Published online May 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i15.5057
Peer-review started: December 11, 2021
First decision: January 26, 2022
Revised: February 3, 2022
Accepted: March 27, 2022
Article in press: March 27, 2022
Published online: May 26, 2022
Processing time: 163 Days and 23 Hours
Rectal melanoma is an uncommon neoplasm that accounts for approximately 1 percent of rectal cancer cases. Abdominoperineal resection was regarded as the radical procedure for disease control. Nevertheless, it led to more postoperative complications than sphincter-sparing wide local excision (WLE) and reduced the patient’s quality of life (QOL) owing to creation of colostomy. Therefore, in this study, WLE, radiotherapy (RT), and a second WLE were conducted on a patient who had been diagnosed with localized rectal melanoma.
The patient was a 79-year-old woman who had been experiencing anal pain and bloody stool for 1 mo. Colonoscopy, magnetic resonance imaging, positron emission tomography–computed tomography, and histological analysis of tissue biopsy using the histological markers Melan-A (+), S-100 (+), and Ki-67 (+, 50%) lead to the diagnosis of localized rectal melanoma. The patient had initially undergone WLE to resolve problem of anal bleeding, followed by RT to treat the residual lesion with partial response. Subsequently, the residual lesion was removed with margin-free resection by the second WLE. The patient’s postoperative course was smooth and uneventful. During the 2-year follow-up, no local recurrence was observed. Additionally, a good functional outcome and improved QOL were reported.
Combining WLE, RT, and repeat WLE is proposed as a viable alternative for treating rectal melanoma accompanied by bleeding symptoms that cannot be completely resected at the beginning.
Core Tip: Combining repeat sphincter-sparing wide excision and radiotherapy is proposed as a viable alternative to achieve negative resection margins, a lowered local recurrence, better functional outcomes, and quality of life using the least radical procedure in patients diagnosed with localized rectal melanoma.
- Citation: Chiu HT, Pu TW, Yen H, Liu T, Wen CC. Is repeat wide excision plus radiotherapy of localized rectal melanoma another choice before abdominoperineal resection? A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(15): 5057-5063
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i15/5057.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i15.5057
Rectal melanoma is a rare disease that occurs in the rectal mucosa. In some cases, the rectal melanoma lesion can be pigmented. It occurs in approximately 1 percent of rectal cancer cases[1], with the poor outcome being recorded regularly, which is commonly accompanied by implantation above the dentate line in elder female. Bloody stool, rectorrhagia, and proctalgia are common symptoms. Mostly, the disease is initially misdiagnosed as hemorrhoids or polyp. However, most patients would have experienced nodal metastasis at diagnosis. In addition, it is estimated that 30% of the patients would have experienced distal organ metastasis[2]. Macroscopically, the tumor appears as a polypoid intraluminal lesion or a mild peripheral wall thickening. In the scan of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), rectal melanoma presents as a polypoid lesion with hyperintense on T1-weighted scan and hypo- or mixed intense on T2-weighted scan with moderate to strong enhancement and diffusion limitations being recorded. In contrast, positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET-CT) is a good tool for tumor staging due to its high sensitivity and specificity. S-100 and HMB-45, as the histological markers, which have frequently been identified microscopically, have also been proposed to help with diagnosis. Moreover, no strong evidence exists in the National Clinical Cancer Network guidelines on the diagnosis of rectal melanoma owing to paucity of the available data. As a result, treatment is highly variable, with no consensus being reached to date. Radical procedure with abdominoperineal resection (APR) is the standard method due to its better local control rate than wide local excision (WLE) before[3,4]. However, it led to more operative complications and lower quality of life (QOL) owing to creation of colostomy. Therefore, WLE has been regarded as an alternative option for better functional performance management to decrease the surgery-related morbidity experienced with APR[5]. Nevertheless, there are many disadvantages of the clinical use of WLE, particularly when the tumor size is too large to be completely resected initially. The incidence of local recurrence after surgery has been reported to be high[6,7]. This consequently compromises the goal of performing limited surgeries. Rectal melanoma was known as a radio-resistant neoplasm previously. Since the late 1980s, Kelly et al[8] presented that combined WLE and post-operative radiotherapy (RT) can reduce the incidence of local recurrence in patients with localized anorectal melanoma[8]. Hence, an adequate surgical approach is proposed in this study to minimize operative complications, achieve R0 resection, lower regional recurrence, maintain functional outcomes, and improve the patient’s QOL. Functional outcomes regarding the frequency of bowel movements, strained defecation, urgency, and perianal irritation are presented in Supplementary Table 1. QOL was also evaluated using the 36-Item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36) (Supplementary Table 2)[9]. Thus, this study combined WLE, RT, and a second WLE as an appropriate strategy to balance functional outcomes and control disease symptoms in an elderly patient diagnosed with localized rectal melanoma.
The patient was a 79-year-old woman who presented with perianal pains and episodes of bloody stool for 1 mo.
The patient reported a 1-mo history of perianal pains and intermittent hematochezia for 1 mo, but denied complaining abdominal discomfort and no body weight loss over the past month.
The patient denied the past medical and surgical histories.
The patient denied the personal and family histories.
Rectal examinations revealed a polypoid mass over the lower rectum.
Serum tumor markers, including carcinoembryonic antigen, cancer antigen-125 and cancer antigen-199 revealed in normal ranges. In addition, normal liver and kidney function were revealed. Mild anemia with hemoglobin of 10.1 g/dL (normal range: 12-16) was revealed.
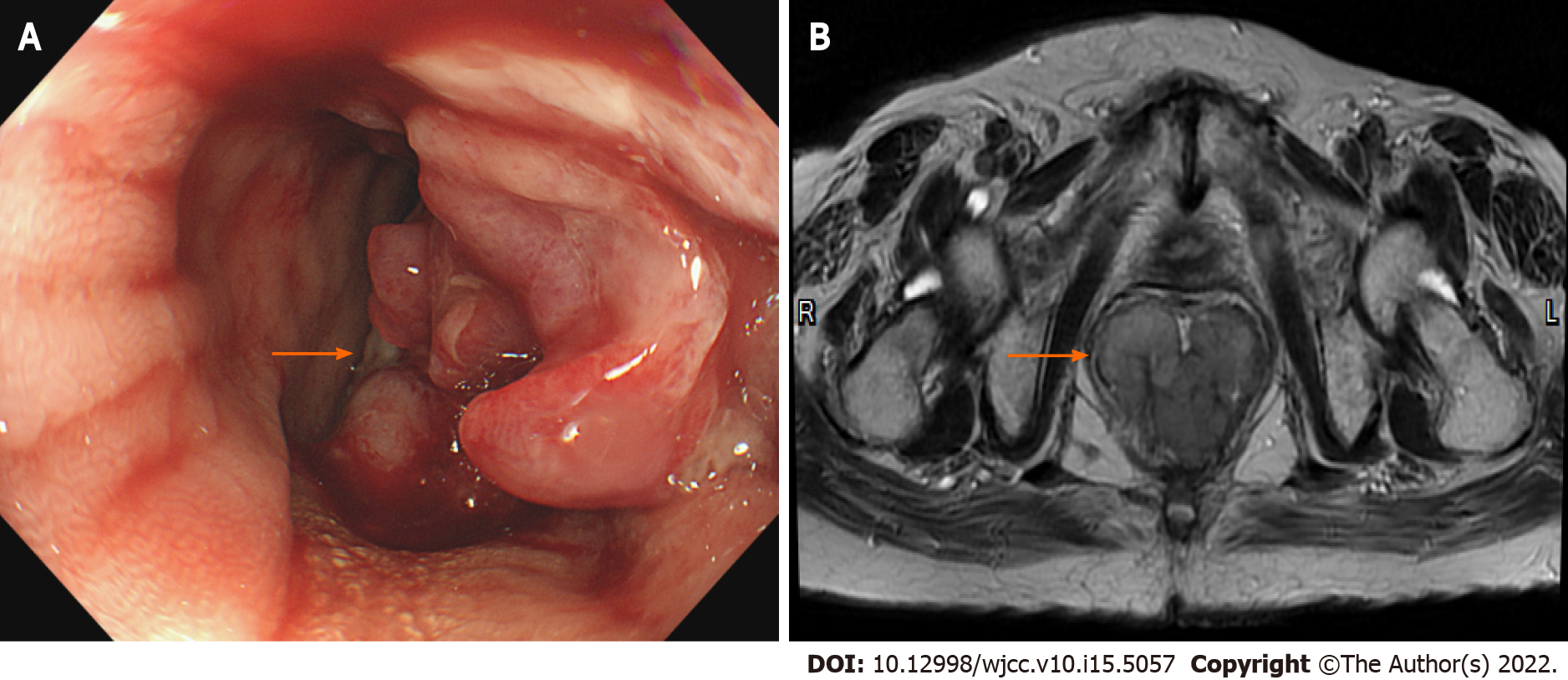
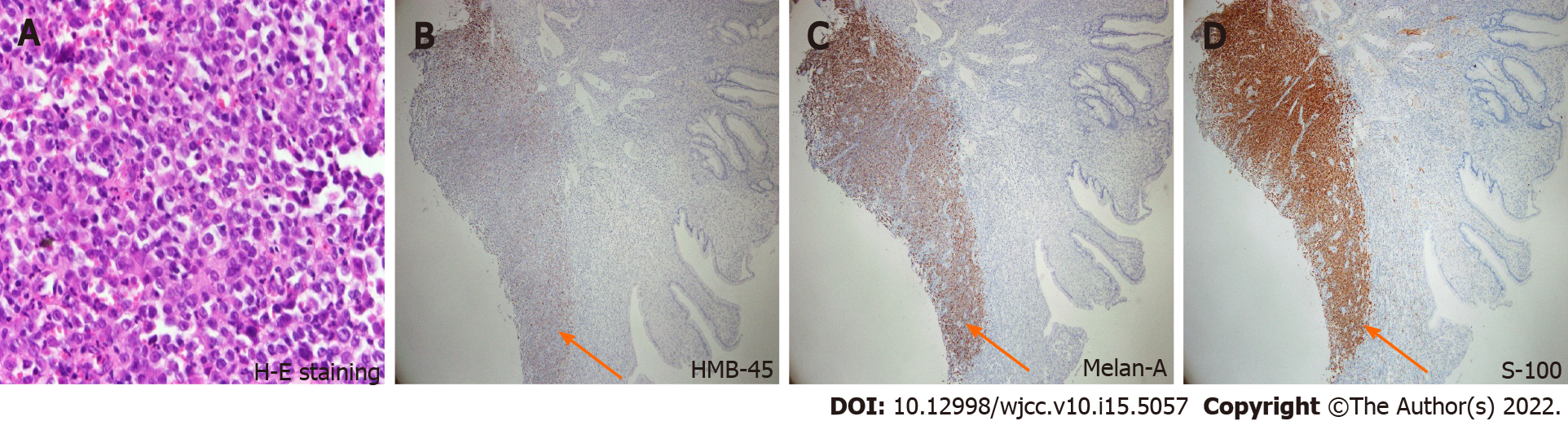
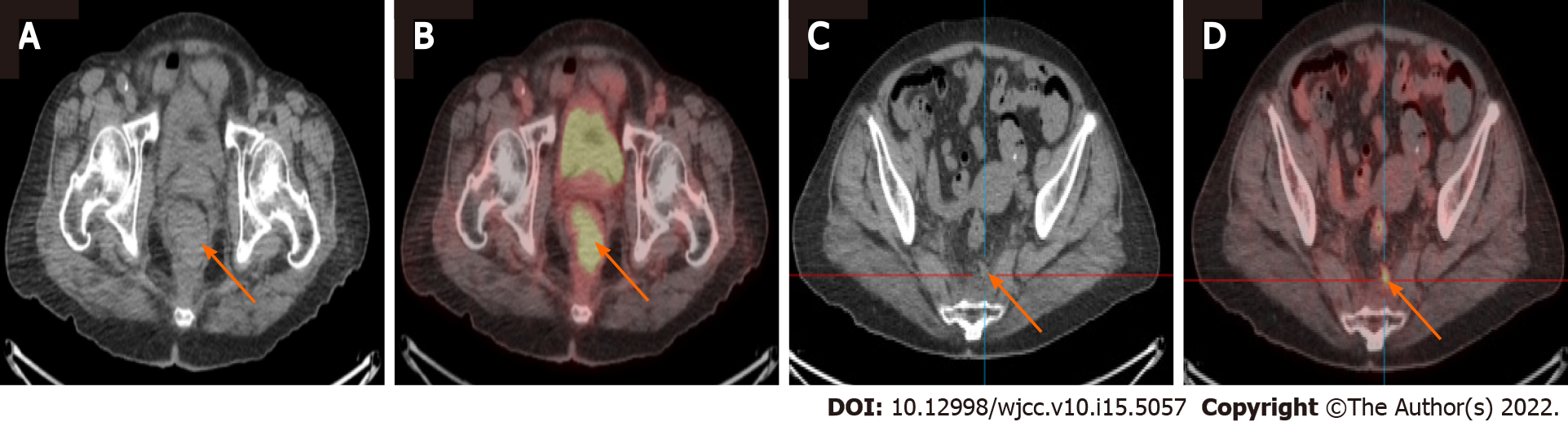
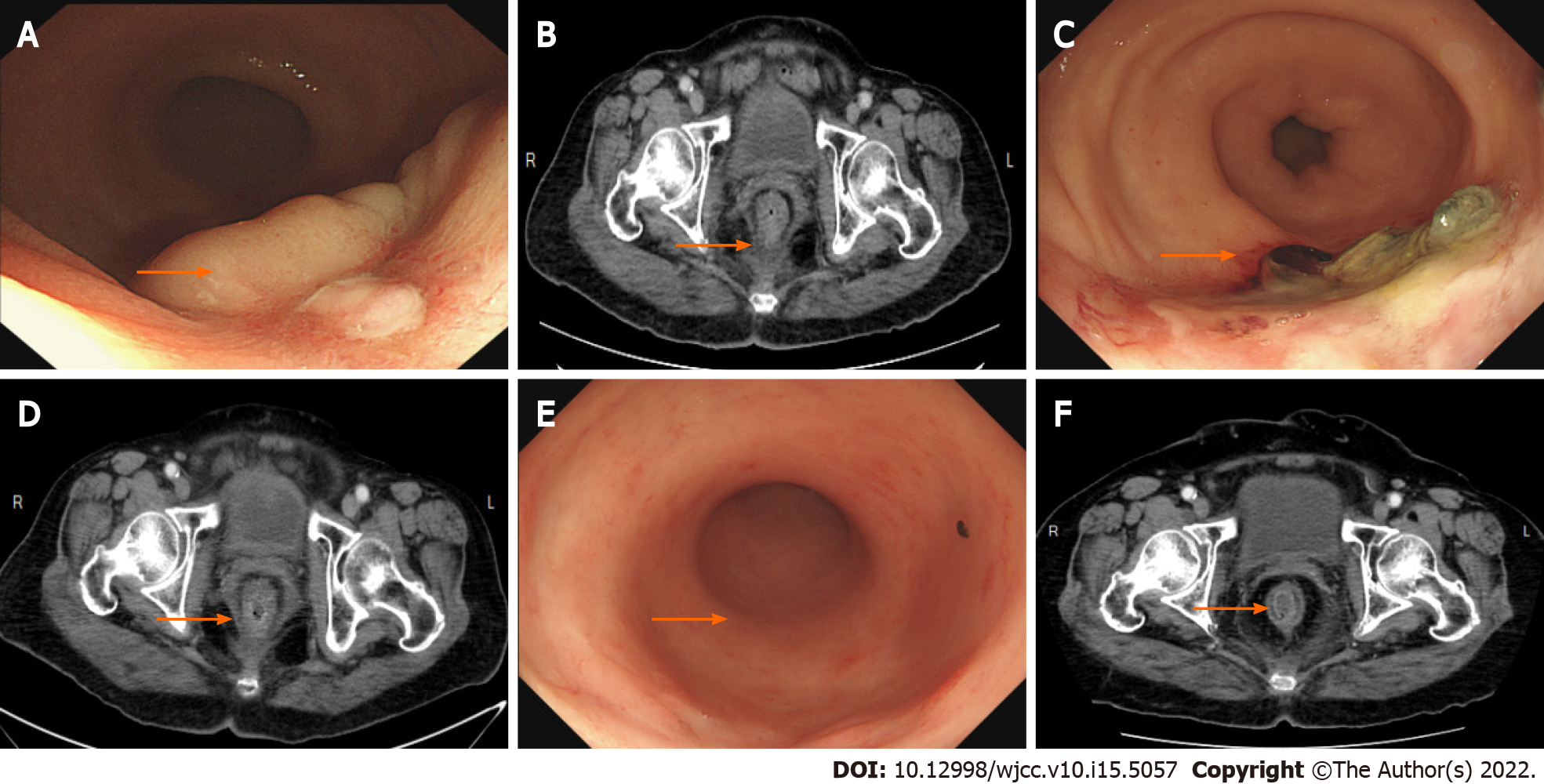
Colonoscopy showed a polypoid lesion which is approximately 6 cm in diameter and 5 cm above the anal verge (Figure 1A). Additionally, the pelvic MRI showed the lobulated mixed-signal intensity lesion at the rectum on the T2-weighted scan (Figure 1B). Therefore, biopsy via colonoscopy was performed and the malignant melanoma was diagnosed by histopathology. The patient’s immunohistochemistry tumor profile was characteristic as Melan-A (+), S-100 (+), and ki-67 (+, 50%; Figure 2), whereas two intense FDG avidity was showed at the rectum [standardized uptake value (SUV) = 11.3 at 9 o'clock and 16.1 at 5 o'clock], including a FDG avidity at the presacral region (SUVmax = 4.6), which was proposed as a suspicious nodal metastasis by PET-CT image (Figure 3).
The final diagnosis was confirmed to be primary rectal melanoma with suspicious nodal metastasis.
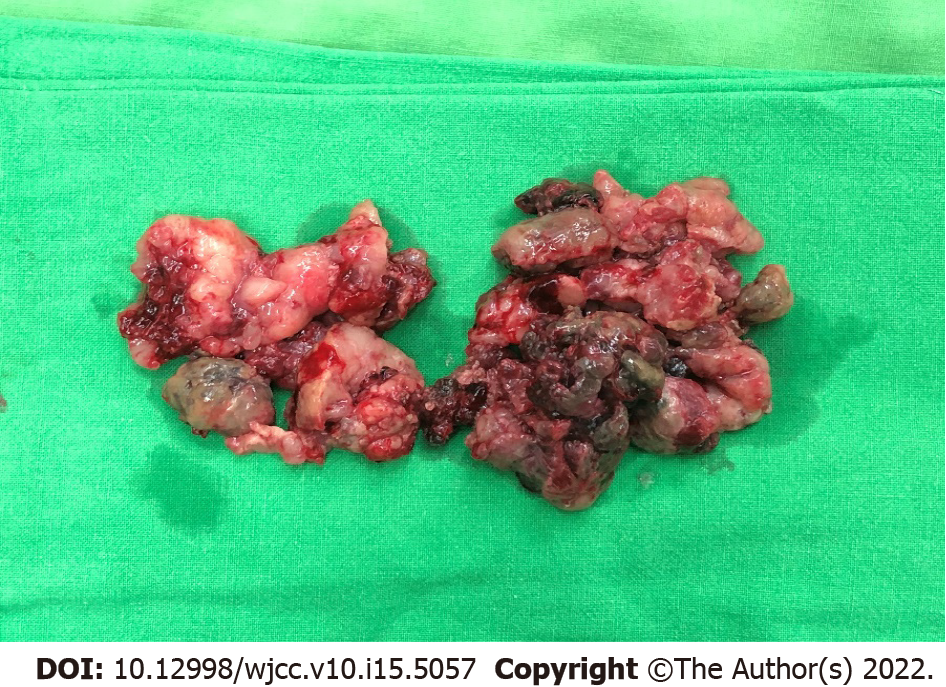
Wide local excision was performed for the first time (Figure 4). For symptom relief, the team combined the excision procedure with adjuvant RT. Follow-up pelvic CT showed a striking shrinkage in the residue lesion compared with the previous image.
Subsequently, the residual lesion was removed with margin-free resection by transanal WLE 3 mo later.
Afterward, the patient underwent regular clinical examinations and imaging scans (CT or colonoscopy) (Figure 5). Currently, she is experiencing a 2-year relapse-free postsurgery period and satisfies all indicators of functional quality and QOL (Supplementary Tables 1 and 2).
Rectal melanoma is a rare type of malignant melanoma. Owing to its aggressiveness, it has a low median survival rate, poor overall 5-year survival rate, and shorter disease-free survival period[3,10]. However, controversy about the best primary surgical strategy for patients with rectal melanoma exists, and the rarity of this condition, including the available quality evidence on this condition, partially limits consensus. Available evidence shows that the use of radical surgery in the form of APR significantly improved the survival rate compared with partial resection or WLE[5,11]. APR is also proposed to reduce the local recurrence rate, but it has a high morbidity rate with functional limitations, thereby lowering the patient’s QOL[12]. As a result, WLE has been selected as the treatment strategy for most patients. If local recurrence occurs, repeated WLE or APR can be used as salvage treatments. Nevertheless, previous studies have reported local recurrence rates after WLE of up to 50%. This high recurrence rate has led some people to question whether WLE alone was sufficient to treat patients diagnosed with rectal melanoma[4,6]. Interestingly, the combination of WLE and adjuvant RT in recently published studies resulted in local recurrence rates of < 20%, demonstrating a substantial decrease in local recurrence rates, in addition to increased sphincter preservation and function[6]. Hence, despite the favorable local control rates, the overall prognosis of patients with anorectal melanoma remains extremely poor. In addition to distant recurrence, Nusrath et al[13] revealed that overall survival rate was related to multiple factor, including tumor size, poor pathological feature such as lymphovascular or perineural invasion, and margin-negative resection[13]. In this study, the patient presented with localized rectal melanoma that we were unable to completely resect at the beginning. Bleeding symptoms also accompanied her condition. As a treatment strategy, WLE was performed first to reduce tumor volume and relieve anal bleeding. Consequent treatment with RT led to substantial residual tumor shrinkage, which was followed by secondary WLE that achieved margin-negative resection without severe side effects in addition to a good postoperative functional outcome and QOL. Subsequently, SF-36 was supplemented (Supplementary Table 2) to assess QOL before and after WLE.
In summary, although no consensus exists on localized rectal melanoma treatments, the current study presented repeat WLE and RT as viable alternatives to achieve negative resection margins, lowered local recurrence, better functional outcomes, and QOL using the least radical procedure in patients diagnosed with localized rectal melanoma. Nevertheless, further studies should be presented to validate its feasibility.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Medicine, research and experimental
Country/Territory of origin: Taiwan
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Menendez-Menendez J, Spain; Rim CH, South Korea S-Editor: Fan JR L-Editor: A P-Editor: Fan JR
| 1. | Heyn J, Placzek M, Ozimek A, Baumgaertner AK, Siebeck M, Volkenandt M. Malignant melanoma of the anal region. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2007;32:603-607. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Ibnian AM, Nagaraja V, Eslick GD, Kalantar JS. Rectal Melanoma with Multiple Metastases: A Rare and Aggressive Tumor. Rare Cancers The. 2014;2:11-16. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 3. | Brady MS, Kavolius JP, Quan SH. Anorectal melanoma. A 64-year experience at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center. Dis Colon Rectum. 1995;38:146-151. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 219] [Cited by in RCA: 181] [Article Influence: 6.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Weyandt GH, Eggert AO, Houf M, Raulf F, Bröcker EB, Becker JC. Anorectal melanoma: surgical management guidelines according to tumour thickness. Br J Cancer. 2003;89:2019-2022. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 69] [Cited by in RCA: 81] [Article Influence: 3.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Zhang S, Gao F, Wan D. Abdominoperineal resection or local excision? Melanoma Res. 2010;20:338-341. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Ballo MT, Gershenwald JE, Zagars GK, Lee JE, Mansfield PF, Strom EA, Bedikian AY, Kim KB, Papadopoulos NE, Prieto VG, Ross MI. Sphincter-sparing local excision and adjuvant radiation for anal-rectal melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:4555-4558. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 111] [Cited by in RCA: 94] [Article Influence: 4.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 7. | Belli F, Gallino GF, Lo Vullo S, Mariani L, Poiasina E, Leo E. Melanoma of the anorectal region: the experience of the National Cancer Institute of Milano. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2009;35:757-762. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 53] [Cited by in RCA: 54] [Article Influence: 3.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Kelly P, Zagars GK, Cormier JN, Ross MI, Guadagnolo BA. Sphincter-sparing local excision and hypofractionated radiation therapy for anorectal melanoma: a 20-year experience. Cancer. 2011;117:4747-4755. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 67] [Cited by in RCA: 75] [Article Influence: 5.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Lins L, Carvalho FM. SF-36 total score as a single measure of health-related quality of life: Scoping review. SAGE Open Med. 2016;4:2050312116671725. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 655] [Cited by in RCA: 631] [Article Influence: 70.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Ishizone S, Koide N, Karasawa F, Akita N, Muranaka F, Uhara H, Miyagawa S. Surgical treatment for anorectal malignant melanoma: report of five cases and review of 79 Japanese cases. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2008;23:1257-1262. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 58] [Cited by in RCA: 54] [Article Influence: 3.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Yeh JJ, Shia J, Hwu WJ, Busam KJ, Paty PB, Guillem JG, Coit DG, Wong WD, Weiser MR. The role of abdominoperineal resection as surgical therapy for anorectal melanoma. Ann Surg. 2006;244:1012-1017. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 121] [Cited by in RCA: 121] [Article Influence: 6.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Li Z, Šandera P, Beer M, Weber M. A rare case of recurrent primary anorectal melanoma emphasizing the importance of postoperative follow-ups. BMC Surg. 2020;20:68. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Nusrath S, Thammineedi SR, Patnaik SC, Raju KVVN, Pawar S, Goel V, Chavali RN, Murthy S. Anorectal Malignant Melanoma-Defining the Optimal Surgical Treatment and Prognostic Factors. Indian J Surg Oncol. 2018;9:519-523. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |