Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 16, 2021; 9(8): 1835-1843
Published online Mar 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i8.1835
Published online Mar 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i8.1835
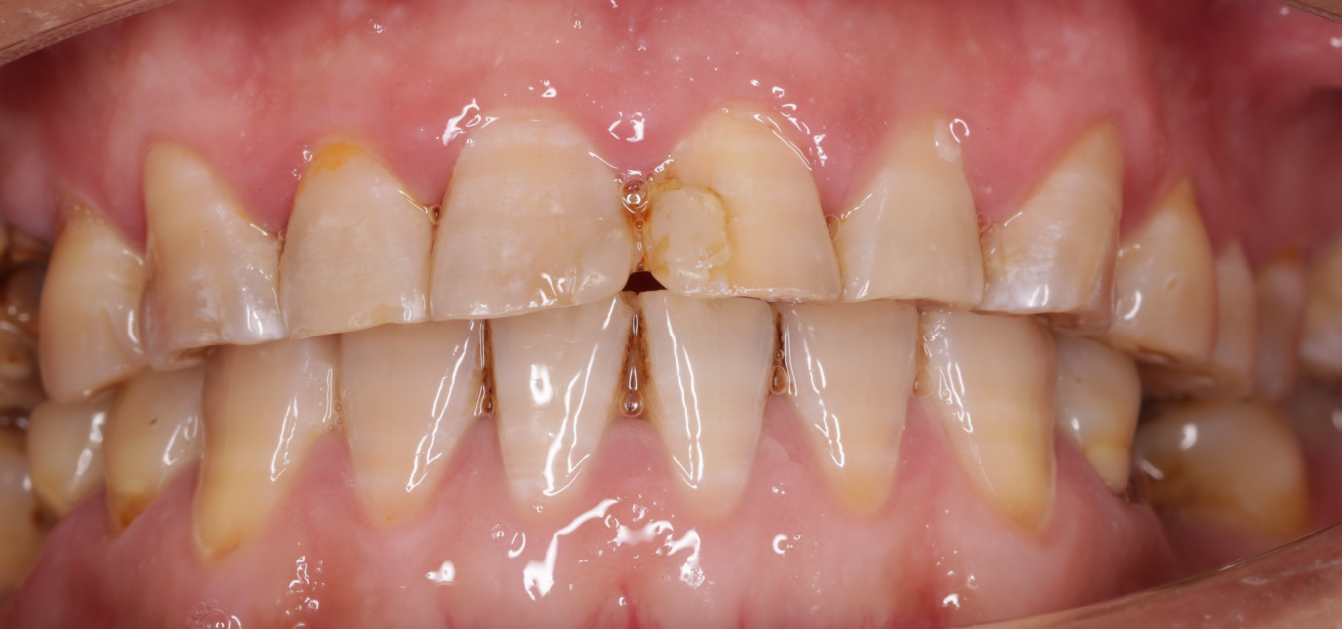
Figure 1 Pre-operative photograph from the lip-side of the anterior teeth.
The composite resin restorations in mesial incisal angle of both maxillary central incisors were stable, but the margins had been stained.
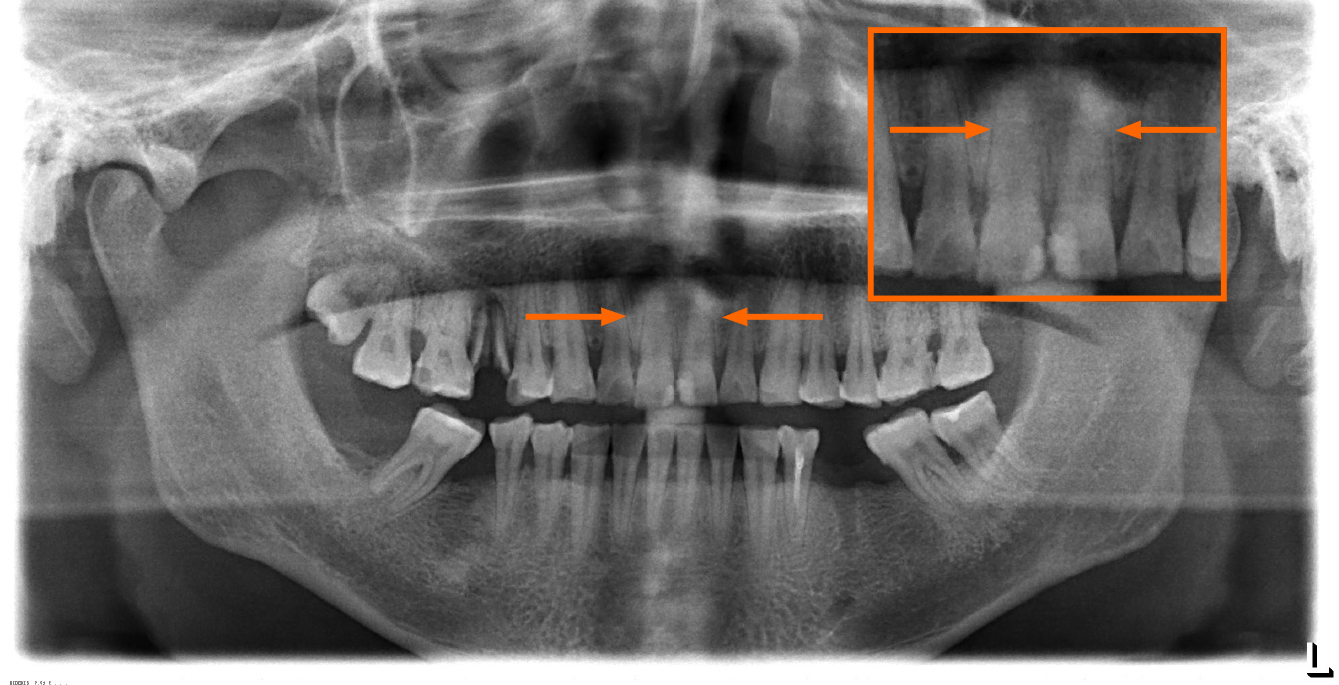
Figure 2 Pre-operative panoramic radiograph.
The orange arrows point to the suspected fracture line.
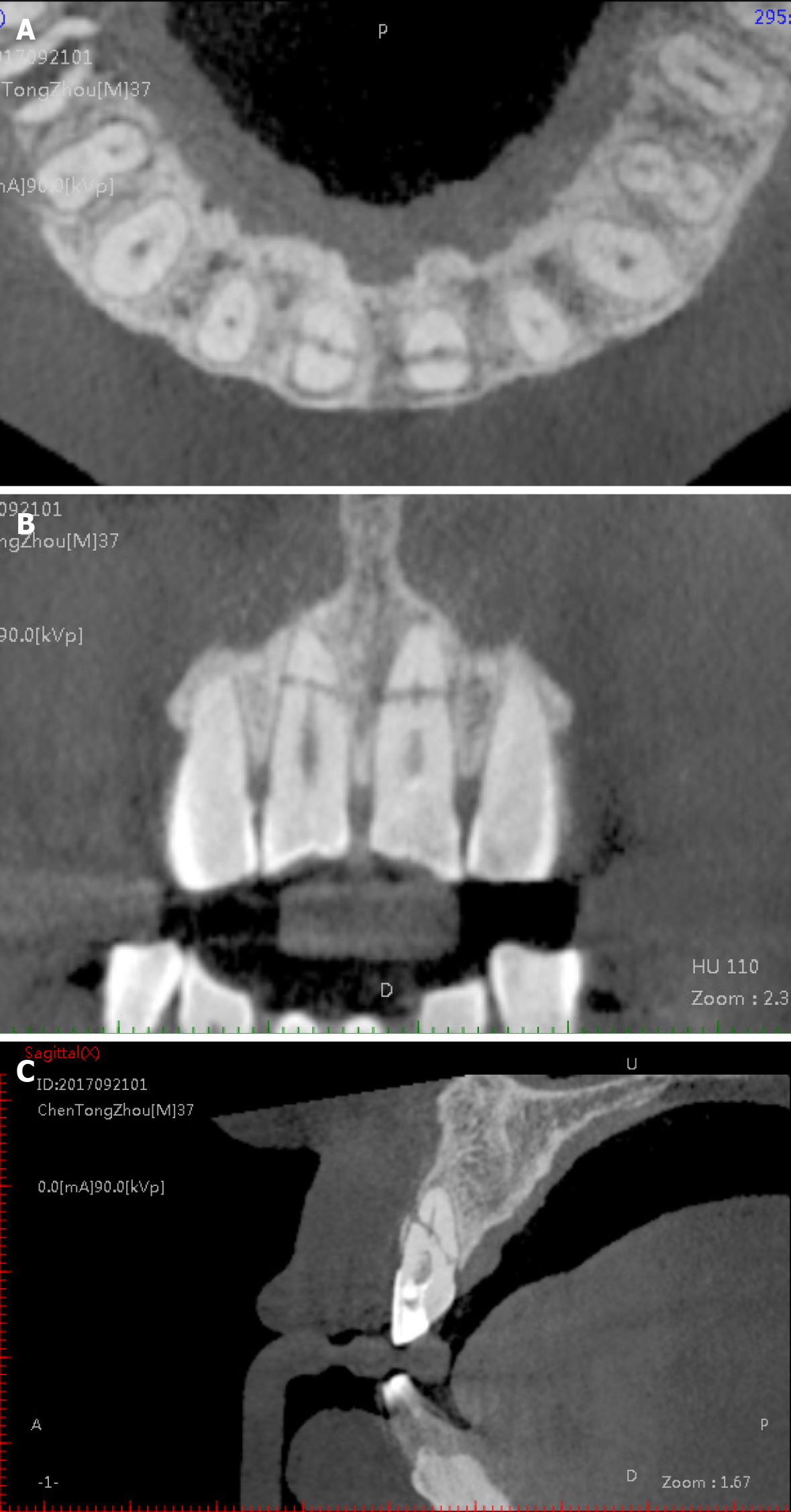
Figure 3 Pre-operative cone beam computed tomography imaging.
A-C: Axial (A), coronal (B), and sagittal (C) views of the cone beam computed tomography showed that both of the maxillary central incisors had oblique fracture lines, and a 3 mm × 4 mm radiolucent lesion set around the fracture line.
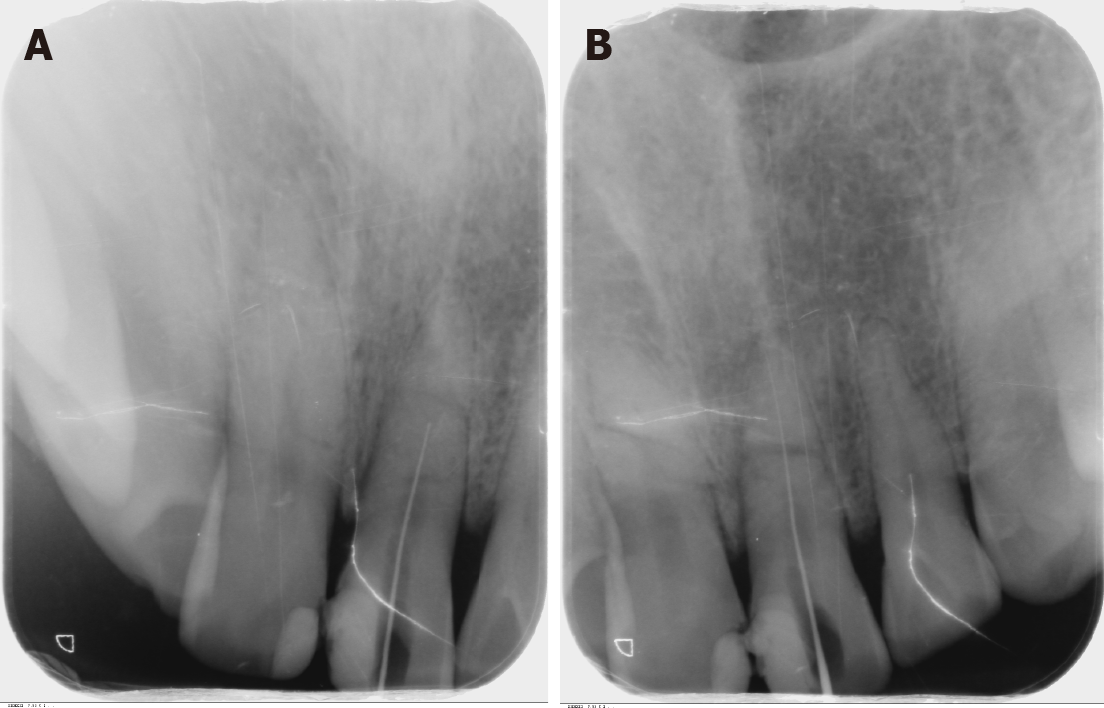
Figure 4 Periapical radiographs.
A: Periapical radiograph showing the file at the fracture line; B: Periapical radiograph for determining the working length.
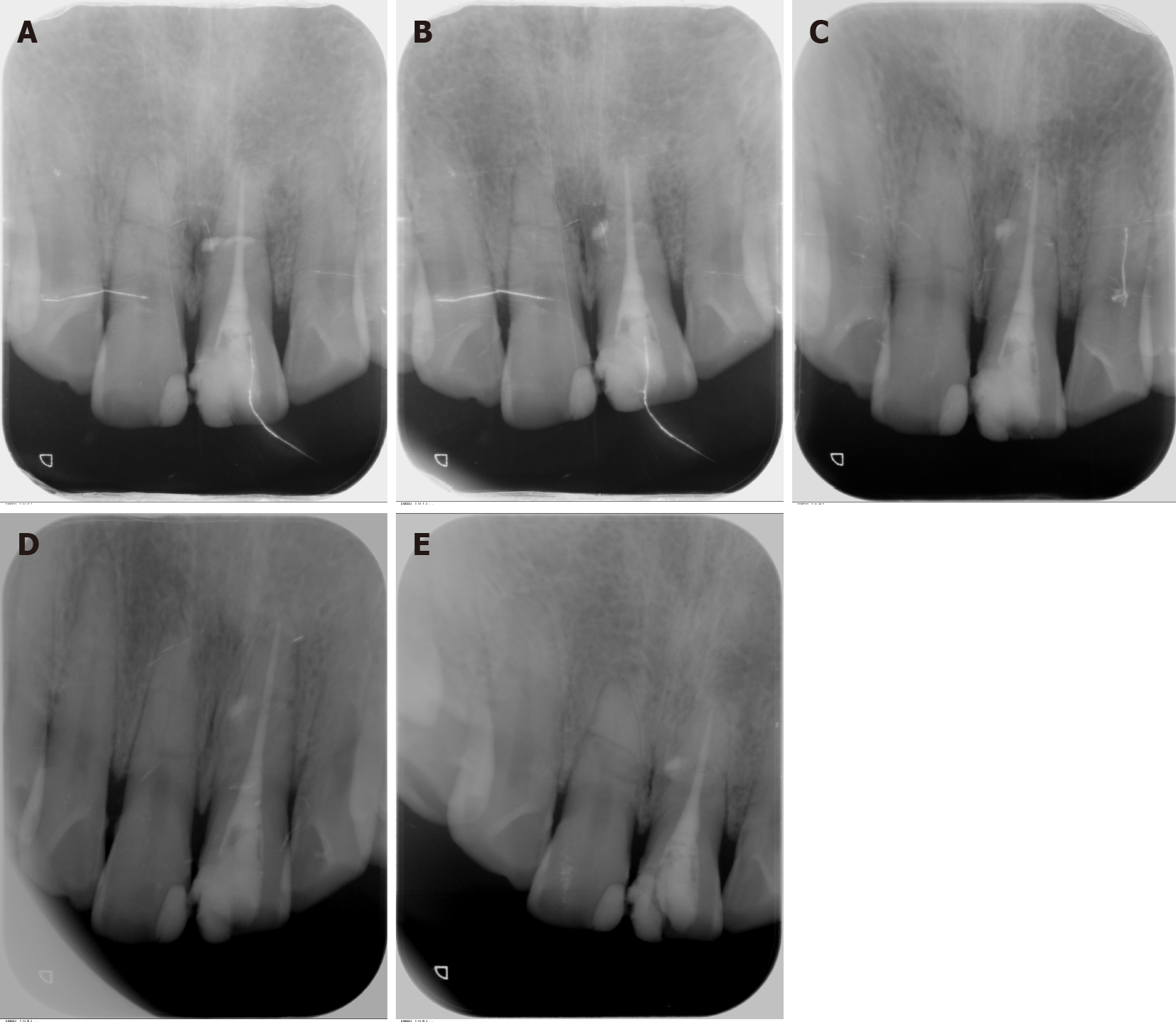
Figure 5 Periapical radiographs.
A: At immediate post-obturation; B: 1-mo follow-up; C: 6-mo follow-up; D: 12-mo follow-up; E: 24-mo follow-up.
- Citation: Zheng P, Shen ZY, Fu BP. Conservative endodontic management using a calcium silicate bioceramic sealer for delayed root fracture: A case report and review of the literature. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(8): 1835-1843
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i8/1835.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i8.1835