Published online May 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i15.5097
Peer-review started: December 22, 2021
First decision: February 21, 2022
Revised: February 22, 2022
Accepted: March 27, 2022
Article in press: March 27, 2022
Published online: May 26, 2022
Processing time: 153 Days and 11.8 Hours
Knot impingement as a complication after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair (ARCR) has been suggested as a cause of persistent pain with limited motion. We report on a case involving a patient who developed knot impingement after ARCR who complained of acute onset of pain with limited motion, which was confused with infection.
A 55-year-old female who complained of severe pain with limited motion of the right shoulder visited our emergency room. Passive range of motion could not be evaluated due to the patient’s severe pain. The patient had undergone ARCR using a suture-bridge technique at a local clinic four months ago for treatment of a small supraspinatus tear of the right shoulder. An erosive change of the undersurface of the acromion was observed on plain radiographs of the right shoulder, and a moderate amount of bursal fluid and synovial thickening with enhancement was observed by magnetic resonance imaging. Results of an analysis of the aspirated fluid showed that the WBC count was 3960 with 90% neutrophils. The arthroscopic view showed healing of the repaired supraspinatus tendon and loose suture threads and knots with severe subacromial bursitis were observed. Debridement of inflammatory tissues of the glenohumeral joint and subacromial space was performed for the removal of all suture materials. The patient’s symptoms subsided immediately after the surgical procedure.
Although the incidence of knot impingement is rare, the possibility of knot impingement after ARCR should be a consideration.
Core Tip: Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair (ARCR) is a procedure that is widely performed with satisfactory outcomes. Development of knot impingement as a rare complication after ARCR has been suggested as a cause of persistent pain with limited motion. Because of its rarity, knowledge regarding clinical features in patients with knot impingement after ARCR is limited. We suggest consideration of knot impingement after ARCR as a cause of acute shoulder pain.
- Citation: Kim DH, Jeon JH, Choi BC, Cho CH. Knot impingement after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair mimicking infection: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(15): 5097-5102
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i15/5097.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i15.5097
Determining the cause of acute joint pain in patients with no history of trauma can be challenging for the orthopedic clinician[1]. Because the destruction of the involved joint can occur rapidly, a septic condition should be considered when making a diagnosis. However, making a differential diagnosis of infection from other problems that can induce acute joint pain is not always easy. Acute onset of shoulder pain is a relatively common symptom observed in the clinical setting. The most common causes of acute shoulder pain include calcific tendinitis, subacromial bursitis, and septic arthritis[1].
Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair (ARCR) is a procedure that is widely performed with satisfactory outcomes[2-5]. Development of knot impingement as a complication after ARCR has been suggested as a cause of persistent pain with limited motion[6,7]. To date, only 13 cases involving knot impingement after ARCR have been reported and most of the patients complained of insidious onset of pain during shoulder motion[6-8]. Previous studies have focused on the pathogenesis of bone erosion on the acromial undersurface caused by suture knots[6-8]. Because of its rarity, information regarding the clinical features in patients with knot impingement after ARCR is limited.
We report on a case involving a patient who developed knot impingement after ARCR who complained of acute onset of pain with limited motion, which was confused with infection. This report describes our experience with a rare case mimicking infection; successful management was achieved by arthroscopic removal of the knot.
A 55-year-old female who complained of severe pain with limited motion of the right shoulder visited our emergency room.
Development of pain had occurred two days ago; the pain was dull and continuous in nature regardless of shoulder motion.
The patient had undergone ARCR using a suture-bridge technique at a local clinic four months ago for treatment of a small supraspinatus tear of the right shoulder.
The patient had no personal or family history.
Tenderness on the involved shoulder was observed and body temperature was 37.4 oC. Her active range of motion was 45o of forward flexion, 30o of abduction, 25o of external rotation at the side, and buttock level of internal rotation at the back. Passive range of motion could not be evaluated because the patient was experiencing severe pain.
According to the results of laboratory tests, the white blood cell count was 7920/μL (normal ranges, 4000-10000/μL) with 66.9% neutrophils. C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) were elevated at 8.4 mg/dL (normal ranges, 0.0-0.5 mg/dL) and 50 mm/hr (normal ranges, 0-25 mm/hr), respectively. Because a septic condition was suspected, aspiration was performed through the subacromial space and 2 cc of yellowish fluid with mucoid nature was obtained. Results of the fluid analysis showed that the WBC count was 3960 with 90% neutrophils.
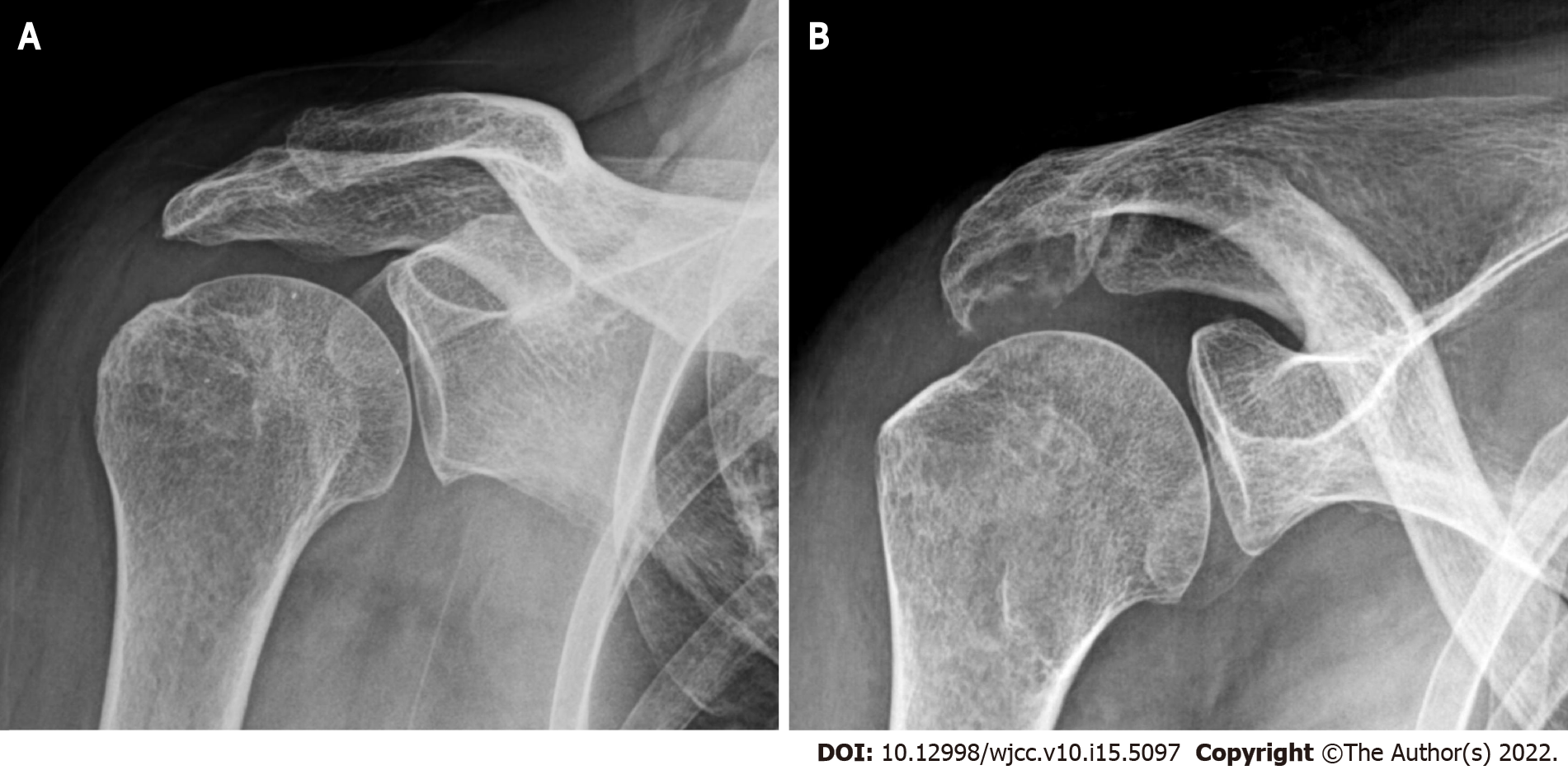
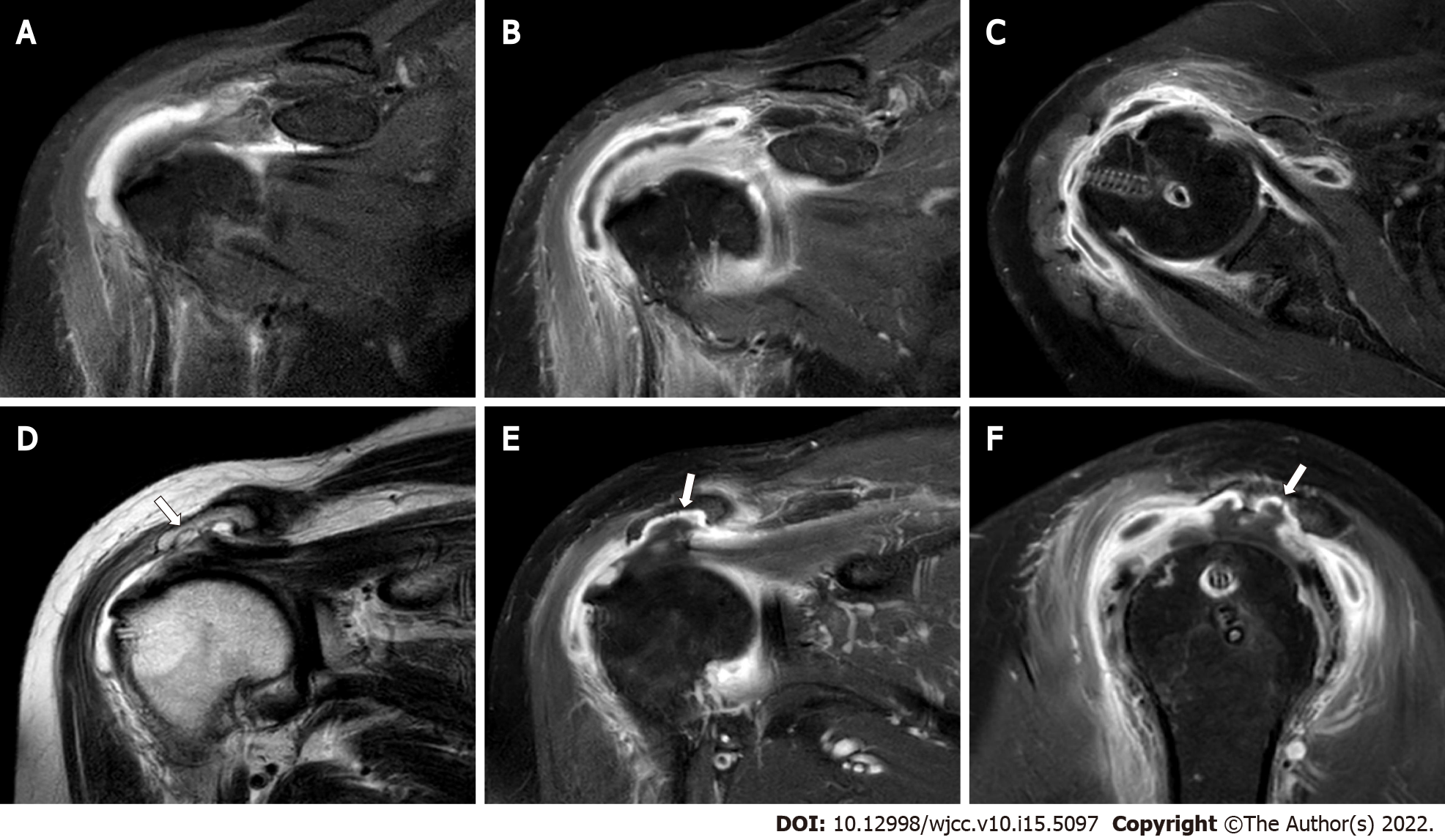
An erosive change of the undersurface of the acromion was observed on plain radiographs of the right shoulder at 30o caudal tilting view (Figure 1). A moderate amount of bursal fluid and synovial thickening with enhancement was observed by enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (Figure 2). In addition, an irregular erosive change of the undersurface of the acromion was also observed.
Although a definite diagnosis of infection was not indicated by these findings, because the possibility of infection could not be ruled out completely based on the clinical symptoms, the patient was scheduled to undergo emergency arthroscopic surgery.
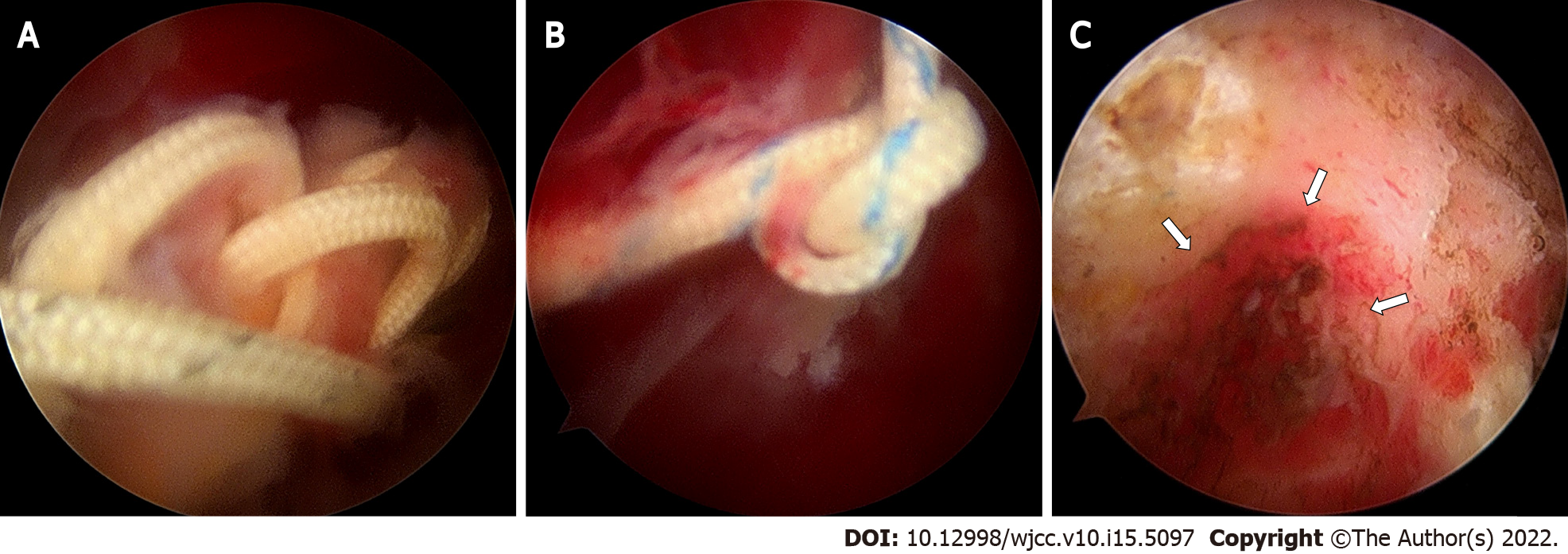
The arthroscopic view showed healing of the repaired supraspinatus tendon and loose suture threads and knots with severe subacromial bursitis were observed. Impingement of suture knots was observed at the undersurface of the acromion, resulting in erosion of subacromial bone (Figure 3). Debridement of inflammatory tissues of the glenohumeral joint and subacromial space was performed for removal of all suture materials.
The final culture from the aspirated bursal fluid showed no growth of organisms. The patient’s symptoms subsided immediately after this procedure. Completely restored range of motion without pain at rest or activity was observed at one-year follow-up after surgery.
Knot impingement has recently been described as a complication occurring after ARCR resulting in pain during motion; additional surgery may be necessary for removal of the suture knots[6,7]. To date, only 13 cases involving knot impingement after ARCR have been reported[6-8]. In 2010, Hotta and Yamashita[6] first reported that acromial erosion was observed in nine of 434 (2.1%) patients who had undergone ARCR. They found an association between the knot position and the portion of osteolysis on the undersurface of the acromion; the patients no longer had symptoms after removal of the knots[6]. They concluded that this complication might have been caused by knot impingement resulting from the knots of the suture thread[6]. Park et al[8] also reported that acromial erosion was observed in three of 221 (1.4%) patients with ARCR. Uchida et al[7] recently reported two cases involving symptomatic knot impingement resulting in subacromial bone erosion.
Suggested causes of knot impingement after ARCR include the position of the knot, exposure of cancellous bone after acromioplasty, and stronger suture materials[6-8]. Hotta and Yamashita[6], who reported observing knots on the top of the greater tuberosity in all cases involving knot impingement, suggested that the use of a knotless or suture-bridge repair technique may be helpful in prevention of symptomatic knot impingement during ARCR. However, Park et al[8] reported that there was no difference in acromial erosion in high-profile knots made using a single row technique compared with a double row suture-bridge technique. Acromial erosion due to knot impingement may be the result of exposure of weak cancellous bone after acromioplasty[6,8]. Anchor suture limbs have recently been replaced by strong braided nonabsorbable suture materials such as FiberWire (Arthrex, Naples, FL, United States), resulting in stronger knots without suture breakage during ARCR[8]. However, these characteristics may contribute to development of knot impingement after ARCR. In our case, acromioplasty and ARCR were performed using suture anchors with strong braided nonabsorbable suture threads. Even though a suture-bridge technique was used in performance of ARCR, an association of knot impingement with loose suture threads and knots was confirmed.
Because of its rarity, there is a poor understanding of clinical features in patients with knot im
A review of the literature found that some shoulder problems such as calcific tendinitis, subacromial bursitis, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, small lymphocytic lymphoma, and deep vein thrombosis can mimic infection by presenting with acute onset of severe pain[1,9,10]. Although the incidence is rare, the possibility of knot impingement should be considered for patients with acute pain and limited motion of the shoulder who have a history of ARCR.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of knot impingement after ARCR mimicking infection with successful management by arthroscopic removal of the knot. We suggest consideration of knot impingement after ARCR as a cause of acute shoulder pain.
The authors thank Eun-Ji Jeon for her support.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Medicine, research and experimental
Country/Territory of origin: South Korea
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Liu P, China; Roach CJ, United States S-Editor: Fan JR L-Editor: A P-Editor: Fan JR
| 1. | Ross G, Cooper J, Minos L, Steinmann SP. Acute calcific tendinitis of the shoulder mimicking infection: arthroscopic evaluation and treatment--a case report. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2006;35:572-574. [PubMed] |
| 2. | Oh SY, Jang YH, Chae IS, Kim SH. Prevalence and Clinical Impact of Acromial Cupping after Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair: Does Acromioplasty Matter? Clin Orthop Surg. 2021;13:520-528. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Lee D, Lee KH, Jo YH, Joo IH, Lee HJ, Jeong SY, Lee BG. Correlation between Severity of Synovitis and Clinical Features in Rotator Cuff Tears. Clin Orthop Surg. 2021;13:88-96. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Kim H, Song HS, Kang SG, Han SB. Arthroscopic Capsular Repair without Relaying Sutures: 'Simple Sewing Technique'. Clin Shoulder Elb. 2019;22:146-148. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Park JY, Lee JH, Oh KS, Chung SW, Choi Y, Yoon WY, Kim DW. Rotator cuff retear after repair surgery: comparison between experienced and inexperienced surgeons. Clin Shoulder Elb. 2021;24:135-140. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Hotta T, Yamashita T. Osteolysis of the inferior surface of the acromion caused by knots of the suture thread after rotator cuff repair surgery: knot impingement after rotator cuff repair. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19:e17-e23. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Uchida A, Mihata T, Neo M. Subacromial bone erosion due to suture-knots in arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: A report of two cases. Asia Pac J Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Technol. 2019;16:30-35. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Park YE, Shon MS, Lim TK, Koh KH, Jung SW, Yoo JC. Knot impingement after rotator cuff repair: is it real? Arthroscopy. 2014;30:1055-1060. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Donovan A, Schweitzer ME, Garcia RA, Nomikos G. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma presenting as septic arthritis of the shoulder. Skeletal Radiol. 2008;37:1035-1039. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Lisse JR, Thurmond-Anderle M, Davis CP. Deep venous thrombosis in intravenous cocaine abuse mimicking septic arthritis of the shoulder. South Med J. 1991;84:278-279. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |