Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 26, 2021; 9(33): 10279-10285
Published online Nov 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i33.10279
Published online Nov 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i33.10279
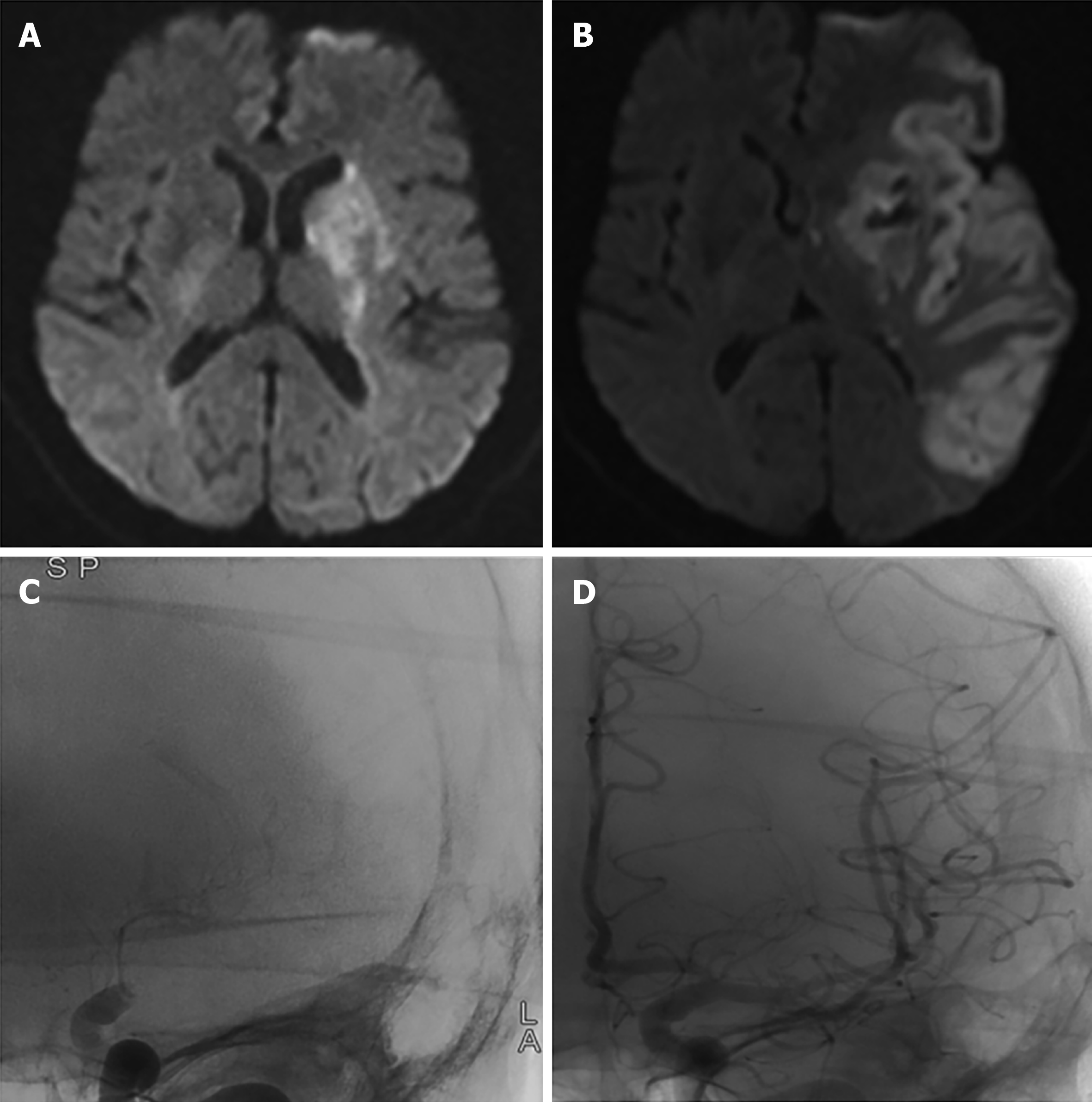
Figure 1 MRI and digital subtraction angiography imaging before and after surgery.
A: Axial brain MRI (DWI) on admission showed acute cerebral infarction in the basal ganglia; B: Postoperative brain MRI (DWI) showed subacute large areas of cerebral infarction with basal ganglia hemorrhage; C: Angiogram of the left internal carotid artery showed proximal occlusion of the left middle cerebral artery before mechanical thrombectomy; D: Postoperative angiography showed complete recanalization of the left internal carotid artery and middle cerebral artery. DWI: Diffusion-weighted imaging; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging.
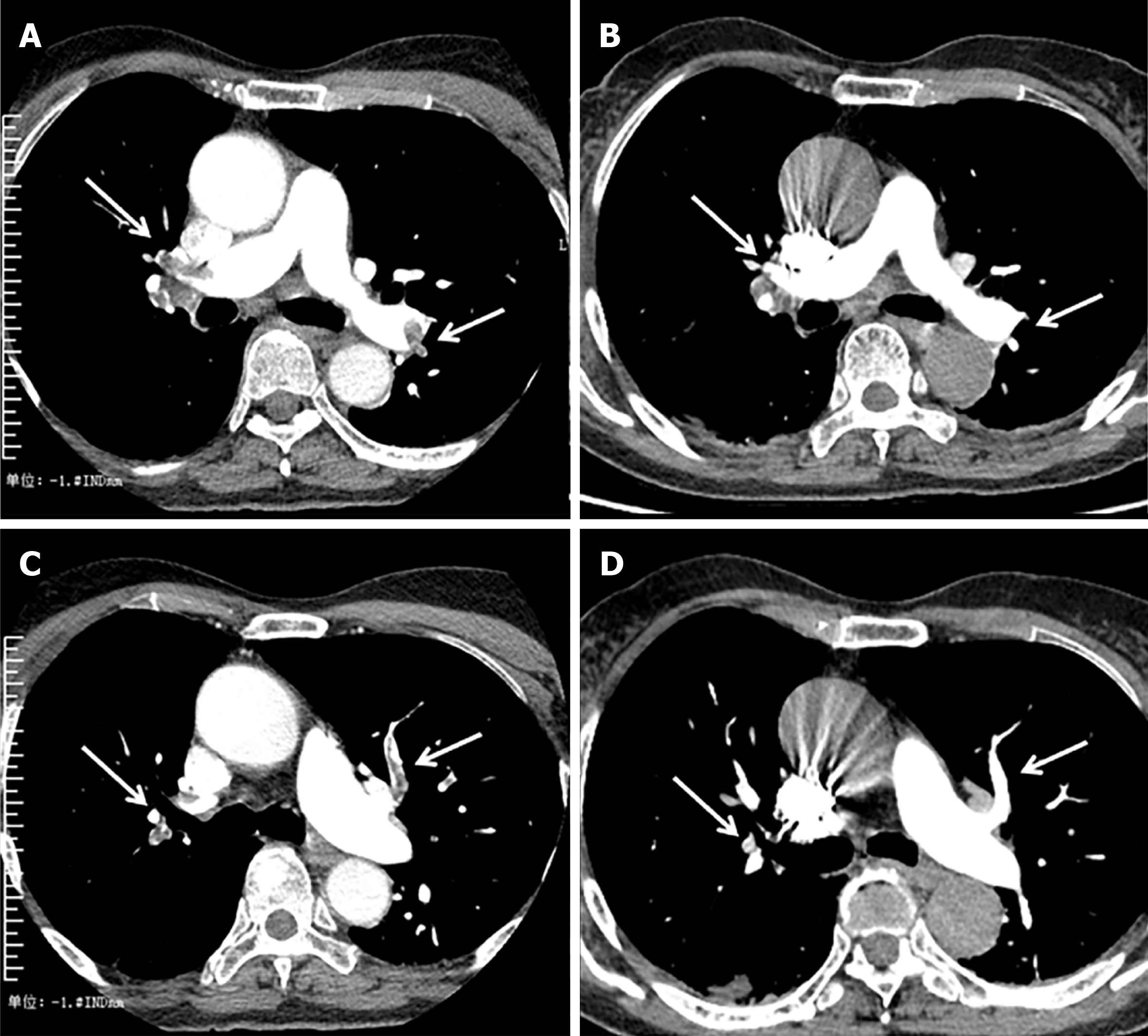
Figure 2 Changes in pulmonary embolism before and after anticoagulation.
A, C: Pulmonary angiogram showed multiple repletion defects in both the pulmonary artery trunks and its branches before anticoagulation; B, D: Pulmonary angiogram showed the thrombus was eliminated after 20 d of treatment.
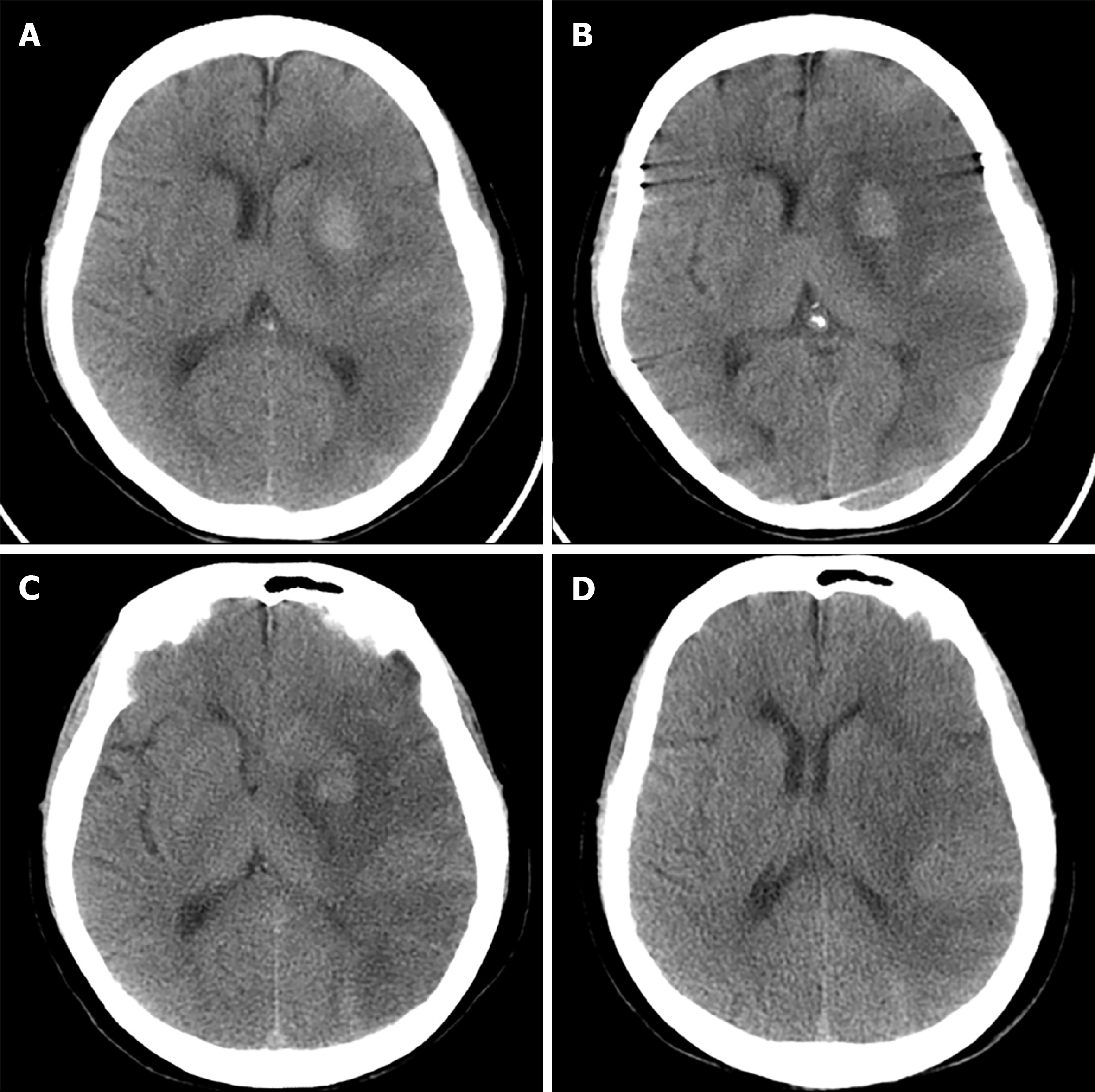
Figure 3 Changes on brain CT scan after surgery.
A: Postprocedural brain CT showed large areas of cerebral infarction and hemorrhage in the left basal ganglia area; B–D: Follow-up brain CT showed no new evidence of cerebral infarction or hemorrhage. CT: computed tomography.
- Citation: Chen XT, Zhang Q, Zhou CQ, Han YF, Cao QQ. Anticoagulant treatment for pulmonary embolism in patient with cerebral hemorrhage secondary to mechanical thrombectomy: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(33): 10279-10285
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i33/10279.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i33.10279