Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 26, 2021; 9(36): 11346-11354
Published online Dec 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i36.11346
Published online Dec 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i36.11346
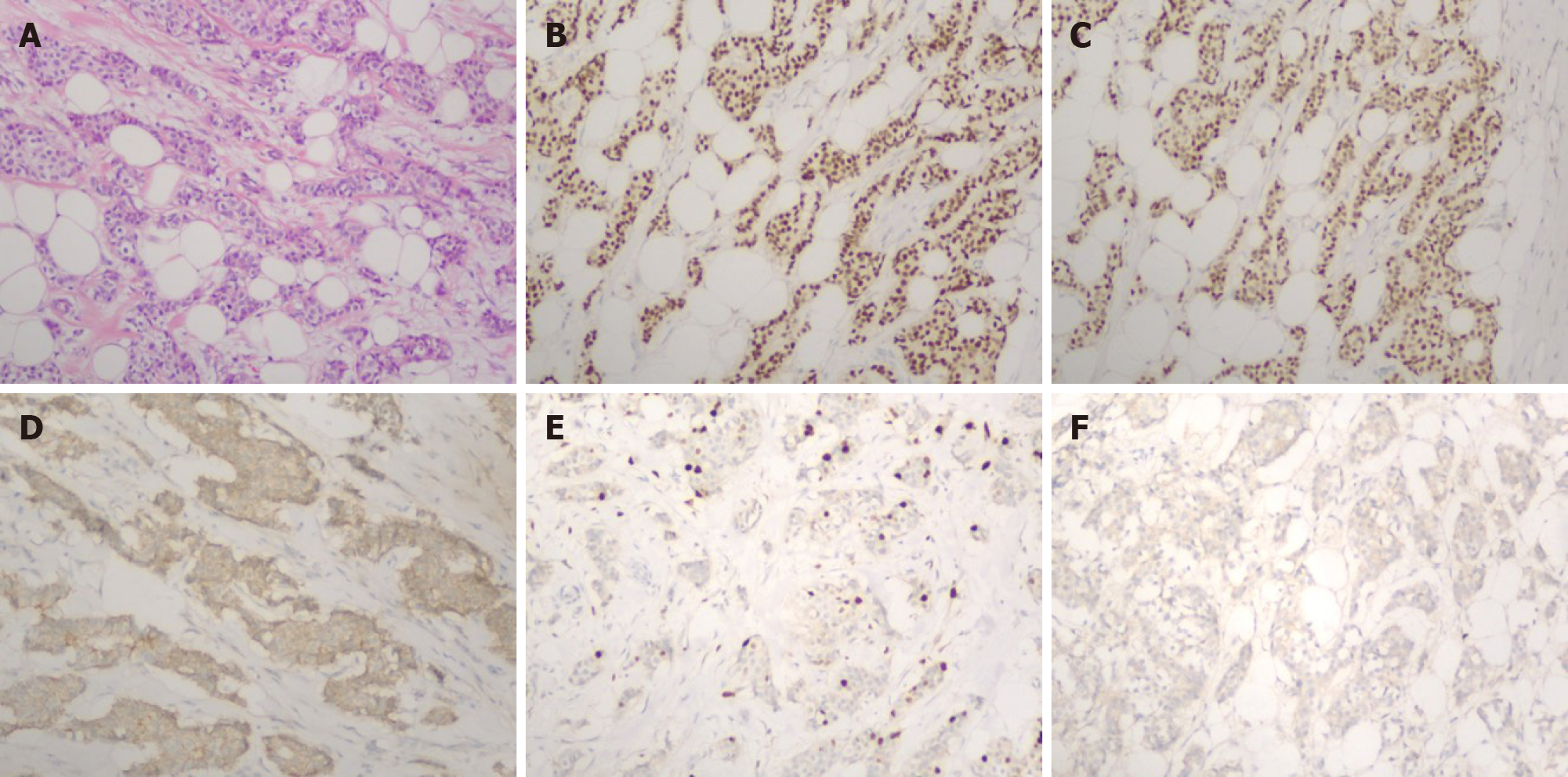
Figure 1 Histopathology and immunohistochemical findings of cancer in the right breast (100 ×).
A: Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining. HE staining for the resected tumor samples suggested invasive ductal breast cancer; B: Estrogen-receptor-positive rate was 70% in all cancer cells; C: Progesterone-receptor-positive rate was 70% in all cancer cells; D: E-cadherin positivity; E: Ki67 positive rate was 15% in all cancer cells; F: Her2 negativity.
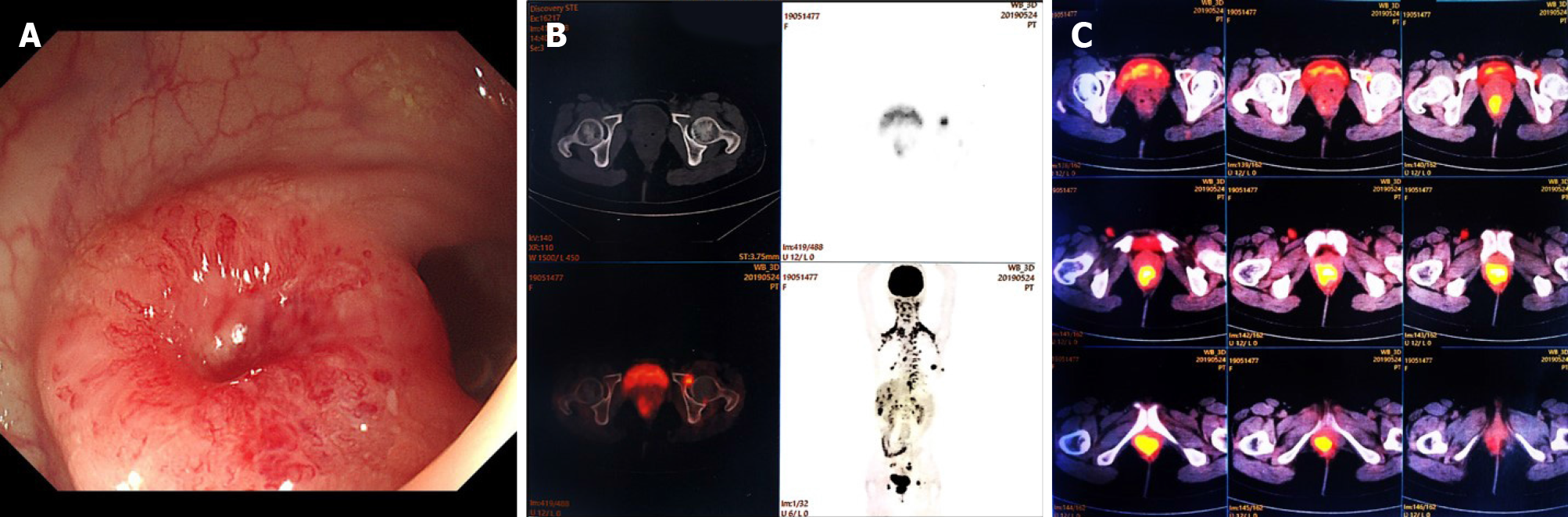
Figure 2 Results of positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET-CT) and colonoscopy.
A: Colonoscopy results indicated a lower rectal swelling, with a red and smooth surface located at 3 cm on the top of the anal verge, which suggested a submucosal tumor; B: Upper left part: local destruction of the bone cortex; lower left part: PET-CT images depicting uptake of fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) within the left acetabulum, with the maximal standardized value of uptake (SUVmax) equal to 5.5; C: PET-CT image depicting FDG uptake in the distal rectum, with SUVmax 11.2.
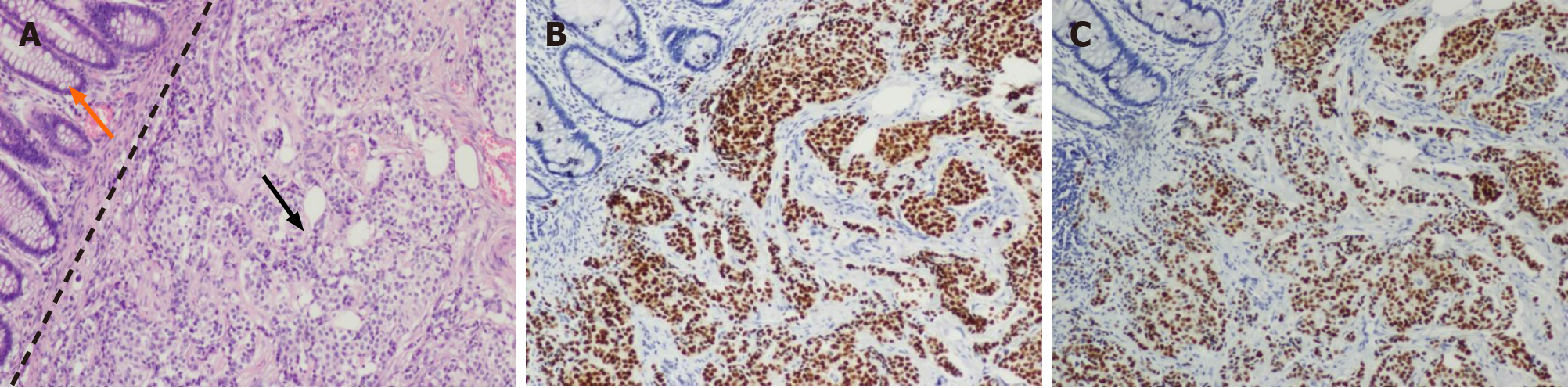
Figure 3 Fast-frozen pathology of the specimen (100 ×).
A-C: Top left corner: Normal rectal mucosal layer; bottom right corner: Tumor infiltrating layer. A: Sections under hematoxylin and eosin (staining suggested that cancer cells had invaded the submucosal layer; B: Estrogen-receptor-positive rate was 90% in all cancer cells; C: Progesterone-receptor-positive rate was 90% in all cancer cells.
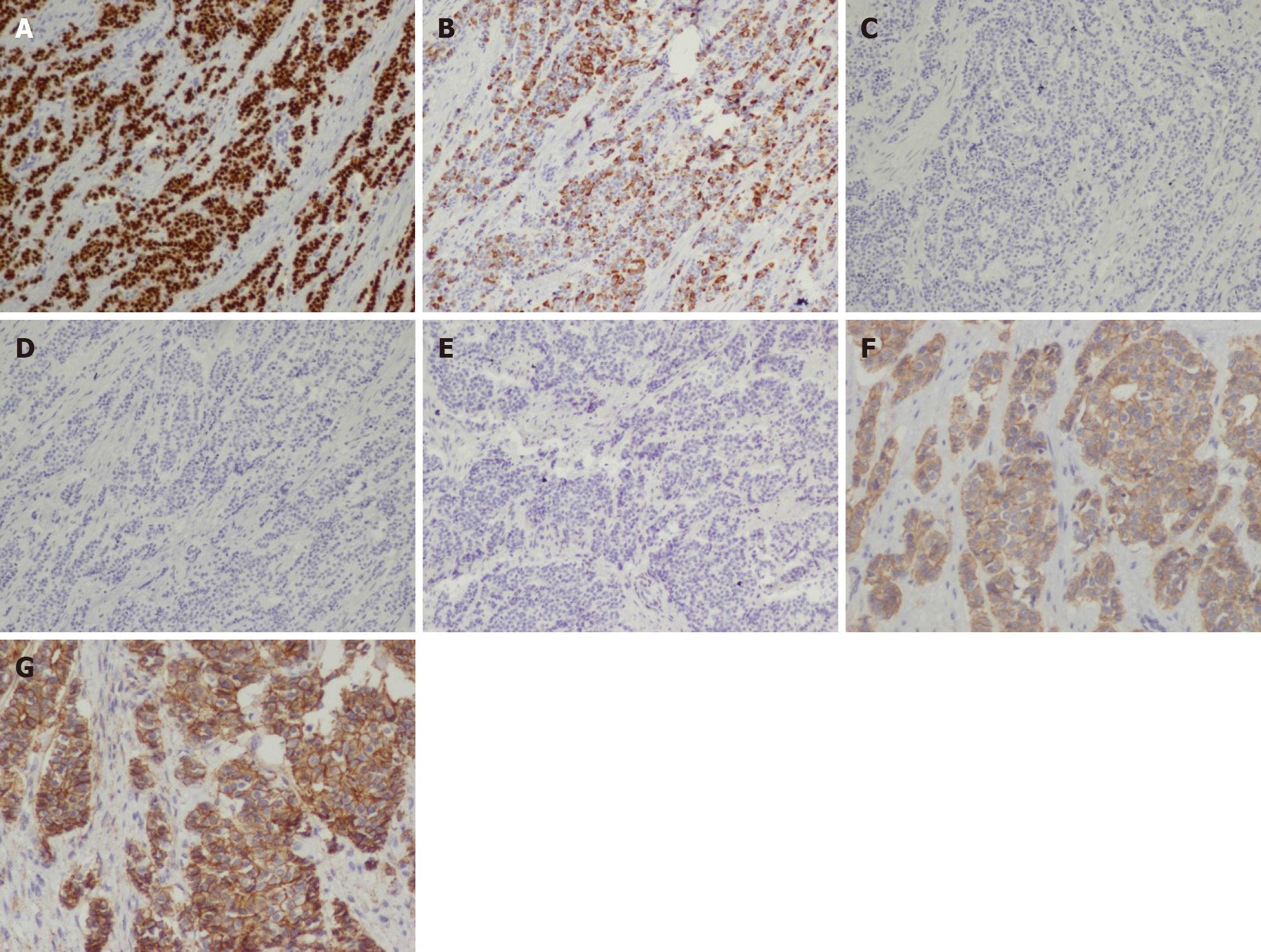
Figure 4 Further immunohistochemical analysis of tumor-infiltrating region (A-E: 100 ×; F, G: 200 ×).
A: GATA3 was positive; B: Cytokeratin (CK)7 was positive; C: CK20 was negative; D: Caudal type homeobox 2 was negative; E: Stabilin 2 was negative; F: E-cadherin was positive; G: P120 exhibited membrane staining.
- Citation: Ban B, Zhang K, Li JN, Liu TJ, Shi J. Ductal breast carcinoma metastasized to the rectum: A case report and review of the literature. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(36): 11346-11354
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i36/11346.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i36.11346