Published online Jul 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i21.4836
Revised: May 19, 2024
Accepted: June 7, 2024
Published online: July 26, 2024
Processing time: 72 Days and 23.4 Hours
The etiological diagnosis of intracranial hypertension is quite complicated but important in clinical practice. Some common causes are craniocerebral injury, intracranial space-occupying lesion, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and hydroce
We present a patient with melanoma which manifested with isolated intracranial hypertension without any other neurological signs. A 22-year-old male had repeated nausea and vomiting for 2 mo with Babinski sign (+) on both sides, nuchal rigidity, and subarachnoid hemorrhage. He had been diagnosed with melanoma and was given surgery and whole-brain radiation. Ultimately, the patient died 2 mo later.
Malignant melanoma should be taken into consideration in the differential dia
Core Tip: This manuscript is a case report. We report on a patient with malignant melanoma who primarily presented with intracranial hypertension. With no other symptoms except intracranial hypertension, the process of etiological diagnosis was hard and thought-provoking. Moreover, there are few melanoma cases that manifested with intracranial hypertension alone.
- Citation: Xie HT, An DH, Wu DB. Intracranial hypertension as the primary symptom of malignant melanoma: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(21): 4836-4841
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i21/4836.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i21.4836
With the morbidity lower than 9%[1], neuromelanin is rarely seen in the nervous system. Most of these are secondary and the metastatic sites of predilection are the ventricular system. From a report, the incidence of brain metastases of malignant melanoma is 8%-46% while 2 out of 3 patients are found to have brain metastasis according to autopsy results[2]. The Pia mater is often affected, and when widely affected, it is called meningeal melanomatosis. Common symptoms of meningeal melanomatosis include intracranial hypertension (IH), signs of meningeal irritation, and cranial nerve lesions[3]. However, its low morbidity, as well as the various and atypical symptoms lead to difficulty in diagnosis, a high rate of misdiagnosis and a poor prognosis[4]. 10% to 40% of melanomas may develop brain metastases in the course of the disease, with autopsy studies reporting a higher incidence (12%-73%). Approximately 6% to 11% of brain metas
This case was primarily presented with IH without any other neurological symptoms. Physical examination was notable for the Babinski sign (+) on both sides and nuchal rigidity. There was a hairy nevus on the left side of the cheek and a pigment spot on the inside left lower arm. Head magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed that the meninges were widely thickening and enhanced. In the right cerebellopontine angle area, there were small nodular abnormal signals. After the investigation, the patient was finally diagnosed with secondary meningeal melanomatosis. Having informed this patient and his family members, this case and the related images were agreed to be reported, and the article was approved by the Ethics Committee of Ethical Research under Zhujiang Hospital of Southern Medical University.
A 22-year-old man presented with repeated nausea and vomiting for 2 mo.
The head computed tomography (CT) scan done in another hospital showed subarachnoid hemorrhage while digital subtraction angiography (DSA) showed cerebral venous thrombosis.
His medical history was unremarkable.
There was no other relevant personal or family history.
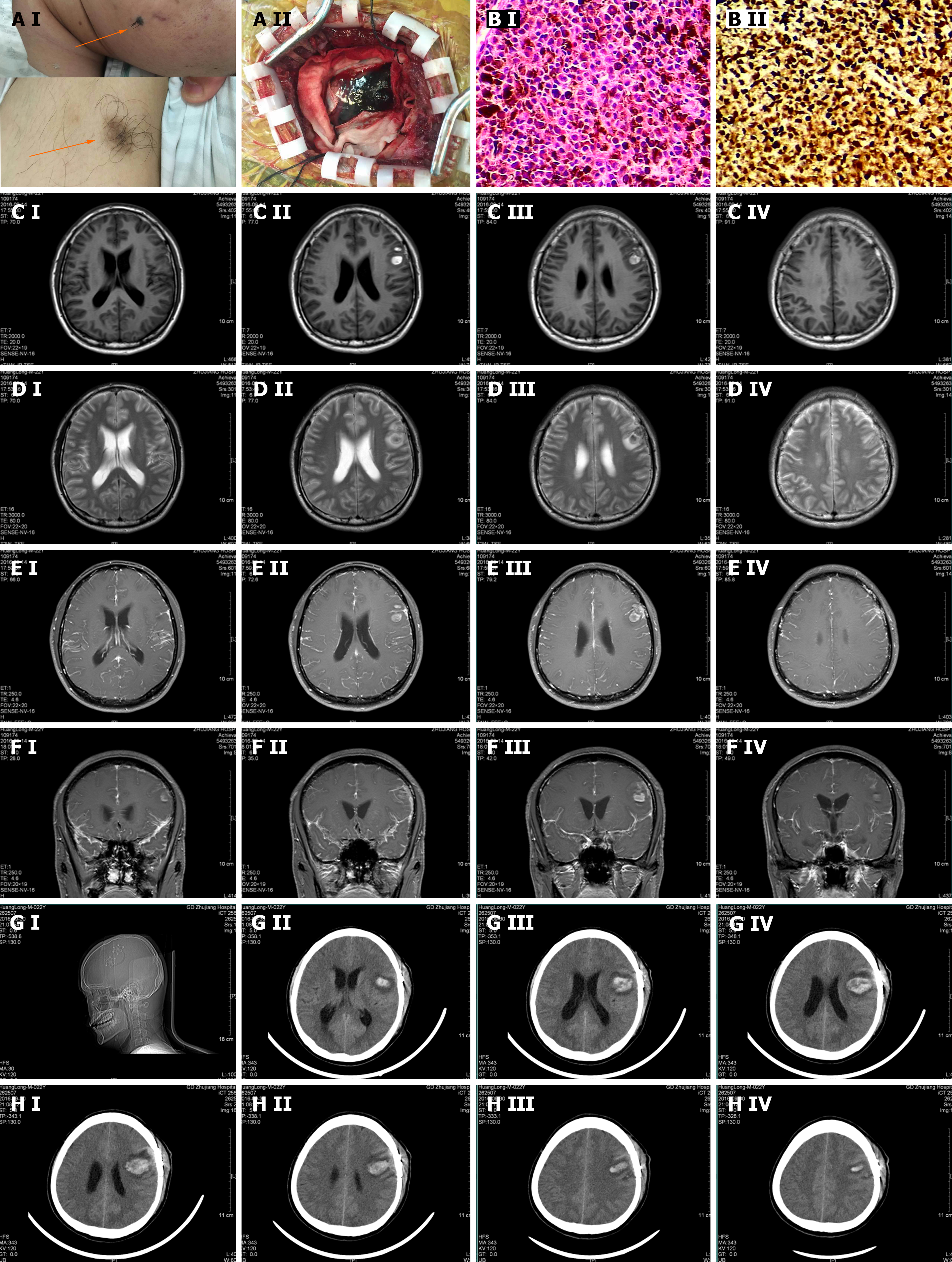
His physical examination was notable for the Babinski sign (+) on both sides and nuchal rigidity. On the left cheek, there was a hairy nevus with the size of 1.5 cm × 2.2 cm and the color was relatively dark with the edges blurred. It was as hard as a nasal tip and no ulcer was found. Meanwhile, there was a hairy pigment spot on the inside left lower arm with the size of 3.1 cm × 2.5 cm and the color was relatively light with the edges blurred, and the rigidity was the same as the former (Figure 1A).
On September 18, 2016, we performed the lumbar puncture. The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressure was over 300 mmH2O. It appeared as yellow. The routine test showed that there was no fungal spores or hypha, no bacteria, and no Cryptococcus neoformans. GXMAg (-). Biochemistry indicators were as follows: Cl 101.2 mmol/L (120-130 mmol/L), glucose 5.0 mmol/L (2.8-4.5 mmol/L), ADA 10.3I U/L (0-8 mmol/L), and protein 1423 mg/L (150-450 mmol/L). TB-DNA was lower than the detection limit. Acid Fast Stain did not find the acid-fast bacillus. Meanwhile, we sent the CSF to the laboratory in Nanfang Hospital and found the tuberculostearic acid test was negative. Therefore, intracranial tuberculosis and fungi infection were excluded. On September 20, 2016, the cytological examination showed that there were a large number of atypical cells with pigment in them. Mitoses were widely observed. It was considered a malignant melanoma (Figure 1B).
On September 14, 2016, an MRI of the head was conducted and resulted as follows: (1) Left frontal lobe hematoma, mild communicating hydrocephalus, and signal abnormalities in the white matter beside the anterior horn of lateral ventricles; (2) The meninges were widely thickening and enhanced while there was poor contrast agent filling in the superior sagittal sinus; (3) In the right cerebellopontine angle area, there were small nodular abnormal signals; and (4) Signal abnormality in the basal ganglia on both sides was considered as lacunae vasorum. We suspected intracranial tuber
Malignant melanoma.
The patient was sent to the neurosurgery department for surgical treatment. After the operation, the patient underwent whole-brain radiation.
The patient was kept in a coma and died 2 mo later. Follow-up was not applicable.
The patient could be diagnosed with malignant melanoma according to the cytological examination. Intracranial melanoma can be primary or secondary. Willis came up with 3 basic conditions to diagnose primary intracranial melanoma: (1) No melanoma was found on skin or eyeballs; (2) the patient has never gone through melanoma resection; and (3) no metastatic melanoma in internal organs[8]. Physical examination found that there was a hairy nevus on the left side of the cheek and a pigment spot on the inside left lower arm. Head MRI showed the meninges were largely thickening and enhanced. It thus should be secondary meningeal melanomatosis.
This case presented with IH. During clinical practice, the mechanism of IH is quite complicated: it can be caused by a narrow cranial cavity, enlargement of brain tissue, increase in CSF or cerebral blood flow, or an intracranial space-occupying lesion[9,10]. Various diseases can lead to IH, among which craniocerebral injury, intracranial space-occupying lesion, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and hydrocephalus are the most common.
Increased intracranial pressure can be classified into the following mechanisms: (1) Cerebral edema; (2) Space-occupying lesions; (3) Increased intracranial blood volume; (4) Increased CSF; and (5) Restricted intracranial space. The causes of elevated intracranial pressure in melanoma may include the first four mechanisms. The mechanism that leads to the IH of this patient might be as follows. Melanoma is rich in blood vessels, and they can spontaneously rupture. Meanwhile, the tumor cells have a predilection to the small blood vessels on the brain surface[11]. Therefore, hematoma and subarachnoid hemorrhage can easily occur. Subarachnoid hemorrhage and tumor cells are transferred to the subarachnoid space with CSF, which leads to the disturbance of CSF circulation and mild hydrocephalus. Both the enlargement of the brain parenchymal and the disorder of CSF circulation cause IH.
According to melanoma cases known for now that were primarily presented with neurological symptoms, the meningeal melanomatosis is often presented with nerve damage symptoms, epilepsy, psychiatric symptoms, and cognitive disorder[2]. The clinical significance of this patient is that he was simply presented with IH, which also makes it difficult to decide the reason for it. Chronic IH with an unremarkable medical history, intracranial space-occupying lesion, congenital malformation, bacterial meningitis, and intracranial tuberculosis and fungi infection thus should be first taken into consideration. Head CT and MRI are the first choices for patients with IH. The left frontal lobe hematoma and subarachnoid hemorrhage shown from the CT scan led us to think about cerebrovascular disease. However, the normal result in DSA excluded this suspect. The head MRI showed several nodules which could be a sign of intracranial tuberculosis and fungi infection. However, the negative result of the bacteriological examination excluded our guess. Because of the wide thickening and enhanced meninges with the abnormal signal nodules, we cannot dismiss intracranial tumors. At last, we verified that it was melanoma.
Melanoma brain metastases typically occur in areas with the highest blood flow, starting from the frontal lobe, while the involvement of the cerebellum, brainstem, and spinal cord is less common. Less than half of the lesions present as isolated tumors, causing corresponding neurological symptoms. Lesions smaller than 1 cm often remain asymptomatic, nonspecific complaints or neurological behavioral changes may occur. Melanoma metastases are more prone to hemorrhage (33%-50%) and seizures (25%), with the latter being the initial symptom in about 15% of cases. Diagnosing cutaneous melanoma can be highly challenging in certain patients, including those with psychiatric disorders, as these symptoms often serve as the first indicators of metastatic cancer[12]. Our patient, however, does not exhibit the early signs and symptoms mentioned earlier, such as altered mental status. It is worth noting that approximately 43% of patients with melanoma brain metastases may exhibit increased intracranial pressure, but it is typically accompanied by other neurological symptoms[13]. In addition, leptomeningeal enhancement diagnosed in the MRI, was the worst prognostic factor[14]. It may also explain the poor prognosis of our secondary melanomatosis patient.
Therefore, it is significant to consider and exclude cerebrovascular disease, intracranial infection, and tumors for the etiological diagnosis in patients with chronic IH. Meanwhile, because some tumors have no imaging manifestation, they must be emphasized enough in clinical practice.
| 1. | Tabouret E, Chinot O, Metellus P, Tallet A, Viens P, Gonçalves A. Recent trends in epidemiology of brain metastases: an overview. Anticancer Res. 2012;32:4655-4662. [PubMed] |
| 2. | Sloan AE, Nock CJ, Einstein DB. Diagnosis and treatment of melanoma brain metastasis: a literature review. Cancer Control. 2009;16:248-255. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 98] [Cited by in RCA: 117] [Article Influence: 7.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Pirini MG, Mascalchi M, Salvi F, Tassinari CA, Zanella L, Bacchini P, Bertoni F, D'Errico A, Corti B, Grigioni WF. Primary diffuse meningeal melanomatosis: radiologic-pathologic correlation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003;24:115-118. [PubMed] |
| 4. | Nicolaides P, Newton RW, Kelsey A. Primary malignant melanoma of meninges: atypical presentation of subacute meningitis. Pediatr Neurol. 1995;12:172-174. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 23] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Amer MH, Al-Sarraf M, Baker LH, Vaitkevicius VK. Malignant melanoma and central nervous system metastases: incidence, diagnosis, treatment and survival. Cancer. 1978;42:660-668. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 6. | Patel JK, Didolkar MS, Pickren JW, Moore RH. Metastatic pattern of malignant melanoma. A study of 216 autopsy cases. Am J Surg. 1978;135:807-810. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 452] [Cited by in RCA: 429] [Article Influence: 9.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Sampson JH, Carter JH Jr, Friedman AH, Seigler HF. Demographics, prognosis, and therapy in 702 patients with brain metastases from malignant melanoma. J Neurosurg. 1998;88:11-20. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 402] [Cited by in RCA: 389] [Article Influence: 14.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 8. | Ma J, Zhang Z, Li S, Chen X, Wang S. Intracranial amelanotic melanoma: a case report with literature review. World J Surg Oncol. 2015;13:182. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Friedman DI, Jacobson DM. Diagnostic criteria for idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurology. 2002;59:1492-1495. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 652] [Cited by in RCA: 726] [Article Influence: 31.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Saitoh S, Momoi MY, Gunji Y. Pseudotumor cerebri manifesting as a symptom of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Pediatr Int. 2000;42:97-99. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Clifford JR, Kirgis HD, Connolly ES. Metastatic melanoma of the brain presenting as subarachnoid hemorrhage. South Med J. 1975;68:206-208. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Avino A, Ion DE, Gheoca-Mutu DE, Abu-Baker A, Țigăran AE, Peligrad T, Hariga CS, Balcangiu-Stroescu AE, Jecan CR, Tudor A, Răducu L. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Particularities of Symptomatic Melanoma Brain Metastases from Case Report to Literature Review. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024;14. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Byun J, Park ES, Hong SH, Cho YH, Kim YH, Kim CJ, Kim JH, Lee S. Clinical outcomes of primary intracranial malignant melanoma and metastatic intracranial malignant melanoma. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2018;164:32-38. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Arai N, Kagami H, Mine Y, Ishii T, Inaba M. Primary Solitary Intracranial Malignant Melanoma: A Systematic Review of Literature. World Neurosurg. 2018;117:386-393. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |