Published online Mar 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i7.1656
Peer-review started: December 8, 2022
First decision: January 3, 2023
Revised: January 11, 2023
Accepted: February 15, 2023
Article in press: February 15, 2023
Published online: March 6, 2023
Processing time: 84 Days and 2.1 Hours
IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a chronic fibrotic disease mediated by immunity recognized by clinicians in recent years. When the kidney is involved, it is called IgG4-related kidney disease (IgG4-RKD). IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis (IgG4-TIN) is a representative manifestation of IgG4-RKD. IgG4-TIN can cause obstructive nephropathy complicated by retroperitoneal fibrosis (RPF). Cases of IgG4-TIN complicated with RPF are rare. Glucocorticoids are the first-line therapeutic medication for IgG4-RD and can significantly improve renal function.
Herein, we report the case of a 56-year-old man with IgG4-RKD complicated with RPF. The patient presented to the hospital with complaints of elevated serum creatinine (Cr), nausea, and vomiting. During hospitalization, Cr was 1448.6 µmol/L, and serum IgG4 was increased. A total abdominal computed tomo
Our case report demonstrates the clinical characteristics of IgG4-RKD complicated with RPF. Serum IgG4 is a favorable indicator for screening. Performing renal biopsy actively plays a vital role in diagnosis and treatment, even if the patient has a long course and manifests with renal insufficiency. It is remarkable to treat IgG4-RKD with glucocorticoids. Hence, early diagnosis and targeted therapy are essential for reversing renal function and improving extrarenal manifestations in patients with IgG4-RKD.
Core Tip: IgG4-related kidney disease is a rare disease with unknown etiology. The disease has various clinical manifestations because it often combines with damage to other organs, which leads to easy missed diagnosis or misdiagnosis. Presently, the diagnosis is mainly dependent on kidney biopsy, and the main treatment is glucocorticoids. Our case report demonstrates the clinical manifestations of IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis complicated with retroperitoneal fibrosis. After diagnosis by renal biopsy, the patient was treated with glucocorticoids and finally removed from dialysis with a favorable outcome.
- Citation: He PH, Liu LC, Zhou XF, Xu JJ, Hong WH, Wang LC, Liu SJ, Zeng JH. IgG4-related kidney disease complicated with retroperitoneal fibrosis: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(7): 1656-1665
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i7/1656.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i7.1656
IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a fibro-inflammatory disorder that can affect almost any organ, and it is characterized by dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates with a high percentage of IgG4-bearing plasma cells, abundant storiform fibrosis, obliterative phlebitis, and frequent tissue eosinophilia[1]. The epidemiology of IgG4-RD is poorly described, partly because of the substantial challenges in its recognition and diagnosis. Renal involvement may manifest itself as an intrinsic kidney disease (IgG4-RKD), such as IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis (IgG4-TIN), or as a consequence of ureteric obstruction from retroperitoneal fibrosis (IgG4-RPF)[2]. Case reports about IgG4-RKD or RPF are rare, while cases of IgG4-TIN complicated with RPF are even rarer.
IgG4-RKD mostly occurs in males aged approximately 65 years[3,4], and its clinical features are diverse because it often involves other organs. Increased serum creatinine (Cr), small to medium amounts of proteinuria, hyperglobulinemia (increased serum IgG and IgG4), and hypocomplementemia (decreased C3 and C4) are the main clinical manifestations of IgG4-RKD. RPF always causes obstructive nephropathy, which may lead to a dramatic deterioration of renal function. Kidney biopsy is the key method of diagnosis. The pathological characteristics of IgG4-RKD are as follows: Lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates with prominent IgG4+ plasma cells, storiform fibrosis, obliterative phlebitis, and an increased IgG4+/IgG+ plasma cell ratio[5]. Glucocorticoids are the first-line therapy for IgG4-RD[6]. It has also been reported that rituximab achieves good efficacy in the treatment of IgG4-RKD[7].
Herein, we report a case of IgG4-RKD complicated with RPF in a 56-year-old man. By reviewing the previous relevant literature, we summarize the clinical features and treatment methods and highlight the important information that may be overlooked by clinicians during the process of diagnosis and treatment.
A 56-year-old Chinese man was admitted to the hospital with symptoms of high Cr for more than 9 mo as well as nausea and vomiting for 2 mo.
The patient had serum Cr 126 µmol/L in another hospital 9 mo prior with no symptoms. He had nausea and vomiting 2 mo prior to admission. In the outpatient department, laboratory data showed Cr 1448.6 µmol/L, uric acid (UA) 653.2 µmol/L, and serum potassium (K) 5.2 mmol/L. The blood test showed hemoglobin (Hb) 95 g/L. The patient was admitted to the hospital on March 24, 2021.
The patient was diagnosed with left lower extremity deep venous thrombosis and inguinal lymphadenopathy due to left lower limb edema at the Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University in 2019. The specific process of diagnosis and treatment is unknown. In the same year, he was treated by thyroidectomy and recovered well. The patient denied hypertension, diabetes, and coronary heart disease.
The patient denied any family history of kidney disease or malignant tumors.
On physical examination, the vital signs were as follows: Body temperature, 36.2°C; blood pressure, 155/112 mmHg; heart rate, 78 beats per min; and respiratory rate, 20 breaths per min. Furthermore, the patient developed symptoms of mild pitting edema in the left lower extremity. The rest of the physical examination was unremarkable.
On admission, laboratory data showed Cr 1448.6 µmol/L. Additionally, relevant urine tests showed urinary microalbumin (U-ALB) 59.6 mg/L and urinary β2-microglobulin (β2-MG) 10.30 mg/L, and the 24 h urine protein quantification was 1400.64 mg/24 h. The map of urine protein electrophoresis did not detect monoclonal protein. There were multiple protein components indicating mixed albuminuria. At the same time, the albumin level decreased to 35.8 g/L. Immunological indicators were as follows: C3 0.40 g/L, C4 0.07 g/L, IgG 22.42 g/L, and IgG4 2.9971 g/L. The result of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA) was the perinuclear type (p-ANCA), which was sensitive to formaldehyde. Antinuclear antibody test results were positive with a ratio of 1:320. The blood test showed hemoglobin (Hb) 95 g/L and serum ferritin 972.7 ng/mL. C-response protein was 7 mg/L. There were no markedly abnormal findings in the routine test of feces, procalcitonin, blood coagulation parameters, thyroid function, rheumatism indicators, nodular vasculitis indicators, M-type phospholipase A2 receptor, serum immunofixation electrophoresis, serum anti-mycobacterium tuberculosis antibody, blood lipid, blood glucose, or tumor markers.
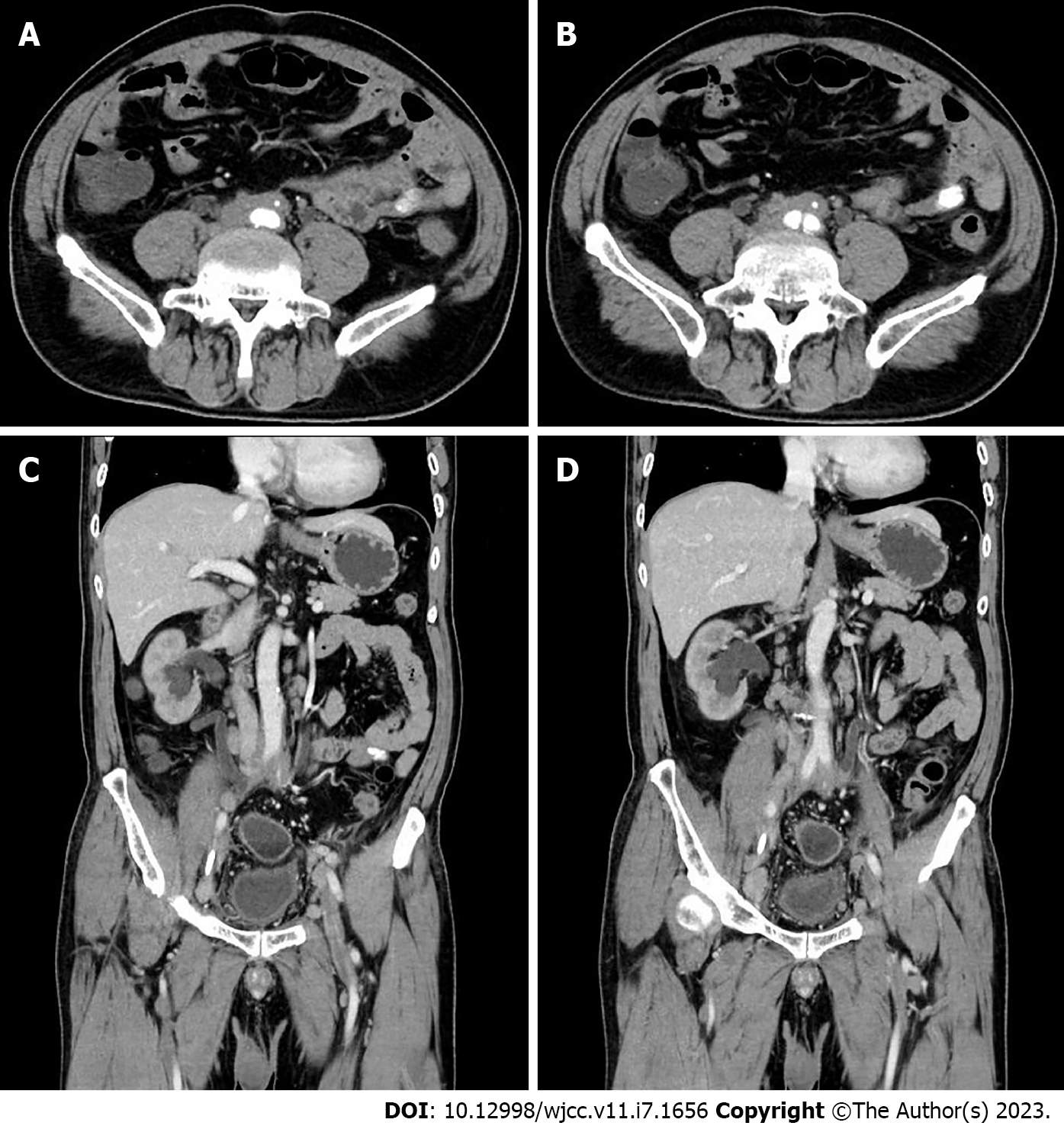
Renal ultrasound showed that hydronephrosis was aggravated to a moderate grade and that both renal parenchyma became slightly thinner with echo thickening and decreasing blood flow. The abdominal aortic ultrasound indicated the following observations: The abdominal aorta was mildly sclerosed; the intima of the iliac artery was unevenly thickened; and the intima of the inferior mesenteric artery was diffusely thickened with luminal stenosis. Combined with the medical history and perivascular and interstitial pathological changes, a total abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan and enhanced CT scan obviously indicated RPF as shown in Figure 1. At the same time, there was no obvious abnormal density shadow in the parenchyma of either kidney on CT, while the enhanced CT scan showed that the parenchymal enhancement in both kidneys was weakened. Moreover, we observed that the middle part of the ureter was narrowed. Consequently, the upper section of the bilateral ureters was dilated, and there was mild hydronephrosis of both kidneys.
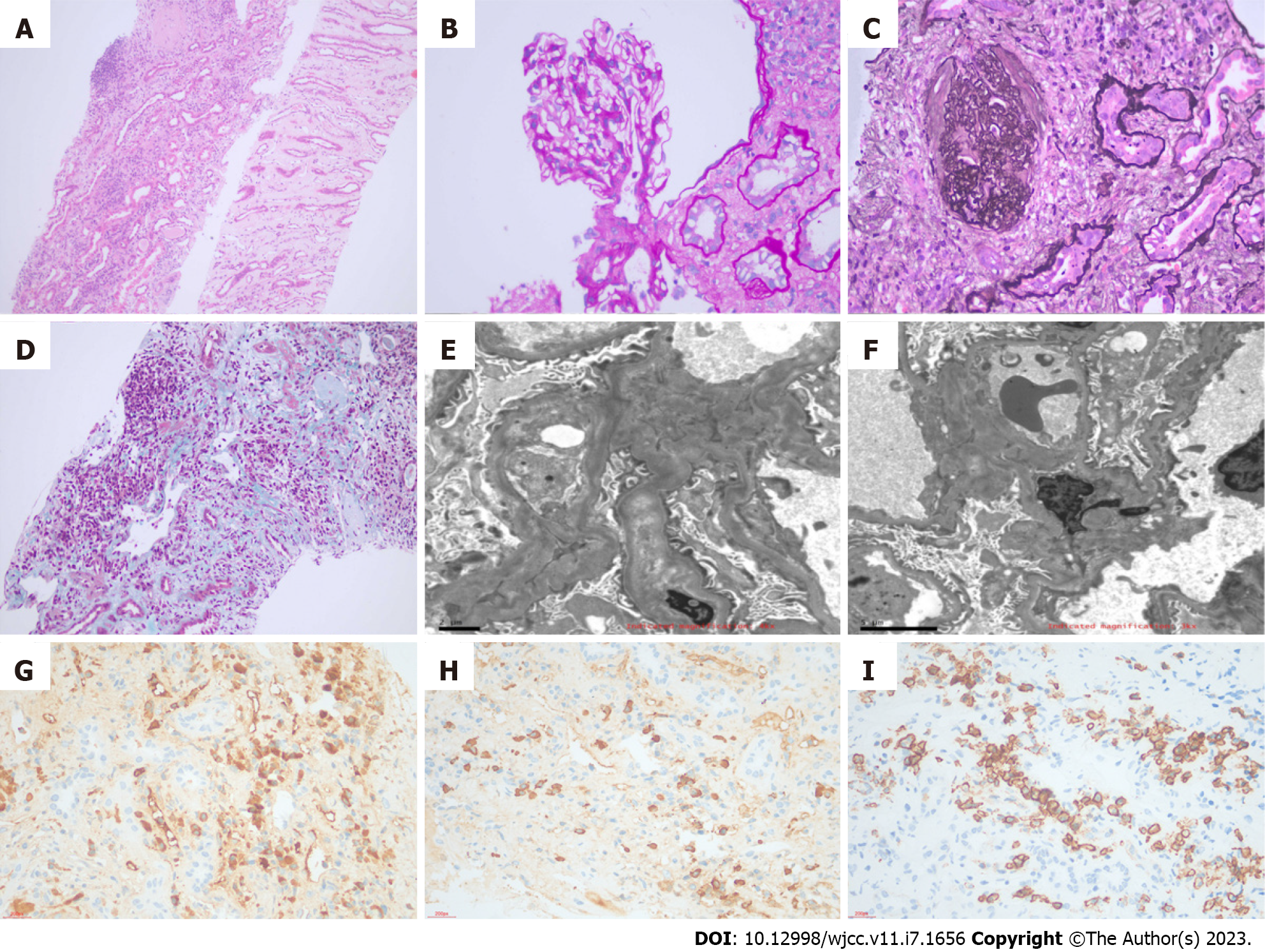
Renal biopsy was performed during the patient's hospitalization. We drew specimen materials from three different levels of the kidney, and the first tissue slice had the largest number of glomeruli. One out of three glomeruli showed global sclerosis. There was no segmental glomerular sclerosis, basement membrane thickening, parietal cell hyperplasia, double-track sign, or crescent formation. The renal tubular epithelial cells showed vacuolar degeneration and proteinaceous casts. Part of the renal tubules showed dilating lumen and epithelial cell detachment with the brush border disappearing. These renal tubules also exhibited focal atrophy with an area of approximately 10%. The renal tubulointerstitial area showed focal plasma cell infiltration and increased lymphocyte infiltration accompanied by fibrosis. The intima of the arterioles was slightly thickened, and the lumen was narrowed. Under immunofluorescence, no glomeruli were observed. It was visible under paraffin fluorescence that IgG, IgA, IgM, C3, C1q, Kappa, Lambda, Fib, and Aib were negative. After combining the biopsy results with immunohistochemistry, it was found that the absolute number of positive IgG4+ cells per high power field exceeded 10, and the ratio of IgG4/IgG was over 40%. CD38 in some cells was positive, and CD138 in some epithelial cells of the renal tubules was also positive. By electron microscopy with toluidine blue staining, we were able to catch one glomerulus. No exact electron-dense granules were deposited in the mesangial area or under the endothelium (Figure 2). The pathological diagnosis was IgG4-TIN. In addition, the patient tested positive for ANCA, while there was no necrosis or crescent formation in the renal biopsy, which supported the diagnosis of ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis.
Combined with the patient’s medical history, laboratory and imaging examinations, and kidney biopsy, the final diagnosis was IgG4-RKD complicated with RPF.
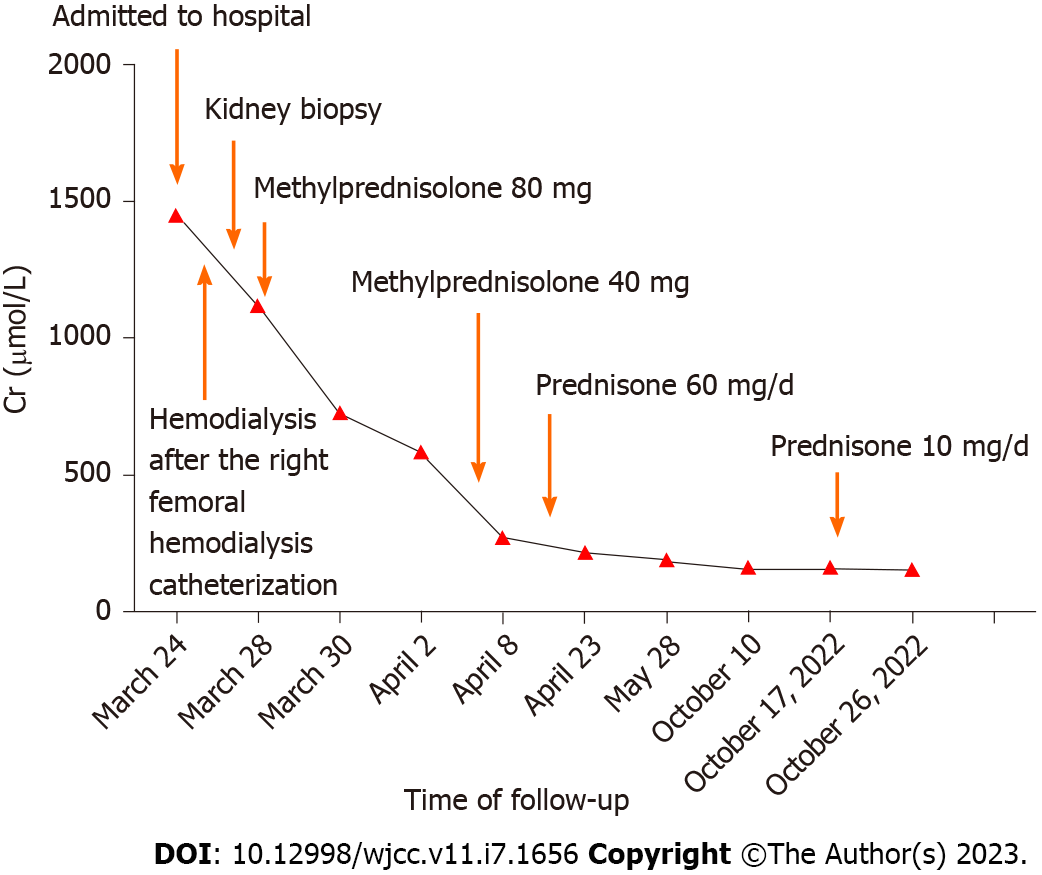
Before collecting the kidney biopsy report, the patient received hemodialysis after a catheter was inserted into the right femoral vein on March 25. As the kidney biopsy confirmed that the patient had IgG4-RKD on March 26, he was treated with 80 mg of methylprednisolone starting on March 28. The patient received hemodialysis for 4 d. On April 4, his Cr level decreased from 1148.6 µmol/L during hospitalization to 432.2 µmol/L. On April 5, we adjusted the dose of methylprednisolone to 40 mg. Before leaving the hospital, Cr was retested as 265.9 µmol/L, and the patient continued to receive a prednisone dosage of 60 mg/d for treatment. The patient started reducing prednisone by 5 mg every 2 wk after receiving adequate glucocorticoids therapy for approximately 3 wk, and the dosage was then maintained at 10 mg/d (Figure 3).
After 6 mo of follow-up, the patient had no obvious symptoms. The Cr level was 156 µmol/L, and the serum IgG4 level was 0.5385 g/L, which were both significantly lower than before. At the same time, the RPF was reduced compared to before, and no water expansion was observed in the bilateral urinary on full abdominal CT. After a follow-up of 19 mo, the patient’s Cr level was 154.9 µmol/L at his visit on November 26, 2022 (Figure 3).
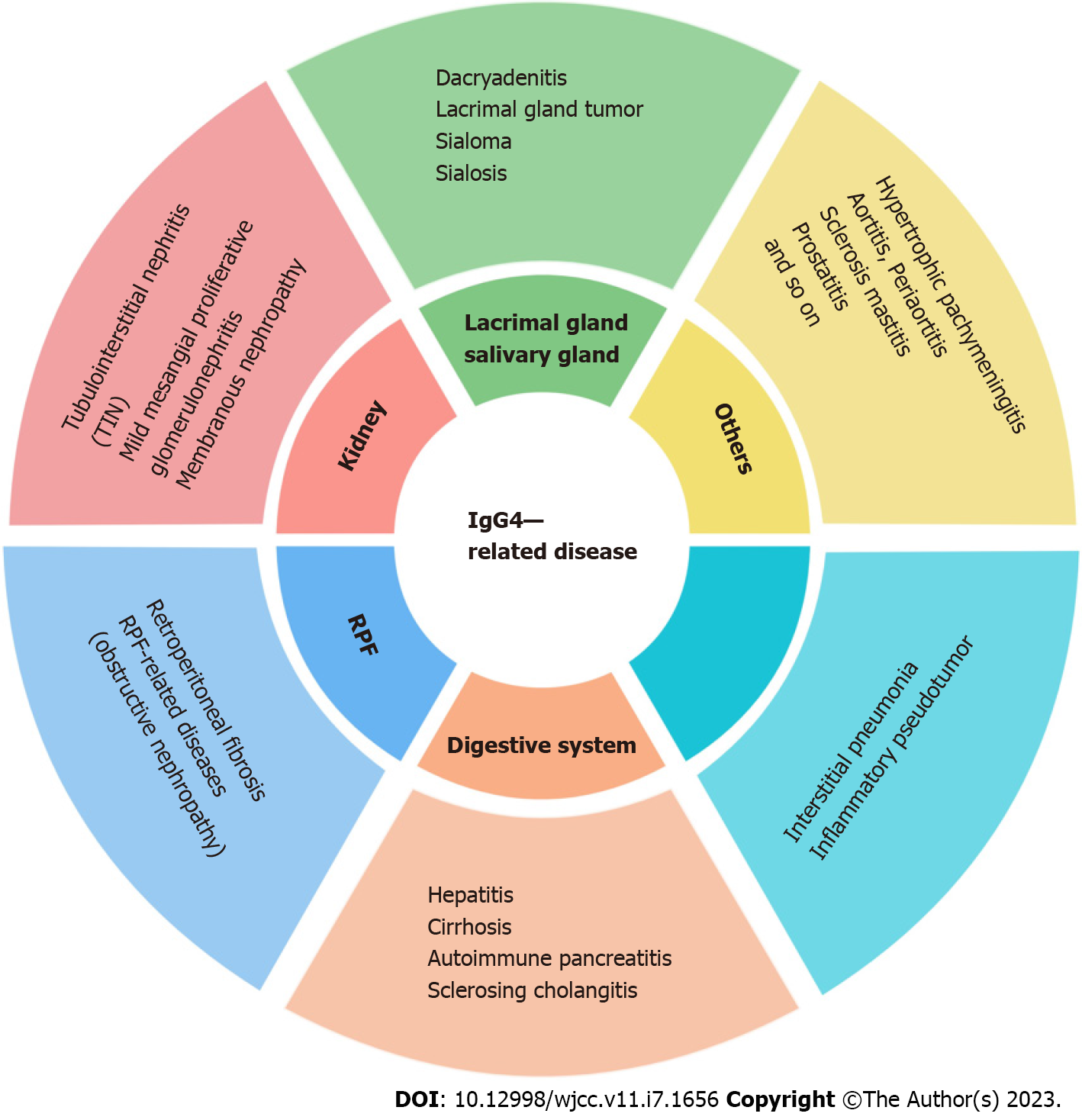
IgG4-RD is a chronic fibrotic disease mediated by immunity. At present, it is considered that immunologic derangement and infection act as risk factors that activate a large number of lymphocytes to participate in the immune response. Lymphocytes release cytokines, such as interleukin (IL)-4, IL-5, IL-10, IL-13, and transforming growth factor β (TGF-β), leading to eosinophilia and elevated serum IgG4 and IgE, which ultimately cause characteristic fibrosis of IgG4-RD. Cases can be traced back to autoimmune pancreatitis proposed in 1995 by Yoshida et al[8], which was officially named in 2010[5]. Middle-aged and elderly individuals are prone to IgG4-RD, and males account for the majority of cases[9,10]. The clinical spectrum of IgG4-RD is extensive and includes a variety of diseases (Figure 4). It often involves two or more organs, with only a few occurring in a single system, and has a series of common and specific pathological, serological, and clinical features. The kidney is one of the most frequently affected organs in IgG4-RD. The proportion of IgG4-RKD in IgG4-RD has been reported as 7.0%-24.6% abroad[11,12]. IgG4-TIN is the representative presentation of IgG4-RKD. The renal pathological feature is lymphoplasmacytic infiltration dominated by IgG4+ plasma cells in the renal interstitium, which is often accompanied by different degrees of fibrosis. The main clinical manifestations of IgG4-TIN are small to medium amounts of proteinuria combined with renal impairment, and some patients can develop end-stage renal failure. In addition, IgG4-RKD can involve the renal tubulointerstitium and cause ureteral obstruction by RPF. A previous study has reported that IgG4-RKD combined with IgG4-RPF accounts for 2.6%[12].
There are no globally consistent diagnostic criteria for IgG4-RKD. Most clinicians refer to the IgG4-RD international classification standards set by the American Society of Nephrology[13] and the Japanese Society of Nephrology[3]. Both standards propose that numerous IgG4+ plasma cells infiltrated in the renal tissue are the renal pathological characteristic of IgG4-RKD. Japanese scholars have further proposed three additional complex classifications. Khosroshahi et al[6] came up with a consensus for the management and treatment of IgG4-RD. Clear diagnosis is recommended by tissue biopsy to exclude malignancy and other diseases similar to IgG4-RD. This further emphasizes the importance of renal biopsy. In 2019, the American Society of Rheumatology and the European Union of Rheumatology Societies jointly approved the following classification steps for IgG4-RD[14]: (1) At least 1 of the 11 organs with possible onset is included in the evaluation; (2) unrelated variables are removed by the exclusion criteria, and a group of values with clinical, serological, radiological, and pathological findings are obtained and weighted to achieve accurate classification and differentiation from malignant tumors, granulomatous disease, and vasculitis, providing a basis for individualized treatment; and (3) through a comprehensive analysis of clinical characteristics, laboratory examination, and imaging and histopathological data, the classification of IgG4-RD can be clarified to promote the precise treatment of the disease. The new diagnostic criteria include specific clinical manifestations of organs that are commonly involved. The advantage is that it is possible to diagnose IgG4-RD even in the absence of pathology or when serum IgG4 is not elevated. Therefore, the diagnosis of IgG4-RKD relies on clinical presentation, serum IgG4 levels, imaging examination, and kidney pathology. In addition, clinically, IgG4-RKD should be differentiated from renal infarction, ANCA-associated vasculitis, sarcoidosis, lymphoma, kidney cancer, and other diseases; otherwise, it is easy to misdiagnose and miss diagnoses. At the same time, clinicians need to note that although a high level of serum IgG4 is largely supportive of IgG4-RD, it cannot be used as the key criterion for diagnosis.
The reported patient was a middle-aged man. The clinical characteristics of this patient were as follows: Nausea and vomiting; markedly increased Cr; small amount of proteinuria; hyperglobulinemia (increased serum IgG and IgG4); hypocomplementemia (decreased C3 and C4); vascular lesion; ureterostenosis; hydronephrosis; and RPF. RPF is a kind of rare connective tissue disease that has the pathological features of chronic nonspecific inflammation of retroperitoneal tissue and fibrosis. The abdominal aorta, iliac artery, and inferior vena cava are wrapped by the fibroinflammatory mass, which is abnormal hyperplasia. It also involves the adjacent ureter, causing ureteral obstruction and hydronephrosis. The most prevalent age for RPF is 40-60 years, and males constitute the majority of patients. RPF can be divided into two categories as follows: One is idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis (iRPF), and the other is secondary retroperitoneal fibrosis (sRPF), which is associated with malignant tumors (such as lymphoma and multiple myeloma) and infectious diseases (such as tuberculosis and schistosomiasis). More than 50% of iRPF cases are IgG4-RD. The diagnosis of RPF in this patient was determined by the clinical manifestations and the results of the total abdominal CT scan. At his initial presentation, the patient had elevated serum creatinine, proteinuria, ureteral stenosis, and hydro
Moreover, this patient was simultaneously serologically positive for p-ANCA, but there was no necrosis or crescent formation in the renal biopsy, which supported the diagnosis of ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis. The patient also had no systemic vascular-related clinical manifestations. Previous cases have reported positive myeloperoxidase (MPO) in patients with a concurrent presentation of IgG4-TIN and ANCA MPO crescentic glomerulonephritis[15,16]. Vasculitis indicators (including MPO) were normal in our case. Therefore, ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis and IgG4-associated nephropathy overlap syndrome were not considered.
The treatment of IgG4-TIN and iRPF is in accordance with the treatment of IgG4-RD. In 2015, the international consensus on IgG4-RD treatment noted that glucocorticoids are the first-line therapy for IgG4-RD[6]. The guidelines recommend that the initial dosage of prednisone should be 30-40 mg/d or 0.6 mg/kg/d and be gradually reduced after 2-4 wk by 5-10 mg every 1-2 wk until reaching a dosage of 20 mg/d. Then, the decrement rate should be determined according to the clinical response or experimental and imaging examinations, and the dosage can be reduced by 5 mg every 2 wk. Maintenance doses of glucocorticoids are commonly recommended for 1-3 years. Immunosuppressants, such as thiourea or rituximab, are recommended in patients with poor effects with glucocorticoids alone. Because the body responds differently to glucocorticoids, individualized treatment strategies should be developed based on the clinical presentation and follow-up outcomes[17]. During treatment, serum IgG4, IgE, eosinophilic granulocytes, C3, C4, and other indicators should be closely monitored.
In this case, the patient was hospitalized with high Cr, and according to the GFR, the patient had reached the dialysis index. Before diagnosis, the patient underwent hemodialysis. By combining the kidney biopsy pathology with the experimental and imaging examination results, a definite diagnosis of IgG4-RKD complicated with RPF was made. Considering that there were no contraindications for glucocorticoid treatment, meanwhile although the patient weighed 60 kg approximately, due to his serious condition and multiple organ injuries, the patient was treated with enough glucocorticoids at 60 mg/d as initial dosage, and the dosage was gradually reduced as renal function getting better and finally maintained at 10 mg/d. This helped the patient be removed from dialysis before leaving the hospital. After a follow-up of 19 mo, the patient’s Cr decreased from 1148.6 µmol/L during hospitalization to 154.9 µmol/L at his visit on November 26, 2022. The performance of RPF also improved, which demonstrated that the patient’s RPF was IgG-RD, even without a tissue biopsy of the retroperitoneum, which also indicates that the condition was controlled with glucocorticoid therapy.
The patient was found to have increased Cr (126 µmol/L) in an external hospital before admission. If clinicians could pay attention to the condition of the patient at that time and perform renal biopsy in a timely manner to make a clear diagnosis, the patient's renal function may not deteriorate, and the prognosis would be better. This also reminds the clinical workers to consider IgG4-RKD when middle- and old-aged males have the following manifestations: Increased Cr, small amount of proteinuria, hyperglobulinemia (increased serum IgG and IgG4), hypocomplementemia (decreased C3 and C4), and RPF. Even when the patient has renal insufficiency and chronic kidney changes, kidney biopsy should be actively performed to make a clear diagnosis in case of missed diagnosis and delayed treatment. Early and fast treatment can avoid long-term consequences and progression to end-stage disease. In addition, there is a certain relationship between treatment being combined with traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and the patient being in a stable condition during glucocorticoid reduction and maintenance treatment. However, the specific role of TCM during glucocorticoid treatment needs further study.
Our case report demonstrates the clinical characteristics of IgG4-RKD complicated with RPF. By reviewing the case, there are several highlights as follows: (1) We made a diagnosis by comprehensively combining the patient's symptoms, signs, and laboratory and imaging examination results; (2) the diagnosis of RPF was dependent on abdominal CT. Although serological testing of IgG4 is a favorable screening indicator, the gold standard for the diagnosis of IgG4-RD is pathology; (3) the first-line treatment drug, glucocorticoids, helped the patient avoid or get rid of dialysis and showed good follow-up efficacy. Treatment with glucocorticoids was of great significance to improve the quality of life of the patient; and (4) this case reminds clinical workers that even if the patient has a long course and kidney failure, renal biopsy can be performed to make a definite diagnosis. In this case, if the patient had maintained dialysis for treatment without performing a kidney biopsy, he may have lost the chance of reverse renal failure. Hence, early diagnosis and targeted therapy are essential for reversing renal function and improving extrarenal manifestations in patients with IgG4-RKD. This case is rare. Long-term follow-up can help us to understand the outcome and prognostic impact of the disease.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Urology and nephrology
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): D
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Ferreira GSA, Brazil; Mizushima I, Japan S-Editor: Liu JH L-Editor: Wang TQ P-Editor: Liu JH
| 1. | Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:539-551. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1856] [Cited by in RCA: 1863] [Article Influence: 143.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (83)] |
| 2. | Boffa JJ, Esteve E, Buob D. Renal involvement in IgG4-related disease. Presse Med. 2020;49:104017. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Raissian Y, Nasr SH, Larsen CP, Colvin RB, Smyrk TC, Takahashi N, Bhalodia A, Sohani AR, Zhang L, Chari S, Sethi S, Fidler ME, Cornell LD. Diagnosis of IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;22:1343-1352. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 250] [Cited by in RCA: 233] [Article Influence: 16.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Nakashima H, Kawano M, Saeki T, Ubara Y, Hisano S, Nagata M, Zen Y, Yanagita M, Yamaguchi Y, Nishi S, Saito T. Estimation of the number of histological diagnosis for IgG4-related kidney disease referred to the data obtained from the Japan Renal Biopsy Registry (J-RBR) questionnaire and cases reported in the Japanese Society of Nephrology Meetings. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2017;21:97-103. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Takahashi H, Yamamoto M, Suzuki C, Naishiro Y, Shinomura Y, Imai K. The birthday of a new syndrome: IgG4-related diseases constitute a clinical entity. Autoimmun Rev. 2010;9:591-594. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 108] [Cited by in RCA: 113] [Article Influence: 7.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Khosroshahi A, Wallace ZS, Crowe JL, Akamizu T, Azumi A, Carruthers MN, Chari ST, Della-Torre E, Frulloni L, Goto H, Hart PA, Kamisawa T, Kawa S, Kawano M, Kim MH, Kodama Y, Kubota K, Lerch MM, Löhr M, Masaki Y, Matsui S, Mimori T, Nakamura S, Nakazawa T, Ohara H, Okazaki K, Ryu JH, Saeki T, Schleinitz N, Shimatsu A, Shimosegawa T, Takahashi H, Takahira M, Tanaka A, Topazian M, Umehara H, Webster GJ, Witzig TE, Yamamoto M, Zhang W, Chiba T, Stone JH; Second International Symposium on IgG4-Related Disease. International Consensus Guidance Statement on the Management and Treatment of IgG4-Related Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67:1688-1699. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 573] [Cited by in RCA: 672] [Article Influence: 67.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Quattrocchio G, Barreca A, Demarchi A, Solfietti L, Beltrame G, Fenoglio R, Ferro M, Mesiano P, Murgia S, Del Vecchio G, Massara C, Rollino C, Roccatello D. IgG4-related kidney disease: the effects of a Rituximab-based immunosuppressive therapy. Oncotarget. 2018;9:21337-21347. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Yoshida K, Toki F, Takeuchi T, Watanabe S, Shiratori K, Hayashi N. Chronic pancreatitis caused by an autoimmune abnormality. Proposal of the concept of autoimmune pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1995;40:1561-1568. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1044] [Cited by in RCA: 924] [Article Influence: 30.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Inoue D, Yoshida K, Yoneda N, Ozaki K, Matsubara T, Nagai K, Okumura K, Toshima F, Toyama J, Minami T, Matsui O, Gabata T, Zen Y. IgG4-related disease: dataset of 235 consecutive patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94:e680. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 284] [Cited by in RCA: 319] [Article Influence: 31.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Wallace ZS, Deshpande V, Mattoo H, Mahajan VS, Kulikova M, Pillai S, Stone JH. IgG4-Related Disease: Clinical and Laboratory Features in One Hundred Twenty-Five Patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67:2466-2475. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 355] [Cited by in RCA: 457] [Article Influence: 45.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Kawano M, Saeki T, Nakashima H. IgG4-related kidney disease and retroperitoneal fibrosis: An update. Mod Rheumatol. 2019;29:231-239. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 3.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Evans RDR, Cargill T, Goodchild G, Oliveira B, Rodriguez-Justo M, Pepper R, Connolly J, Salama A, Webster G, Barnes E, Culver EL. Clinical Manifestations and Long-term Outcomes of IgG4-Related Kidney and Retroperitoneal Involvement in a United Kingdom IgG4-Related Disease Cohort. Kidney Int Rep. 2019;4:48-58. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 32] [Article Influence: 5.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Kawano M, Saeki T, Nakashima H, Nishi S, Yamaguchi Y, Hisano S, Yamanaka N, Inoue D, Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Nomura H, Taguchi T, Umehara H, Makino H, Saito T. Proposal for diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2011;15:615-626. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 284] [Cited by in RCA: 289] [Article Influence: 20.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Wallace ZS, Naden RP, Chari S, Choi HK, Della-Torre E, Dicaire JF, Hart PA, Inoue D, Kawano M, Khosroshahi A, Lanzillotta M, Okazaki K, Perugino CA, Sharma A, Saeki T, Schleinitz N, Takahashi N, Umehara H, Zen Y, Stone JH; Members of the ACR/EULAR IgG4-RD Classification Criteria Working Group. The 2019 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for IgG4-related disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79:77-87. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 431] [Cited by in RCA: 386] [Article Influence: 77.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 15. | Wu HHL, Wang CCY, Woywodt A, Ponnusamy A. Concurrent presentation of IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis and ANCA MPO crescentic glomerulonephritis. Clin Nephrol Case Stud. 2022;10:47-53. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Faz-Muñoz D, Hinojosa-Azaola A, Mejía-Vilet JM, Uribe-Uribe NO, Rull-Gabayet M, Muñoz-Castañeda WR, Vargas-Parra NJ, Martín-Nares E. ANCA-associated vasculitis and IgG4-related disease overlap syndrome: a case report and literature review. Immunol Res. 2022;70:550-559. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Wallace ZS, Zhang Y, Perugino CA, Naden R, Choi HK, Stone JH; ACR/EULAR IgG4-RD Classification Criteria Committee. Clinical phenotypes of IgG4-related disease: an analysis of two international cross-sectional cohorts. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:406-412. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 280] [Cited by in RCA: 260] [Article Influence: 43.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |