Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 26, 2021; 9(33): 10249-10256
Published online Nov 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i33.10249
Published online Nov 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i33.10249
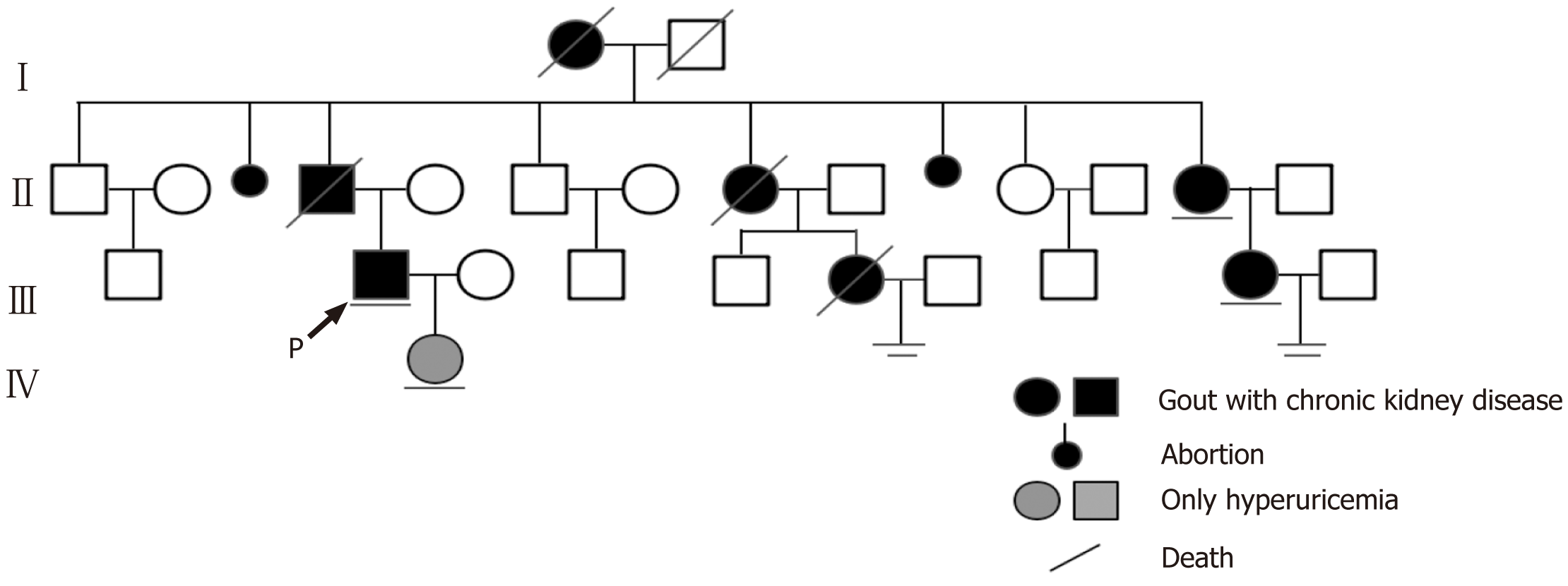
Figure 1 Pedigree for the family of the patient, indicating individuals affected by familial hyperuricemia and chronic kidney diseases.
(1) Black and gray symbols corresponding to the affected individuals, with the patient described in this case report marked with an arrow; and (2) Lines under individuals indicate people who provided DNA samples, while the two underlines denote couples with no children.
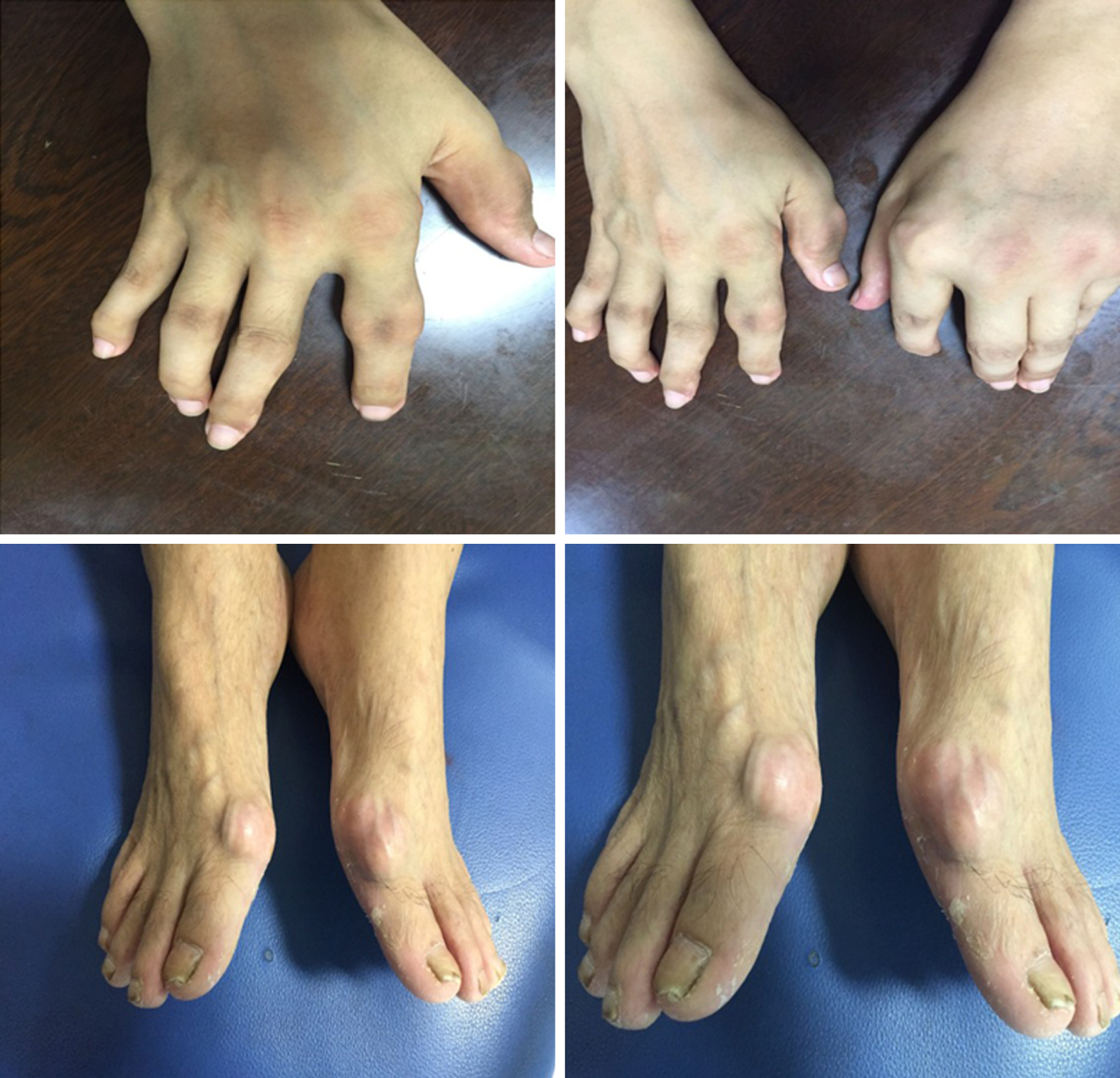
Figure 2 Swelling, gout stones, and deformity of the interphalangeal joints, with two large gout stones affecting the 1s metatarsal joints of the feet in the patient.
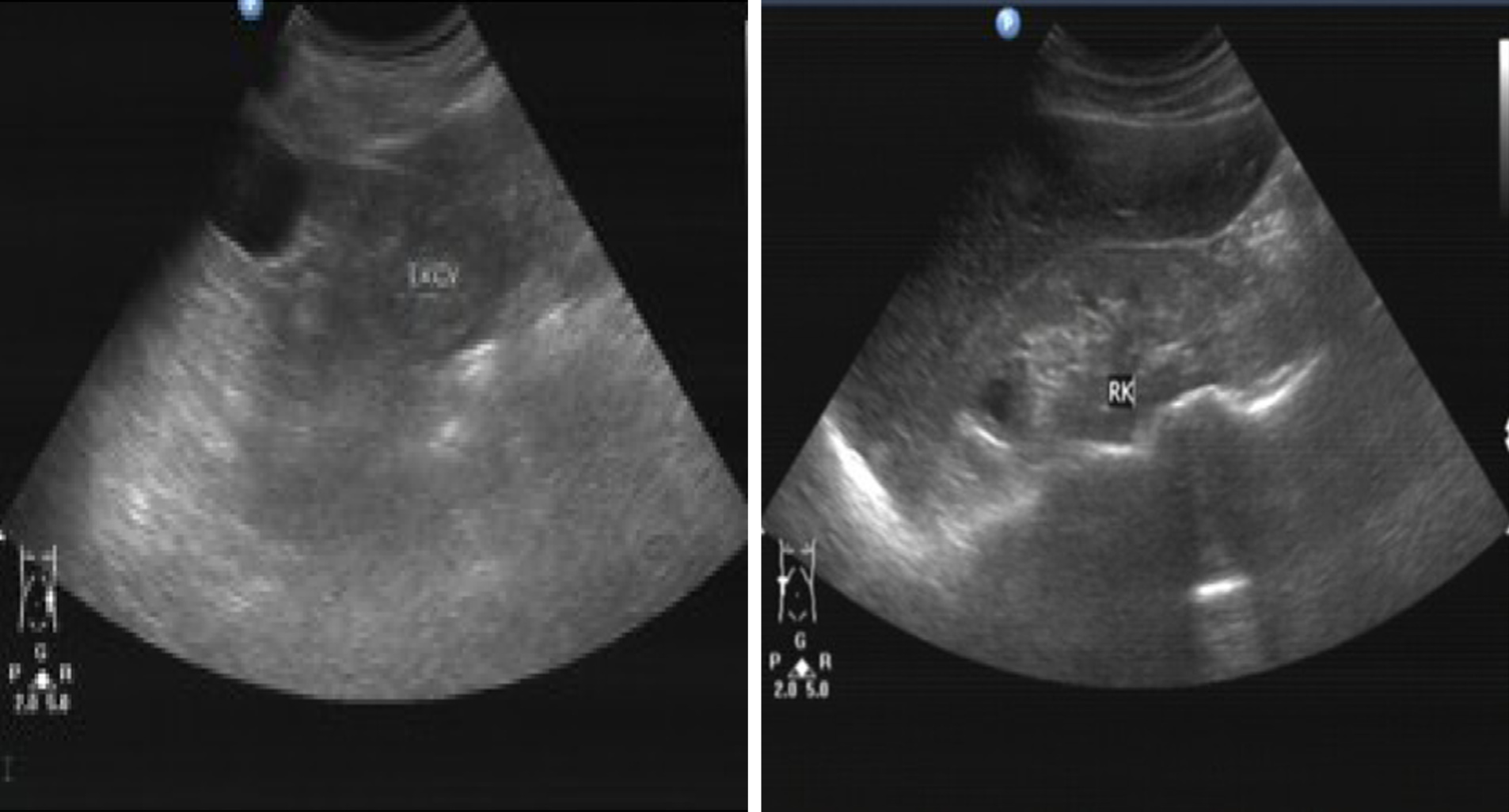
Figure 3 Renal ultrasound findings of the patient, revealing relatively atrophic kidneys with multiple secondary cysts.
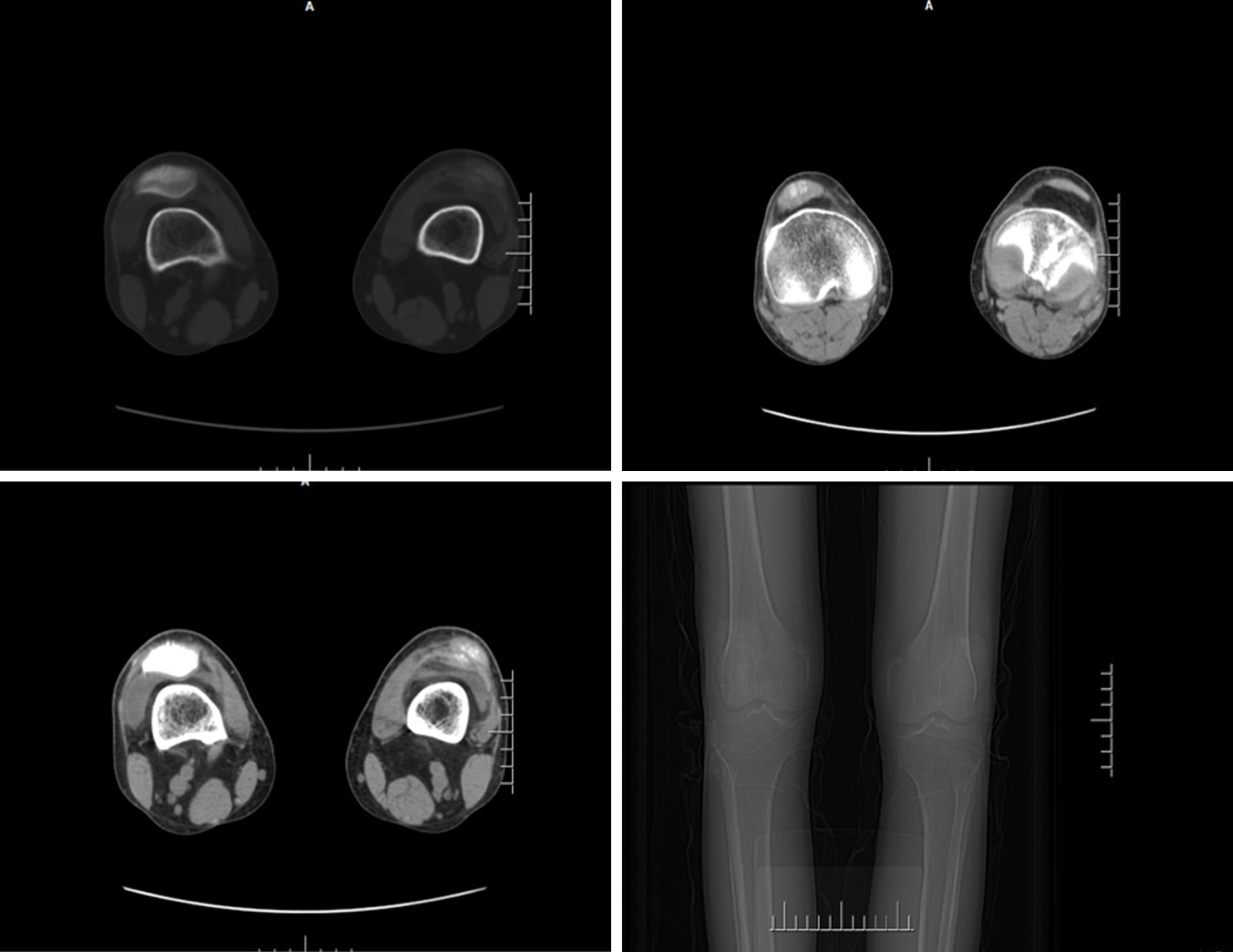
Figure 4 Computed tomography scans demonstrating joint space narrowing, soft tissue swelling, and high density urate crystal deposition in the patient.
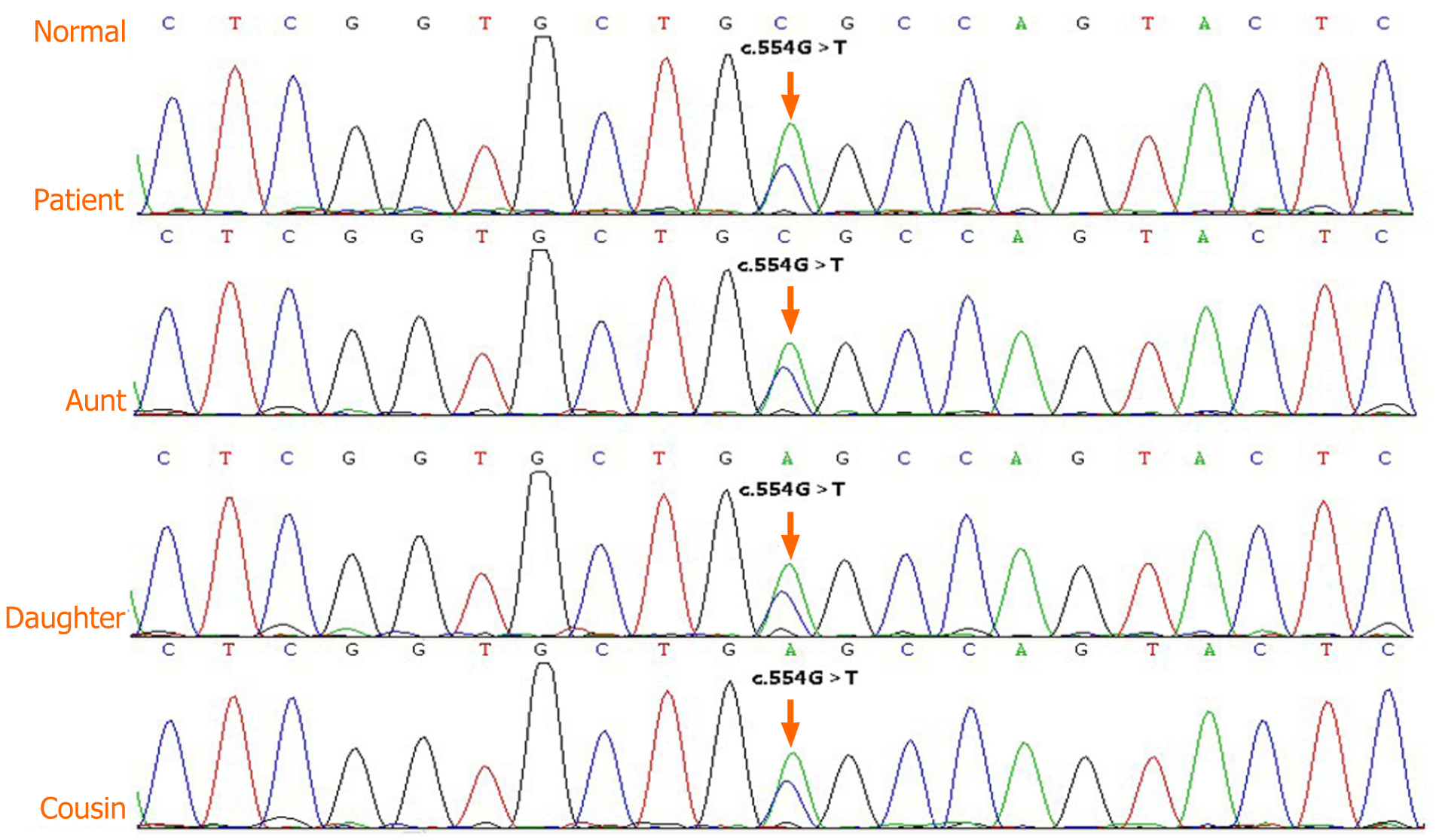
Figure 5 Genomic DNA sequence electropherograms for the proband, affected family members, and normal DNA.
The arrow corresponds to a G>T transversion at position 554 of the uromodulin in chr16 (GenBank accession number NM_003361.3). This mutation was heterozygous in the proband, his daughter, his aunt, and his younger female cousin, respectively.
- Citation: Zhang LL, Lin JR, Zhu TT, Liu Q, Zhang DM, Gan LW, Li Y, Ou ST. Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease with a novel heterozygous missense mutation in the uromodulin gene: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(33): 10249-10256
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i33/10249.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i33.10249