Published online Apr 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i11.2521
Peer-review started: December 20, 2022
First decision: February 17, 2023
Revised: February 27, 2023
Accepted: March 22, 2023
Article in press: March 22, 2023
Published online: April 16, 2023
Processing time: 107 Days and 3.5 Hours
SMARCA4-deficient undifferentiated tumors (SMARCA4-DUTs) present with diverse clinical manifestations and progress to metastasis and even cause death within a few months. This novel subset of undifferentiated tumors occurs in the middle-aged population and is strongly associated with a smoking history. Distinguishing it from other malignancies is challenging.
A 62-year-old man presented with chest pain for 7 d. The patient had no respiratory symptoms and normal pulmonary function test results. The patient had been a smoker for 8 years and quit smoking 2 years ago. Chest computed tomography revealed a huge mass involving the left upper and lower lung lobes with pericardial invasion and multiple metastases. Tumor samples were obtained using open frozen biopsy, after several unsuccessful attempts. The tumor was composed of sheets of undifferentiated disclosive cells with vesicular nuclei and prominent nucleoli. The differential diagnosis included high-grade lymphoma, germ cell tumor, NUT carcinoma, undifferentiated carcinoma, and sarcoma. The tumor cells were large, arranged in sheets, and did not exhibit glandular or squamous differentiation. Frequent foci of necrosis were noted. There was no evidence of epithelial differentiation on immunohistochemical staining. The SMARCA4 stain showed complete loss of expression of SMARCA4, which is diagnostic.
In the present case, thoracic SMARCA4-DUT was diagnosed based on clinical features, absence of epithelial differentiation, and negative SMARCA4 expression.
Core Tip: SMARCA4-deficient undifferentiated tumors are highly aggressive neoplasms. Here, we report a case of a SMARCA4-deficient undifferentiated tumor with characteristic clinical and histological features. The findings of this case could serve as a resource for future studies.
- Citation: Kwon HJ, Jang MH. SMARCA4-deficient undifferentiated thoracic tumor: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(11): 2521-2527
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i11/2521.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i11.2521
SMARCA4-deficient undifferentiated tumors (SMARCA4-DUTs) are aggressive neoplasms that characteristically involve the thorax. They present with undifferentiated or rhabdoid morphological features with deficiency of Brahma-related gene 1 (BRG1) encoded by SMARCA4. The newly discovered tumor has recently been included in the World Health Organization Classification of Tumors: Thoracic Tumors. The most frequent sites where this tumor occurs are the mediastinum, pulmonary hilum, lung, pleura, and chest wall[1,2]. Most patients present with lung involvement, including variable metastases, at the time of initial diagnosis. Associated symptoms include dyspnea, pain, weight loss, and symptoms based on the involved organs. This tumor is often diagnosed in middle-aged heavy smokers and leads to death within a few months. Over half of the cases are associated with smoking-related emphysema[2,3]. Most cases occur in the fourth to fifth decades of life with a male predominance. Here, we report a case of thoracic SMARCA4-DUT in an older man with a characteristic clinical presentation.
A 62-year-old man presented with pain in the left chest and right flank for 7 d.
The patient had no respiratory symptoms, and pulmonary function test results were normal.
The patient was previously healthy and had no relevant medical history.
The patient had been a smoker for 8 years (35 pack-years) and quit smoking 2 years earlier.
Physical examination was unremarkable.
A routine blood examination, including tests for white blood cell count, hemoglobin, and other electrolytes, indicated that all levels were within normal range. However, the results of the biochemical tests indicated a slight increase in lactate dehydrogenase (1824 IU/L, with a reference range of 208-450 IU/L) and C-reactive protein (0.885 mg/dL, with a reference range of 0.0-0.5 mg/dL). A polymerase chain reaction test for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) was conducted, but no evidence of the virus that causes COVID-19 was found.
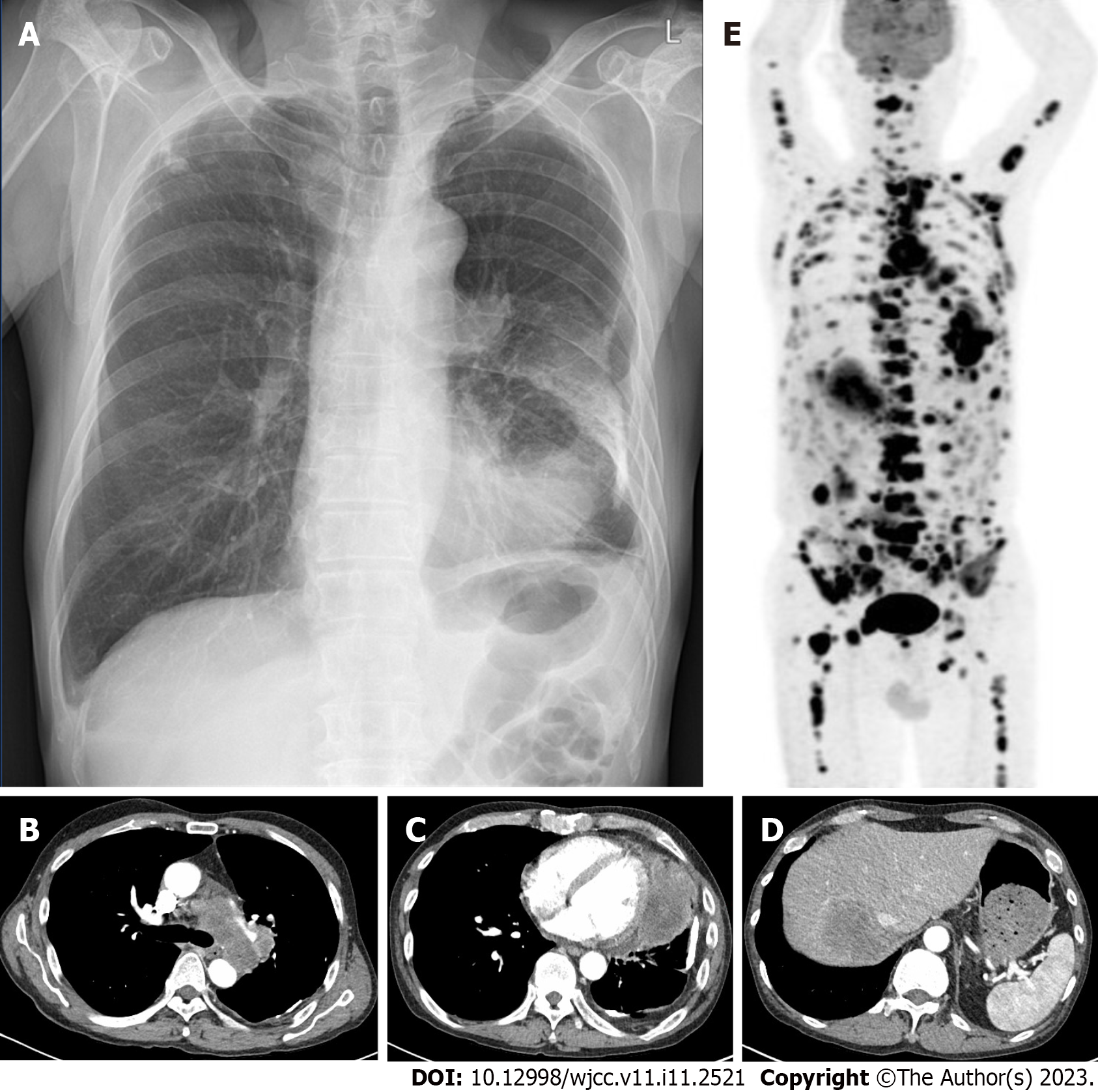
The posteroanterior view of the chest radiograph showed a lesion of dense consolidation in the left lower pericardial area and calcific nodules consistent with an old tuberculosis scar in both upper lobes (Figure 1A). Additional chest computed tomography revealed several enlarged mediastinal lymph nodes (Figure 1B) and a huge mass with necrosis, involving the upper and lower lobes of the left lung, with invasion of the pericardium (Figure 1C). In addition, a low-attenuation lesion was present in the liver, consistent with a metastatic tumor (Figure 1D). Further, multiple lymphadenopathies were found in the bilateral paratracheal, subcarinal, left hilar, left cardiophrenic, internal mammary, and upper abdominal areas. The right lower lung lobe showed small nodules and mild pericardial effusion, also consistent with metastasis. An approximately 9-cm sized lesion in the left lung showed uneven 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake on positron emission tomography (PET; Figure 1E). Further, PET showed numerous metastatic lesions involving the mediastinum; liver; bilateral lung lobes; bones of the skull, bilateral humeri, scapula, left clavicle, sternum, vertebras (cervical, thoracic, lumbar), bilateral ribs, pelvis, and bilateral femurs; peritoneum; and retroperitoneum.
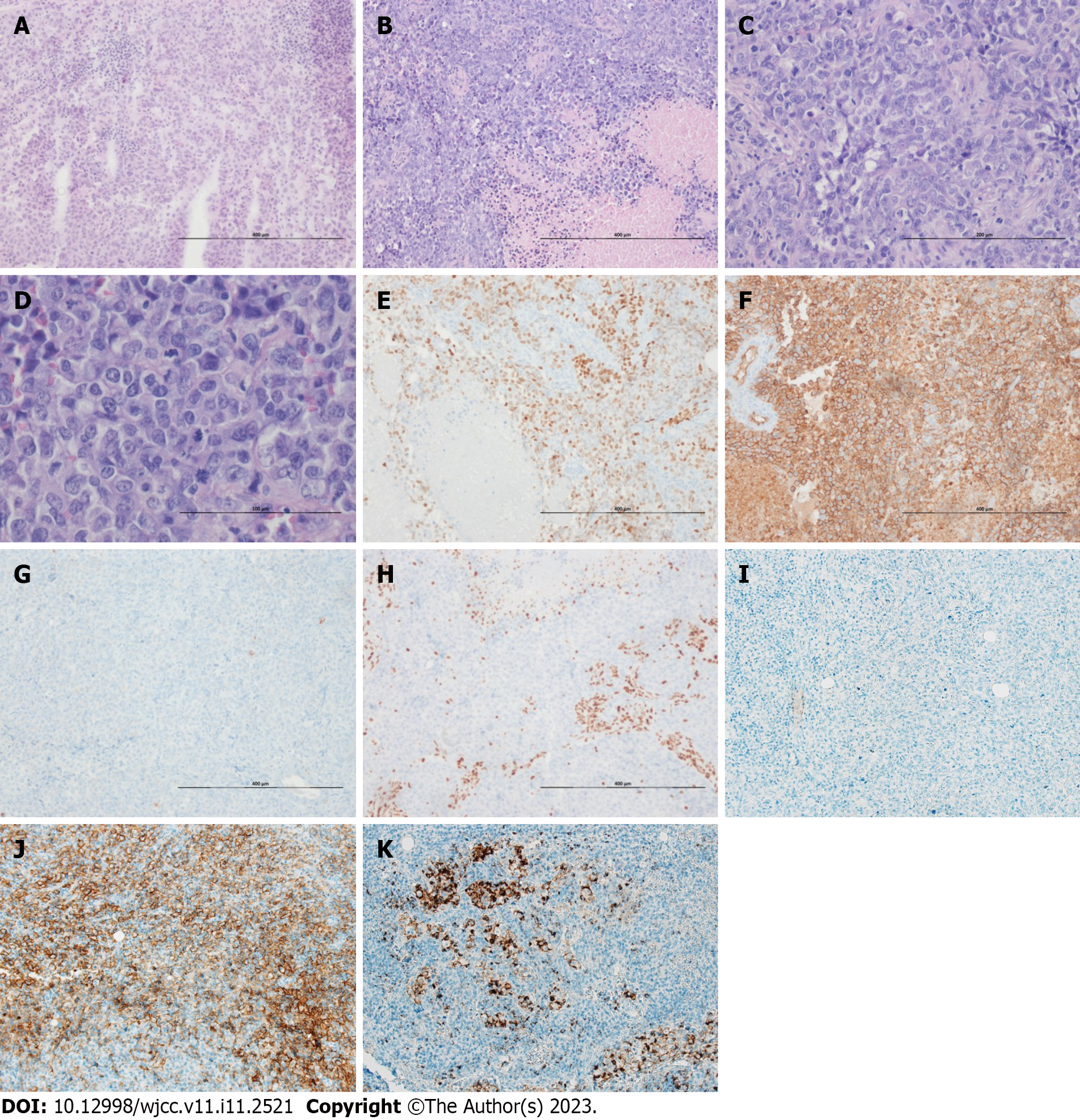
Despite the large size of the tumor, both endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial lung biopsy and bronchial washing performed twice failed to obtain a sufficient amount of tumor cells. Due to necrosis, tumor cells were insufficient for a definitive diagnosis. Tumor specimens were finally obtained from the mediastinal node using mediastinoscopy and pleural biopsy. The largest biopsy sample, measuring 2.5 cm × 1.8 cm × 0.5 cm in size, was received from the operation theater in the fresh state. The mass had a tan to yellowish cut surface. The representative tissue was fixed in 10% neutral formalin and processed for pathologic examination after a frozen section diagnosis. On hematoxylin and eosin staining, the tumor cells were large, round to epithelioid, arranged in diffuse sheets, and did not exhibit glandular or squamous differentiation (Figure 2). Frequent foci of necrosis were noted on frozen and post fixation tissue sections (Figure 2A and B). The tumor cells showed moderate pleomorphism and had abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm (Figure 2C and D). Nuclei were monotonous and vesicular with conspicuous nucleoli. The mitotic activity was high (Figure 2D). Immunohistochemically, the tumor cells were positive for spalt-like transcription factor 4 (SALL4; Figure 2E), CD34 (Figure 2F), and cytoplasmic p53 (aberrant expression) and negative for CAM5.2, erythroblast transformation-specific-related gene, AE1/AE3 cytokeratin (Figure 2G), thyroid transcription factor-1, p40, CK5/6, nuclear protein in testis (NUT), CD20, and S100 protein. The SMARCA4 stain showed complete loss of expression, which was diagnostic. (Figure 2H). Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK, D5F3) showed negative activity (Figure 2I). Programmed death-ligand 1 (PDL1) tests showed positivity (Figure 2J, Ventana SP263; Figure 2K, SP142). No epidermal growth factor receptor mutation was detected on pyrosequencing.
Histopathology confirmed the diagnosis of SMARCA4-DUT.
After mediastinoscopy and pleural biopsy, the patient was discharged on postoperative day 13 with pain control.
Twenty days after the biopsy, the patient complained of dyspnea on exercise, hoarseness, and a poor general condition. He has not visited the hospital for over 10 mo, thereafter.
Thoracic SMARCA4-DUT is a newly discovered aggressive malignancy whose pathogenesis remains unclear. The most frequent sites of occurrence of this tumor are the mediastinum, pulmonary hilum, lungs, and pleura or chest wall. SMARCA4-DUTs have undifferentiated or rhabdoid morphological features with deficiency of SMARCA4. They occur most commonly in young men with a history of heavy smoking, but can occur in patients of any age. In addition to our patient, there have been other reports of the tumor presenting at an advanced age. Associated symptoms include dyspnea, pain, weight loss, and symptoms based on the involved organs. Common sites of metastasis include the lymph nodes, bones, and adrenal glands and rarely the brain[4,5].
The tumor-suppressor role of SMARCA4 (or BRG1) was reported in 2000[6]. Nonsense and frameshift mutations in SMARCA4 are the dominant oncogenic molecular alterations underlying the pathogenesis of this neoplasm. The hallmark of the diagnosis is loss of SMARCA4 (BRG1) expression on immunohistochemical staining. SMARCA4 deficiency is found in most cases. However, sequencing of SMARCA4 alteration is not necessary for the diagnosis, as the truncated protein can occasionally be partially recognized by the antibody, which leads to unstable binding and degradation, explaining the attenuated immunoreactivity in certain cases[7]. Additional molecular tests may help confirm the diagnosis of SMARCA4-deficient tumors when immunohistochemistry findings cannot be interpreted with certainty[7].
Concurrent loss of the SMARCA2 expression and expression of one or more stem cell markers, such as sex determining region Y-box 2, SALL4, or CD34, is common. SMARCA4 deficiency is a passenger somatic alteration in multiple solid tumors manifesting as focal dedifferentiation and a rhabdoid morphology[8]. SMARCA4-DUT and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with SMARCA4-deficiency show considerable overlap in their clinicopathological features, such as male preponderance, association with smoking, pattern of metastasis, rapidly fatal outcomes, immunohistology findings, and molecular alterations[1]. Morphologically, SMARAC4-DUT is differentiated from SMARCA4-deficient NSCLC by the absence of squamous and solid components[9].
However, the incidence of SMARAC4-DUTs is too low to be included in the differential diagnosis of poorly differentiated tumors. To date, approximately 100 cases of SMARCA4-DUTs have been reported in the literature[10]. Further, SMARAC4-DUTs are commonly located in the thorax, from which only small biopsy samples are usually available. The present patient underwent frozen biopsy after endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial lung biopsy and bronchial washing performed twice failed to obtain sufficient amount of tumor cells because of tumor necrosis. Owing to metastasis, other organs, such as the adrenal gland, may be biopsied first[4]. These issues make it difficult to reach a definitive diagnosis.
SMARCA4-DUTs show an undifferentiated morphology with occasional rhabdoid features. Considering histological findings and clinical presentation, such as significant progression at the time of initial diagnosis, it will not be difficult to include SMARCA4-DUT in the differential diagnosis using integrase interactor 1 (INI1) staining in the ancillary test.
SMARCA4-DUTs are rapidly fatal and are refractory to conventional therapies. Although responses vary, immunotherapy is promising. The PDL1 expression appears to be of a poor predictive value. Drugs targeting genetic and epigenetic mechanisms of SMARCA4 antagonism have therapeutic potential[10].
This case demonstrates the typical clinical presentation and morphological features of SMARCA4-DUTs: Diffuse sheets of large round to epithelioid poorly cohesive cells with a high nuclear grade and frequent necrosis on frozen sections. Tumor cell nuclei are typically vesicular, monotonous with moderate pleomorphism, and with a markedly increased mitotic activity. These features were also observed in the frozen sections of the tumor in the present case. A clinicopathologic correlation is crucial for patients’ care because of the aggressive behavior of the tumor.
We report a case of SMARCA4-DUT with characteristic clinical manifestations. This novel subset of tumors should be suspected in patients with rapidly growing mediastinal and pulmonary nodules. The diagnosis can be obtained based on combined clinical features and histopathological features, such as absence of epithelial differentiation and negative SMARCA4 expression.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Pathology
Country/Territory of origin: South Korea
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B, B
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): D
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Moshref L, Saudi Arabia; Vyshka G, Albania; Yang L, China S-Editor: Yan JP L-Editor: A P-Editor: Yan JP
| 1. | Perret R, Chalabreysse L, Watson S, Serre I, Garcia S, Forest F, Yvorel V, Pissaloux D, Thomas de Montpreville V, Masliah-Planchon J, Lantuejoul S, Brevet M, Blay JY, Coindre JM, Tirode F, Le Loarer F. SMARCA4-deficient Thoracic Sarcomas: Clinicopathologic Study of 30 Cases With an Emphasis on Their Nosology and Differential Diagnoses. Am J Surg Pathol. 2019;43:455-465. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 75] [Cited by in RCA: 131] [Article Influence: 26.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Rekhtman N, Montecalvo J, Chang JC, Alex D, Ptashkin RN, Ai N, Sauter JL, Kezlarian B, Jungbluth A, Desmeules P, Beras A, Bishop JA, Plodkowski AJ, Gounder MM, Schoenfeld AJ, Namakydoust A, Li BT, Rudin CM, Riely GJ, Jones DR, Ladanyi M, Travis WD. SMARCA4-Deficient Thoracic Sarcomatoid Tumors Represent Primarily Smoking-Related Undifferentiated Carcinomas Rather Than Primary Thoracic Sarcomas. J Thorac Oncol. 2020;15:231-247. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 96] [Cited by in RCA: 207] [Article Influence: 34.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Yoshida A, Kobayashi E, Kubo T, Kodaira M, Motoi T, Motoi N, Yonemori K, Ohe Y, Watanabe SI, Kawai A, Kohno T, Kishimoto H, Ichikawa H, Hiraoka N. Clinicopathological and molecular characterization of SMARCA4-deficient thoracic sarcomas with comparison to potentially related entities. Mod Pathol. 2017;30:797-809. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 105] [Cited by in RCA: 153] [Article Influence: 19.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Ashour S, Reynolds JP, Mukhopadhyay S, McKenney JK. SMARCA4-Deficient Undifferentiated Tumor Diagnosed on Adrenal Sampling. Am J Clin Pathol. 2022;157:140-145. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Yadav R, Sun L, Salyana M, Eric M, Gotlieb V, Wang JC. SMARCA4-Deficient Undifferentiated Tumor of Lung Mass-A Rare Tumor With the Rarer Occurrence of Brain Metastasis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2022;10:23247096221074864. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 6. | Wong AK, Shanahan F, Chen Y, Lian L, Ha P, Hendricks K, Ghaffari S, Iliev D, Penn B, Woodland AM, Smith R, Salada G, Carillo A, Laity K, Gupte J, Swedlund B, Tavtigian SV, Teng DH, Lees E. BRG1, a component of the SWI-SNF complex, is mutated in multiple human tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 2000;60:6171-6177. [PubMed] |
| 7. | Kuwamoto S, Matsushita M, Takeda K, Tanaka N, Endo Y, Yamasaki A, Kohashi K, Oda Y, Horie Y. SMARCA4-deficient thoracic sarcoma: report of a case and insights into how to reach the diagnosis using limited samples and resources. Hum Pathol. 2017;70:92-97. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 32] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Chatzopoulos K, Boland JM. Update on genetically defined lung neoplasms: NUT carcinoma and thoracic SMARCA4-deficient undifferentiated tumors. Virchows Arch. 2021;478:21-30. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 39] [Article Influence: 9.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 9. | Nambirajan A, Singh V, Bhardwaj N, Mittal S, Kumar S, Jain D. SMARCA4/BRG1-Deficient Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinomas: A Case Series and Review of the Literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2021;145:90-98. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 53] [Article Influence: 13.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Nambirajan A, Jain D. Recent updates in thoracic SMARCA4-deficient undifferentiated tumor. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2021;38:83-89. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 48] [Article Influence: 12.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |