Published online Nov 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i21.5313
Peer-review started: July 8, 2020
First decision: August 8, 2020
Revised: August 22, 2020
Accepted: September 22, 2020
Article in press: September 22, 2020
Published online: November 6, 2020
Processing time: 121 Days and 2.9 Hours
Reactive lymphoid hyperplasia (RLH) of the liver is a rare liver lesion. It is considered difficult to differentiate radiologically from hepatocellular carcinoma, metastatic liver tumor and other pathologies.
A 54-year-old woman presented to our hospital with RLH of the liver. The patient had a diagnosis of metastatic carcinoma of the liver from an unknown origin and subsequently underwent partial hepatectomy. However, histopathological analysis revealed RLH. The lesion showed perinodular enhancement in the arterial phase on contrast-enhanced computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. On diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), we encountered linear hyperintensity along the portal tract consecutive to the liver lesion, which is a new characteristic radiologic finding. This finding corresponded to the lymphoid cell infiltration of the portal tract. Furthermore, there was strongly restricted diffusion on the apparent diffusion coefficient map. We used these characteristic radiologic findings to diagnose the lesion as a lymphoproliferative disease.
The linear hyperintensity consecutive to the liver lesion on DWI provided additional valuable diagnostic information.
Core Tip: Reactive lymphoid hyperplasia of the liver is a rare liver lesion. It is known to be difficult to differentiate radiologically from hepatocellular carcinoma, metastatic liver tumor and other pathologies. We encountered a new radiologic characteristic finding on diffusion-weighted imaging. This new finding was linear hyperintensity along the portal tract, consecutive to the liver lesion and corresponded to the lymphoid cell infiltration of the portal tract. Perinodular enhancement in the arterial phase or equilibrium phase on contrast-enhanced computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging indicated lymphocytic infiltration.
- Citation: Tanaka T, Saito K, Yunaiyama D, Matsubayashi J, Nagakawa Y, Tanigawa M, Nagao T. Diffusion-weighted imaging might be useful for reactive lymphoid hyperplasia diagnosis of the liver: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(21): 5313-5319
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i21/5313.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i21.5313
Reactive lymphoid hyperplasia (RLH) is a benign condition of unknown etiology that was first described in the English literature in 1972[1]. RLH occurs throughout the entire body and occurs predominantly in middle-aged women and is associated with chronic liver disease, autoimmune disease and malignant tumors. RLH of the liver is rare and difficult to distinguish radiologically from hepatocellular carcinoma, metastatic liver tumor and other pathologies[2-7]. Most cases of RLH of the liver have shown perinodular or moderate enhancement in the arterial phase on contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)[4,5,8,9]. Obvious restricted diffusion, which is stronger than that of the spleen, is another characteristic sign[10]. Herein, we propose the additional characteristic radiologic finding on diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI).
There were no chief complaints.
A 54-year-old woman underwent abdominal ultrasound during a medical checkup, which revealed liver lesions. Abdominal ultrasonography revealed well-defined hypoechoic lesions in liver segments 1 and 2.
She had no history of persistent viral infection, autoimmune disease, inflammatory bowel disease or malignant tumors. She had a medical history of polyp in the pharynx and maxillary osteomyelitis.
There were no physical findings to note.
Blood tests revealed normal liver function and were negative for hepatitis B surface antigen, hepatitis B core antibody, hepatitis C antibody, and antinuclear antibody. Her tumor marker levels were as follows: alpha-fetoprotein, 2.1 ng/mL; PIVKA-2, 21 mAU/mL; carbohydrate antigen 19-9, 4.1 U/mL; and carcinoembryonic antigen, 2.3 ng/mL. All markers were in the normal range.
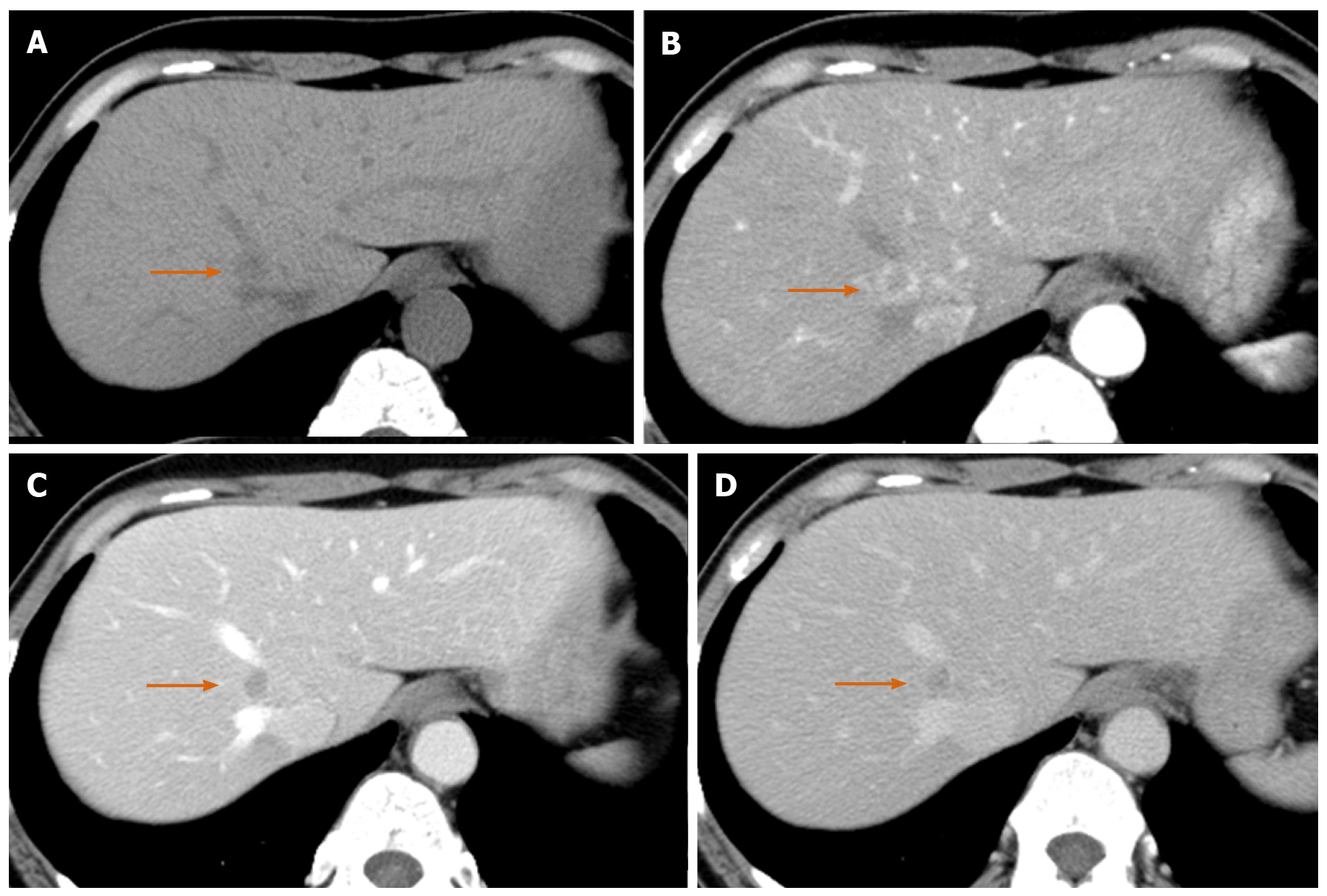
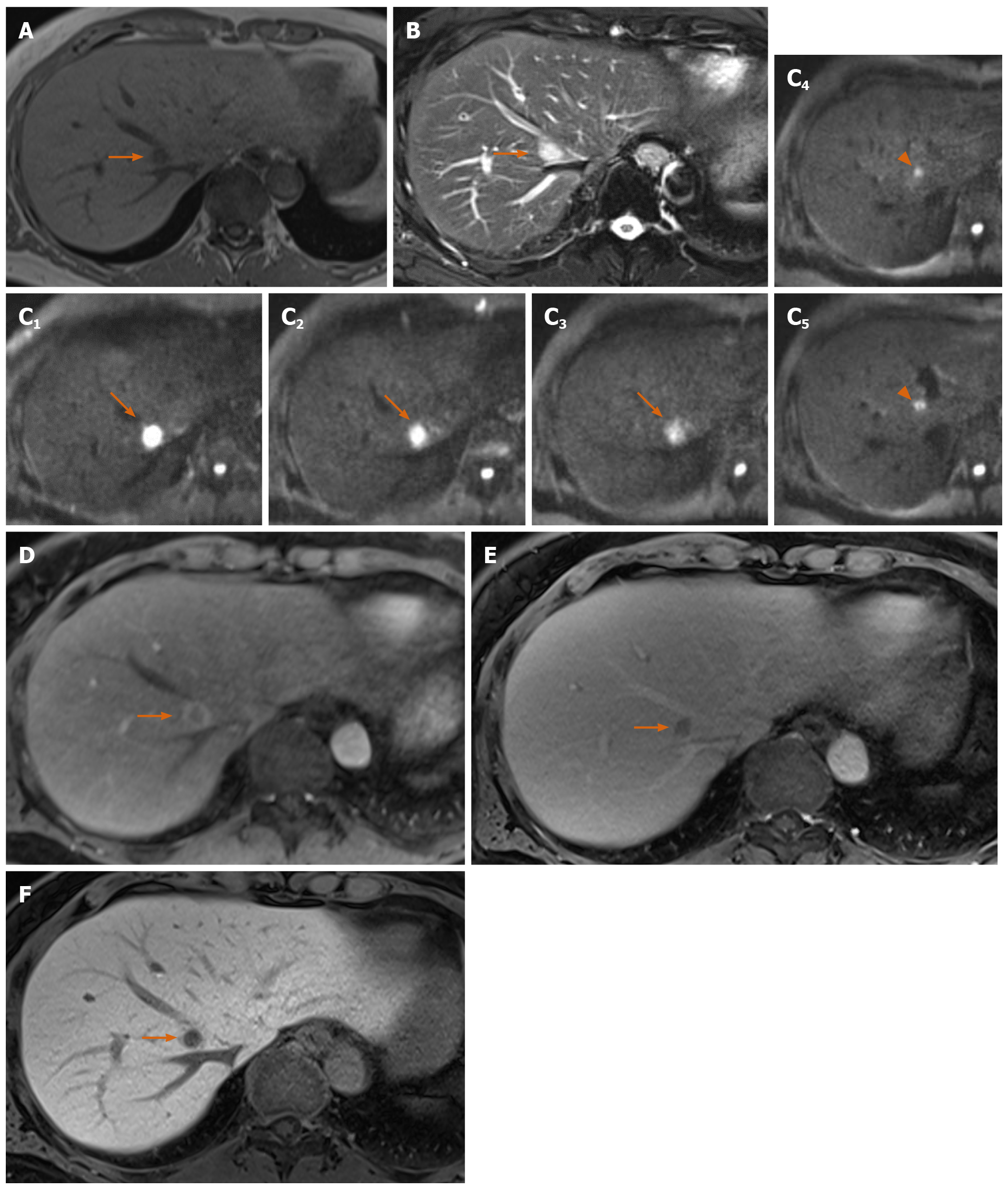
Precontrast CT showed three liver nodules with slight low attenuation relative to the liver parenchyma at segments 1, 2 and 8 (Figure 1A). There was perinodular enhancement (PNE) in the arterial phase in the nodules (Figure 1B) with washout of contrast medium in the portal and equilibrium phase (Figure 1C and 1D). On precontrast MRI, the nodules showed hypointensity on T1-weighted image and hyperintensity on fat-saturated T2-weighted image (Figure 2A and 2B). There was no fat component. The nodule showed obvious hyperintensity on DWI (b = 800 m2/s) and strongly restricted diffusion on apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) mapping (ADC of the lesion: 0.54 × 10-3 mm2/s, ADC of the spleen: 1.03 × 10-3 mm2/s). There was linear hyperintensity along the portal tract consecutive to the liver lesions on DWI (Figures 2C and 3D). However, that of the S2 lesion was faint because of heart beating heart and susceptibility artifact. On gadoxetic acid-dynamic enhanced MRI, the nodule showed PNE in the arterial phase (Figure 2D), washout of contrast medium in the portal and transitional phase and low signal intensity in the hepatobiliary phase (Figure 2E and 2F).
Because we considered the PNE to be a ring-like enhancement, we believed these lesions to be metastatic tumors of unknown origin.
The patient underwent a partial hepatectomy to obtain a definitive diagnosis and partial resection of the liver (segments 2 and 8) for the two superficially located lesions.
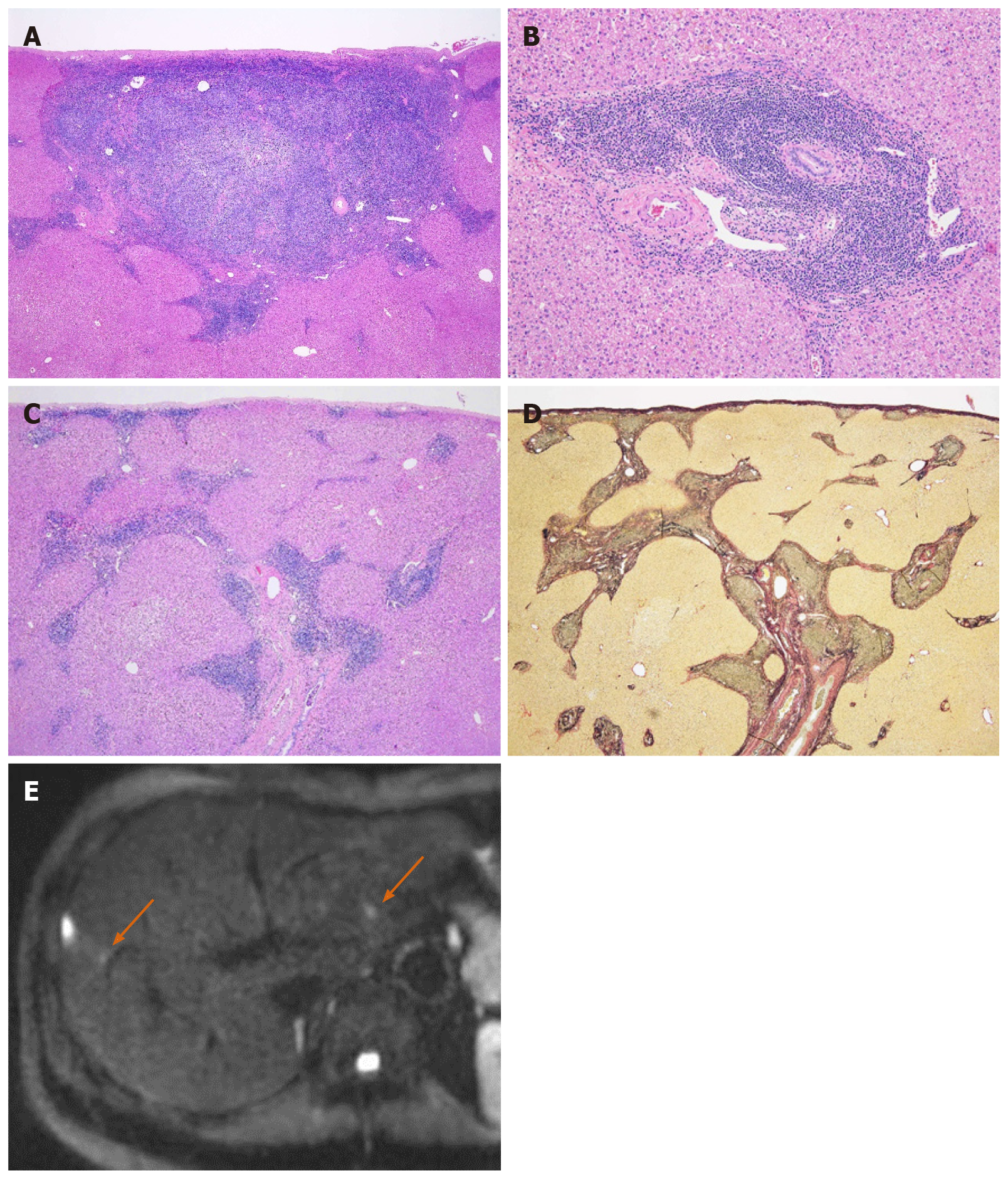
Grossly, there were two well-circumscribed whitish nodules in the subserosa region. Histopathologic examination showed the dense mature lymphocyte and plasma cell infiltration in these nodules, which formed various-size lymphoid follicles with enlarged germinal centers. The presence of tingible body macrophages and lack of expression of BCL2 protein at the germinal center signified nonneoplastic follicles. Scattered large lymphoid cells with prominent nucleoli were also seen mainly in the interfollicular region. These large cells were CD30-positive B-cells, but there were no signs of Epstein-Barr virus infection or light chain restriction. When including immunohistochemical staining, we were unable to detect abnormal B-cell and T-cell distribution indicative of lymphoma. Furthermore, there were few IgG4-positive plasma cells. Therefore, we pathologically diagnosed the lesions as follicular hyperplasia. Interestingly, the lymphoplasmacytic infiltration extended to the surrounding portal tracts in a radial pattern, but there was no definite evidence of portal venular stenosis or fibrosis (Figure 3).
The patient underwent gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI 6 mo after surgery, which showed no progression of residual tumors or relapse.
This case report focused on the linear hyperintensity along the portal tract on DWI consecutive to the mass lesion. One of the characteristic radiologic findings of RLH is strongly restricted diffusion[10]. Zhou et al[10] reported that the ADC value of RLH was lower than that of the spleen; the present case was consistent with their result. The RLH consisted of massive infiltration of mature lymphoid cells, forming lymphoid follicles of various sizes with germinal centers and with prominent sinusoidal dilatation around the lesion. Therefore, the low ADC value reflects the hypercellularity of RLH. The lymphoproliferative disease may occur with portal or sinusoidal infiltration[11]. Kobayashi et al[12] found portal tract hyperintensity on DWI, a finding that was similar to this present case. Many reports have pointed out portal tract infiltration around the lesion pathologically[3-10,12-16]. We supposed that linear hyperintensity along the portal tract is consistent with the portal tract infiltration. There was also massive hypercellularity in this linear region, which was due to infiltrating mature lymphoid cells. Therefore, similar findings of RLH nodules can be seen in this linear region on DWI.
Another characteristic finding of RLH is PNE in the arterial phase or equilibrium phase[2,4,5,8-10,13,15-18]. Yoshida et al[16] first clarified the PNE mechanism from a histological point of view. They considered that because of the marked lymphoid cell infiltration in the perinodular portal tracts, PNE reflects increased arterial supply to the perinodular hepatic parenchyma as a result of venular portal stenosis or disappearance. On the other hand, Sonomura et al[9] reported that the prominent sinusoidal dilatation surrounding the nodule was the main reason for the PNE. They also found no definite evidence of venular portal stenosis or fibrous tissue in the perinodular portal tracts in their case. The present case was pathologically similar to the case from Sonomura et al. However, we did not confirm sinusoidal dilatation. We believe the amount of sinusoidal and portal tract infiltration affected the discrepancy. As mentioned above, hepatic lymphoproliferative disease demonstrates some infiltration pattern[11]; for this reason, the radiologic findings of RLH were relatively variable.
RLH is associated with some diagnostic clues. First, the RLH occurs more frequently in patients with a history, such as viral infection, autoimmune disease, inflammatory bowel disease or malignant tumors and in middle-aged women[3,4,6-8,13,15-20]. Second, PNE in the arterial or equilibrium phase and a strongly restricted diffusion on DWI are also useful diagnostic clues.
In this case, linear hyperintensity consecutive to the liver lesion on DWI was additional valuable diagnostic information. This finding indicates that the lesion is lymphoproliferative disease; thus, we can rule out hepatocellular carcinoma, cholangiocellular carcinoma or metastatic liver tumor. These findings nearly enabled us to make a diagnosis of RLH, although mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma may be present.
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Specialty type: Medicine, research and experimental
Country/Territory of origin: Japan
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Kim YJ S-Editor: Ma YJ L-Editor: Filipodia P-Editor: Wu YXJ
| 1. | Ryan SJ, Zimmerman LE, King FM. Reactive lymphoid hyperplasia. An unusual form of intraocular pseudotumor. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1972;76:652-671. [PubMed] |
| 2. | Hayashi M, Yonetani N, Hirokawa F, Asakuma M, Miyaji K, Takeshita A, Yamamoto K, Haga H, Takubo T, Tanigawa N. An operative case of hepatic pseudolymphoma difficult to differentiate from primary hepatic marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. World J Surg Oncol. 2011;9:3. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Lv A, Liu W, Qian HG, Leng JH, Hao CY. Reactive lymphoid hyperplasia of the liver mimicking hepatocellular carcinoma: incidental finding of two cases. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8:5863-5869. [PubMed] |
| 4. | Machida T, Takahashi T, Itoh T, Hirayama M, Morita T, Horita S. Reactive lymphoid hyperplasia of the liver: a case report and review of literature. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13:5403-5407. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 41] [Cited by in RCA: 41] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 5. | Maehara N, Chijiiwa K, Makino I, Ohuchida J, Kai M, Kondo K, Moriguchi S, Marutsuka K, Asada Y. Segmentectomy for reactive lymphoid hyperplasia of the liver: Report of a case. Surg Today. 2006;36:1019-1023. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Marchetti C, Manci N, Di Maurizio M, Di Tucci C, Burratti M, Iuliano M, Giorgini M, Salerno L, Benedetti Panici P. Reactive lymphoid hyperplasia of liver mimicking late ovarian cancer recurrence: case report and literature review. Int J Clin Oncol. 2011;16:714-717. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Okada T, Mibayashi H, Hasatani K, Hayashi Y, Tsuji S, Kaneko Y, Yoshimitsu M, Tani T, Zen Y, Yamagishi M. Pseudolymphoma of the liver associated with primary biliary cirrhosis: a case report and review of literature. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15:4587-4592. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Kunimoto H, Morihara D, Nakane SI, Tanaka T, Yokoyama K, Anan A, Takeyama Y, Irie M, Shakado S, Noritomi T, Takeshita M, Yoshimitsu K, Sakisaka S. Hepatic Pseudolymphoma with an Occult Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Intern Med. 2018;57:223-230. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Sonomura T, Anami S, Takeuchi T, Nakai M, Sahara S, Tanihata H, Sakamoto K, Sato M. Reactive lymphoid hyperplasia of the liver: Perinodular enhancement on contrast-enhanced computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:6759-6763. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Zhou Y, Wang X, Xu C, Zhou G, Zeng M, Xu P. Hepatic pseudolymphoma: imaging features on dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI and diffusion-weighted imaging. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2018;43:2288-2294. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Baumhoer D, Tzankov A, Dirnhofer S, Tornillo L, Terracciano LM. Patterns of liver infiltration in lymphoproliferative disease. Histopathology. 2008;53:81-90. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 37] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Kobayashi A, Oda T, Fukunaga K, Sasaki R, Minami M, Ohkohchi N. MR imaging of reactive lymphoid hyperplasia of the liver. J Gastrointest Surg. 2011;15:1282-1285. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Kwon YK, Jha RC, Etesami K, Fishbein TM, Ozdemirli M, Desai CS. Pseudolymphoma (reactive lymphoid hyperplasia) of the liver: A clinical challenge. World J Hepatol. 2015;7:2696-2702. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Osame A, Fujimitsu R, Ida M, Majima S, Takeshita M, Yoshimitsu K. Multinodular pseudolymphoma of the liver: computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging findings. Jpn J Radiol. 2011;29:524-527. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Takahashi H, Sawai H, Matsuo Y, Funahashi H, Satoh M, Okada Y, Inagaki H, Takeyama H, Manabe T. Reactive lymphoid hyperplasia of the liver in a patient with colon cancer: report of two cases. BMC Gastroenterol. 2006;6:25. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 47] [Cited by in RCA: 41] [Article Influence: 2.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Yoshida K, Kobayashi S, Matsui O, Gabata T, Sanada J, Koda W, Minami T, Ryu Y, Kozaka K, Kitao A. Hepatic pseudolymphoma: imaging-pathologic correlation with special reference to hemodynamic analysis. Abdom Imaging. 2013;38:1277-1285. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Fukuo Y, Shibuya T, Fukumura Y, Mizui T, Sai JK, Nagahara A, Tsukada A, Matsumoto T, Suyama M, Watanabe S. Reactive lymphoid hyperplasia of the liver associated with primary biliary cirrhosis. Med Sci Monit. 2010;16:CS81-CS86. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Taguchi K, Kuroda S, Kobayashi T, Tashiro H, Ishiyama K, Ide K, Ohira M, Tahara H, Arihiro K, Ohdan H. Pseudolymphoma of the liver: a case report and literature review. Surg Case Rep. 2015;1:107. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Zen Y, Fujii T, Nakanuma Y. Hepatic pseudolymphoma: a clinicopathological study of five cases and review of the literature. Mod Pathol. 2010;23:244-250. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 49] [Cited by in RCA: 44] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Zhang W, Zheng S. Reactive lymphoid hyperplasia of the liver: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98:e16491. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |