Published online Jun 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i18.4681
Peer-review started: January 26, 2021
First decision: February 28, 2021
Revised: March 11, 2021
Accepted: April 22, 2021
Article in press: April 22, 2021
Published online: June 26, 2021
Processing time: 135 Days and 23.3 Hours
Keratosis pilaris is a hereditary abnormal keratosis of the hair follicle orifice. Gray-brown keratotic plugs in the pores and dark red keratotic papules at the openings of hair follicles can be seen, which contain coiled hair and are often accompanied by perifollicular erythema and pigmentation. Glycolic acid can correct the abnormalities of hair follicular duct keratosis and eliminate excessive accumulation of keratinocytes. It also promotes skin metabolism and accelerates the melanin metabolism. The therapeutic effect is related to the glycolic acid concentration.
To evaluate the efficacy and safety of a high concentration of glycolic acid in the treatment of keratosis pilaris, and to observe the outcomes at 5-year of follow-up.
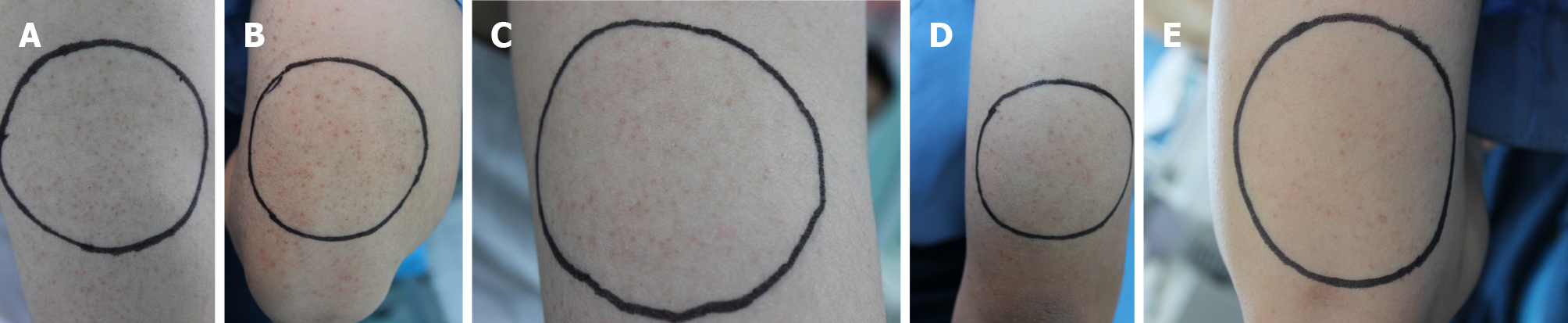
Twenty-five participants were recruited and areas with typical keratosis pilaris were selected as testing sites. High concentrations of glycolic acid (50% or 70%) were applied to a circular area (d = 8 cm, S = 50 cm2) and repeated four times, on days 0, 20, 40 and 60. Before each treatment and 20 d after the last treatment, on days 0, 20, 40, 60, and 80 and at a 5-year follow-up, The number of follicular keratotic papules were counted and the extent of perifollicular erythema and pigmentation was determined. At the same time, the participants provided subjective evaluations of treatment efficacy and safety.
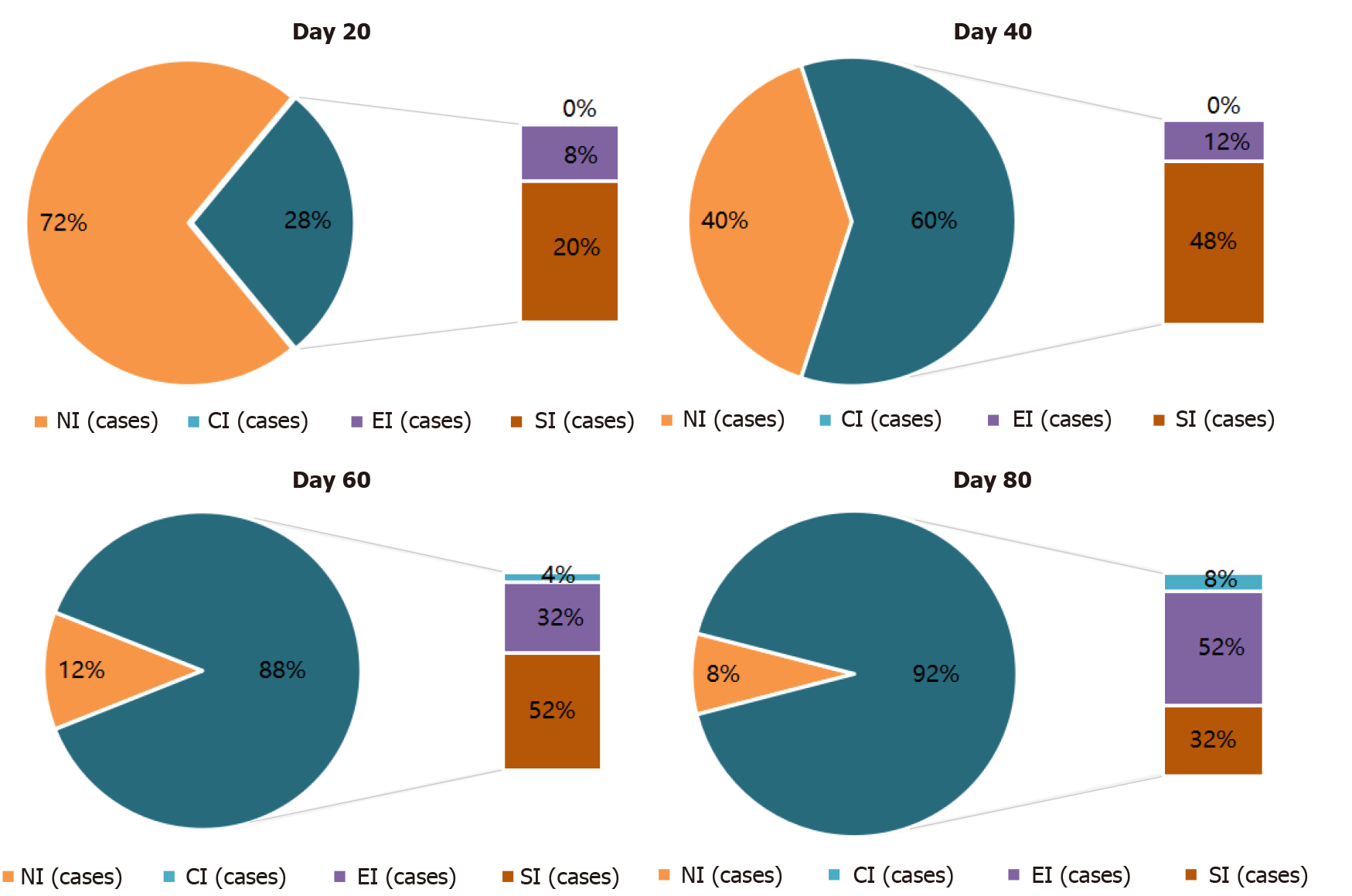
Treatment effectiveness was indicated by the percentage of keratotic papules in the test site, on days 20, 40, 60 and 80, which were 8%, 12%, 36%, and 60%, respectively. Compared with day 0, each difference was significant (P < 0.05). Compared with day 0, differences in melanin content (M) in the skin and skin lightness (L) on days 40, 60 and 80, the were statistically significant (P < 0.05); skin hemoglobin content (E) on days 60 and 80 was statistically different as compared with before treatment (P < 0.05). There were no significant differences in the number of keratotic papules, M, L, and E in 9 participants at the 5-year follow-up compared with before treatment (P > 0.05%).
A high concentration of glycolic acid significantly improved skin roughness as well as follicular hyperpigmentation of patients with keratosis pilaris. The treatment was relatively safe, but there was no significant difference at the 5-year follow-up compared to before treatment.
Core Tip: A high concentration of glycolic acid (50%, 70%) was applied to 25 subjects suffering from keratosis pilaris. The treatment was repeated every 20 d for a total of four times, 20 d after each treatment, perifollicular erythema, papules, and pigmen
- Citation: Tian Y, Li XX, Zhang JJ, Yun Q, Zhang S, Yu JY, Feng XJ, Xia AT, Kang Y, Huang F, Wan F. Clinical outcomes and 5-year follow-up results of keratosis pilaris treated by a high concentration of glycolic acid. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(18): 4681-4689
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i18/4681.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i18.4681
Keratosis pilaris is a hereditary abnormal keratosis of the hair follicular orifice. Clinically, gray-brown keratotic plugs in the pores and dark red keratotic papules at the openings of hair follicles that contain coiled hair and are often accompanied by perifollicular erythema and pigmentation can be seen. As mild or severe manifestations are present in more than half of the population, the condition can be understood as a normal variant, as opposed to a disease. However, because keratosis pilaris tends to affect exposed areas such as the face, extremities, and shoulder blades, with the highest incidence in adolescence[1], young people have a strong desire for treatment. Glycolic acid can correct abnormal hair follicular duct keratosis and eliminate excessive accumulation of keratinocytes. It can also promote skin metabolism and accelerate the metabolism of melanin. The therapeutic effect is related to the concentration of glycolic acid. We used a high concentration of glycolic acid to evaluate the efficacy and safety of glycolic acid in the treatment of keratosis pilaris, with long-term follow-up of 5 years.
All 25 subjects were clinically confirmed cases treated at the Dermatology Clinic of our hospital. They had typical rashes on their limbs or trunk, 7 were men and 18 were women. The average age was 27.2 ± 2.5 years and the average medical history was 18 ± 3.1 years.
Inclusion criteria: The limbs or trunk of eligible subjects had typical keratosis pilaris, with perifollicular erythema, papules, and pigmentation. No other treatment had been received within the last 6 mo. All subjects was willing to complete the study process and signed the informed consent form.
Exclusion criteria: Patients with serious underlying diseases, pregnancy, women with expected pregnancy or lactating, allergic to alpha hydroxy acid or sugar cane, being treated for localized healing wounds or other skin conditions, unable to guarantee they will not be using other exfoliant products or other treatment methods (including phototherapy and others) were excluded.
Exclusion and termination criteria: Subject withdrawal of informed consent; severe adverse reactions during the trial and termination of the treatment.
This was an open trial with a planned enrollment of 25 participants. After the attending physician assessed the skin lesions, an area with typical skin lesions was selected and a circular area delineated (d = 8 cm, S = 50 cm2). A high concentration of glycolic acid (Kunming Botanee Biological Technology Co., Ltd., Yunnan Food and Drug Administration License No. 20150002) was used for treatment for a total of four times, with an interval of 20 d, on days 0, 20, 40, and 60. The concentration and treatment duration were, 50%, 5 min; 50%, 7 min; 70%, 5 min; 70%, 7 min. Following each treatment, a neutralizing solution was sprayed evenly onto the application area until no further irritation was found at the test site. Following the procedure, the patient was advised to avoid light exposure to the area for a week. Those who completed the entire trial were considered valid cases, and those who did not com
Determination of the number of follicular keratotic papules: Before each treatment and 20 d after the last treatment, that is, on day 0, 20, 40, 60 and 80, the same dermatologist examined the test sites and counted the number of follicular keratotic papules (overall, d = 8 cm, S = 50 cm2, in a circular area). A 0%-25% reduction in the number of papules was considered ineffective. A 26%-50% reduction in the number of papules was considered an improvement. A 51%-75% reduction in the number of papules was considered as obvious improvement, and a 76%-100% reduction in the number of papules was considered as excellent improvement.
Standardized evaluation of noninvasive skin testing: Before each treatment, 20 d after the last treatment, and 5 year after treatment, that is, on days 0, 20, 40, 60, 80 at the 5-year follow-up, the melanin content (M) and skin hemoglobin of the erythema and pigmentation of the hair follicular orifice was determined by a pigment measuring instrument (Mexameter, CK, Germany), and a spectrophotometer (CM-2600d, Konica Minolta, Japan) was used to measure skin lightness (L). Measurements were repeated three times in each area and the average value was taken. The M value reflects the melanin content in the skin, the E value indicates the degree of redness of the skin, and the L value indicated the balance between white and black. Pure black is 0 and pure white is 100.
Global esthetic improvement scale: Before each treatment, 20 days after the last treatment, and at 5 years after treatment, that is, on days 0, 20, 40, 60, 80 at the 5-year follow-up, the Global aesthetic improvement scale (Table 1) was used by subjects for self-assessment.
| Grading | Description |
| Excellent improvement | The best aesthetic results are achieved after treatment |
| Significant improvement | There is significant improvement in appearance compared to the initial situation |
| Some improvement | Compared with the initial situation, there is obvious improvement |
| No improvement | The appearance is essentially the same as the initial situation |
| Worse | The appearance is worse than the initial situation |
Before and after comparison of the number of keratotic papules per unit area (S = 50 cm2), the M, E, and L values was carried out using the paired t-test.
The number of follicular keratotic papules: The number of follicular orifice keratotic papules was monitored. On days 0, 20, 40, 60, and 80, the number of follicular keratotic papules was 53.12 ± 18.49, 43.04 ± 17.53, 36.92 ± 16.24, 28.72 ± 13.51, 22.16 ± 11.61, respectively. The differences in the numbers of keratotic papules of days 20, 40, 60 and 80, compared to before treatment were significant. Moreover, the differences between each treatment were significant. On day 20, there were 2 cases of obvious improve
The rate of effectiveness was calculated by dividing the summed number of cases with complete improvement, excellent improvement, and those with improvement by the overall total number of cases. The paired t-test was used to compare the number of keratotic papules before and after treatment, and the differences in the number of keratotic papules with improvement on days 20, 40, 60, and 80 were significant (Table 2, P < 0.05).
The number of keratotic papules on days 20, 40, 60 and 80 were compared with the number on day 0 and whether the differences between each treatment (i.e. whether the differences between days 40, 60, 80 and day 20; between days 60, 80, and day 40; and between days 80 and 60) were significant.
The M and E values at the hair follicle orifice of the test site were determined before treatment and on days 20, 40, 60, and 80. The L values were measured by a spectrophotometer, repeated three times at each site, and the average value was taken for statistical analysis. The M values on days 40, 60, and 80 were significantly different compared with the value before treatment (P < 0.05). The E values on days 60 and 80 were significantly different compared with the value before treatment (P < 0.05). The L values on days 40, 60, and 80 were significantly different compared with the value before treatment (P < 0.05, Table 3). Nine subjects were followed-up at 5 years. Some subjects had left Beijing for work or study and some had changed their contact information. Six subjects were able to return to the outpatient clinic for photographs and measurement of M, E, and L values. There were no significant differences compared with the pretreatment values (Table 3).
| Case | Day 0 | Day 20 | Day 40 | Day 60 | Day 80 |
| 1 | 52 | 25 | 20 | 16 | 10 |
| 2 | 26 | 22 | 21 | 15 | 14 |
| 3 | 95 | 80 | 71 | 58 | 28 |
| 4 | 46 | 38 | 32 | 25 | 24 |
| 5 | 58 | 49 | 33 | 29 | 21 |
| 6 | 35 | 23 | 19 | 14 | 10 |
| 7 | 80 | 58 | 43 | 37 | 26 |
| 8 | 66 | 47 | 58 | 23 | 19 |
| 9 | 35 | 21 | 18 | 15 | 11 |
| 10 | 75 | 59 | 50 | 38 | 36 |
| 11 | 38 | 25 | 16 | 15 | 12 |
| 12 | 43 | 37 | 33 | 26 | 13 |
| 13 | 55 | 53 | 48 | 43 | 42 |
| 14 | 61 | 30 | 22 | 15 | 11 |
| 15 | 48 | 45 | 41 | 31 | 25 |
| 16 | 57 | 55 | 51 | 45 | 43 |
| 17 | 39 | 33 | 28 | 21 | 14 |
| 18 | 72 | 65 | 55 | 43 | 37 |
| 19 | 28 | 22 | 19 | 12 | 7 |
| 20 | 30 | 27 | 21 | 16 | 12 |
| 21 | 42 | 38 | 33 | 27 | 23 |
| 22 | 58 | 53 | 45 | 37 | 29 |
| 23 | 65 | 62 | 57 | 49 | 33 |
| 24 | 36 | 29 | 23 | 16 | 9 |
| 25 | 88 | 80 | 66 | 52 | 45 |
| Average | 53.12 ± 18.49 | 43.04 ± 17.53 | 36.92 ± 16.24 | 28.72 ± 13.51 | 22.16 ± 11.61 |
| Measurement index | Pretreatment | Day 20 | Day 40 | Day 60 | Day 80 | 5 yr |
| M value | 219.48 ± 64.09 | 215.80 ± 63.87 | 213.12 ± 60.421 | 203.92 ± 58.621 | 197.04 ± 59.231 | 223.56 ± 45.51 |
| E value | 261.76 ± 60.31 | 256.16 ± 64.00 | 258.48 ± 67.86 | 248.36 ± 62.501 | 242.2 ± 66.391 | 255.13 ± 51.25 |
| L value | 61.41 ± 4.23 | 61.94 ± 4.17 | 62.20 ± 3.941 | 62.57 ± 3.781 | 63.24 ± 3.601 | 61.89 ± 3.83 |
After the first round of treatment, on day 20, 2 subjects reported significant improvement, 9 reported some improvement, and 12 reported no change. On day 40, 4 subjects reported significant improvement, 11 reported some improvement, and 10 reported no change. On day 60, 1 subject reported excellent improvement, 5 reported significant improvement, 12 reported some improvement, and 7 reported no change. On day 80, 1 case reported excellent improvement, 7 reported significant improve
| Day 20 | Day 40 | Day 60 | Day 80 | 5 yr | |
| Excellent improvement | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Significant improvement | 2 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 0 |
| Some improvement | 9 | 11 | 12 | 11 | 3 |
| No change | 12 | 10 | 7 | 6 | 4 |
| Worse | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Total | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 9 |
The subjects were tolerant of high concentrations of glycolic acid. All 25 completed the 80-d study; no subjects dropped out. Only 1 subject experienced burning, itching, and discomfort when treated with 70% glycolic acid. The symptoms disappeared after treatment with the neutralizing solution. There was no irritation, skin sensitivity, or crusting after the procedure.
After 5 years, we were only able to contact 9 of the subjects (6 males and 3 females). Six of them (3 males and 3 females) returned to the outpatient clinic for measurements and photographs, and the other 3 were followed-up by telephone. It was found that after 5 year, neither the number of follicular papules nor the M, E, and L values were significantly different from those before treatment (Table 3). Three patients (2 males and 1 female) reported that they felt less self-conscious than before. Two patients (1 male and 1 female) reported that they were worse than before treatment, and 4 patients (3 males and 1 female) did not notice any changes in the skin lesions (Table 4).
Keratosis pilaris is a chronic abnormal hair follicle keratosis. It is a cosmetic condition and does not affect physical health. Therefore, the need for treatment depends on the individual’s wishes. As part of traditional treatment, people with extensive and severe skin rashes can take large doses of vitamin A or isotretinoin to relieve symptoms, but long-term large amounts of oral vitamin A may be toxic, and oral isotretinoin is not suitable for women who are planning pregnancy soon because of the risk of teratogenicity. Topical tretinoin[2] to regulate and control keratinization or topical exfoliants such as salicylic acid and lactic acid are often slow in their effects, and are associated with poor patient compliance, frequent relapse. Long-term use may lead to skin redness, desquamation, and itching. Apart from those therapies, laser treatment has also been used for the treatment of keratosis pilaris[3]. However, it is generally only effective for erythema and pigmentation around the hair follicle and not effective for hair follicle papules. There are currently no laser therapies that can treat papules, erythema and pigmentation of keratosis pilaris at the same time. In addition, laser treatment has disadvantages of obvious pain, long recovery time, high cost, and long treatment cycles[4].
Glycolic acid is a weak acid that interferes with the binding force on the cell surface, reduces adhesion and keratin accumulation in keratinocytes, accelerates the renewal and shedding of epidermal cells, enables smooth flow in the hair follicle infundi
In this study, it was found that the treatment of keratosis pilaris with a high concentration of glycolic acid alone had a therapeutic effect on keratotic papules after the first treatment. Treatment efficacy gradually improved with the increase in the number of treatments and the therapeutic concentration. A concentration of 70% glycolic acid achieved 92% effectiveness after four treatment cycles. A high concentration of glycolic acid had a therapeutic effect on perifollicular pigmentation after the second treatment, with a decrease in M value and an increase in L value. As the number of treatments and the treatment concentration increased, the therapeutic effect improved further. At the same time, a high concentration of glycolic acid was also effective in the treatment of perifollicular erythema, but the improvement appeared later than the reduction in the number of follicular keratotic papules and the improvement of perifollicular pigmentation, with the effects appearing after the third treatment. Once again, an increase in the number of treatments resulted in further improvement. The treatment was safe and well tolerated during the study period. Only 1 subject experienced burning and itching discomfort during the procedure. At the same time, the level of subjective satisfaction of the participants was high, with 76% of the subjects (19 of 25) reporting an improvement after completing four treatments.
The treatment process was simple and the effects were observed soon after appli
The incidence of keratosis pilaris is high, and although there are many treatments, the results usually do not persist.
Keratosis pilaris affects the appearance of patients; Glycolic acid can improve the texture and color of the skin.
We followed subjects for 5 year, which allowed evaluation of both short-term and long-term efficacy of high-concentration glycolic acid for treating periceratosis.
We used spectrophotometry and the L*a*b color system as an innovative evaluation of both the treatment effects and the color and luster of the lesions.
Compared with pretreatment values, differences in the number of keratotic papules, melanin content, skin lightness, and skin hemoglobin on days 20, 40, 60, and 80 were significant. The differences were not significant at the 5-year follow-up.
A high concentration of glycolic acid significantly improved skin roughness as well as follicular hyperpigmentation in patients with keratosis pilaris. The treatment was relatively safe, but there was no significant difference at the 5-year follow-up compared with pretreatment values.
High-concentration glycolic acid can be used as a novel treatment for keratosis pilaris.
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Specialty type: Dermatology
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Carroll G S-Editor: Wang JL L-Editor: Filipodia P-Editor: Yuan YY
| 1. | Zhao B. Clinical Dermatology. Jiangsu: Jiangsu Science and Technology Press, 2012: 793-794. |
| 2. | Zhao JB. Treatment of keratosis pilaris with tretinoin cream. Zhonghua Pifuke Zazhi. 2004;37:631. |
| 3. | Jiang L, Tu P, Tan YH, Shu XF, Zhang C, Li M, Han Y. Clinical efficacy of 810nm semiconductor laser in the treatment of keratosis pilaris. Zhonghua Yixue Meixu Meirong Zazhi. 2015;21:226-228. |
| 4. | Lee SJ, Choi MJ, Zheng Z, Chung WS, Kim YK, Cho SB. Combination of 595-nm pulsed dye laser, long-pulsed 755-nm alexandrite laser, and microdermabrasion treatment for keratosis pilaris: retrospective analysis of 26 Korean patients. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2013;15:150-154. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Yu RJ. Discover and development of alpha hydroxy1 acids and polyhydroxy acids for use in various dermatological condition. Inter Cong Dermatol. 2004;35. |
| 6. | Zeng BB, Yang T, Li JJ, Lu WJ, Wang LM, Zhang J, Lin XX. Clinical observation of keratosis pilaris treated with glycolic acid and retinoid cream. Zhongguo Meirong Yixue. 2014;23:1988-1989. |
| 7. | Gao L, Chen Y, Gao TW, Wang G. Experience of tartaric acid in the treatment of keratosis pilaris. Zhongguo Jiguang Yixue Zazhi. 2012;21:328. |
| 8. | Feng KN. Outcomes of keratosis pilaris treated by glycolic acid. Zhongguo Meirong Yixue. 2013;22:2220-2221. |
| 9. | Li W, Li MS, Guo GZ. Quantitative measurement of skin color. Zhongguo Zhengxing Waike Zazhi. 2002;18:111-113. |
| 10. | Alaluf S, Atkins D, Barrett K, Blount M, Carter N, Heath A. The impact of epidermal melanin on objective measurements of human skin colour. Pigment Cell Res. 2002;15:119-126. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 112] [Cited by in RCA: 97] [Article Influence: 4.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |