Published online Sep 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i26.7850
Peer-review started: March 30, 2021
First decision: April 28, 2021
Revised: May 6, 2021
Accepted: August 4, 2021
Article in press: August 4, 2021
Published online: September 16, 2021
Processing time: 164 Days and 4.7 Hours
Primary omental tumors are uncommon, and omental fibromas account for 2% of these tumors. Due to the low incidence of omental fibromas and the limited relevant literature, it is challenging for clinicians to make an accurate diagnosis of this condition, especially before surgery.
A 30-year-old man was admitted to the hospital because of a left epididymal mass with vague discomfort for more than 1 mo. A physical examination was performed, and the findings showed that the epididymal mass may have entered the abdominal cavity. Pelvic computed tomography was performed in our hospital and revealed a left inguinal hernia with a mass in the hernial contents, and no masses were found in the left epididymis. A traditional inguinal hernia incision was made. Intraoperative hernia contents were found to be of the greater omentum, and a 2.5 cm-diameter mass was found at the distal end of the greater omentum. The scrotum and epididymis did not exhibit other masses. Then, the mass of the greater omentum was excised. Intraoperative frozen pathological examination suggested a spindle cell tumor. The postoperative pathological examination suggested that the mass was an omental angiofibroma. Postoperatively, the patient recovered well and was discharged. Outpatient re-examinations were performed at 1 mo and half a year after the operation and showed no obvious abnormalities.
Due to the low morbidity rate associated with and latent nature of omental tumors, these tumors are difficult to diagnose preoperatively; thorough medical history taking, detailed physical examinations, and necessary imaging auxiliary examinations can help clinicians diagnose and treat these cases.
Core Tip: Primary omental tumors are not common, and omental fibromas account for 2% of these tumors. No previous studies have reported an omental fibroma combined with indirect hernia showing an epididymal mass. This case reminds us of the importance of detailed medical history, strict physical examination, and necessary imaging examinations when clinicians dealing with similar cases.
- Citation: Liu JY, Li SQ, Yao SJ, Liu Q. Omental mass combined with indirect inguinal hernia leads to a scrotal mass: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(26): 7850-7856
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i26/7850.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i26.7850
Primary omental tumors are not common, and omental fibromas account for 2% of these tumors[1-4]. Due to the low incidence of omental fibromas and the limited relevant literature, it is challenging for clinicians to make an accurate diagnosis of this condition[1,2,5]. No previous studies have reported an omental fibroma combined with indirect hernia showing an epididymal mass. Herein, we report a case of omental angiofibroma combined with an indirect inguinal hernia, as well as important information regarding the diagnosis and treatment of omental masses.
A 30-year-old man was admitted to the Urological Department of Tianjin First Central Hospital because of a left epididymal mass with vague discomfort for more than 1 mo.
One month before the patient visited the hospital, he underwent a scrotal ultrasonographic (US) examination at another hospital for scrotal vague discomfort, which illustrated that there was a mass within the left epididymis.
The patient did not have any previous history of chronic disease, surgery, blood transfusion, or trauma.
The patient was not a smoker and drank little liquor occasionally. No family history of malignancy was identified.
A physical examination was performed, and the findings showed that the epididymal mass may have entered the abdominal cavity after the patient was admitted to the hospital. Small movement of the mass was felt when the patient coughed or performed a Valsalva maneuver.
Routine blood tests, biochemical examinations, and alpha-fetoprotein, carcinoembryonic antigen, carbohydrate antigen-19-9, carbohydrate antigen-72-4, and neuron-specific enolase tests were performed, and all of the resulting values were within the normal ranges. The patient denied experiencing weight loss, decreased appetite, fatigue, or malaise.
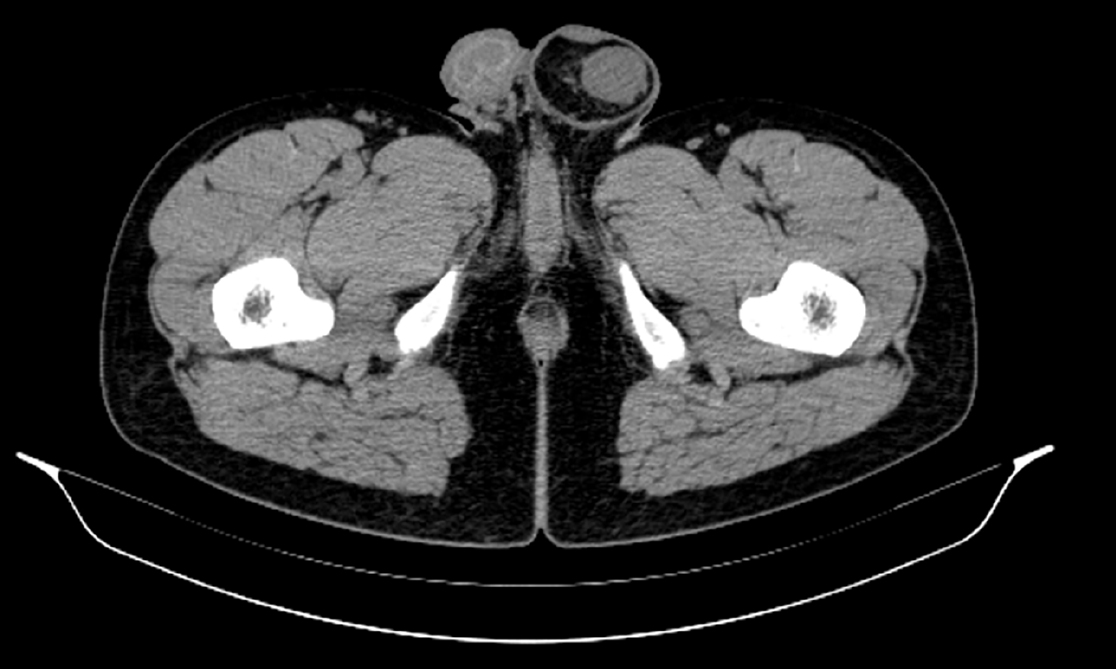
The scrotal US examination performed at another hospital illustrated that there was a mass within the left epididymis. Pelvic computed tomography (CT) was performed in Tianjin First Central Hospital and showed intraperitoneal fat herniation in the left scrotum through the widened left inguinal canal, and the mass appeared as dense soft tissue within a hernia with a size of approximately 2.5 cm × 1.3 cm × 3.0 cm. The CT value was approximately 24 Hu (Figure 1). CT revealed a left inguinal hernia with a mass in the hernial contents, and no masses were found in the left epididymis.
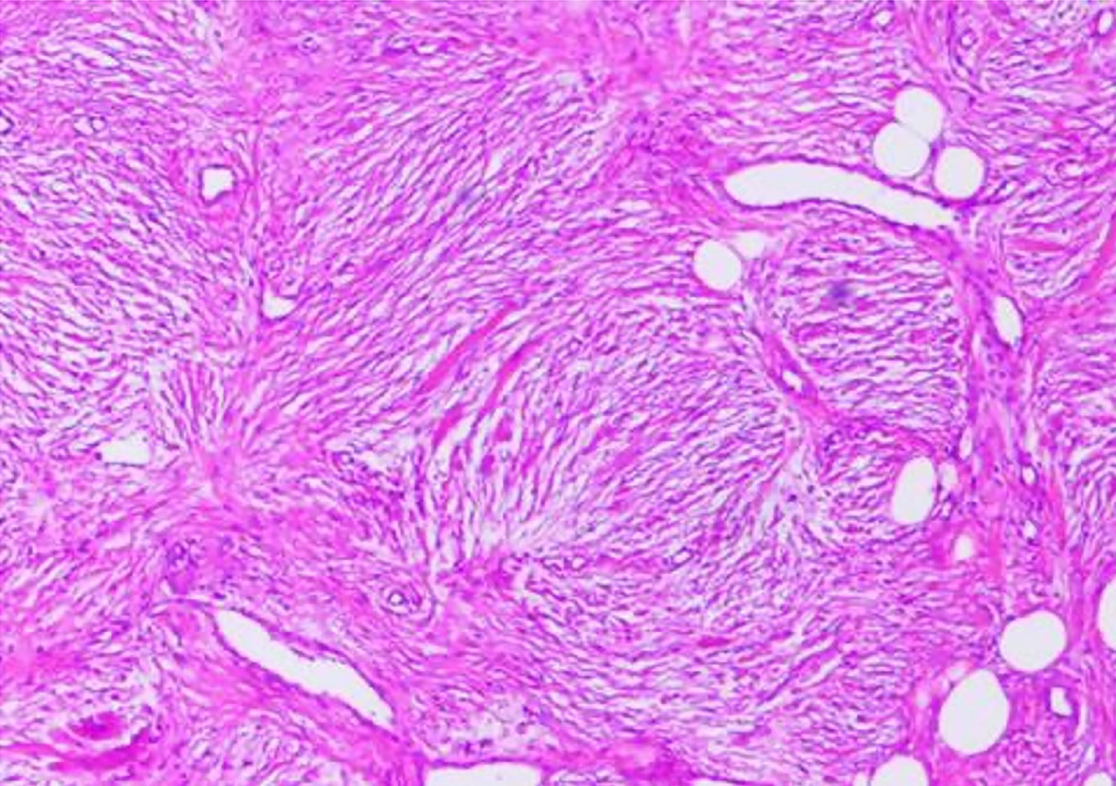
Intraoperative frozen pathological examination suggested a spindle cell tumor. Subsequently, inguinal hernia repair was performed. Postoperative pathological examination suggested that the mass was an omental angiofibroma (Figure 2), and the immunohistochemical examination showed Vimentin (+), CK (-), CD43 (+), SMA (-), S100 (-), CD31 (+), F8 (-), and Ki-67 sporadic positivity.
A traditional inguinal hernia incision was made and served as the projection point from the outer upper part of the pubic tubercle to the internal ring orifice. Intraoperative hernia contents were found to be of the greater omentum, and a 2.5 cm-diameter mass was found at the distal end of the greater omentum. The scrotum and epididymis did not exhibit other masses. Then, a surgical mesh was placed in the inguinal canal and the mass at the distal end of the greater omentum was excised.
Postoperatively, the patient recovered well and was discharged. Outpatient re-examinations were performed at 1 mo and half a year after the operation and showed no obvious abnormalities.
The primary diagnosis for the patient was an epididymal mass. Clinically, diseases for which epididymal masses are the main manifestations include epididymal tuberculosis, seminal cysts, epididymal cysts, epididymal benign tumors, epididymal malignant tumors, etc. It is difficult to diagnose epididymal masses solely based on the patient’s medical history and clinical manifestations, and misdiagnoses easily occur. Epididymal masses are mainly identified on the basis of clinical manifestations such as the location, texture, and tenderness of the mass, combined with imaging modalities such as US, plain CT, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)[5-9].
The results of the physical examination and CT led us to diagnose the patient with left inguinal hernia. Inguinal hernias most commonly involve the small intestine, followed by the greater omentum. Preoperative imaging examinations alone, such as US and CT examinations, to determine hernia contents are prone to misdiagnosis. Michele et al[10] reported a patient who was diagnosed with an inguinal hernia and whose preoperative CT examination findings showed that the hernia content was of the small intestine, but the postoperative pathological examination demonstrated that the hernia content included Hodgkin's lymphoma. Tajti et al[11] also reported a patient who was diagnosed with an inguinal hernia and whose preoperative US examination findings showed that the hernia content was of an edematous intestinal loop with no circulation detected, but the hernia content was found to be of the gallbladder that was incarcerated during the operation. Taskovska and Janez[12] reported a patient who was diagnosed with an inguinal hernia and whose preoperative US examination findings showed that the hernia contents were of aperistaltic small intestine loops without dilatation, but the hernia content was found to be of the urinary bladder. In our study, the preoperative CT examination demonstrated that the hernia contents contained a mass that could not be diagnosed by imaging tests alone.
The vast majority of omental tumors are metastatic tumors. In contrast, tumors originating from the greater omentum are extremely rare, and the pathogenesis is still not clear. The most common clinical symptoms of omental tumors include abdominal pain, abdominal masses, and bloating. In most patients, abdominal pain is aggravated in the supine position and relieved in the upright position. Some patients also experience nausea and weight loss. In addition, the local symptoms of benign and malignant omental lesions are the same. In the initial stage when the tumor is small, as in the patient in this study, omental tumors are usually asymptomatic. Although imaging examinations are becoming increasingly popular and Chinese people are paying increasing attention to physical examination findings, primary omental tumors are still extremely rare[2,4].
The most common primary malignant omental tumors include leiomyosarcoma, hemangiopericytoma, and fibrosarcoma, and liposarcoma has also been reported[13-20]. The most common benign omental tumors include gastrointestinal stromal tumors, leiomyomas, lipomas, and fibroids. Only a few studies have reported cases of omental angiofibroma, and all of these cases were considered to be intra-abdominal[2,4]. No previous studies have reported an omental mass combined with indirect inguinal hernia showing an epididymal mass. In this study, a primary omental tumor herniated into the scrotum and formed an indirect inguinal hernia. The tumor was located near the epididymis. Therefore, US at another hospital showed an epididymal tumor.
In addition to regular preoperative examinations, US, CT, MRI, positron emission tomography (PET), and angiography can be used to detect omental tumors[2]. Abdominal US examinations are considered the first-line screening imaging examinations for most patients, as US can detect abdominal masses and distinguish cystic tumors from solid tumors. However, US usually cannot provide additional information about the tumor. For this reason, abdominal CT is the primary choice for the diagnosis of omental tumors. CT can provide more anatomical details, which can assist in determining the location of the primary tumor and indicate whether adjacent organs and tissues are significantly dislocated or compressed. MRI is another imaging modality that can help distinguish cystic tumors from solid tumors. MRI findings are not affected by the examiner, and contrast agents do not need to be prepared. However, MRI is time-consuming and expensive compared to other imaging methods. PET scans can also be used to help distinguish between benign and malignant tissues, necrotic scars, and active tumors when omental gastrointestinal stromal tumors are suspected. Angiography may also be helpful for patients suspected of having omental tumors. If angiography shows a tumor with rich blood supply in the greater omentum accompanied by neovascularization, it is likely to be malignant. At this time, angiography can also determine the distribution of supplying arteries and peripheral blood vessels of the tumor. At present, there is still considerable controversy about whether fine-needle aspiration biopsy should be performed for omental tumors. Although needle biopsy helps determine the pathological diagnosis preoperatively, it also increases the risk of tumor intra-abdominal implantation. However, these imaging examinations cannot help clinicians make an accurate preoperative diagnosis[2]. Usually, the definitive diagnosis still depends on postoperative pathological examination findings.
Total omentectomy is performed to treat primary omental tumors, as it seems to significantly improve the survival time of patients postoperatively, even with peritoneal implantation metastasis. The first symptoms of omental tumors can also be rupture-related bleeding and intestinal obstruction, requiring emergency surgery. The inability to safely remove the tumor due to local invasion is an absolute contraindication for surgical resection[21,22].
Owing to the rarity of primary omental tumors, the role of other adjuvant therapies, such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy, in the treatment of omental malignant tumors is currently unclear. In this study, because the intraoperative frozen pathological test results suggested a benign spindle cell tumor, only omental tumor resection and inguinal hernia repair were performed instead of total omental resection.
The pathology of this case was considered to be angiofibroma, which is mainly composed of proliferating blood vessels and fibrous tissue[23]. It mostly takes place in the nasopharynx of male adolescents, rarely occurs outside the nasopharyngeal area, and even more rarely occurs in the genitourinary system[24,25]. Studies have suggested that angiofibroma may originate from the periosteum of the skull base, but its exact pathogenesis is still not clear[1-3].
The median survival time of patients with primary malignant tumors of the greater omentum is only 6 mo. Two years after surgery, only approximately 10%-20% of patients are alive. The reasons for this poor prognosis are still unclear, potentially due to the small sample sizes of studies and the fact that some patients have had distant metastases at the time of admission. The prognosis of benign tumors of the greater omentum is significantly better than that of malignant tumors. Studies have reported that the 5-year survival rate for benign tumors of the greater omentum is approximately 75% and that this rate varies by the specific pathological type[1,2,4]. Due to the limited number of clinical studies on patients with omental tumors, there is no consensus on the postoperative management of patients with omental tumors. Some omental tumors, such as sarcoma, may recur and metastasize 20 years after surgery. Therefore, it is recommended that patients with omental tumors undergo long-term follow-ups after surgery[26]. In this study, although the postoperative pathology of this case was benign angiofibroma, we still recommended that the patient undergo active reexamination and follow-ups.
Due to the low morbidity rate associated with and latent nature of omental tumors, these tumors are difficult to diagnose preoperatively; thorough medical history taking, detailed physical examinations, and necessary imaging auxiliary examinations can help clinicians diagnose and treat these cases.
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Specialty type: Urology and nephrology
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Ferreira GSA S-Editor: Liu M L-Editor: Wang TQ P-Editor: Ma YJ
| 1. | Ono M, Tanaka K, Ikezawa N, Kobayashi Y, Inoue Y, Yokota M, Matsumura S, Uehara I, Hattori Y, Kurahashi T, Shimada T, Nakagawa H. Fibroma of the omentum resembling an ovarian tumor in the pelvis. Keio J Med. 2009;58:234-236. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Iusco D, Donadei E, Sgobba G, Sarli L. Giant fibroma of the lesser omentum: report of a rare case. Acta Biomed. 2005;76:42-44. [PubMed] |
| 3. | Paksoy Y, Sahin M, Açikgözoğlu S, Odev K, Omeroğlu E. Omental fibroma: CT and US findings. Eur Radiol. 1998;8:1422-1424. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Ishida H, Ishida J. Primary tumours of the greater omentum. Eur Radiol. 1998;8:1598-1601. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 37] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Gao L, Song H, Mu K, Wang J, Guo B, Shi B, Li G. Primary epididymis malignant triton tumor: case report and review of the literature. Eur J Med Res. 2015;20:79. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Bedir R, Şehitoğlu İ, Uzun H, Yurdakul C. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the epididymis: a case report and review of the literature. Turk J Urol. 2013;39:281-284. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Borges WM, Bechara GR, de Miranda MML, de Figueiredo GB, Venturini BA, Laghi CR. Epididymis tuberculosis: Case report and brief review of the literature. Urol Case Rep. 2019;26:100969. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Huang Y, Song J, Xu M, Zan Q. Primary Leydig cell tumour of epididymis: a rare case report with review of literature. Andrologia. 2013;45:430-433. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Marcou M, Perst V, Cacchi C, Lehnhardt M, Vögeli TA. Epididymal leiomyoma: a benign intrascrotal tumour. Andrologia. 2017;49. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Teodoro M, Mannino M, Vitale M, Mattone E, Palumbo V, Fraggetta F, Toro A, Di Carlo I. Small bowel lymphoma presenting as inguinal hernia: case report and literature review. World J Surg Oncol. 2018;16:91. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Tajti J Jr, Pieler J, Ábrahám S, Simonka Z, Paszt A, Lázár G. Incarcerated gallbladder in inguinal hernia: a case report and literature review. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020;20:425. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Taskovska M, Janež J. Inguinal hernia containing urinary bladder-A case report. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2017;40:36-38. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 33] [Article Influence: 4.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Becker JHR, Koto MZ, Matsevych OY, Bida NM. Haemangiopericytoma/solitary fibrous tumour of the greater omentum. S Afr J Surg. 2014;52:111-113. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Brañes A, Bustamante C, Valbuena J, Pimentel F, Quezada N. Primary leiomyosarcoma of the greater omentum: a case report. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2016;28:317-320. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Okamoto K, Okada Y, Ohno K, Yagi T, Tsukamoto M, Akahane T, Shimada R, Hayama T, Tsuchiya T, Nozawa K, Matsuda K, Ishida T, Kondo F, Hashiguchi Y. A rare case of perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa) of the greater omentum. World J Surg Oncol. 2018;16:113. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Llenas-García J, Guerra-Vales JM, Moreno A, Ibarrola C, Castelbon FJ, Fernández-Ruiz M, Meneu JC, Ballestin C, Moreno E. Primary extragastrointestinal stromal tumors in the omentum and mesentery: a clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study. Hepatogastroenterology. 2008;55:1002-1005. [PubMed] |
| 17. | Schwartz RW, Reames M, McGrath PC, Letton RW, Appleby G, Kenady DE. Primary solid neoplasms of the greater omentum. Surgery. 1991;109:543-549. [PubMed] |
| 18. | Todoroki T, Sano T, Sakurai S, Segawa A, Saitoh T, Fujikawa K, Yamada S, Hirahara N, Tsushima Y, Motojima R, Motojima T. Primary omental gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST). World J Surg Oncol. 2007;5:66. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Chauhan U, Udiya AK, Prabhu SM, Shetty GS. Malignant nerve sheath tumour of omentum and the "omental vascular pedicle sign". BJR Case Rep. 2016;2:20150037. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Urabe M, Yamagata Y, Aikou S, Mori K, Yamashita H, Nomura S, Shibahara J, Fukayama M, Seto Y. Solitary fibrous tumor of the greater omentum, mimicking gastrointestinal stromal tumor of the small intestine: a case report. Int Surg. 2015;100:836-840. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Alves M. Primary omental gastrointestinal stromal tumor- what we know based on case series and literature review. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2020;46:E135-E136. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Hashimoto S, Arai J, Nishimuta M, Matsumoto H, Fukuoka H, Muraoka M, Nakashima M, Yamaguchi H. Resection of liposarcoma of the greater omentum: A case report and literature review. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2019;61:20-25. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | López F, Triantafyllou A, Snyderman CH, Hunt JL, Suárez C, Lund VJ, Strojan P, Saba NF, Nixon IJ, Devaney KO, Alobid I, Bernal-Sprekelsen M, Hanna EY, Rinaldo A, Ferlito A. Nasal juvenile angiofibroma: Current perspectives with emphasis on management. Head Neck. 2017;39:1033-1045. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 59] [Cited by in RCA: 76] [Article Influence: 9.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Pérez-Navarro JV, Flores-Cardoza A, Anaya-Prado R, González-Izquierdo Jde J, Ramírez-Barba EJ. Angiofibrolipoma of the greater omentum: case report and literature review. Cir Cir. 2009;77:229-232. [PubMed] |
| 25. | Windfuhr JP, Vent J. Extranasopharyngeal angiofibroma revisited. Clin Otolaryngol. 2018;43:199-222. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 2.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Vasdeki D, Bompou E, Diamantis A, Anagnostou A, Tepetes K, Efthimiou M. Haemangiopericytoma of the greater omentum: a rare tumour requiring long-term follow-up. J Surg Case Rep. 2018;2018:rjy087. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |