Published online Jun 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i16.3664
Peer-review started: December 27, 2022
First decision: March 24, 2023
Revised: March 29, 2023
Accepted: April 27, 2023
Article in press: April 27, 2023
Published online: June 6, 2023
Processing time: 156 Days and 23.1 Hours
Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease, a rare form of necrotizing lymphadenitis, is an uncommon, benign, self-limiting disorder of obscure etiology. It affects mostly young adults of both genders. Clinically, it presents with fever and lymphadenopathy of a firm to rubbery consistency frequently involving cervical lymph nodes while weight loss, splenomegaly, leucopenia, and elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate feature in severely affected patients. Cutaneous involvement occurs in about 30%-40% of cases as facial erythema and nonspecific erythe
Core Tip: Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease or Kikuchi disease described originally in young Japanese women is a rare benign cause of fever and lymphadenopathy usually involving cervical lymph nodes. The disease has been reported worldwide in both genders across ethnic and age groups. Histopathologically, histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis is characteristic and needs differentiation from more serious conditions such as malignant lymphoma in acute or subacute form. Its long-term prognosis is favorable albeit long-term follow-up is recommended because of a rare but increased risk of developing systemic lupus erythematosus/other autoimmune disorders. Patients with a severe or recurrent disease need treatment with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, systemic corticosteroids, and/or other immunomodulators.
- Citation: Mahajan VK, Sharma V, Sharma N, Rani R. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: A comprehensive review. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(16): 3664-3679
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i16/3664.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i16.3664
Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease (KFD; syn: Kikuchi’s disease, histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis), a rare self-limiting disorder of uncertain etiology, presents with prolonged lymphadenopathy with or without systemic features. The exact role of microbial infection and other non-infectious triggers in its etiopathogenesis remains obscure. Most patients present with firm to rubbery cervical lymphadenopathy and intermittent fever while weight loss, splenomegaly, leucopenia, and elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate occur in severely affected patients. Cutaneous involvement occurs in about 30% to 40% of cases[1,2]. Its diagnosis is mainly retrospective from characteristic histopathology of a diseased lymph node whereas treatment mostly remains empirical. Interestingly, both KFD and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) share a complex and as-yet unelucidated relationship as SLE may occasionally precede, develop subsequently, or sometimes be associated concurrently with KFD[3]. KFD is a clinical entity often misdiagnosed as malignant lymphoma in acute or subacute form or missed altogether owing to its rarity, similarity to other common conditions, and lack of awareness among clinicians. Herein we revisit the clinicoepidemiological, diagnostic, and management aspects of KFD from the perspective of practicing clinicians.
Kikuchi[4] and Fujimoto et al[5] in the year 1972 independently described two separate cases from Japan one presenting with ‘lymphadenitis showing focal reticulum cell hyperplasia, nuclear debris, and phagocytosis’ and another having ‘subacute necrotizing cervical lymphadenitis’, hence the nomen
The clinicopathologic features of KFD favor a T-cell and histiocytes-mediated immune response to an infectious or a non-infectious trigger. Increased levels of IFN-α and its stimulators including 2',5'-oligoadenylate synthetase, and tubuloreticular structures in the cytoplasm of stimulated lymphocytes, histiocytes, and vascular endothelium favor a viral etiology whereas a favorable therapeutic response to minocycline, ciprofloxacin, and ofloxacin in few studies suggest a pathogenic role of other non-viral microorganisms sensitive to these antimicrobial agents[8,22-25]. Nonetheless, several microbial agents including Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), human herpesvirus (HHV) 6 and 8, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), parvovirus B19, paramyxoviruses, parainfluenza virus, Yersinia enterocolitica, and Toxoplasma, Streptococcus pneumoniae have been implicated as inciting factors[26-31]. Although EBV had been the most observed trigger, immunohistochemistry detected EBV-encoded protein in only one of the 10 patients showing EBV by in-situ hybridization[23,26,27,30]. A minivirus resembling circovirus, the causative agent for swine necrotizing lymphadenitis, too has been isolated in three Korean patients[32].Although the exact relationship remains obscure, a postviral hyperimmune reaction too is a potential trigger for KFD[33,34]. B-cell lymphoma, rupture of silicone breast implant, infections due to cat-scratch disease, and Mycobacterium szulgai are other proposed triggers for KFD[8,35,36].
KFD has been infrequently reported following vaccination for influenza, Japanese encephalitis, and HPV[37,38]. Recently, KFD has been linked to coronavirus disease 2019 infection and SARS CoV2 vaccination[39-48]. However, whether the association is causal or epiphenomenon remains uncertain as most patients recovered rapidly and completely. One of the two patients developed KFD disease 10 d after vaccination while hemophagocytic reticulosis complicated KFD after the vaccination in another[45,46].
It has been suggested that KFD most likely develops due to an autoimmune mechanism disease as cases had reportedly developed clinicopathological features similar to Sjögren’s syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus/mixed connective tissue disease[49,50]. Since KFD shares age and gender predisposition as well as histologic features with SLE, it has been also proposed that KFD perhaps represents a self-limiting SLE-like autoimmune disorder caused by virus-infected transformed lymphocytes[51]. The hypothesis of autoimmune pathogenesis is further supported by an association of KFD with an increased risk of its evolution into an autoimmune syndrome, particularly in females or the concurrent presence of other autoimmune disorders such as Hashimoto thyroiditis, primary Sjögren’s syndrome, antiphospholipid syndrome, and leukocytoclastic vasculitis as observed in 53% of thirteen women in a follow-up study of twenty patients with KFD[52-55].
The reports implicating allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and bariatric surgery for triggering KFD remain anecdotal[56,57].
No genetic transmission or inheritance of a definite pattern has been identified despite being reported uncommonly to affect twins and even human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-identical non-twin siblings[58-61]. Some of these familial cases were from the common living environment and developed symptoms almost simultaneously and demonstrated serological evidence for the same infection. However, one of the two HLA-identical sisters but not twins from Saudi Arabia developed KFD after a gap of 10 years with no identifiable infectious trigger[58,59]. Stasiuket al[58] reported a similar case of two Aboriginal sisters from northern Ontario reflecting a genetic predisposition among affected individuals. KFD and HLA class 2 alleles have been linked suggesting a possible positive relationship between DPA1*01 and DPB1*0202 alleles which are much more frequent in Japan than in Europe and the United States[62]. This perhaps accounts for a higher prevalence of KFD in the Asian population.
Up-regulation of cell-cycle-associated genes and apoptosis-associated genes including caspase, and down-regulation of apoptosis-inhibitory genes such as BCL2 too have been observed in KFD-associated lymph nodes and not in nonspecific lymphadenitis[63]. The apoptotic cell death induced by the Fas-Fas ligand system mediated by cytotoxic CD8+ cells is the principal mechanism of cellular destruction in KFD[64-66]. The apoptosis is enhanced by histiocytes as evident from the morphology of apoptotic cells on transmission electron microscopy characterized by nuclear chromatin condensation, fragmentation along the nuclear membrane with intact organelles, and histiocytes phagocytosing karyorrhectic debris (apoptotic bodies). To summarise, primarily the activation of T lymphocytes and histiocytes occurs and the activated T cells enter the apoptotic cycle manifesting with areas of necrosis in lymph nodes, and the cellular debris is then cleaned up by the histiocytes. Also the cytokine and chemokine pathways of interferon (IFN)-γ, interleukin (IL)-18, MIG, and IFN-γ-induced protein 10 have been suggested to play a significant role in the apoptosis associated with KFD[67]. The serum levels of IFN-γ and IL-6 were elevated but not of IFN-α, tumor necrosis factor (TNF), or IL-2 in these patients during the acute phase of illness which returned to normal during convalescence[68,69]. This further reinforces the possible role of IFN-γ and IL-6 in the pathogenesis of KFD. In general, the shared and common HLA and cytokines involved in the molecular pathogenesis of this disease suggests that like other HLA-linked disorders, KFD is a two-step disease requiring a predisposing HLA and a secondary trigger such as an infection in individuals with a genetic predisposition for the exuberant T-cell mediated immune/inflammatory response[70]. However, the exact molecular pathogenesis of KFD remains complex and needs further elucidation.
KFD usually manifests as an acute or subacute illness with fever and painful posterior cervical lymphadenopathy generally in a previously well individual and evolving over 2-3 wk[71]. Lymph nodes of firm to rubbery consistency are usually small ranging from 0.5 to 4 cm in size[18,70,72]. The most common signs and symptoms were lymphadenopathy (100%), fever (35%), erythematous rash (10%), arthritis (7%), fatigue, (7%), and hepatosplenomegaly in 3% of patients in a series of 244 individuals with KFD[73]. The association of splenomegaly too has been reported as an uncommon feature of KFD[74]. Typically, the fever is of low grade and intermittent which persists for about one week, rarely lasting for up to one month (median duration 9 d), and is a primary symptom in 30%-50% of patients[6]. Patients with higher fever (≥ 39.0 °C), larger lymph nodes, and leucopenia can have a more prolonged clinical course[75]. However, the diagnosis of KFD is unlikely to be considered without lymph node biopsy in patients with pyrexia of unknown origin. Other sporadic symptoms and signs include rigors, myalgia, arthralgia, and chest and abdominal pain[6]. Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, night sweats, and weight loss have been reported more often in patients with extranodal disease[76].
The lymph node involvement is the commonest presenting feature. The lymph nodes are usually enlarged only moderately varying in size from 1 to 2 cm in diameter but sometimes they are much bigger up to 7 cm in diameter[77]. The enlarged lymph nodes are typically discrete, mobile, firm, smooth, and often associated with dull or acute pain. In the majority, the lymph node involvement is limited to unilateral cervical lymphadenitis particularly localized to posterior cervical lymph nodes but there may rarely be bilateral cervical adenopathy[6,77]. Generalized lymphadenopathy involving axillary, epitrochlear, mediastinal, mesenteric, inguinal, intraparotid, iliac, retrocrural, celiac, peripancreatic, and retroperitoneal nodes occurs in about 1% to 22% of patients[71]. Extracervical disease especially with bilateral cervical adenopathy and leukopenia in a review of 60 patients (mean age of 21years) with confirmed KFD manifested with abdominal in 52%, pelvic in 47%, inguinal in 41%, and axillary lymph nodes in 30% of patients, respectively[78]. Mediastinum lymphadenopathy can occur more often while the involvement of mesenteric lymphadenitis is rare and often mimic appendicitis[79-82]. However, nodal enlargement may be minimal or remain limited to mediastinal or retroperitoneal nodes only[83,84].
The involvement of skin in 30%-40% of KFD patients is the most commonly affected extranodal organ[1,2]. Facial erythema, SLE-like malar rash, and other nonspecific lesions including macules, patches, papules, nodules, or plaques, occasionally pruritic, and histologically resembling KFD occur typically and are observed more frequently in children than adults[2,21,85,86]. More sick patients may develop transient skin rashes resembling rubella or drug-induced eruptions[87,88]. Other cutaneous manifestations include pruritus, lichen planus, polymorphous light eruptions, scattered indurated lesions, leukocytoclastic vasculitis, ulcers, scales, and alopecia[2,26,85,89]. Mucosal involvement in the form of oropharyngeal redness, oral ulceration, and conjunctival injection/papillary conjunctivitis may occur[8,90].
Multiple systemic complications may occur. Weight loss is common in adult patients and leukocytosis is perhaps more frequent than leukopenia[20,86]. An association of KFD with various other inflammatory disorders such as hemophagocytic syndrome, arthritis, myocarditis, and hepatic dysfunction has been indicated[86,90-96]. Macrophage activation syndrome, a secondary form of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), has been recognized in some older patients hospitalized under intensive care with KFD and HLH who required systemic corticosteroids or had ended fatally[97].
Involvement of the central nervous system presenting as aseptic meningitis, meningoencephalitis, acute cerebellar symptoms with tremors and ataxia, and optic neuritis has been reported frequently[92,97-102]. Aseptic meningitis mostly at the time of the lymphadenopathy is the commonest neurological complication seen in some of these cases and may be associated with very high levels of intracranial pressure, low cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)-serum glucose, and recurrent subdural effusions requiring intervention[103,104]. While recurrent meningitis occurs more often in males, encephalopathy in children may occur after 10 d to 3 mo which is characterized by very high CSF protein levels and extensive magnetic resonance imaging changes requiring early treatment.
Distinguishing KFD from malignant lymphoma and SLE remains a major diagnostic challenge owing to similar histopathologic appearances. Patients with KFD especially in its proliferative phase have been often misdiagnosed as having non-Hodgkin or Hodgkin lymphoma leading to extensive investigations and, in some cases, aggressive treatment with cytotoxic agents owing more so to unfamiliarity with this uncommon entity[6]. Parotid gland tumor, lupus lymphadenitis, Kawasaki’s disease, cat-scratch disease, Sweet’s syndrome, sarcoidosis, lymphogranuloma venereum, drug eruptions, infectious mononucleosis, and viral or tubercular lymphadenitis are other more common differentials[6,8,105-107]. Mesenteric lymphadenopathy presenting as acute appendicitis too has been described[69].
The diagnosis of KFD is mostly retrospective and based exclusively on lymph node histopathology and excisional biopsy has been recommended frequently in the past. However, fine needle aspiration (FNA) histology with features varying from nonspecific reactive lymphadenitis to those of KFD can be a useful diagnostic tool with an overall accuracy of about 56% in expert hands; nonetheless, it provides clues to exclude other common causes of lymphadenopathy[108]. Ultrasound-guided FNA using smears and cell block preparations designed to preserve lymph node architecture is considered a better alternative[109-111]. However, ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy with a diagnostic accuracy of 95.6% as compared with FNA is now the suggested diagnostic modality of choice[112]. Extracellular debris and intracellular apoptotic debris embedded in the cytoplasm of crescentic and phagocytic macrophages are characteristic of KFD[113,114]. Nevertheless, lymph node biopsy should be preferred for an early diagnosis, to avoid unnecessary investigative work up, and to exclude more serious conditions such as lymphoma requiring early and intensive therapeutic intervention.
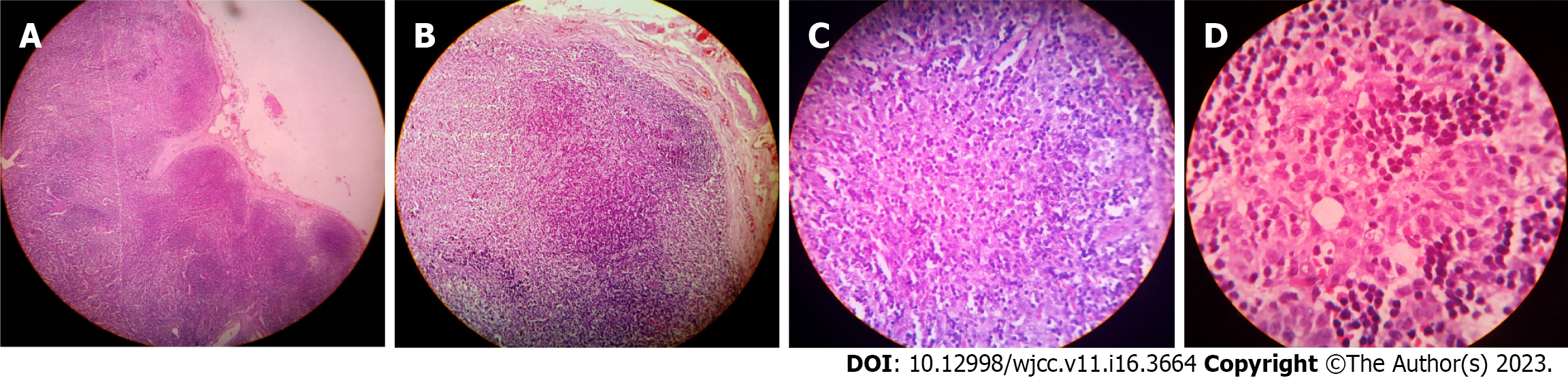
The cut surface of the involved lymph nodes may show yellowish necrotic foci on gross examination. Histological examination (Figure 1) usually shows single or multiple foci of focal or complete loss of follicular architecture often with necrosis of the cortical and paracortical areas and extensive infiltrate consisting of small lymphocytes, immunoblasts, histiocytes, and plasmacytoid T-cells[8]. Perinodal inflammation is common and the capsule may be infiltrated. The necrotizing process is often localized to areas of eosinophilic fibrinoid material with fragments of nuclear debris distributed irregularly. However, obvious coagulative necrosis is not essentially diagnostic of KFD.
The histologic appearance changes as the disease progresses and can be classified into three histologic subtypes; an early phase of “proliferative type” in more than 30%, a late phase of “necrotizing type” in 50% being the commonest, and the end phase of “xanthomatous type” the least common form seen in < 20% cases[77]. The presence of follicular hyperplasia and paracortical expansion by lymphocytes, T and B cell blasts, plasmacytoid monocytes, and histiocytes with numerous background apoptoses is the hallmark of the early "proliferative phase" of KFD. The numerous blast cells may evoke the possibility of lymphoma or EBV/HHV infection. While preservation of the nodal architecture, polyclonal infiltrate, absence of monoclonal T-cell receptor rearrangement, and negative viral serology will exclude these possibilities, its oligoclonal pattern and spontaneous regression favor a more benign immune reaction[115]. The "necrotizing phase" with an absence of a neutrophilic infiltrate is predominately associated with progressive dominance of histiocytes often with crescentic nuclei and phagocytosed debris as the major cell type. Histiocytes with predominantly CD8+ T lymphocytes and CD68+ plasmacytoid monocytes are visualized on immunohistochemical staining[63]. The absence of neutrophils in the necrotizing phase differentiates KFD from SLE and drug-induced lymphadenopathy. The “xanthomatous type” seems to be a distinct histologic variant or perhaps indicates a healing phase characterized by the predominance of foamy histiocytes, and necrosis may or may not be present[116,117].
Systemic lupus erythematosus, tubercular or viral lymphadenitis, and Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma are common histological differentials. The absence of Reed-Sternberg cells, the presence of numerous histiocytes, and relatively low mitotic rates favor the diagnosis of KFD rather than lymphoma[118]. The histology of the lymph node in KFD can be differentiated easily from most known infectious causes of fever and lymphadenopathy but its differentiation from lymphadenopathy in SLE may be particularly difficult. However, positive results for immunohistochemistry taken together with clinicopathologic features may be of diagnostic help[2,6,13,119].
In contrast, the histologic features of skin lesions in KFD are mostly nonspecific and highly variable featuring epidermal changes mainly of interface dermatitis, necrotic keratinocytes, non-neutrophilic karyorrhectic debris, basal vacuolar change, papillary dermal edema, and a lymphocytic infiltrate[2,120]. Vacuolar interface changes in 75%, necrotic keratinocytes in 68%, karyorrhexis in 100%, superficial and deep lymphohistiocytic infiltration in 100% and 56%, respectively, and panniculitis in 60% were major histologic features noted in a retrospective review of skin biopsies from sixteen patients with KFD[121]. Atwater et al[2] proposed that diagnosis of KFD can be reasonably made in an appropriate clinical setting if the biopsy specimen meets the following criteria: (1) A dermal (lympho)-histiocytic infiltrate; (2) epidermal changes with an emphasis on necrotic keratinocytes; (3) non-neutrophilic karyorrhectic debris; (4) basal vacuolar change; and (5) papillary dermal edema. However, confirmation is needed by immunohistochemical staining with CD68 for the presence of histiocytes.
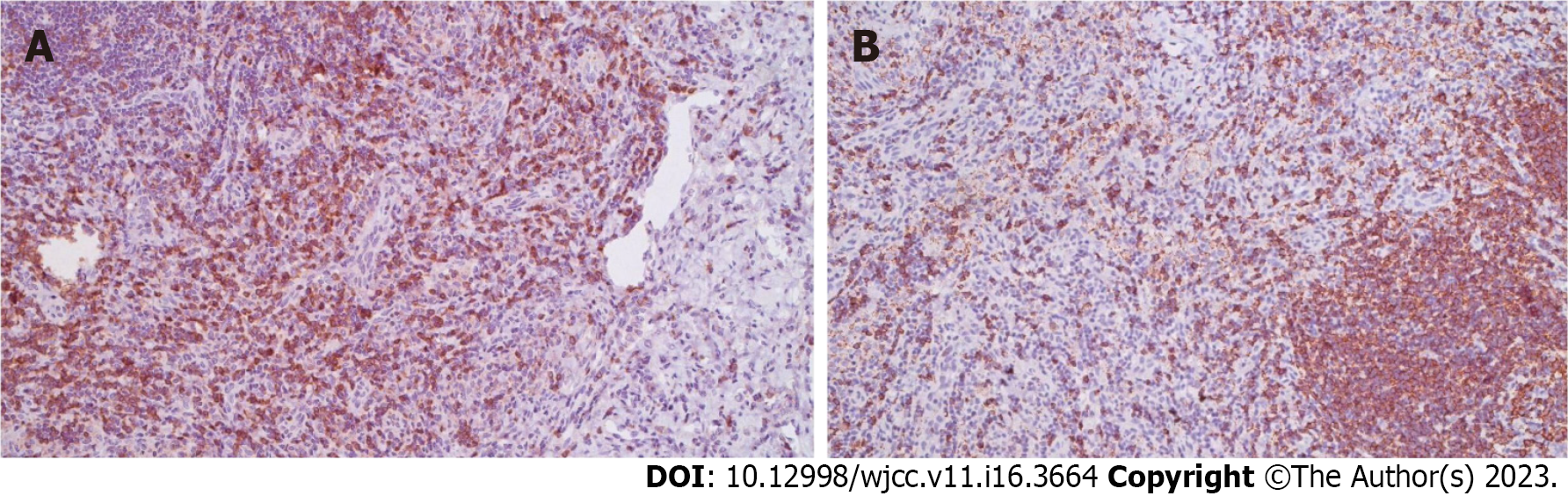
Hassan et al[122] observed positive immunostaining by antibodies Mac 387, KP1 (CD 68), and Ki M1P, and the majority of the cells were a mixture of CD8+ and CD68+ in the affected foci (Figure 2).
Additionally, a variable number of T-cells immunostained by antibody MT1 (CD 43) or UCHL1 and (CD 45RO) and CD8+ T cells stained positive with antibody CD8/144 in all lesions. They opined that immunohistochemistry can be useful in differentiating KFD from other chronic cervical lymphadenopathies. KFD can be distinguished from necrotizing lymphadenitis due to other causes with digital quantification of CD123 immunohistochemical staining[123]. There are fewer surrounding mononuclear cells and neutrophils are usually present in HHV-associated lymphadenitis. Contrasting with KFD, necrosis in Hodgkin lymphoma usually includes neutrophils and CD15, CD30, and CD45 positive Reed-Sternberg cells, the large atypical cell variants. The plasmacytoid dendritic cells infiltrate the lymph nodes more frequently in KFD irrespective of its duration than in either reactive lymphadenitis or T or B cell lymphoma and can be useful cytologic indicators in the diagnosis of KFD[124]. The presence of abundant CD8+ cytotoxic T cells around necrotic areas can help in differentiating necrotic lymph nodes from head and neck cancer or metastatic disease from SLE and reactive lymphoid hyperplasia[125,126]. CD68+ and CD163+ histiocytes and CD3+ T lymphocytes are predominant infiltrating cells in skin lesions whereas, neutrophil-predominant inflammation with superficial dermal edema features in skin lesions with Sweet syndrome-like morphology[121,127].
No specific laboratory investigations are recommended for the diagnosis of KFD but these are advocated to exclude other causes of (cervical) lymphadenopathy. Although atypical lymphocytes in up to 25% and leukopenia in up to 43% have been observed, the blood counts are usually normal in a majority of the patients with KFD[6,12,17,73]. Thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, and anemia of chronic disease in those with severe disease are other reported hematological abnormalities[26,73,128]. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C reactive protein can be normal but were elevated (> 60 mm/h) in 70% of patients in one series[83]. Mildly abnormal liver function tests and elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase are other nonspecific findings[96].
Increased macrophages without atypical cells are frequently seen in bone marrow cytology whereas, increased numbers of mature hemophagocytic histiocytes in the bone marrow may cause diagnostic confusion with virus-associated hemophagocytic syndrome[17,77]. However, bone marrow studies are rarely recommended for the diagnosis of KFD.
Serology for EBV, HHV, cytomegalovirus, HIV, toxoplasmosis, Y. enterocolitica, cat scratch disease, and other infectious agents is often performed in a suspected case of KFD to exclude other differentials of fever and lymphadenopathy. Antinuclear antibodies (ANA) and other investigations for SLE, and rheumatoid factor are, although not always, negative and help distinguish the two. However, patients initially diagnosed with KFD may have concurrent or developed SLE subsequently, it is generally recommended to perform an ANA test in patients suspected of KFD with features suggestive of SLE and to exclude this diagnosis[6,129]. There may be a transient rise in anti-deoxyribonucleic acid and anti-ribonuclear protein antibody levels[17]. Screening for the presence of adult-onset Still’s disease in patients with suspected KFD is also recommended because of reports of their concurrent occurrence[130].
No specific radiographic finding has been established to make a diagnosis of KFD. However, a chest X-ray should be obtained in a routine workup of a patient with fever and cervical lymphadenopathy for any evidence of pulmonary tuberculosis or malignancy. Ultrasonography of the neck for lymph nodes can be performed but results need careful interpretation as in a series of 29 lymph nodes evaluated by sonography 66% showed features suggestive of malignancy whereas tubercular lymphadenitis remains another common differential[119,131]. Features such as posterior neck involvement, echogenic hilum, absence of internal calcification and necrosis (rarely present in partial necrosis), normal vascular pattern (hilar vascular structures are central or branch radially from the hilum in both longitudinal and transverse planes) on power Doppler ultrasound are considered typical of KFD[119]. In Doppler ultrasonography, the lymph nodes are smaller, less rounded, and mostly have an echogenic hilum and abnormal posterior cervical region but necrosis and internal calcifications are less likely in KFD as compared to tuberculous adenitis[119]. Computed tomography (CT) of the neck may be helpful before biopsy and the features may be similar to lupus lymphadenitis and malignant lymphoma. It exhibits unilateral, uniform homogeneous enlargement and post-contrast enhancement of cervical lymph nodes preferably affecting levels II-V in most patients with KFD[132]. Perinodal infiltration is typically seen in about 81% and homogenous nodal contrast enhancement occurs in 83% of affected lymph nodes[132]. The pattern of necrosis, when present, suggests tuberculosis while the absence of necrotic lymphadenopathy and nodal cortical attenuation and its ratio to adjacent muscle on CT imaging differentiates KFD from tuberculous lymphadenopathy and nodal reactive hyperplasia[133]. Magnetic resonance imaging findings of 52 enlarged cervical lymph nodes predominantly showed unilateral distribution at level II-V in a study[134]. Areas of hypointensity in peripheral distribution and clear margins representing necrosis in paracortical areas, and occasional focal non-enhancing areas suggestive of necrosis within the enlarged lymph nodes were observed in T2-weighted images in the same study. Positron emission tomography scanning has been used to assess disease severity and most patients are found to have multiple hypermetabolic lymph nodes but only a few were enlarged[135,136]. Radiating vessels from the central hilum to the periphery of the lymph node and normal or scant hilar vascularity within the whole lesion in 92% of patients with KFD on color Doppler imaging indicates its benign nature[137]. Lee et al[138] performed real-time elastography in two patients with KFD to measure the elasticity score of affected cervical lymph nodes. Based on a scale of 1 to 4 devised by Ying et al[139] the elasticity score of 1 in both patients was consistent with the benign nature of KFD. However, all these investigative modalities need further evaluation for their diagnostic accuracy compared to histopathology, the gold standard in diagnosis.
Although considered benign and self-limiting, systemic complications in KFD may develop prompting urgent intervention. These include cardiac tamponade, pleural effusions, pulmonary infiltrates and nodules (interstitial lung disease), symmetrical polyarthritis, thyroiditis and parotid enlargement, autoimmune hepatitis, acute renal failure, bilateral papillary conjunctivitis and panuveitis, ocular vasculitis and subretinal macular infiltrates, polymyositis, hemophagocytosis, limb paresis because of brachial plexus neuritis, peripheral neuropathy, and antiphospholipid syndrome with multiorgan failure[91,92,140-154]. Still's disease, cryptogenic organizing pneumonia, hemophagocytic syndrome, and B cell lymphoma have been described occasionally in association with KFD[35,155-160].
KFD shares gender and age predisposition as well as histologic features with SLE. SLE may occasionally precede, sometimes be associated with KFD, or develop subsequently. In a review of 55 patients with KFD in the context of definite connective tissue disorder fifty were associated with SLE; 22 (40%) patients had simultaneous onset, 19 (35%) patients predated the onset, and 14 (25%) patients developed KFD after the onset of SLE[3]. KFD may also complicate preexisting SLE as described by Tarabichi et al[161] requiring intensive therapeutic intervention. Their patient of SLE, a 20-year-old girl, had been doing well with hydroxychloroquine (HCQS 200 mg/d)/analgesics. But, after two months she developed KFD affecting multiple cervical/extra cervical lymph nodes and hepatomegaly and needed high doses of systemic methylprednisolone (250 mg/d, given as pulse therapy for 5 d) and 40 mg/d thereafter in addition to HCQS (200 mg twice daily) for adequate control.
Many reports of KFD cases also support the idea that the two diseases share common immunopathological and clinical features such as the disappearance of the lesions without any specific treatment whereas, the possibility of recurrence suggests the involvement of immune mechanisms and that KFD could be a common aspect of SLE[151,162,163]. One ultrastructural study proposed that KFD perhaps reflects a self-limiting, SLE-like autoimmune condition triggered by virus-infected transformed lymphocytes[51]. The histological findings of focal necrosis with immunoblastic infiltration in lupus lymphadenitis are indistinguishable from KFD. The absence of neutrophils is characteristic of both KFD and lupus lymphadenitis[8]. The tubuloreticular structures in the lymphocytes and endothelial cells in patients with SLE have similarities to those seen in KFD whereas a similar tubuloreticular structure in human lymph nodes is not seen except in cases of SLE. However, the detection of this peculiar structure of unknown origin in an ultrastructural study of necrotizing lymphadenitis suggests a direct relationship between SLE and KFD[51]. In addition, the key distinguishing histologic feature of SLE lymphadenitis is the presence of hematoxylin bodies, an amorphous aggregate of basophilic material[163].
Skin lesions in KFD may also clinically and histologically resemble those seen in SLE or subacute lupus erythematosus[164]. Skin biopsy of KFD lesions reveals a pattern of interface dermatitis in KFD that evolved into SLE suggesting that it could be a histopathological marker of evolution into SLE and might predict clinical outcomes in KFD[125]. An association of KFD with hemophagocytic syndrome also suggests a common pathogenesis[148].
According to Tabata et al[126], CD30 immunostaining may help in differentiating KFD from SLE as CD30+ cells significantly are more numerous in KFD than in SLE and most of these were located around necrotic areas in their study of 30 patients with KFD and six patients with SLE. These CD30+ cells were CD8+ activated cytotoxic T cells around necrotic areas and characteristic of KFD and occurred predominantly in females having only mild symptoms and normal laboratory data[126]. The relationship between KFD and SLE remains complex and uncertain requiring long-term follow-up because of late evolution of KFD to SLE or other autoimmune diseases after several months to years[49,120,165].
Although KFD affects women younger than 40 years of age more often, there is a paucity of data on its impact on gestation and pregnancy outcomes. The treatment with antibiotics, steroids, or both had no adverse impacts on the mother, fetus, or the course of pregnancy in two patients with KFD manifesting during pregnancy[166,167]. Another patient with KFD had a miscarriage reportedly with evolving SLE[168].
The presenting clinical features in children are similar to those in adults, although fever, rash, and bilateral cervical lymphadenopathy are more frequent in children younger than 18 years than in adults[72,169-171]. Generalized lymphadenopathy was less common while fever and rash were more common in children as compared to adults[170]. The presentation may be atypical in children < 6 years old. Recurrent disease seen in approximately 3% of pediatric patients is uncommon and occurs more often in boys compared to adults where recurrences have been more frequent in women[21,73].
No specific treatment has been established as signs and symptoms usually resolve spontaneously within 1 to 4 mo without serious sequelae[172]. Fever usually subsides after removal of the affected lymph node suggesting the possible therapeutic benefit of excisional biopsy by removal of the focus for the inflammatory process in addition to being diagnostic[173]. Pharmacotherapy is usually targeted to reduce morbidity and prevent complications. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) usually suffice to alleviate fever and lymph node tenderness in mild cases. Patients with prolonged fever, severe or symptoms lasting for more than 2 wk, and recurrent disease have been treated with immunomodulators, systemic corticosteroids (prednisolone 1-2 mg/kg body weight) alone or in combination, high-dose corticosteroids and intravenous immune globulin (IVIg) especially in patients presenting with extranodal or generalized severe disease or hemophagocytic syndrome with good therapeutic outcome[174-176]. There have been reports of recurrent or steroid-resistant KFD treated successfully with hydroxychloroquine monotherapy or in combination with systemic corticosteroids[177,178]. Rezai et al[177] treated a patient of KFD with systemic symptoms with chloroquine and achieved a rapid response in four days. One patient unresponsive to steroid therapy reportedly responded well to the IL-1 inhibitor, anakinra[179]. The anecdotal efficacy of ciprofloxacin, minocycline, and ofloxacin in remitting KFD needs further evaluation[8,24,25].
In general, the prognosis in KFD is good as it is self-limiting in a majority of the patients and the symptoms may spontaneously subside in 1-6 mo, although recurrences can occur in 3% to 4% cases[128,180-182]. In a series with a median of 32 mo of follow-up 92% of patients were alive and well[6]. Recurrences respond well to treatment similar to the first occurrence. Nevertheless, affected patients should be followed up for some years as unpredictably they may develop SLE, and sometimes recurrences of KFD can continue for many years. For instance, in a Korean case series recurrence was seen in 11.3% and 2.7% of patients who developed autoimmune diseases after an initial diagnosis of KFD[183]. Similarly, four episodes of lymphadenopathy over 18 years occurred in a patient and another had two episodes separated by 6 years[128,180]. In another Korean series of 102 patients (mean age 26.7 years) followed up between 2001 and 2006, late recurrence happened in 13% of patients and early relapse occurred in 8% of patients while 3% of patients developed SLE[181]. These recurrent cases had fever and fatigue with extranodal involvement and remained symptomatic for a longer period than non-recurrent cases. A positive fluorescent antinuclear antibody test was found to be associated with a significantly higher risk of recurrent disease. An EBV seropositive and ANA negative KFD presenting initially with severe disease relapsed frequently despite being treated with multiple courses of systemic corticosteroids and hydroxychloroquine[184]. With a reported fatality rate of 2.1% and severe and fatal cases having been generally associated with hemophagocytic syndrome or connective tissue disease, a long-term follow-up remains essential[3,73,185].
Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease is an uncommon, idiopathic, benign lymphadenopathy primarily affecting both genders at a young age between 20 and 40 years worldwide across ethnicities. The acute or subacute onset of adenopathy is usually associated with fever, body aches, night sweats, and weight loss (B symptoms). Its exact etiology remains obscure. The results of studies looking for viral etiology have been inconsistent. Molecular pathways implicated in its pathobiology are also not well understood. Concomitant autoimmune disorders have been reported or they may also be diagnosed more frequently following the resolution of KFD. Despite differing opinions, SLE is perhaps the commonest disorder linked to KFD and has been suggested to be its forme fruste. However, further research is necessary to reach a definitive conclusion.
Although modern hematopathological methods have made misdiagnosis less likely, a diagnosis of malignant lymphoma for KFD is still reported. Since the diagnosis is exclusively based on histo
Treatment guidelines for KFD have not been established and recommendations are mostly based on case reports, small case series, and the opinion of the experts. Treatment with systemic corticosteroids, NSAIDs, hydroxychloroquine or other immunomodulators, used alone or in combination, in a few patients with severe symptoms or recurrent disease remains the mainstay in therapeutics. Anecdotal therapeutic efficacy and place of chloroquine, anakinra, IVIg, and antimicrobial agents in the treatment ladder need to be evaluated further.
Provenance and peer review: Invited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Dermatology
Country/Territory of origin: India
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Dauyey K, Kazakhstan; Hasan A, Egypt S-Editor: Gong ZM L-Editor: A P-Editor: Zhao S
| 1. | Seno A, Torigoe R, Shimoe K, Tada J, Arata J, Suwaki M. Kikuchi's disease (histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis) with cutaneous involvement. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;30:504-506. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 50] [Cited by in RCA: 50] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Atwater AR, Longley BJ, Aughenbaugh WD. Kikuchi's disease: case report and systematic review of cutaneous and histopathologic presentations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:130-136. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 50] [Cited by in RCA: 57] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Sharma V, Rankin R. Fatal Kikuchi-like lymphadenitis associated with connective tissue disease: a report of two cases and review of the literature. Springerplus. 2015;4:167. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Kikuchi M. Lymphadenitis showing focal reticulum cell hyperplasia with nuclear debris and phagocytosis. Nippon Ketsueki Gakkai Zasshi. 1972;35:379-380. |
| 5. | Fujimoto Y, Kojima Y, Yamaguchi K. Cervical subacute necrotizing lymphadenitis. Intern Med. 1972;20:920-927. |
| 6. | Dorfman RF, Berry GJ. Kikuchi's histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis: an analysis of 108 cases with emphasis on differential diagnosis. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1988;5:329-345. [PubMed] |
| 7. | Turner RR, Martin J, Dorfman RF. Necrotizing lymphadenitis. A study of 30 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1983;7:115-123. [PubMed] |
| 8. | Mahajan VK, Sharma NL. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: immediate remission with ciprofloxacin. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:370-372. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Achappa B, Herath NC, Sebastian B, Dsouza NV, Raghuram PM, Holla R, Chowta N, Kini JR. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease in a tertiary care teaching hospital in Coastal South India: A 8-year retrospective study. F1000Res. 2022;11:492. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Lame CA, Loum B, Fall AK, Cucherousset J, Ndiaye AR. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease, a rare cause of lymphadenopathy in Africa. Description of the first case in Senegal and review of the literature. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2017;134:347-349. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Kutty MK, Anim JT, Sowayan S. Histiocytic necrotising lymphadenitis (Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease) in Saudi Arabia. Trop Geogr Med. 1991;43:68-75. [PubMed] |
| 12. | Song JY, Cheong HJ, Kee SY, Lee J, Sohn JW, Kim MJ, Seo SI, Kim IS, Kim WJ. Disease spectrum of cervical lymphadenitis: analysis based on ultrasound-guided core-needle gun biopsy. J Infect. 2007;55:310-316. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 37] [Cited by in RCA: 38] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Tsang WY, Chan JK, Ng CS. Kikuchi's lymphadenitis. A morphologic analysis of 75 cases with special reference to unusual features. Am J Surg Pathol. 1994;18:219-231. [PubMed] |
| 14. | Lee KY, Yeon YH, Lee BC. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease with prolonged fever in children. Pediatrics. 2004;114:e752-e756. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 54] [Cited by in RCA: 52] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Payne JH, Evans M, Gerrard MP. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: a rare but important cause of lymphadenopathy. Acta Paediatr. 2003;92:261-264. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Ray A, Muse VV, Boyer DF. Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Case 38-2013. A 30-year-old man with fever and lymphadenopathy. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:2333-2343. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Asano S, Akaike Y, Jinnouchi H, Muramatsu T, Wakasa H. Necrotizing lymphadenitis: a review of clinicopathological, immunohistochemical and ultrastructural studies. Hematol Oncol. 1990;8:251-260. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 36] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Lin HC, Su CY, Huang CC, Hwang CF, Chien CY. Kikuchi's disease: a review and analysis of 61 cases. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003;128:650-653. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Seo JH, Shim HS, Park JJ, Jeon SY, Kim JP, Ahn SK, Hur DG, Ahn SY, Kwon OJ. A clinical study of histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis (Kikuchi's disease) in children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2008;72:1637-1642. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Batton E, Alali M, Hageman JR, Parilla M, Yu KOA. Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease in Children: An Important Diagnostic Consideration for Cervical Lymphadenitis. Pediatr Ann. 2019;48:e406-e411. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Kim HY, Jo HY, Kim SH. Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics of Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease According to Age. Front Pediatr. 2021;9:745506. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Rich SA. De novo synthesis and secretion of a 36-kD protein by cells that form lupus inclusions in response to alpha-interferon. J Clin Invest. 1995;95:219-226. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Chiu CF, Chow KC, Lin TY, Tsai MH, Shih CM, Chen LM. Virus infection in patients with histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis in Taiwan. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus, type I human T-cell lymphotropic virus, and parvovirus B19. Am J Clin Pathol. 2000;113:774-781. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 84] [Cited by in RCA: 84] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Takada K, Suzuki K, Hidaka T, Konishi T, Shinohara T, Kataharada K, Matsumoto M, Okada M, Ohsuzu F. Immediate remission obtained by minocycline in a patient with histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis. Intern Med. 2001;40:1055-1058. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Ramkumar A. Kikuchi-fujimoto disease as a differential diagnosis for cervical lymphadenopathy in India: a case report and review of literature. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011;63:110-112. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Yen A, Fearneyhough P, Raimer SS, Hudnall SD. EBV-associated Kikuchi's histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis with cutaneous manifestations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;36:342-346. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 81] [Cited by in RCA: 80] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Hudnall SD, Chen T, Amr S, Young KH, Henry K. Detection of human herpesvirus DNA in Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease and reactive lymphoid hyperplasia. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2008;1:362-368. [PubMed] |
| 28. | Huh J, Kang GH, Gong G, Kim SS, Ro JY, Kim CW. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus in Kikuchi's disease. Hum Pathol. 1998;29:1091-1096. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 63] [Cited by in RCA: 65] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Yufu Y, Matsumoto M, Miyamura T, Nishimura J, Nawata H, Ohshima K. Parvovirus B19-associated haemophagocytic syndrome with lymphadenopathy resembling histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis (Kikuchi's disease). Br J Haematol. 1997;96:868-871. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 59] [Cited by in RCA: 53] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Hudnall SD. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease. Is Epstein-Barr virus the culprit? Am J Clin Pathol. 2000;113:761-764. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 28] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | de losÁngelesValcárcel-García M, Aliste-Santos C, González-Quintela A, Díaz-Peromingo JA. Association between Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease and Streptococcus pneumoniae infection. Cent Eur J Med. 2014;9:709-713. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Chong Y, Lee JY, Kang CS, Lee EJ. Identification of Torque Teno Virus/Torque Teno-Like Minivirus in the Cervical Lymph Nodes of Kikuchi-Fujimoto Lymphadenitis Patients (Histiocytic Necrotizing Lymphadenitis): A Possible Key to Idiopathic Disease. Biomed Hub. 2020;5:1-5. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Stéphan JL, Jeannoël P, Chanoz J, Gentil-Përret A. Epstein-Barr virus-associated Kikuchi disease in two children. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2001;23:240-243. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 29] [Cited by in RCA: 28] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Madle-Samardzija N, Turkulov V, Vukadinov J, Stajnic S, Canak G. [Histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis (Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease)]. Med Pregl. 2000;53:513-516. [PubMed] |
| 35. | Yoshino T, Mannami T, Ichimura K, Takenaka K, Nose S, Yamadori I, Akagi T. Two cases of histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis (Kikuchi-Fujimoto's disease) following diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Hum Pathol. 2000;31:1328-1331. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 36. | Maek-a-nantawat W, Viriyavejakul P. Mycobacterium szulgai lymphadenitis mimicking Kikuchi's disease in Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2001;32:537-540. [PubMed] |
| 37. | Podugu A, Kobe M. Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease (KFD): A rare cause of fever and lymphadenopathy following influenza vaccination. Chest. 2013;144:230. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | Watanabe T, Hashidate H, Hirayama Y, Iinuma Y. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease following vaccination against human papilloma virus infection and Japanese encephalitis. Eur J Pediatr. 2012;171:1409-1411. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 39. | Stimson L, Stitson R, Bahhadi-Hardo M, Renaudon-Smith E. COVID-19 associated Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease. Br J Haematol. 2021;192:e124-e126. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 6.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 40. | Jaseb K, Nameh Goshay Fard N, Rezaei N, Sadeghian S. COVID-19 in a case with Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease. Clin Case Rep. 2021;9:1279-1282. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 3.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 41. | Racette SD, Alexiev BA, Angarone MP, Bhasin A, Lima K, Jennings LJ, Balasubramanian S, Matsuoka AJ. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease presenting in a patient with SARS-CoV-2: a case report. BMC Infect Dis. 2021;21:740. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 4.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 42. | Al Ghadeer HA, AlKadhem SM, AlMajed MS, AlAmer HM, AlHabeeb JA, Alomran SH, AlMajed AS. Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease Following COVID-19. Cureus. 2022;14:e21049. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 43. | Saito Y, Suwa Y, Kaneko Y, Tsujiwaki M, Odagawa Y. Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease Following COVID-19 Infection in a 7-Year-Old Girl: A Case Report and Literature Review. Cureus. 2022;14:e26540. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 44. | Guan Y, Xia X, Lu H. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease following vaccination against COVID-19. J Hematop. 2022;15:21-23. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 5.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 45. | Soub HA, Ibrahim W, Maslamani MA, A Ali G, Ummer W, Abu-Dayeh A. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease following SARS CoV2 vaccination: Case report. IDCases. 2021;25:e01253. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 4.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 46. | Caocci G, Fanni D, Porru M, Greco M, Nemolato S, Firinu D, Faa G, Scuteri A, La Nasa G. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease associated with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis following the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccination. Haematologica. 2022;107:1222-1225. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 6.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 47. | Ikeda K, Kakehi E, Adachi S, Kotani K. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease following SARS-CoV-2 vaccination. BMJ Case Rep. 2022;15. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 48. | Daghri S, Belmoufid N, Rami A, Al Bouzidi A, Bouanani N. Kikuchi-Fujimoto's Disease or Histiocytic Necrotizing Lymphadenitis Following mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination: A Rare Case. Cureus. 2022;14:e24155. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 49. | Ogata S, Bando Y, Saito N, Katsuoka K, Ishii M. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease developed into autoimmune disease: a report of two cases. Mod Rheumatol. 2010;20:301-305. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 50. | Radfar L, Radfar M, Moser KL, Scofield RH. Kikuchi-Fijimoto disease in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Open J Pathology 2013; 3: 32-36. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 51. | Imamura M, Ueno H, Matsuura A, Kamiya H, Suzuki T, Kikuchi K, Onoe T. An ultrastructural study of subacute necrotizing lymphadenitis. Am J Pathol. 1982;107:292-299. [PubMed] |
| 52. | Lee EJ, Lee HS, Park JE, Hwang JS. Association Kikuchi disease with Hashimoto thyroiditis: a case report and literature review. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2018;23:99-102. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 53. | Wang TJ, Yang YH, Lin YT, Chiang BL. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease in children: clinical features and disease course. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2004;37:219-224. [PubMed] |
| 54. | Guadarra MBR, Guzmán-Aguilar OD, López-Ugalde AC, Navarro JSA, Cruz-Ortíz H. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease associated to the Epstein-Barr virus. A type of rare necrotizing lymphadenitis and its differential diagnosis. Open J Pathol 2013; 3:186-192. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 55. | Sopeña B, Rivera A, Vázquez-Triñanes C, Fluiters E, González-Carreró J, del Pozo M, Freire M, Martínez-Vázquez C. Autoimmune manifestations of Kikuchi disease. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012;41:900-906. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 41] [Cited by in RCA: 55] [Article Influence: 3.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 56. | Lin CC, Yeh SP, Chiang IP, Chiu CF. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease after allogeneic hematopoietic SCT mimicking post transplant lymphoproliferative disorder. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2011;46:1389-1390. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 57. | Garcia-Arnes J, Bernal-Lopez MR, Gallego-Perales JL, Vazquez-Camuñas ML, Gomez-Huelgas R. Histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis (Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease) after laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for morbid obesity: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2012;6:340. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 58. | Stasiuk A, Teschke S, Williams GJ, Seftel MD. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: lymphadenopathy in siblings. CMAJ. 2011;183:E58-E60. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 59. | Amir AR, Amr SS, Sheikh SS. Kikuchi-Fujimoto's disease: report of familial occurrence in two human leucocyte antigen-identical non-twin sisters. J Intern Med. 2002;252:79-83. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 60. | Asano S, Akaike Y, Muramatsu T, Wakasa H, Yoshida H, Kondou R, Kojima M, Jyoushita T. Necrotizing lymphadenitis: a clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of four familial cases and five recurrent cases. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1991;418:215-223. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 34] [Cited by in RCA: 34] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 61. | Quadir A, Peacock K, Hsu P, Singh-Grewal D, Alexander S. A familial case of Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease in dizygotic twins. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2020;18:62. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 62. | Tanaka T, Ohmori M, Yasunaga S, Ohshima K, Kikuchi M, Sasazuki T. DNA typing of HLA class II genes (HLA-DR, -DQ and -DP) in Japanese patients with histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis (Kikuchi's disease). Tissue Antigens. 1999;54:246-253. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 60] [Cited by in RCA: 58] [Article Influence: 2.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 63. | Ohshima K, Karube K, Hamasaki M, Makimoto Y, Fujii A, Kawano R, Tutiya T, Yamaguchi T, Suzumiya J, Kikuchi M. Apoptosis- and cell cycle-associated gene expression profiling of histiocytic necrotising lymphadenitis. Eur J Haematol. 2004;72:322-329. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 64. | Iguchi H, Sunami K, Yamane H, Konishi K, Takayama M, Nakai Y, Nakagawa T, Shibata S, Nishimura K. Apoptotic cell death in Kikuchi's disease: a TEM study. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1998;538:250-253. [PubMed] |
| 65. | Ohshima K, Shimazaki K, Kume T, Suzumiya J, Kanda M, Kikuchi M. Perforin and Fas pathways of cytotoxic T-cells in histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis. Histopathology. 1998;33:471-478. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 58] [Cited by in RCA: 63] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 66. | Ura H, Yamada N, Torii H, Imakado S, Iozumi K, Shimada S. Histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis (Kikuchi's disease): the necrotic appearance of the lymph node cells is caused by apoptosis. J Dermatol. 1999;26:385-389. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 67. | Ohshima K, Haraoka S, Takahata Y, Takada H, Tsutiya K, Suzuk K, Suzumiya J, Kikuchi M. Interferon-gamma, interleukin-18, monokine induced by interferon-gamma and interferon-gamma-inducible protein-10 in histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis. Leuk Lymphoma. 2002;43:1115-1120. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 68. | Kubota M, Tsukamoto R, Kurokawa K, Imai T, Furusho K. Elevated serum interferon gamma and interleukin-6 in patients with necrotizing lymphadenitis (Kikuchi's disease). Br J Haematol. 1996;95:613-615. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 43] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 69. | Min KW, Jang KS, Jang SH, Song YS, Na W, Song SY, Paik SS. Kikuchi’s disease of the mesenteric lymph nodes presenting as acute appendicitis. Korean J Pathol. 2007;41:44-46. |
| 70. | Bosch X, Guilabert A, Miquel R, Campo E. Enigmatic Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: a comprehensive review. Am J Clin Pathol. 2004;122:141-152. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 120] [Article Influence: 5.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 71. | Deaver D, Horna P, Cualing H, Sokol L. Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management of Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease. Cancer Control. 2014;21:313-321. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 55] [Cited by in RCA: 69] [Article Influence: 6.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 72. | Deaver D, Naghashpour M, Sokol L. Kikuchi-fujimoto disease in the United States: three case reports and review of the literature [corrected]. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2014;6:e2014001. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 73. | Kucukardali Y, Solmazgul E, Kunter E, Oncul O, Yildirim S, Kaplan M. Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease: analysis of 244 cases. Clin Rheumatol. 2007;26:50-54. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 211] [Cited by in RCA: 243] [Article Influence: 12.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 74. | Rudniki C, Kessler E, Zarfati M, Turani H, Bar-Ziv Y, Zahavi I. Kikuchi's necrotizing lymphadenitis: a cause of fever of unknown origin and splenomegaly. Acta Haematol. 1988;79:99-102. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 31] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 75. | Kang HM, Kim JY, Choi EH, Lee HJ, Yun KW, Lee H. Clinical Characteristics of Severe Histiocytic Necrotizing Lymphadenitis (Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease) in Children. J Pediatr. 2016;171:208-12.e1. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 36] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Article Influence: 5.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 76. | Kuo TT. Cutaneous manifestation of Kikuchi's histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis. Am J Surg Pathol. 1990;14:872-876. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 73] [Cited by in RCA: 68] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 77. | Kuo TT. Kikuchi's disease (histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis). A clinicopathologic study of 79 cases with an analysis of histologic subtypes, immunohistology, and DNA ploidy. Am J Surg Pathol. 1995;19:798-809. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 267] [Cited by in RCA: 249] [Article Influence: 8.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 78. | Chen LC, Wang CJ, Chang YC, Shie SS, Lin TY, Hsieh YC, Arthur Huang KY, Kuo CY, Chiu CH, Huang YC, Chen CJ. Distribution of lymphadenopathy in patients with Kikuchi disease. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2021;54:299-304. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 3.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 79. | Naito N, Shinohara T, Machida H, Hino H, Naruse K, Ogushi F. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease associated with community acquired pneumonia showing intrathoratic lymphadenopathy without cervical lesions. Springerplus. 2015;4:693. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 80. | Hino H, Nishimura T, Nitadori J, Miyakoshi S, Seki A, Arai T, Nakajima J. An uncommon presentation of Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease as mediastinal lymphadenopathy. J Thorac Dis. 2016;8:E330-E333. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 81. | Pandey V, Khatib Y, Pandey R, Khade AL, Khare M. Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease Masquerading as Acute Appendicitis. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017;11:ED26-ED28. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 82. | Shrestha A, Newton K, Benbow E, Kushwaha R. Kikuchi- Fujimoto disease of mesenteric lymph nodes mimicking acute appendicitis. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 2013;52:627-630. [PubMed] |
| 83. | Norris AH, Krasinskas AM, Salhany KE, Gluckman SJ. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: a benign cause of fever and lymphadenopathy. Am J Med. 1996;101:401-405. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 72] [Cited by in RCA: 74] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 84. | Kim YT, Yoo KH, Cho HD, Oh MH, Shin HC. Kikuchi Disease Presented with External Iliac Lymphadenitis in a 7-year-old Girl: A Case Report. J Korean SocRadiol. 2010;63:483-486. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 85. | Yasukawa K, Matsumura T, Sato-Matsumura KC, Takahashi T, Fujioka Y, Kobayashi H, Shimizu H. Kikuchi's disease and the skin: case report and review of the literature. Br J Dermatol. 2001;144:885-889. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 63] [Cited by in RCA: 59] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 86. | Inamo Y. The Difficulty of Diagnosing Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease in Infants and Children Under Six Years Old: Case Report and Literature Review. Cureus. 2020;12:e7383. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 87. | Trivedi ND, Parsons AS. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: an unusual presentation of meningitis in a returning traveller. BMJ Case Rep. 2017;2017. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 88. | Kikuchi M, Takeshita M, Okamura S. Histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis. Path Clin Med. 1983;1:1541. |
| 89. | Alosaimi S, Hijazi B, Alhumidi A, Alsaif F. A Case of Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease Associated with Erosive Lichen Planus. Cureus. 2020;12:e7312. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 90. | Galor A, Georgy M, Leder HA, Dunn JP, Peters GB 3rd. Papillary conjunctivitis associated with Kikuchi disease. Cornea. 2008;27:944-946. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 91. | Lim GY, Cho B, Chung NG. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis preceded by Kikuchi disease in children. Pediatr Radiol. 2008;38:756-761. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 92. | Sato Y, Kuno H, Oizumi K. Histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis (Kikuchi's disease) with aseptic meningitis. J Neurol Sci. 1999;163:187-191. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 52] [Cited by in RCA: 55] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 93. | Moon JS, Il Kim G, Koo YH, Kim HS, Kim WC, Kim OJ, Oh SH. Kinetic tremor and cerebellar ataxia as initial manifestations of Kikuchi-Fujimoto's disease. J Neurol Sci. 2009;277:181-183. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 94. | Douglas M, Bradbury R, Kannangara S, Mitchell D. Arthritis as an unusual manifestation of Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003;42:1010-1012. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 95. | Chan JK, Wong KC, Ng CS. A fatal case of multicentric Kikuchi's histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis. Cancer. 1989;63:1856-1862. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 96. | Bailey EM, Klein NC, Cunha BA. Kikuchi's disease with liver dysfunction presenting as fever of unknown origin. Lancet. 1989;2:986. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 97. | Ahn SS, Lee B, Kim D, Jung SM, Lee SW, Park MC, Park YB, Hwang YG, Song JJ. Evaluation of macrophage activation syndrome in hospitalised patients with Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease based on the 2016 EULAR/ACR/PRINTO classification criteria. PLoS One. 2019;14:e0219970. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 98. | Mathew LG, Cherian T, Srivastava VM, Raghupathy P. Histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis (Kikuchi's disease) with aseptic meningitis. Indian Pediatr. 1998;35:775-777. [PubMed] |
| 99. | Vaz M, Pereira CM, Kotha S, Oliveira J. Neurological Manifestations in a Patient of Kikuchi's Disease. J Assoc Physicians India. 2014;62:57-61. [PubMed] |
| 100. | Khishfe BF, Krass LM, Nordquist EK. Kikuchi disease presenting with aseptic meningitis. Am J Emerg Med. 2014;32:1298.e1-1298.e2. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 101. | Byun JH, Park SE, Nam SO, Kim YA, Kim YM, Yeon GM, Lee YJ. Three children of meningoencephalitis with Kikuchi necrotizing lymphadenitis. Brain Dev. 2018;40:251-255. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 102. | Arslan A, Kraus CL, Izbudak I. Optic Neuritis as an Isolated Presentation of Kikuchi–Fujimoto Disease in a Pediatric Patient. Balkan Med J. 2020;37:172-173. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 103. | Iwamoto N, Funahashi M, Shinohara K, Nakaya Y, Motobayashi H, Tochitani K, Yamamoto S, Shimizu T. Two Cases of Kikuchi Disease Presenting with Aseptic Meningitis and Encephalitis. Intern Med. 2022;61:2687-2689. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 104. | Rana G, Awad A, Wang E, Webb S, Zahir H, Ree A. Unique presentation of recurrent subdural effusions and subsequent abdominal lymphadenopathy in a patient diagnosed with Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease. Radiol Case Rep. 2022;17:1163-1168. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 105. | Ramirez AL, Johnson J, Murr AH. Kikuchi-Fujimoto's disease: an easily misdiagnosed clinical entity. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001;125:651-653. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 106. | Chiang YC, Chen RM, Chao PZ, Yang TH, Lee FP. Intraparotid Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease masquerading as a parotid gland tumor. Am J Otolaryngol. 2005;26:408-410. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 107. | Mital D, Desai V, Chin K. Kikuchi-Fujimoto syndrome presenting to a sexual health clinic. Int J STD AIDS. 2009;20:140-141. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 108. | Tong TR, Chan OW, Lee KC. Diagnosing Kikuchi disease on fine needle aspiration biopsy: a retrospective study of 44 cases diagnosed by cytology and 8 by histopathology. Acta Cytol. 2001;45:953-957. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 69] [Cited by in RCA: 60] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 109. | Kung IT, Ng WF, Yuen RW, Chan JK. Kikuchi's histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis. Diagnosis by fine needle aspiration. Acta Cytol. 1990;34:323-328. [PubMed] |
| 110. | Tsang WY, Chan JK. Fine-needle aspiration cytologic diagnosis of Kikuchi's lymphadenitis. A report of 27 cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1994;102:454-458. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 48] [Cited by in RCA: 49] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 111. | Mannarà GM, Boccato P, Rinaldo A, La Rosa F, Ferlito A. Histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis (Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease) diagnosed by fine needle aspiration biopsy. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 1999;61:367-371. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 112. | Park SG, Koo HR, Jang K, Myung JK, Song CM, Ji YB, Park JS, Tae K. Efficacy of Ultrasound-Guided Needle Biopsy in the Diagnosis of Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease. Laryngoscope. 2021;131:E1519-E1523. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 113. | Osborn M, Aqel N, Levine TS. The fine needle aspiration appearances of Kikuchi's lymphadenitis. Cytopathology. 2009;20:36-43. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 114. | Ryoo I, Suh S, Lee YH, Seo HS, Seol HY. Comparison of Ultrasonographic Findings of Biopsy-Proven Tuberculous Lymphadenitis and Kikuchi Disease. Korean J Radiol. 2015;16:767-775. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 115. | Lin CW, Chang CL, Li CC, Chen YH, Lee WH, Hsu SM. Spontaneous regression of Kikuchi lymphadenopathy with oligoclonal T-cell populations favors a benign immune reaction over a T-cell lymphoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 2002;117:627-635. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 116. | Kuo TT, Lo SK. Significance of histological subtypes of Kikuchi's disease: comparative immunohistochemical and apoptotic studies. Pathol Int. 2004;54:237-240. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 117. | Resende C, Araújo C, Duarte Mda L, Vieira AP, Brito C. Kikuchi's disease of the xanthomathous type with cutaneous manifestations. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90:245-247. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 118. | Williams DS. Kikuchi Disease. J Insur Med. 2017;47:55-57. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 119. | Yu SC, Chang KC, Wang H, Li MF, Yang TL, Chen CN, Chen CJ, Chen KC, Shen CY, Kuo PY, Lin LW, Lin YM, Lin WC. Distinguishing lupus lymphadenitis from Kikuchi disease based on clinicopathological features and C4d immunohistochemistry. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021;60:1543-1552. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 2.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 120. | Paradela S, Lorenzo J, Martínez-Gómez W, Yebra-Pimentel T, Valbuena L, Fonseca E. Interface dermatitis in skin lesions of Kikuchi-Fujimoto's disease: a histopathological marker of evolution into systemic lupus erythematosus? Lupus. 2008;17:1127-1135. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 32] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 121. | Kim JH, Kim YB, In SI, Kim YC, Han JH. The cutaneous lesions of Kikuchi's disease: a comprehensive analysis of 16 cases based on the clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and immunofluorescence studies with an emphasis on the differential diagnosis. Hum Pathol. 2010;41:1245-1254. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 31] [Cited by in RCA: 28] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 122. | Hassan M, Anees A, Zaheer S. Kikuchi-fujimoto disease: diagnostic dilemma and the role of immunohistochemistry. J Clin Med Res. 2009;1:244-246. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 123. | Nelson ND, Meng W, Rosenfeld AM, Bullman S, Sekhar Pedamallu C, Nomburg JL, Wertheim GB, Paessler ME, Pinkus G, Hornick JL, Meyerson M, Luning Prak ET, Pillai V. Characterization of Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells, Microbial Sequences, and Identification of a Candidate Public T-Cell Clone in Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2021;24:193-205. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 124. | Kishimoto K, Tate G, Kitamura T, Kojima M, Mitsuya T. Cytologic features and frequency of plasmacytoid dendritic cells in the lymph nodes of patients with histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis (Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease). Diagn Cytopathol. 2010;38:521-526. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 125. | Maruyama T, Nishihara K, Saio M, Nakasone T, Nimura F, Matayoshi A, Goto T, Yoshimi N, Arasaki A. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease in the regional lymph nodes with node metastasis in a patient with tongue cancer: A case report and literature review. Oncol Lett. 2017;14:257-263. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 126. | Tabata T, Takata K, Miyata-Takata T, Sato Y, Ishizawa S, Kunitomo T, Nagakita K, Ohnishi N, Taniguchi K, Noujima-Harada M, Maeda Y, Tanimoto M, Yoshino T. Characteristic Distribution Pattern of CD30-positive Cytotoxic T Cells Aids Diagnosis of Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2018;26:274-282. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 127. | Gates GA, Li Y, Magyar C, Sarantopoulos GP. Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease With Unusual Cutaneous Findings. Am J Dermatopathol. 2021;43:e213-e217. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 128. | Smith KG, Becker GJ, Busmanis I. Recurrent Kikuchi's disease. Lancet. 1992;340:124. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 28] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 129. | Patra A, Bhattacharya SK. SLE Developing in a Follow-Up Patient of Kikuchi's Disease: A Rare Disorder. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013;7:752-753. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 130. | Rai B, Pillinger MH, Panush RS. Coincident Kikuchi-Fujimoto's disease and adult-onset Still's disease: report of a patient from an uncommonly affected population and case-directed systematic review. Clin Rheumatol. 2021;40:4791-4805. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 131. | Youk JH, Kim EK, Ko KH, Kim MJ. Sonographic features of axillary lymphadenopathy caused by Kikuchi disease. J Ultrasound Med. 2008;27:847-853. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 132. | Kwon SY, Kim TK, Kim YS, Lee KY, Lee NJ, Seol HY. CT findings in Kikuchi disease: analysis of 96 cases. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004;25:1099-1102. [PubMed] |
| 133. | Shim EJ, Lee KM, Kim EJ, Kim HG, Jang JH. CT pattern analysis of necrotizing and nonnecrotizing lymph nodes in Kikuchi disease. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0181169. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 134. | Kato H, Kanematsu M, Kato Z, Teramoto T, Kondo N, Hirose Y, Hoshi H. MR imaging findings of cervical lymphadenopathy in patients with Kikuchi disease. Eur J Radiol. 2011;80:e576-e581. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 135. | Seong H, Jeong YH, Lee WJ, Kim JH, Ahn JY, Jeong SJ, Choi JY, Park YS, Yeom JS, Song YG, Cho A, Ku NS. Splenic uptake on FDG PET/CT correlates with Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease severity. Sci Rep. 2021;11:10836. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 136. | Zhang R, Liang L, Li D, Bai Y, Li X. Analysis of the clinical manifestations and 18F-FDG PET-CT findings in 40 patients with histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100:e27189. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 137. | Yoo JL, Suh SI, Lee YH, Seo HS, Kim KM, Shin BK, Song JY, Seol HY. Gray scale and power Doppler study of biopsy-proven Kikuchi disease. J Ultrasound Med. 2011;30:957-963. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 138. | Lee KH, Ryu J. Real-time elastography of cervical lymph nodes in Kikuchi disease. J Ultrasound Med. 2014;33:2201-2205. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 139. | Ying L, Hou Y, Zheng HM, Lin X, Xie ZL, Hu YP. Real-time elastography for the differentiation of benign and malignant superficial lymph nodes: a meta-analysis. Eur J Radiol. 2012;81:2576-2584. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 60] [Cited by in RCA: 65] [Article Influence: 4.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 140. | Keogh MA, Williamson RM, Denaro CP. Kikuchi's disease associated with parotidomegaly, thyroiditis and a rash in a young man. Aust N Z J Med. 2000;30:633-634. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 141. | Liu X, Huang S, Jiang G. Report of a rare case of histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis with bilateral pleural effusion diagnosed via cervical lymph node biopsy. Sao Paulo Med J. 2018;136:368-371. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 142. | Egashira R, Nakazono T, Yamaguchi K, Kai K, Ono N, Yoshimura M, Irie H. A Rare Case of Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease With Diffuse Lung Involvement Presenting a Lymphatic-like Distribution on Thin-section Computed Tomography. J Thorac Imaging. 2018;33:W51-W53. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 143. | Patel J, Haltom M, Jackson C. The great masquerader: Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease presenting as fever of unknown origin. J Natl Med Assoc. 2022;113:680-682. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 144. | Mansoor CA, Shemin Z. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease with multiple extra-nodal features - A clinical mimic. Reumatismo. 2019;71:105-107. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 145. | Khan ST, Naqvi R, Rashid R, Naqvi SA. A rare presentation of Kikuchi Disease with Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Pak J Med Sci. 2019;35:586-588. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 146. | Wilkinson CE, Nichol F. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease associated with polymyositis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2000;39:1302-1304. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 34] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 147. | Chen JS, Chang KC, Cheng CN, Tsai WH, Su IJ. Childhood hemophagocytic syndrome associated with Kikuchi's disease. Haematologica. 2000;85:998-1000. [PubMed] |
| 148. | Kelly J, Kelleher K, Khan MK, Rassam SM. A case of haemophagocytic syndrome and Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease occurring concurrently in a 17-year-old female. Int J Clin Pract. 2000;54:547-549. [PubMed] |
| 149. | Duan W, Xiao ZH, Yang LG, Luo HY. Kikuchi's disease with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: A case report and literature review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99:e23500. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 150. | Pérez Alvarez MJ, Moreno López M. [Panuveitis as a possible ophthalmic complication of Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease]. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2005;80:41-44. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 151. | Shusang V, Marelli L, Beynon H, Davies N, Patch D, Dhillon AP, Burroughs AK. Autoimmune hepatitis associated with Kikuchi-Fujimoto's disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;20:79-82. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 152. | Sugiyama A, Araki E, Arakawa K, Kikuchi H, Iwaki T, Yamada T, Kira J. [A case of subacute necrotizing lymphadenitis complicated with brachial plexus neuritis]. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1998;38:941-944. [PubMed] |
| 153. | Longaretti P, Savasta S, Caimmi D, Possenti I, Marseglia GL. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease complicated by peripheral neuropathy. Pediatr Neurol. 2012;46:319-321. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 154. | de Larrañaga GF, Remondino GI, Forastiero RR, Cunto ER, Narbaitz M, Olenchuk AB, Zala NS, San Juan JA. Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome and Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: the first case reported. Lupus. 2005;14:967-969. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 155. | Cousin F, Grézard P, Roth B, Balme B, Grégoire-Bardel M, Perrot H. Kikuchi disease associated with Still disease. Int J Dermatol. 1999;38:464-467. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 156. | Hua F, Zhu L. Kikuchi Fujimoto disease associated with cryptogenic organizing pneumonia: case report and literature review. BMC Infect Dis. 2010;10:64. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 157. | Thai LH, Ingen-Housz-Oro S, Godeau B, Rethers L, Wolkenstein P, Limal N, Papillon V, Kapfer J, Chosidow O, Ortonne N. Kikuchi Disease-Like Inflammatory Pattern in Cutaneous Inflammatory Infiltrates Without Lymph Node Involvement: A New Clue for the Diagnosis of Lupus? Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94:e2065. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 158. | Dumas G, Prendki V, Haroche J, Amoura Z, Cacoub P, Galicier L, Meyer O, Rapp C, Deligny C, Godeau B, Aslangul E, Lambotte O, Papo T, Pouchot J, Hamidou M, Bachmeyer C, Hachulla E, Carmoi T, Dhote R, Gerin M, Mekinian A, Stirnemann J, Charlotte F, Farge D, Molina T, Fain O. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: retrospective study of 91 cases and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2014;93:372-382. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 118] [Cited by in RCA: 127] [Article Influence: 11.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 159. | Ruaro B, Sulli A, Alessandri E, Fraternali-Orcioni G, Cutolo M. Kikuchi-Fujimoto's disease associated with systemic lupus erythematous: difficult case report and literature review. Lupus. 2014;23:939-944. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 160. | Kim HA, Im SA, Chung NG, Kang JH, Park GS. Disseminated Kikuchi disease associated with hemophagocytic syndrome in an infant: whole-body MRI. Indian J Pediatr. 2011;78:616-619. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 161. | Tarabichi S, Nicola AA, Radu R, Enache S, Busuioc C, Moldovianu AM, Nitu AF, Predeteanu D, Sarafoleanu C. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease and systemic lupus erythematosus-an enigmatic association for clinicians and pathologists: Case report and short literature review. Romanian J Rhinol. 2022;12:11-21. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 162. | Tumiati B, Bellelli A, Portioli I, Prandi S. Kikuchi's disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: an independent or dependent event? Clin Rheumatol. 1991;10:90-93. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 29] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 163. | Eisner MD, Amory J, Mullaney B, Tierney L Jr, Browner WS. Necrotizing lymphadenitis associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1996;26:477-482. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 56] [Cited by in RCA: 53] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 164. | Mauleón C, Valdivielso-Ramos M, Cabeza R, Rivera T, García I. Kikuchi disease with skin lesions mimicking lupus erythematosus. J Dermatol Case Rep. 2012;6:82-85. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 165. | Jokar M, Mirfeizi Z, Javidi K. Rare association between Kikuchi's disease and systemic lupus erythematosus. Iran J Med Sci. 2009;34:289-291. |
| 166. | Altuntas F, Sari I, Canoz O, Yildiz O, Eser B, Cetin M, Unal A. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: a rare but important cause of fever and lymphadenopathy in pregnant women. Am J Hematol. 2006;81:118-120. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 167. | DuBois RE, Bondell S, Krissman PH. Kikuchi-Fujimoto syndrome during pregnancy. South Med J. 1991;84:1029-1030. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 168. | Alijotas-Reig J, Casellas-Caro M, Ferrer-Oliveras R, Cabero-Roura L, Vilardell-Tarres M. Recurrent Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease during pregnancy: report of case evolving into systemic lupus erythematosus and review of published work. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2008;34:595-598. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 169. | Chuang CH, Yan DC, Chiu CH, Huang YC, Lin PY, Chen CJ, Yen MH, Kuo TT, Lin TY. Clinical and laboratory manifestations of Kikuchi's disease in children and differences between patients with and without prolonged fever. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005;24:551-554. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 32] [Cited by in RCA: 29] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 170. | Kim TY, Ha KS, Kim Y, Lee J, Lee K. Characteristics of Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease in children compared with adults. Eur J Pediatr. 2014;173:111-116. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 40] [Article Influence: 3.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 171. | Seo JH, Kang JM, Lee H, Lee W, Hwang SH, Joo YH. Histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis in children: a clinical and immunohistochemical comparative study with adult patients. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2013;77:429-433. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 172. | Parappil A, Rifaath AA, Doi SA, Pathan E, Surrun SK. Pyrexia of unknown origin: Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39:138-143. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 173. | Sawant SP, Amin AS, Gaddam PR, Chaturvedi UP. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: A clinical enigma. Indian Pediatr Case Rep. 2021;1:102-104. |
| 174. | Noursadeghi M, Aqel N, Gibson P, Pasvol G. Successful treatment of severe Kikuchi's disease with intravenous immunoglobulin. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006;45:235-237. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 29] [Cited by in RCA: 32] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 175. | Lin DY, Villegas MS, Tan PL, Wang S, Shek LP. Severe Kikuchi's disease responsive to immune modulation. Singapore Med J. 2010;51:e18-e21. [PubMed] |
| 176. | Jang YJ, Park KH, Seok HJ. Management of Kikuchi's disease using glucocorticoid. J Laryngol Otol. 2000;114:709-711. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 71] [Cited by in RCA: 81] [Article Influence: 3.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 177. | Rezai K, Kuchipudi S, Chundi V, Ariga R, Loew J, Sha BE. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: hydroxychloroquine as a treatment. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39:e124-e126. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 47] [Cited by in RCA: 58] [Article Influence: 2.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 178. | Hyun M, So IT, Kim HA, Jung H, Ryu SY. Recurrent Kikuchi's Disease Treated by Hydroxychloroquine. Infect Chemother. 2016;48:127-131. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 179. | Faheem B, Kumar V, Ashkar H, Komal F, Sultana Y. Recurrent Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease Masquerading as Lymphoma Successfully Treated by Anakinra. Cureus. 2020;12:e11655. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 180. | Herman TS, Jones SE, McMahon LJ, Lloyd RE, Heusinkveld RS, Miller RC, Salmon SE. Combination chemotherapy with adriamycin and cyclophosphamide (with or without radiation therapy) for carcinoma of the lung. Cancer Treat Rep. 1977;61:875-879. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 181. | Song JY, Lee J, Park DW, Sohn JW, Suh SI, Kim IS, Kim WJ, Kim MJ, Cheong HJ. Clinical outcome and predictive factors of recurrence among patients with Kikuchi's disease. Int J Infect Dis. 2009;13:322-326. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 46] [Cited by in RCA: 61] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 182. | Yoo IH, Na H, Bae EY, Han SB, Lee SY, Jeong DC, Kang JH. Recurrent lymphadenopathy in children with Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease. Eur J Pediatr. 2014;173:1193-1199. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 183. | Jung HJ, Lee IJ, Yoon SH. Risk Assessment of Recurrence and Autoimmune Disorders in Kikuchi Disease. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2020;13:1687-1693. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 184. | Rezayat T, Carroll MB, Ramsey BC, Smith A. A case of relapsing kikuchi-fujimoto disease. Case Rep Otolaryngol. 2013;2013:364795. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 185. | Mahadeva U, Allport T, Bain B, Chan WK. Haemophagocytic syndrome and histiocytic necrotising lymphadenitis (Kikuchi's disease). J Clin Pathol. 2000;53:636-638. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 38] [Cited by in RCA: 38] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 186. | Anuntakarun S, Larbcharoensub N, Payungporn S, Reamtong O. Identification of genes associated with Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease using RNA and exome sequencing. Mol Cell Probes. 2021;57:101728. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 187. | Omachi T, Atsumi N, Yamazoe T, Yamanouchi S, Matsuno R, Kitawaki T, Kaneko K. Differential Diagnosis of Histiocytic Necrotizing Lymphadenitis and Malignant Lymphoma with Simple Clinical Findings. Children (Basel). 2022;9. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |