Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 26, 2021; 9(30): 9310-9319
Published online Oct 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i30.9310
Published online Oct 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i30.9310
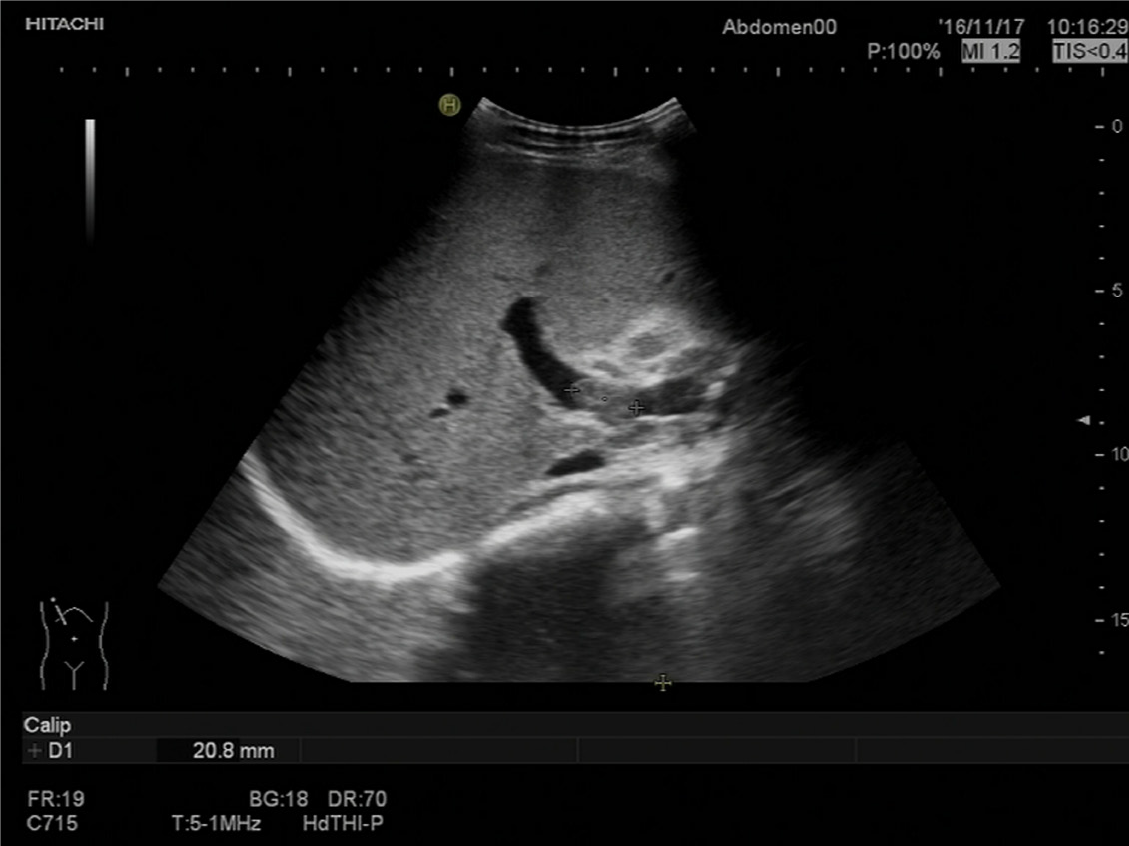
Figure 1 Abdominal ultrasound findings before treatment.
The right branch of the portal vein showed evidence of a 2.1 cm thrombosis.
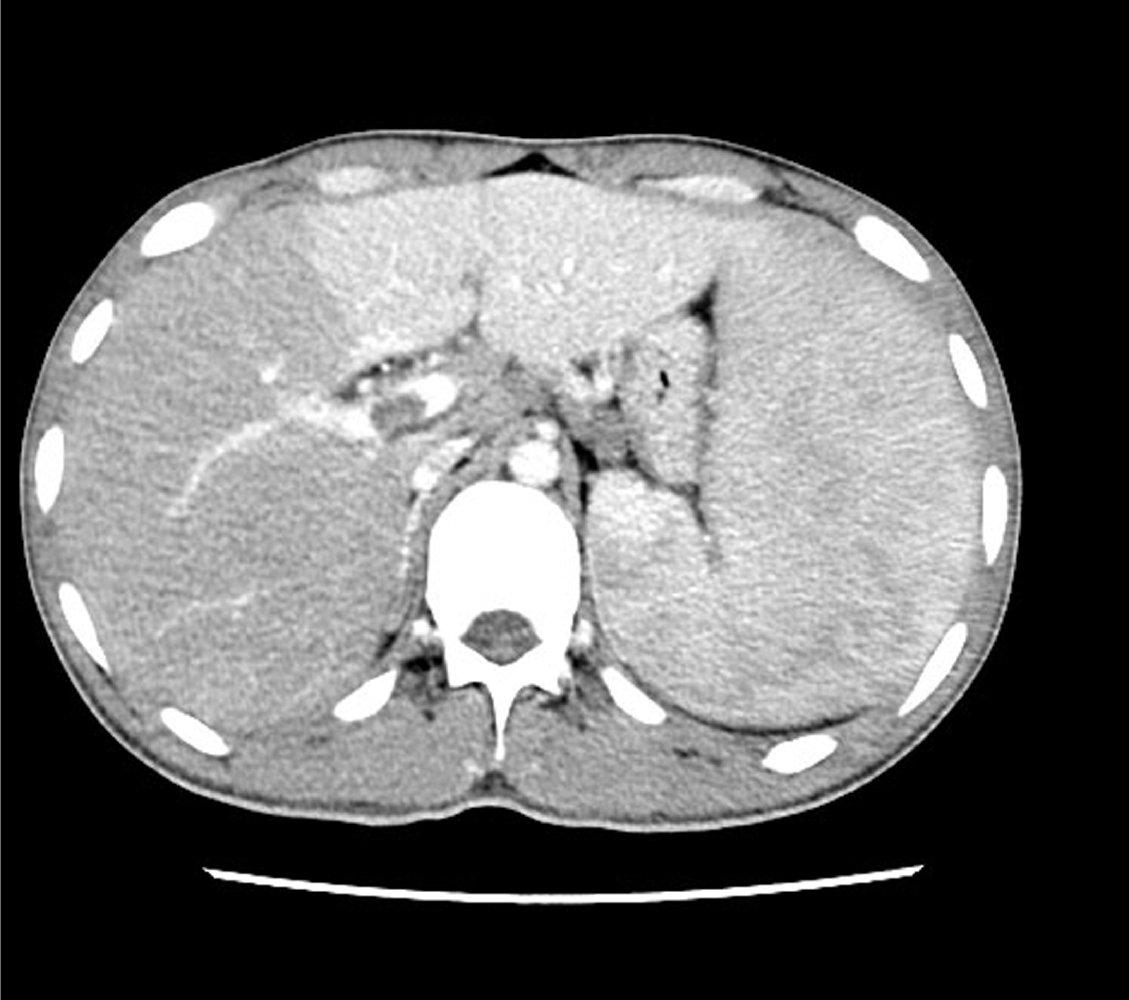
Figure 2 Abdominal computed tomography findings.
Abdominal contrast-enhanced computed tomography confirmed hepatosplenomegaly, with hypodensity of the right lobe of the liver, and thrombosis of the right branch of the portal vein.
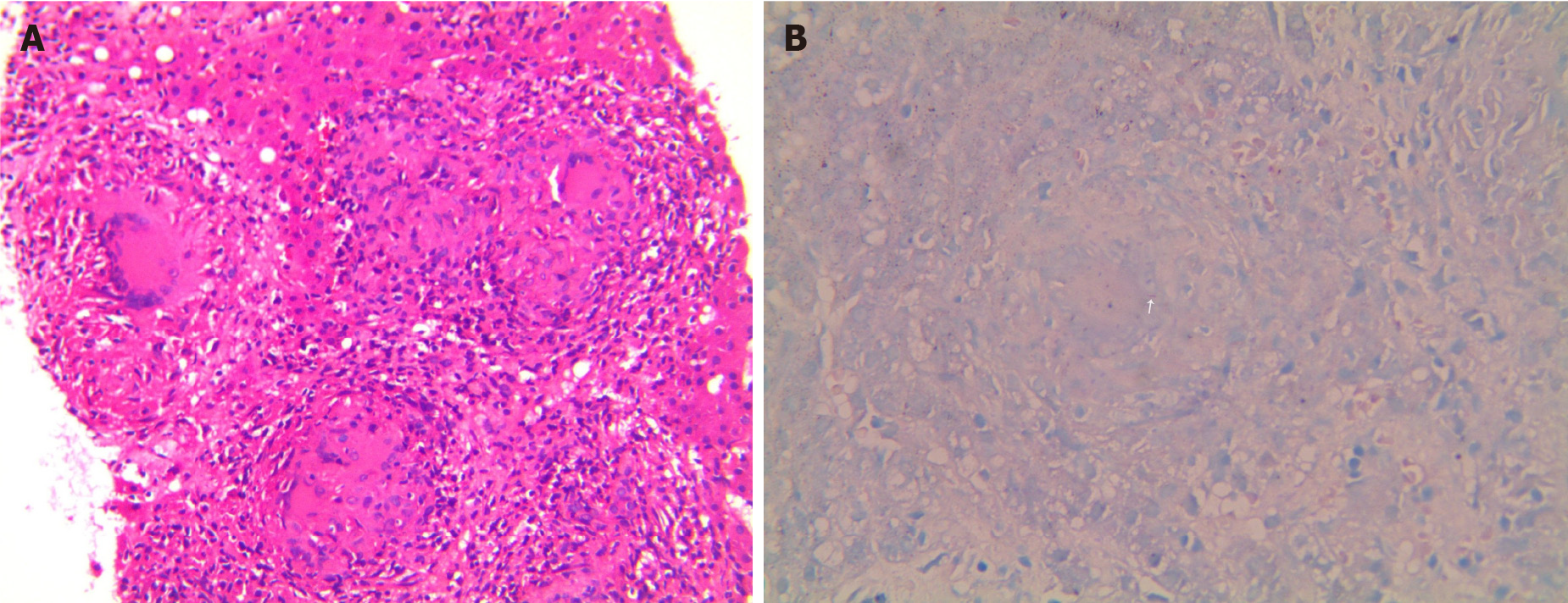
Figure 3 Histopathological examination.
A: Histology of the liver biopsy showed entirely effaced architecture of hepatic parenchymal and portal areas by inflammation and necrosis. Central caseating necrosis was surrounded by lymphocytes, multinucleated giant cells, and epithelioid macrophages (Hematoxylin and eosin staining, 40 ×); B: Ziehl-Nelson staining showed acid-fast bacilli (arrow) within the granulomas (Ziehl-Nelson staining, 40 ×).
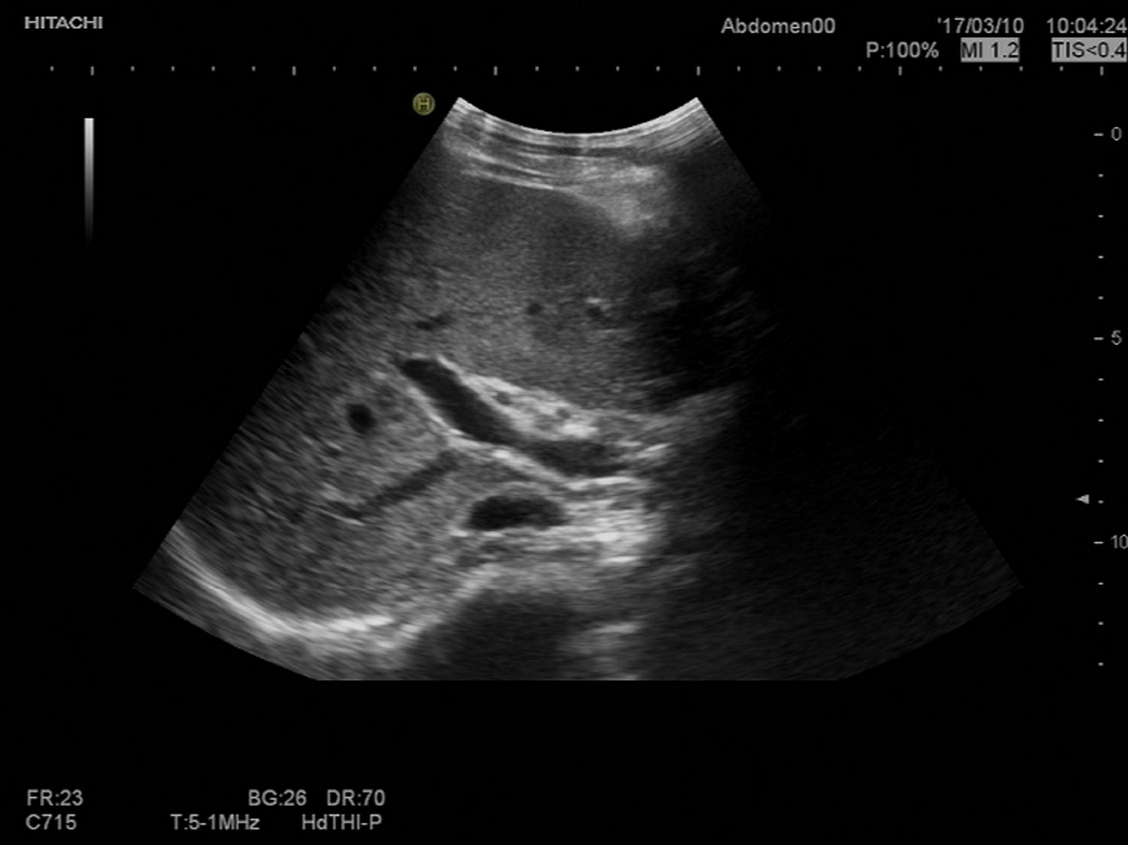
Figure 4 Abdominal ultrasound findings at 4 mo of treatment.
At 4 mo of therapy, repeat sonography of the abdomen showed regression of hepatosplenomegaly and complete resolution of the portal vein thrombosis.
- Citation: Zheng SM, Lin N, Tang SH, Yang JY, Wang HQ, Luo SL, Zhang Y, Mu D. Isolated hepatic tuberculosis associated with portal vein thrombosis and hepatitis B virus coinfection: A case report and review of the literature. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(30): 9310-9319
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i30/9310.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i30.9310