Published online Oct 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i20.3247
Peer-review started: June 12, 2019
First decision: July 21, 2019
Revised: August 16, 2019
Accepted: September 9, 2019
Article in press: September 9, 2019
Published online: October 26, 2019
Processing time: 136 Days and 14.7 Hours
Recent evidence indicates that malignant ascites may be associated with the high malignancy and poor prognosis of gastric cancer (GC) with peritoneal metastasis (PM), but no robust consensus has been reached until now.
To evaluate the prognostic significance of malignant ascites in GC patients with PM.
Two independent authors conducted database searches. The searches were performed in the EMBASE, PubMed, and Cochrane Library databases, and the terms used to search included stomach neoplasms, GC, ascites, peritoneal effusion, survival, and survival analysis. Outcomes included overall survival and hazard ratios with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Three pairs of comparisons for measuring survival were made: (1) Patients with ascites vs those without ascites; (2) Patients with massive ascites vs those with mild to moderate ascites; and (3) Patients with massive ascites vs those with no to moderate ascites.
Fourteen articles including fifteen studies were considered in the final analysis. Among them, nine studies assessed the difference in prognosis between patients with and without malignant ascites. A pooled HR of 1.63 (95%CI: 1.47-1.82, P < 0.00001) indicated that GC patients with malignant ascites had a relatively poor prognosis compared to patients without ascites. We also found that the prognosis of GC patients with malignant ascites was related to the volume of ascites in the six other studies.
GC patients with malignant ascites tend to have a worse prognosis, and the volume of ascites has an impact on GC outcomes.
Core tip: Recent evidence indicates that malignant ascites may be associated with the high malignancy and poor prognosis of gastric cancer (GC) with peritoneal metastasis (PM), but no robust consensus has been reached until now. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first systematic meta-analysis to demonstrate the prognostic significance of malignant ascites in GC patients with PM. This meta-analysis reveals that GC patients with malignant ascites tend to have a worse prognosis and that the volume of ascites has an impact on GC outcomes.
- Citation: Zheng LN, Wen F, Xu P, Zhang S. Prognostic significance of malignant ascites in gastric cancer patients with peritoneal metastasis: A systemic review and meta-analysis. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(20): 3247-3258
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i20/3247.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i20.3247
Gastric cancer (GC) is the fifth most common malignancy and the third leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide[1]. Surgical resection remains the gold standard treatment for GC, but the majority of patients with GC are diagnosed at a relatively advanced stage, some even with metastatic disease[2,3]. The common locations of metastases are local lymph nodes, the liver, lung, bone, and peritoneum[4]. For patients with GC, the most life-threatening type of metastasis is peritoneal metastasis (PM), which occurs mainly as a result of direct serosal invasion and omentum and peritoneal seeding. PM often accompanies oral intake deficiency, overconsumption, bowel obstruction, cancer pain, and malignant ascites. The prognosis of GC patients with peritoneal dissemination remains very poor, even with the development of chemotherapy and targeted therapy[5,6]. In the course of treatment, we have often found that GC patients with PM and malignant ascites tend to have a worse prognosis. Recent evidence indicates that malignant ascites may be associated with the high malignancy and poor prognosis of GC with PM, but a relevant consensus has not been reached until now.
Meta-analysis, regarded as a well-established statistical method, may help to clarify some controversial issues by quantitatively pooling homogeneous evidence that can serve as the basis for a general conclusion[7-9]. Therefore, we conducted this meta-analysis to evaluate the prognostic significance of malignant ascites in GC patients with PM.
No protocol had been previously published for this meta-analysis. Additionally, patient consent or ethical approval is not necessary for systematic reviews and meta-analyses. We conducted our systematic meta-analysis in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines[10].
Two independent authors searched the following databases: MEDLINE (Ovid), EMBASE (Ovid), Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL, Ovid), Epub Ahead of Print, In-Process and Other Non-Indexed Citations, Daily and Versions (Ovid), and CBM. The search terms “stomach neoplasms”, “gastric cancer”, “ascites”, “peritoneal effusion”, “survival”, and “survival analysis” were used in combination with the Boolean operators. To further identify potential closely related studies, the reference lists of relevant articles were also screened. The last search was performed on January 01, 2019 (Supplementary material).
The following inclusion and exclusion criteria were applied to determine which studies could be included in our meta-analysis.
The inclusion criteria were: (1) Histologically proven GC; (2) PM diagnosed by histopathological methods or computed tomography (CT); (3) Demographics or statistics assessing the relationship between malignant ascites and the overall survival of GC patients with PM; and (4) No other concomitant malignancies or other severe medical conditions.
The exclusion criteria were (1) Reviews, meta-analyses, preclinical experiments, letters, and conference abstracts; (2) Patients had other diseases that can cause ascites; and (3) Necessary data were unavailable.
There was no limitation on language or the minimum number of subjects in a study.
The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) was used to evaluate the quality of the original nonrandomized studies[11]. The NOS includes four items regarding the selection of subjects, one item regarding intergroup comparability, and three items regarding the measurement of results. After assessing all the included studies, we considered those with a score of 8-9 as having good quality, those with a score of 6-7 as having fair quality, and those with a score lower than 6 as having poor quality.
To ensure accuracy, all eligible articles were reviewed independently by two investigators. The following items were collected from each included study: First author’s name, year of publication, study period, country of origin of the study population, previous treatment, sample size, and median overall survival (mOS).
Ascites grades were classified according to the criteria used in the Japan Clinical Oncology Group 0106 study[12]: None, ascites undetected by CT; mild, ascites localized in only one area such as the pelvic cavity; moderate, ascites neither mild nor massive; and massive, ascites extending throughout the abdominal cavity. Mild ascites was also defined as a volume < 500 mL identified during surgery or as estimated on CT scanning, moderate defined as neither mild nor massive, and massive as a volume > 1000 mL.
RevMan 5 software, downloaded from the Cochrane Collaboration, was used for this meta-analysis. The hazard ratio (HR) is generally considered the only statistic compatible for both censoring and time to event[13]. To assess the prognostic value of malignant ascites in GC patients with PM, the HR with a 95%CI served as the appropriate summary statistic. A P value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. HRs with 95% CIs were extracted from each study and used to generate a pooled HR. If the HRs were not available in the original studies, a practical method described by Tierney et al[14] was applied to extrapolate the HRs with 95%CIs. The relevant formula is listed as follows: The median event-free time in the research arm = the median event-free time in the control arm/HR.
Statistical heterogeneity was assessed using Cochran’s Q test and Higgins I-squared statistic. P > 0.10 and I² ≤ 50% were considered the values that indicated acceptable homogeneity, and a fixed-effects model was subsequently applied. Conversely, if severe heterogeneity was revealed by P ≤ 0.10 or I² > 50%, a random-effects model was applied to calculate the pooled HR.
The potential publication bias of the meta-analysis was assessed by the visual inspection of funnel plots. We performed an additional sensitivity analysis to further examine the robustness of our meta-analysis.
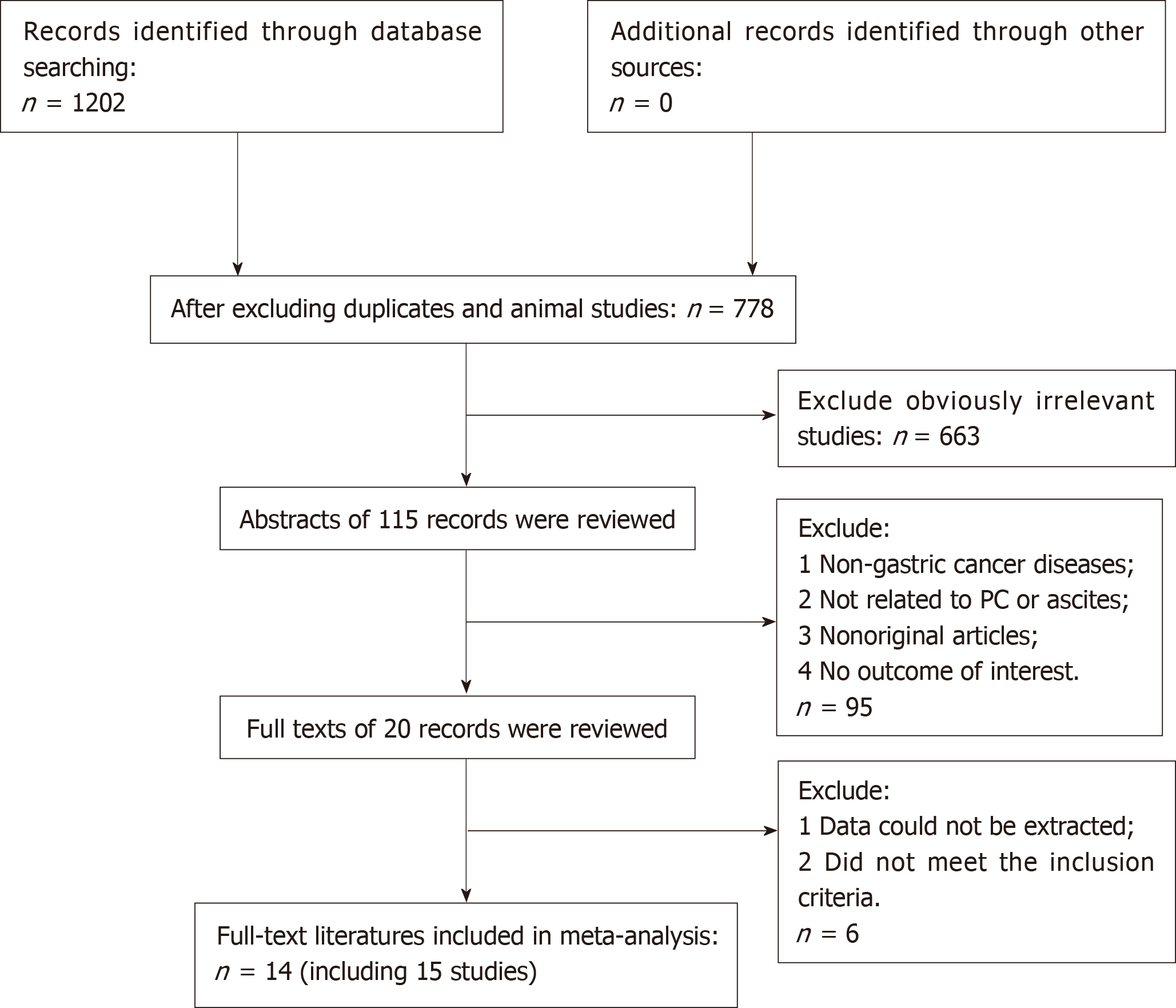
A flow chart of the literature search is shown in Figure 1. The initial search algorithm retrieved a total of 1202 records from the four electronic databases. After excluding duplicates, animal studies, and obviously irrelevant studies, only 115 records were further evaluated. Then, we screened the abstracts of those studies, and 95 of them were excluded for the following reasons: (1) Non-gastric cancer; (2) Not related to PM or ascites; (3) Non-original articles; and (4) No outcome of interest. Further filtration was based on reading through the full texts of the remaining 20 studies. After excluding 4 articles that did not meet the inclusion criteria and 2 articles that did not offer the data we needed, 14 articles[4,15-27] with 15 studies were included in our meta-analysis.
Among the 15 studies, 9[15-17,19,21,22,25-27] assessed the difference in prognosis between patients with and without ascites, and 3[15,20,24] compared the prognosis between patients with massive ascites with those with mild to moderate ascites. The other 3 studies[4,18,23] compared the prognosis of the massive ascites group with the none-mod group (including patients with no ascites, mild ascites, and moderate ascites). The characteristics of the included studies are summarized in Tables 1-3.
| Ref. | Year | Patients’ origin | Study design | Study period | GC with PM | Previous treatment | No. of samples | mOS (mo) |
| Ascites (+)/ascites (-) | Ascites (+)/ascites (-) | |||||||
| Sadeghi et al[16] | 2000 | France | PS | 1995-1997 | Yes | Chemotherapy, surgery | 35/90 | 1.4/3.8 |
| Chen et al[27] | 2017 | China | RS | 2010-2014 | Yes | Chemotherapy, surgery | 207/311 | 9.87/14.27 |
| Glehen et al[25] | 2004 | France | PS | 1989-2000 | Yes | Chemotherapy, surgery | 17/32 | 5.0/15.6 |
| Lan et al[21] | 2010 | China | RS | 1993-2007 | Yes | Surgery | 24/67 | 7.3/10.1 |
| Kitayama et al[22] | 2012 | Japan | PS | 2004-2009 | Yes | Chemotherapy, surgery | 71/29 | 19.0/39.3 |
| Peng et al[17] | 2013 | China | RS | 1998-2011 | Yes | Surgery | 84/49 | 7.3/10.1 |
| Shitara et al[15] | 2013 | Japan | RS | 2005-2011 | Yes | Chemotherapy, surgery | 11/70 | 9.5/18.1 |
| Nie et al[19] | 2016 | China | RS | 2000-2014 | Yes | Chemotherapy, surgery | 313/347 | - |
| Emoto et al[26] | 2012 | Japan | RS | 2005-2010 | Yes | Chemotherapy | 73/29 | - |
| Total | 835/1024 |
| Ref. | Year | Patients’ origin | Study design | Study period | GC with PM | Previous treatment | No. of samples | mOS (mo) |
| Massive/Mild to moderate | Massive/Mild to moderate | |||||||
| Matsumoto et al[20] | 2018 | Japan | RS | 2015-2016 | Yes | Chemotherapy, surgery | 14/26 | 3.9/9.6 |
| Hara et al[24] | 2017 | Japan | RS | 2006-2011 | Yes | Chemotherapy | 8/22 | 1.9/7.2 |
| Shitara et al[15] | 2013 | Japan | RS | 2005-2011 | Yes | Chemotherapy, surgery | 11/39 | 9.5/13.5 |
| Total | 33/87 |
| Ref. | Year | Patients’ origin | Study design | Study period | GC with PM | Previous treatment | No. of samples | mOS (mo) |
| Massive/None-mod | Massive/None-mod | |||||||
| Ohnuma et al[18] | 2018 | Japan | RS | 2004-2015 | Yes | Chemotherapy | 15/22 | 16.8/21.7 |
| Ji et al[23] | 2018 | China | RS | 2005-2017 | Yes | Chemotherapy, surgery | 33/77 | 9.0/16.6 |
| Iwasa et al[4] | 2010 | Japan | RS | 1999-2006 | Yes | Chemotherapy | 21/58 | - |
| Total | 69/157 |
The mean NOS score of the included studies was 7.21 (ranging from 7 to 8), suggesting a generally good quality level of the studies included in our meta-analysis (Table 4).
| Ref. | Selection of subjects (score) | Intergroup comparability (score) | Result measurement (score) | NOS |
| Sadeghi et al[16] | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 |
| Chen et al[27] | 3 | 1 | 3 | 7 |
| Glehen et al[25] | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 |
| Lan et al[21] | 3 | 1 | 3 | 7 |
| Kitayama et al[22] | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 |
| Peng et al[17] | 3 | 1 | 3 | 7 |
| Shitara et al[15] | 3 | 1 | 3 | 7 |
| Nie et al[19] | 3 | 1 | 3 | 7 |
| Ohnuma et al[18] | 3 | 1 | 3 | 7 |
| Matsumoto et al[20] | 3 | 1 | 3 | 7 |
| Hara et al[24] | 3 | 1 | 3 | 7 |
| Ji et al[23] | 3 | 1 | 3 | 7 |
| Iwasa et al[4] | 3 | 1 | 3 | 7 |
| Emoto et al[26] | 3 | 1 | 3 | 7 |
The basic characteristics of the 14 eligible papers[4,15-27] including 3 prospective studies and 12 retrospective studies are summarized in Tables 1-3. In total, 2194 patients diagnosed with GC with PM were included. Most of the included studies were based on Asian populations, including 5 from China, 8 from Japan, and 2 from France. There are three comparisons, which are described in the following sections.
Patients with ascites vs those without ascites: Nine studies[15-17,19,21,22,25-27] including 1859 patients accessed the difference in prognosis between patients with and without ascites, and the mOS of the 835 GC patients with malignant ascites ranged from 1.4 to 19.0 mo, while that of the 1024 GC patients without malignant ascites ranged from 3.8 to 39.3 mo (Table 1).
Patients with massive ascites vs those with mild to moderate ascites: Three studies[15,20,24] including 120 patients compared the prognosis of patients with massive ascites with that of patients with mild to moderate ascites. The mOS of 33 patients with massive ascites ranged from 1.9 to 9.5 mo, and that of the 87 patients with mild to moderate ascites ranged from 7.2 to 13.5 mo (Table 2).
Patients with massive ascites vs those with none to moderate ascites: The other 3 studies[4,18,23] including 226 patients divided the patients into a massive group and a none-mod group. The mOS of the 69 patients with massive ascites ranged from 9.0 to 16.8 mo, and that of the 157 patients with no, small, or moderate ascites ranged from 16.6 to 21.7 mo (Table 3).
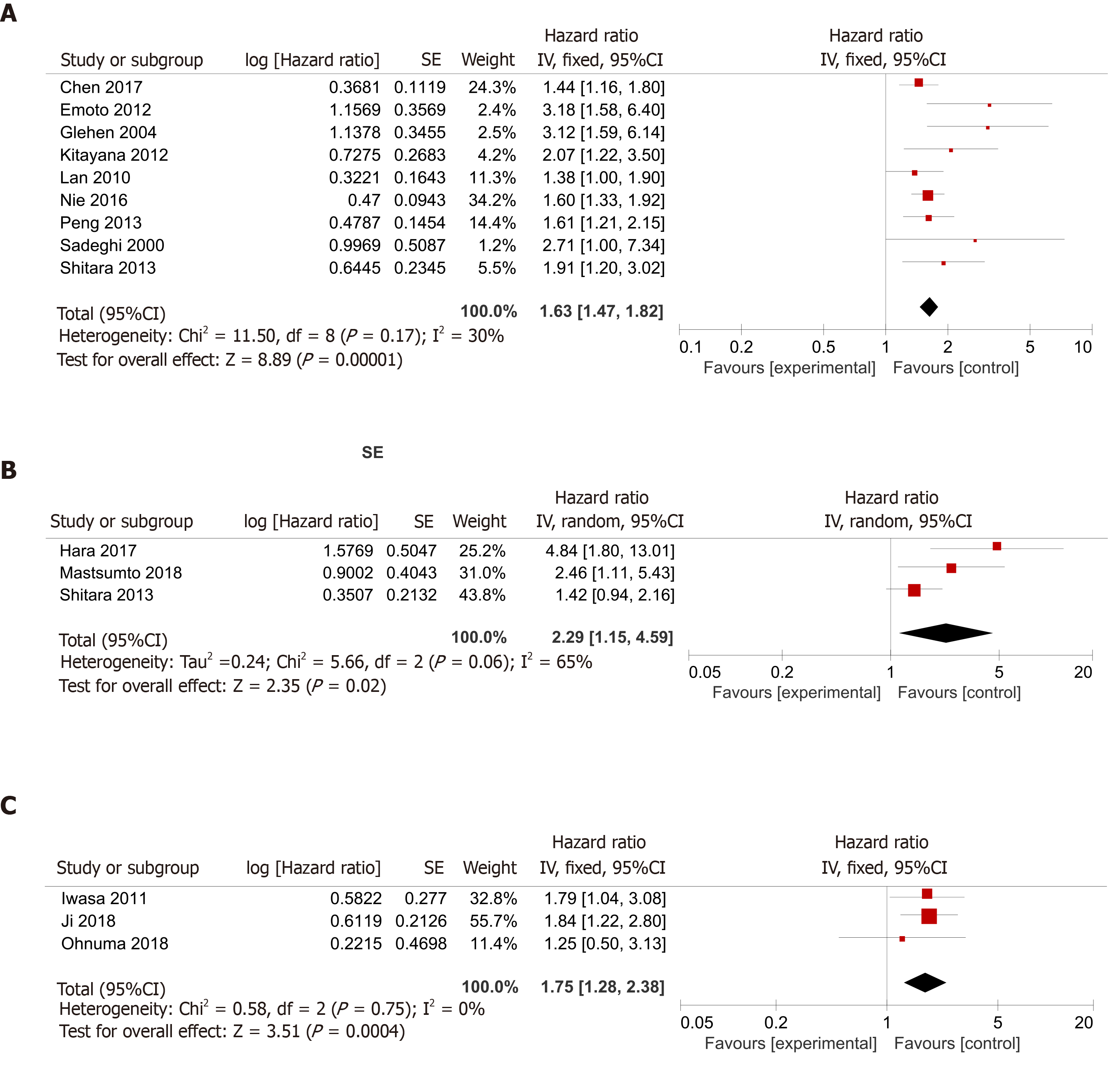
Patients with ascites vs those without ascites: The application of Cochran’s Q test and Higgins I-squared statistic showed that minor heterogeneity existed (P = 0.17, I² = 30%) among the nine studies[15-17,19,21,22,25-27], and a fixed-effects model was used for the analysis (Figure 2A). A pooled HR of 1.63 (95%CI: 1.47-1.82, P < 0.00001) indicated that GC patients with malignant ascites suffered a relatively worse prognosis and shorter OS compared to patients without ascites.
Patients with massive ascites vs those with mild to moderate ascites: We also found three articles[15,20,24] comparing the prognosis of patients with massive ascites with that of patients with mild or moderate ascites. Because the Cochran’s Q test and I² statistic showed that some heterogeneity existed (P = 0.06, I² = 65%) among those studies, a random-effects model was applied for the analysis. A pooled HR of 2.29 (95%CI: 1.15-4.59, P = 0.02) indicated that the prognosis of gastric patients with malignant ascites was related to the volume of the ascites (Figure 2B).
Patients with massive ascites vs those with none to moderate ascites: There were three studies[4,18,23] dividing patients into the massive group and none-mod group. Because the Cochran’s Q test and Higgins I-squared statistic showed that minor heterogeneity existed (P = 0.75, I² = 0%) among those studies, a fixed-effects model was used for the analysis. The patients with massive ascites had a worse prognosis than the patients with no, mild, or moderate ascites, with a pooled HR of 1.75 (95%CI: 1.28-2.38, P = 0.0004) (Figure 2C).
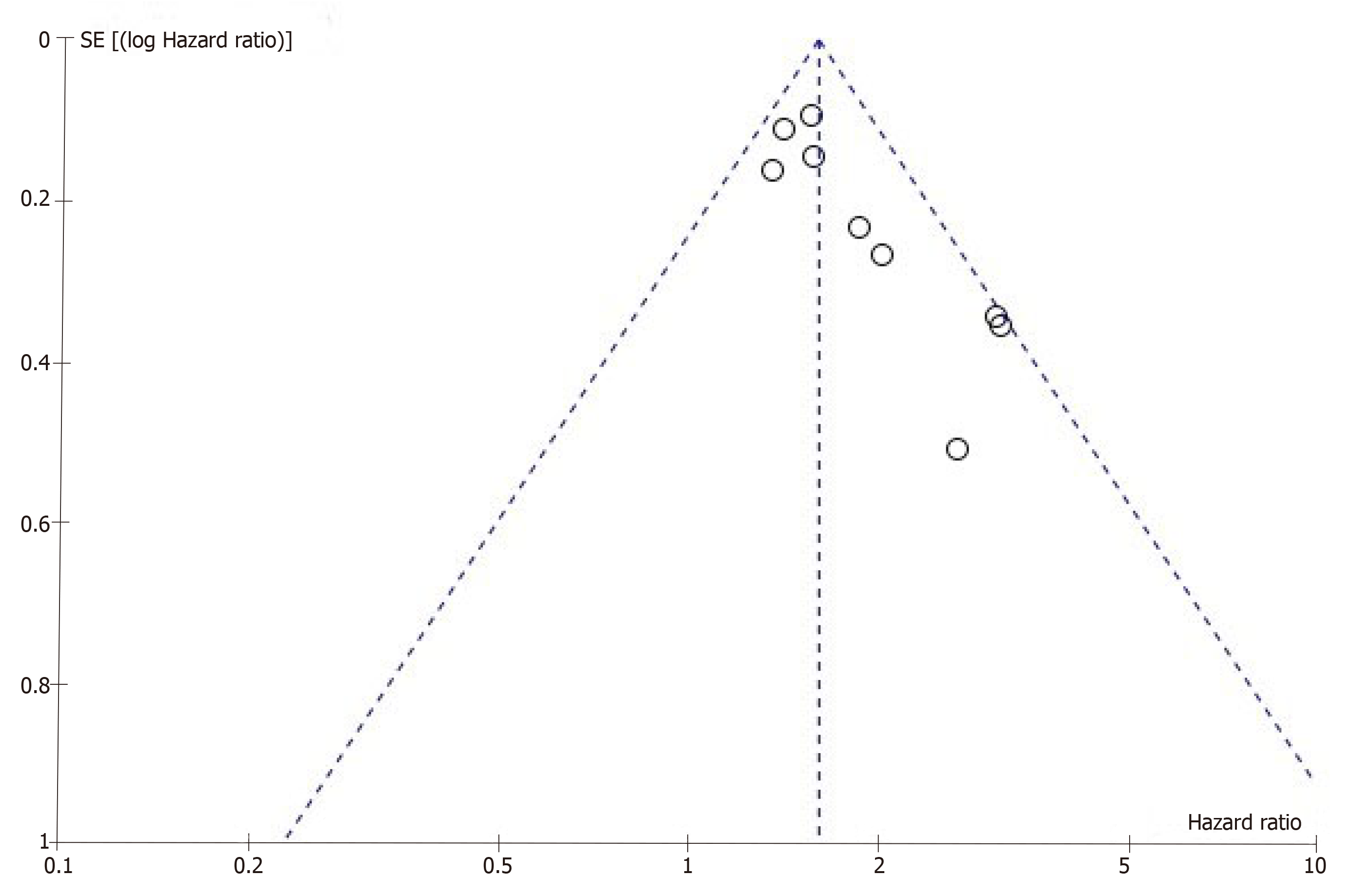
Publication bias remains a major concern for all kinds of meta-analyses because positive results tend to have a better chance of being accepted by journals than negative results. A funnel plot was constructed to evaluate the reliability of the meta-analysis results. The results of the funnel plot revealed some publication bias in this meta-analysis (Figure 3). Because the number of studies we included was too small, Egger’s test and Begg’s test could not be applied to explore publication bias adequately.
To further examine the robustness of our meta-analysis, we performed a sensitivity analysis. The corresponding HR was not changed noticeably after excluding each study in our meta-analysis one at a time (data not shown).
With a 5-year OS less than 20%, PM is considered a manifestation of the end stage of GC[28-30]. GC patients with peritoneal dissemination often have malignant ascites, which is associated with a deterioration in the quality of life and poor prognosis. In our clinical practice, we have observed that GC patients with malignant ascites usually have a worse prognosis than those without ascites. Currently, few data exist concerning whether malignant ascites is associated with the high malignancy and poor prognosis of GC patients with PM, and a relevant consensus has not been reached until now. Therefore, we conducted this meta-analysis to evaluate the prognostic significance of malignant ascites in GC patients with PM.
In our meta-analysis, nine studies[15-17,19,21,22,25-27] assessed the difference in prognosis between patients with and without ascites, and the mOS was worse in patients with ascites than in patients without ascites in every study. Finally, we concluded that malignant ascites was significantly associated with an unfavorable prognosis, with a pooled HR of 1.63 (95%CI: 1.47-1.82, P < 0.00001) (Figure 2A).
We also found three articles[15,20,24] comparing the prognosis of patients with massive ascites with that of patients with mild or moderate ascites. A pooled HR of 2.29 (95%CI: 1.15-4.59, P = 0.02) indicated that the prognosis of patients with malignant ascites was related to the volume of the ascites (Figure 2B). Meanwhile, there were three studies[4,18,23] dividing patients into massive and none-mod groups. The patients with massive ascites had a worse prognosis than patients with no, mild, or moderate ascites, with a pooled HR of 1.75 (95%CI: 1.28-2.38, P = 0.0004) (Figure 2C).
Undoubtedly, it is important to develop effective treatments for GC patients with malignant ascites. Ni et al[31] reported that a good response of malignant ascites after intraperitoneal perfusion chemotherapy was associated with improved patient survival. A study by Yuan et al[32] demonstrated that the OS of GC patients with malignant ascites that disappeared/decreased/were stable appeared to be better than that in patients with ascites that increased after hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC), although the difference was not statistically significant. However, current treatments remain unsatisfactory. Further studies will be necessary to explore more effective treatments and therapeutic targets.
Recently, some studies focused on anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) therapies in the course of treatment. Intraperitoneal VEGF may come from various sources, such as human peritoneal mesothelial cells, subperitoneal capillaries, peritoneal metastatic tumors, fibroblasts, and macrophages[33,34]. VEGF mediates the formation of malignant ascites by increasing the permeability of blood vessels[35]. Fushida et al[36] reported that the ascites volume correlated with the ascites VEGF concentration and that elevated ascites VEGF levels were significantly associated with shorter overall survival in patients with GC. Bekes et al[37] reported that VEGF can induce angiogenesis to allow tumor growth and increase endothelial permeability via suppression of VE-cadherin and subsequent claudin 5 in the peritoneal vasculature, which finally induces ascites and thereby facilitates dissemination of cancer cells in the abdominal cavity. Yin et al[38] reported that malignant exudates could induce cancer cells to undergo epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and endow tumor cells with stem cell properties, which promoted tumor growth, chemoresistance, and immune evasion. VEGF blockade reduced EMT and cancer stem cell (CSC) properties, which might be a reasonable option for patients with malignant ascites. However, more studies are needed to validate the efficacy of anti-VEGF therapy for malignant ascites.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first systematic meta-analysis to demonstrate the prognostic significance of malignant ascites in GC patients with PM. Although our meta-analysis shows that malignant ascites is an important prognostic factor for gastric patients with PM, it carries a few other implications for future studies. First, both the number of included studies and the number of included patients were relatively small, and most of the included studies were based on Asian populations. Second, the following factors may influence the reliability of the results: the numbers of patients in the experimental group and control group were not completely equal, and there were no uniform standards for the grading of ascites (some studies were based on the volume of ascites, and some on the extent of ascites). Last, we did not obtain data comparing the prognosis of patients with mild ascites with that of patients without ascites, which could further confirm the prognostic significance of malignant ascites.
In conclusion, this meta-analysis may shed some light on the prognostic significance of malignant ascites in GC patients with PM. Patients with malignant ascites tend to have a worse prognosis, and the volume of the ascites has an impact on GC outcomes. The treatment of these patients should be decided discreetly, taking into consideration the general status of patients. For GC patients with mild to moderate ascites, we can choose cytoreductive surgery with HIPEC, laparoscopic HIPEC alone, intravenous chemotherapy, intraperitoneal chemotherapy, or molecular targeting therapy[39,40]. For GC patients with massive ascites, benefit for delivering chemotherapy should be weighed carefully against the risk, and best supportive care should be considered as an alternative[39]. Previous reports have implied that ascites volume correlates with ascites VEGF concentration and that elevated ascites VEGF levels are significantly associated with shorter overall survival in patients with GC. GC patients with malignant ascites have an extremely poor prognosis not only because of the advanced stage but also because cancer cells in malignant exudates could acquire more aggressive properties undergoing EMT and CSC processes. VEGF may be the most relevant to EMT and CSC processes in malignant ascites microenvironments. Anti-VEGF therapy, which can impair the EMT and CSC processes, may be a promising option for patients with malignant ascites. More studies are needed to explore effective therapies to improve these patients’ prognoses and quality of life. Because most of the studies included in this meta-analysis are retrospective studies, some confounding factors exist. Higher quality prospective studies with more patients will be necessary to validate malignant ascites as a predictive marker of poor outcome.
Gastric cancer (GC) is the fifth most common malignancy globally. The majority of patients with GC are diagnosed at a relatively advanced stage, some even with metastatic disease. For patients with GC, the most life-threatening type of metastasis is peritoneal metastasis (PM), which often accompanies malignant ascites. GC patients with PM and malignant ascites tend to have a worse prognosis.
Recent evidence indicates that malignant ascites may be associated with the high malignancy and poor prognosis of GC with PM, but no robust consensus has been reached until now.
We conducted this meta-analysis to evaluate the prognostic significance of ascites in GC patients with PM.
Two independent authors conducted database searches. The searches were performed in the EMBASE, PubMed, and Cochrane Library databases, and the terms used to search included stomach neoplasms, GC, ascites, peritoneal effusion, survival, and survival analysis. RevMan 5 software was used for this meta-analysis. The hazard ratio (HR) with a 95%CI served as the appropriate summary statistic. Three pairs of comparisons measuring survival were made: (1) Patients with ascites vs those without ascites; (2) Patients with massive ascites vs those with mild to moderate ascites; and (3) Patients with massive ascites vs those with no to moderate ascites.
Fourteen articles including fifteen studies were considered in the final analysis. Among them, nine studies assessed the difference in prognosis between patients with and without malignant ascites. A pooled HR of 1.63 (95% CI: 1.47-1.82, P < 0.00001) indicated that GC patients with malignant ascites had a relatively poor prognosis compared to patients without ascites. We also found that the prognosis of GC patients with malignant ascites was related to the volume of ascites in the six other studies.
GC patients with malignant ascites tend to have a worse prognosis, and the volume of ascites has an impact on GC outcomes.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first systematic meta-analysis to demonstrate the prognostic significance of malignant ascites in GC patients with PM. Because most of the studies included in this meta-analysis are retrospective studies, some confounding factors exist. Higher quality prospective studies with more patients will be necessary to validate malignant ascites as a predictive marker of poor outcome.
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Specialty type: Medicine, Research and Experimental
Country of origin: China
Peer-review report classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Yamamoto M, Farhat S S-Editor: Dou Y L-Editor: Wang TQ E-Editor: Liu MY
| 1. | Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359-E386. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20108] [Cited by in RCA: 20495] [Article Influence: 2049.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (20)] |
| 2. | Zhang XF, Huang CM, Lu HS, Wu XY, Wang C, Guang GX, Zhang JZ, Zheng CH. Surgical treatment and prognosis of gastric cancer in 2,613 patients. World J Gastroenterol. 2004;10:3405-3408. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 78] [Cited by in RCA: 77] [Article Influence: 3.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Chen S, Li YF, Feng XY, Zhou ZW, Yuan XH, Chen YB. Significance of palliative gastrectomy for late-stage gastric cancer patients. J Surg Oncol. 2012;106:862-871. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 41] [Article Influence: 3.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Iwasa S, Nakajima TE, Nakamura K, Takashima A, Kato K, Hamaguchi T, Yamada Y, Shimada Y. Systemic chemotherapy for peritoneal disseminated gastric cancer with inadequate oral intake: a retrospective study. Int J Clin Oncol. 2011;16:57-62. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Koizumi W, Narahara H, Hara T, Takagane A, Akiya T, Takagi M, Miyashita K, Nishizaki T, Kobayashi O, Takiyama W, Toh Y, Nagaie T, Takagi S, Yamamura Y, Yanaoka K, Orita H, Takeuchi M. S-1 plus cisplatin versus S-1 alone for first-line treatment of advanced gastric cancer (SPIRITS trial): a phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 2008;9:215-221. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1320] [Cited by in RCA: 1419] [Article Influence: 83.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A, Chung HC, Shen L, Sawaki A, Lordick F, Ohtsu A, Omuro Y, Satoh T, Aprile G, Kulikov E, Hill J, Lehle M, Rüschoff J, Kang YK; ToGA Trial Investigators. Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2010;376:687-697. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5541] [Cited by in RCA: 5298] [Article Influence: 353.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (3)] |
| 7. | Zhong B, Wang T, Zou J, Zheng F, Huang R, Zheng X, Yang W, Chen Z. Association of the intermediate filament nestin with cancer stage: a meta-analysis based on 223 positive/high nestin cases and 460 negative/low case-free controls. Oncotarget. 2015;6:22970-22977. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Li YJ, Dai YL, Zhang WB, Li SJ, Tu CQ. Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of chemokine receptor CXCR4 in patients with bone and soft tissue sarcoma: a meta-analysis. Clin Exp Med. 2017;17:59-69. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Li SJ, Chen DL, Zhang WB, Shen C, Che GW. Prognostic value of stromal decorin expression in patients with breast cancer: a meta-analysis. J Thorac Dis. 2015;7:1939-1950. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J, Moher D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ. 2009;339:b2700. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13930] [Cited by in RCA: 13320] [Article Influence: 832.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25:603-605. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8858] [Cited by in RCA: 12583] [Article Influence: 838.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Shirao K, Boku N, Yamada Y, Yamaguchi K, Doi T, Goto M, Nasu J, Denda T, Hamamoto Y, Takashima A, Fukuda H, Ohtsu A; Gastrointestinal Oncology Study Group of the Japan Clinical Oncology Group. Randomized Phase III study of 5-fluorouracil continuous infusion vs. sequential methotrexate and 5-fluorouracil therapy in far advanced gastric cancer with peritoneal metastasis (JCOG0106). Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2013;43:972-980. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 74] [Cited by in RCA: 90] [Article Influence: 7.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Parmar MK, Torri V, Stewart L. Extracting summary statistics to perform meta-analyses of the published literature for survival endpoints. Stat Med. 1998;17:2815-2834. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Tierney JF, Stewart LA, Ghersi D, Burdett S, Sydes MR. Practical methods for incorporating summary time-to-event data into meta-analysis. Trials. 2007;8:16. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4738] [Cited by in RCA: 4944] [Article Influence: 274.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Shitara K, Mizota A, Matsuo K, Sato Y, Kondo C, Takahari D, Ura T, Tajika M, Muro K. Fluoropyrimidine plus cisplatin for patients with advanced or recurrent gastric cancer with peritoneal metastasis. Gastric Cancer. 2013;16:48-55. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Sadeghi B, Arvieux C, Glehen O, Beaujard AC, Rivoire M, Baulieux J, Fontaumard E, Brachet A, Caillot JL, Faure JL, Porcheron J, Peix JL, François Y, Vignal J, Gilly FN. Peritoneal carcinomatosis from non-gynecologic malignancies: results of the EVOCAPE 1 multicentric prospective study. Cancer. 2000;88:358-363. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Peng W, Hua RX, Jiang R, Ren C, Jia YN, Li J, Guo WJ. Surgical treatment for patients with Krukenberg tumor of stomach origin: clinical outcome and prognostic factors analysis. PLoS One. 2013;8:e68227. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 29] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Ohnuma H, Sato Y, Hirakawa M, Kikuchi S, Miyanishi K, Sagawa T, Takahashi Y, Nobuoka T, Okamoto K, Miyamoto H, Takemasa I, Takayama T, Kato J. Docetaxel, cisplatin and S-1 (DCS) combination chemotherapy for gastric cancer patients with peritoneal metastasis: a retrospective study. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2018;81:539-548. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Nie R, Yuan S, Chen S, Chen X, Chen Y, Zhu B, Qiu H, Zhou Z, Peng J, Chen Y. Prognostic nutritional index is an independent prognostic factor for gastric cancer patients with peritoneal dissemination. Chin J Cancer Res. 2016;28:570-578. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Matsumoto H, Kawazoe A, Shimada K, Fukuoka S, Kuboki Y, Bando H, Kojima T, Ohtsu A, Yoshino T, Doi T, Shitara K. A retrospective study of the safety and efficacy of paclitaxel plus ramucirumab in patients with advanced or recurrent gastric cancer with ascites. BMC Cancer. 2018;18:120. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Lan XW, Xue YW, Zhang YL, Wei YZ, Song HJ, Ma Y, Li CF, Zhang T. The analysis of clinicopathoigic features and prognosis in gastric cancer With Peritoneal dissemination. Shiyong Zhongliuxue Zazhi. 2010;24:428-434. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 22. | Kitayama J, Ishigami H, Yamaguchi H, Yamashita H, Emoto S, Kaisaki S. S-1 plus intravenous and intraperitoneal Paclitaxel for gastric cancer with peritoneal metastasis. Gastrointest Cancer Res. 2012;5:S10-S13. [PubMed] |
| 23. | Ji ZH, Li XB, Liu G, Yu Y, Lin YL, Zhang YB, Li Y. [Cytoreductive surgery plus hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy to treat peritoneal carcinomatosis from gastric cancer: a clinical study of 110 patients]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018;98:3079-3083. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Hara H, Kadowaki S, Asayama M, Ooki A, Yamada T, Yoshii T, Yamaguchi K. First-line bolus 5-fluorouracil plus leucovorin for peritoneally disseminated gastric cancer with massive ascites or inadequate oral intake. Int J Clin Oncol. 2018;23:275-280. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Glehen O, Schreiber V, Cotte E, Sayag-Beaujard AC, Osinsky D, Freyer G, François Y, Vignal J, Gilly FN. Cytoreductive surgery and intraperitoneal chemohyperthermia for peritoneal carcinomatosis arising from gastric cancer. Arch Surg. 2004;139:20-26. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 161] [Cited by in RCA: 176] [Article Influence: 8.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Emoto S, Ishigami H, Yamashita H, Yamaguchi H, Kaisaki S, Kitayama J. Clinical significance of CA125 and CA72-4 in gastric cancer with peritoneal dissemination. Gastric Cancer. 2012;15:154-161. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 99] [Cited by in RCA: 120] [Article Influence: 9.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Chen S, Nie RC, OuYang LY, Li YF, Xiang J, Zhou ZW, Chen Y, Peng J. Body mass index (BMI) may be a prognostic factor for gastric cancer with peritoneal dissemination. World J Surg Oncol. 2017;15:52. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Eveno C, Jouvin I, Pocard M. PIPAC EstoK 01: Pressurized IntraPeritoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy with cisplatin and doxorubicin (PIPAC C/D) in gastric peritoneal metastasis: a randomized and multicenter phase II study. Pleura Peritoneum. 2018;3:20180116. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 50] [Article Influence: 7.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Ji ZH, Peng KW, Yu Y, Li XB, Yonemura Y, Liu Y, Sugarbaker PH, Li Y. Current status and future prospects of clinical trials on CRS + HIPEC for gastric cancer peritoneal metastases. Int J Hyperthermia. 2017;33:562-570. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 37] [Article Influence: 5.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Rau B, Brandl A, Piso P, Pelz J, Busch P, Demtröder C, Schüle S, Schlitt HJ, Roitman M, Tepel J, Sulkowski U, Uzunoglu F, Hünerbein M, Hörbelt R, Ströhlein M, Beckert S, Königsrainer I, Königsrainer A; Peritoneum Surface Oncology Group and members of the StuDoQ|Peritoneum Registry of the German Society for General and Visceral Surgery (DGAV). Peritoneal metastasis in gastric cancer: results from the German database. Gastric Cancer. 2019;. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 54] [Cited by in RCA: 81] [Article Influence: 16.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Ni X, Wu P, Wu J, Ji M, Tian B, Jiang Z, Sun Y, Xing X, Jiang J, Wu C. Hyperthermic intraperitoneal perfusion chemotherapy and response evaluation in patients with gastric cancer and malignant ascites. Oncol Lett. 2017;14:1691-1696. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Yuan M, Wang Z, Hu G, Yang Y, Lv W, Lu F, Zhong H. A retrospective analysis of hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy for gastric cancer with peritoneal metastasis. Mol Clin Oncol. 2016;5:395-399. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Sako A, Kitayama J, Yamaguchi H, Kaisaki S, Suzuki H, Fukatsu K, Fujii S, Nagawa H. Vascular endothelial growth factor synthesis by human omental mesothelial cells is augmented by fibroblast growth factor-2: possible role of mesothelial cell on the development of peritoneal metastasis. J Surg Res. 2003;115:113-120. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 47] [Cited by in RCA: 49] [Article Influence: 2.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Harmey JH, Dimitriadis E, Kay E, Redmond HP, Bouchier-Hayes D. Regulation of macrophage production of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) by hypoxia and transforming growth factor beta-1. Ann Surg Oncol. 1998;5:271-278. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 132] [Cited by in RCA: 140] [Article Influence: 5.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 35. | Chu DZ, Lang NP, Thompson C, Osteen PK, Westbrook KC. Peritoneal carcinomatosis in nongynecologic malignancy. A prospective study of prognostic factors. Cancer. 1989;63:364-367. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Fushida S, Oyama K, Kinoshita J, Yagi Y, Okamoto K, Tajima H, Ninomiya I, Fujimura T, Ohta T. VEGF is a target molecule for peritoneal metastasis and malignant ascites in gastric cancer: prognostic significance of VEGF in ascites and efficacy of anti-VEGF monoclonal antibody. Onco Targets Ther. 2013;6:1445-1451. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 36] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 37. | Bekes I, Friedl TW, Köhler T, Möbus V, Janni W, Wöckel A, Wulff C. Does VEGF facilitate local tumor growth and spread into the abdominal cavity by suppressing endothelial cell adhesion, thus increasing vascular peritoneal permeability followed by ascites production in ovarian cancer? Mol Cancer. 2016;15:13. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 41] [Cited by in RCA: 44] [Article Influence: 4.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | Yin T, Wang G, He S, Shen G, Su C, Zhang Y, Wei X, Ye T, Li L, Yang S, Li D, Guo F, Mo Z, Wan Y, Ai P, Zhou X, Liu Y, Wang Y, Wei Y. Malignant Pleural Effusion and ascites Induce Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Cancer Stem-like Cell Properties via the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)/Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase (PI3K)/Akt/Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Pathway. J Biol Chem. 2016;291:26750-26761. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 39. | Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Japanese gastric cancer treatment guidelines 2014 (ver. 4). Gastric Cancer. 2017;20:1-19. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1575] [Cited by in RCA: 1911] [Article Influence: 238.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 40. | Maeda H, Kobayashi M, Sakamoto J. Evaluation and treatment of malignant ascites secondary to gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:10936-10947. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 51] [Cited by in RCA: 56] [Article Influence: 5.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |