Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 16, 2021; 9(35): 11108-11114
Published online Dec 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i35.11108
Published online Dec 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i35.11108
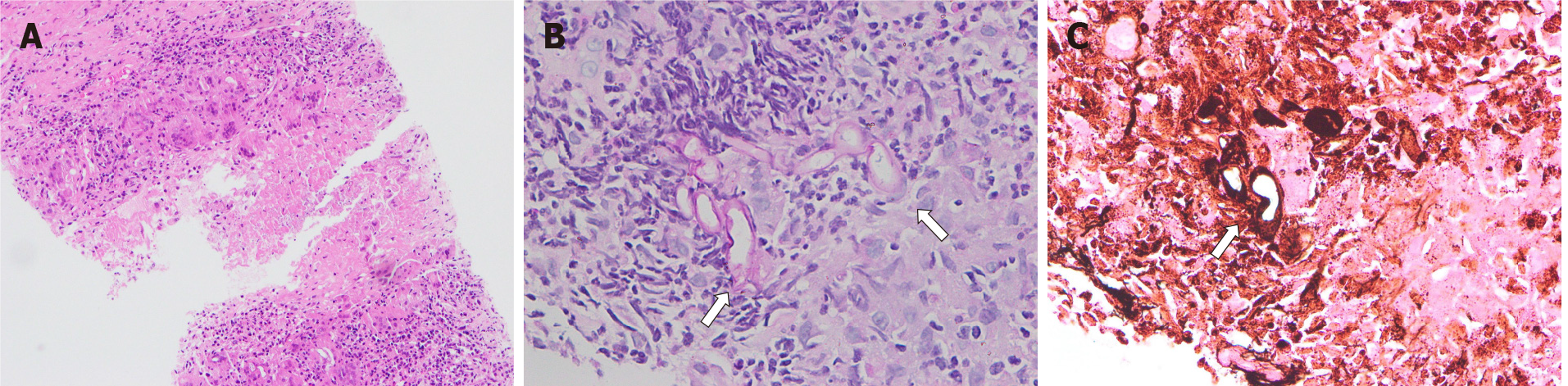
Figure 1 Histology.
A: A needle biopsy of the pathological tissue of the right lower lung showed granulomatous inflammation, necrosis, and inflammatory cells (hematoxylin-eosin staining, 100 ×); B and C: The hyphae indicated mucormycosis that lacked regular septa and was pauciseptate, marked with white arrows by periodic acid-Schiff fungal staining (B, 400 ×) and hexamine silver staining (400 ×, C).
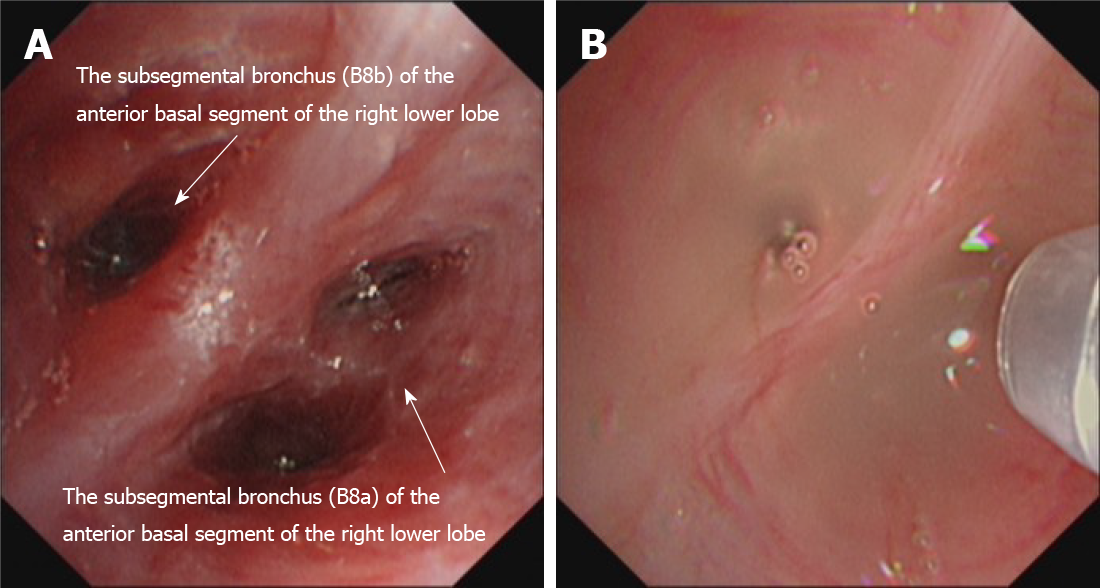
Figure 2 Images in electronic bronchoscopy.
A: The anterior basal branch was swollen, accompanied by a deformed and narrowed lumen of the anterior basal branch; B: Perfusion with amphotericin B (10 mg dissolved in 10 mL saline) on the anterior basal segment of the right lower lobe was performed through a microtube in an electronic bronchoscope.
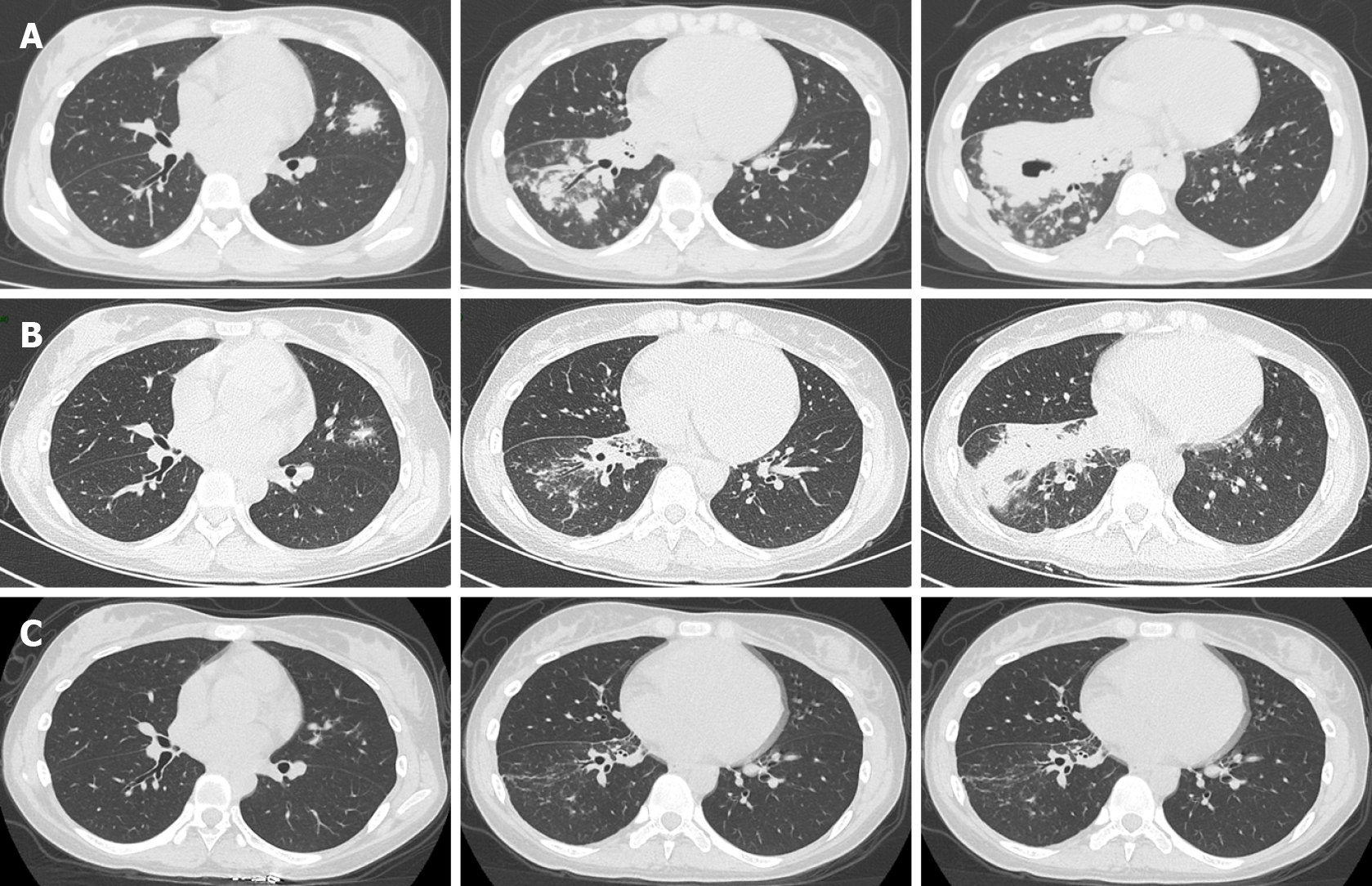
Figure 3 Computed tomography images.
A: Thoracic computed tomography (CT) images showing bilateral pulmonary infection with cavitation in the right lower lobe upon arrival; B: After 30 d of antifungal treatment, chest CT showed a decrease in lung inflammation and an absorption of cavitation in the right lower lobe; C: Chest CT follow-showed that lung inflammation dissipated after 80 d.
- Citation: Chen L, Su Y, Xiong XZ. Rhizopus microsporus lung infection in an immunocompetent patient successfully treated with amphotericin B: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(35): 11108-11114
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i35/11108.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i35.11108