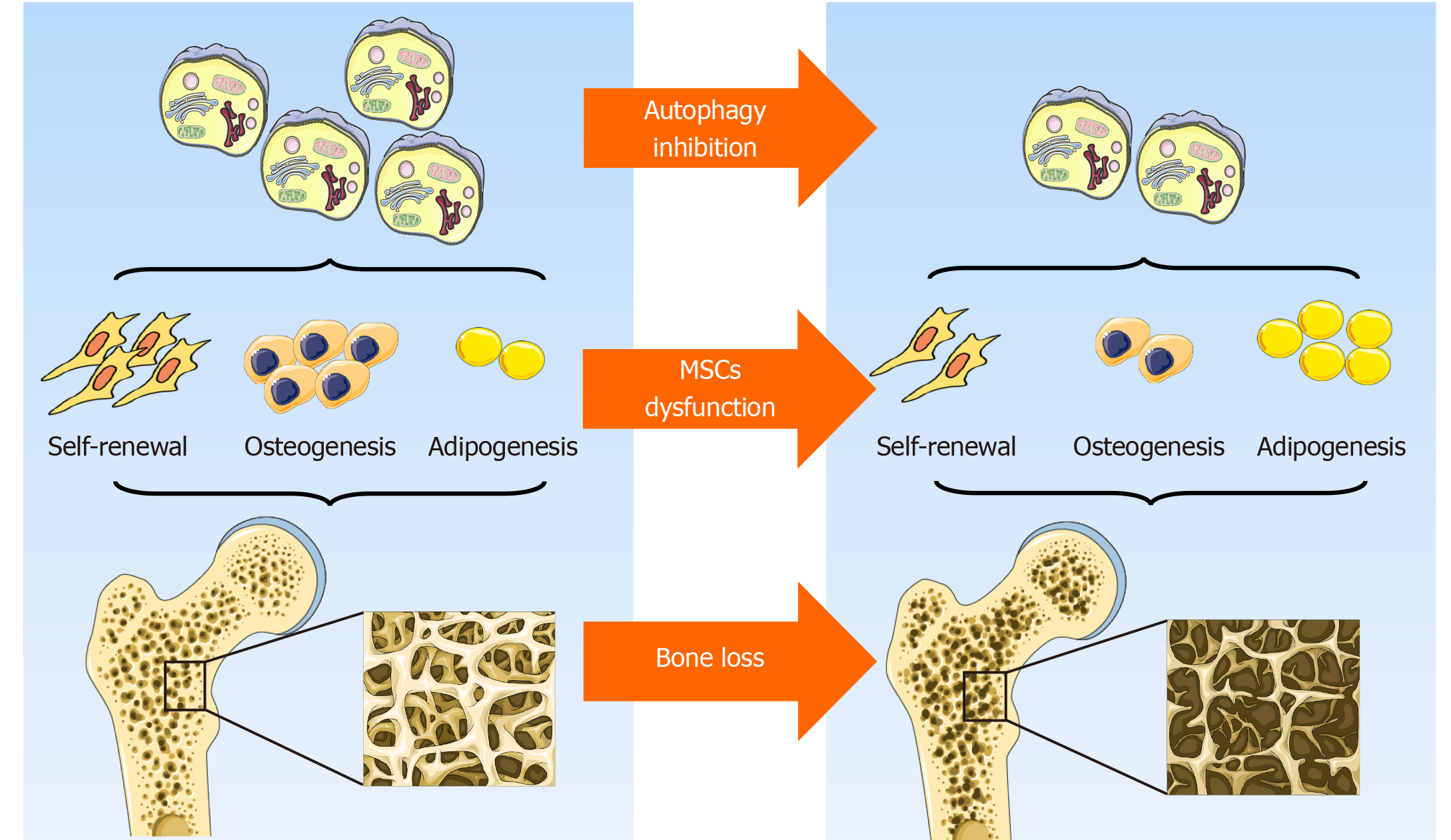
Figure 2 Role of autophagy in mesenchymal stem cells integrity and bone homeostasis.
Autophagy contributes to the maintenance of mesenchymal stem cells integrity by preserving their self-renewal and osteoblast differentiation potential while inhibiting adipocyte differentiation, thus orchestrating bone homeostasis. Original elements used in this diagram are from Servier Medical Art (http://smart.servier.com/). MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells.
- Citation: Chen XD, Tan JL, Feng Y, Huang LJ, Zhang M, Cheng B. Autophagy in fate determination of mesenchymal stem cells and bone remodeling. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(8): 776-786
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i8/776.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i8.776