Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 26, 2021; 9(30): 9159-9167
Published online Oct 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i30.9159
Published online Oct 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i30.9159
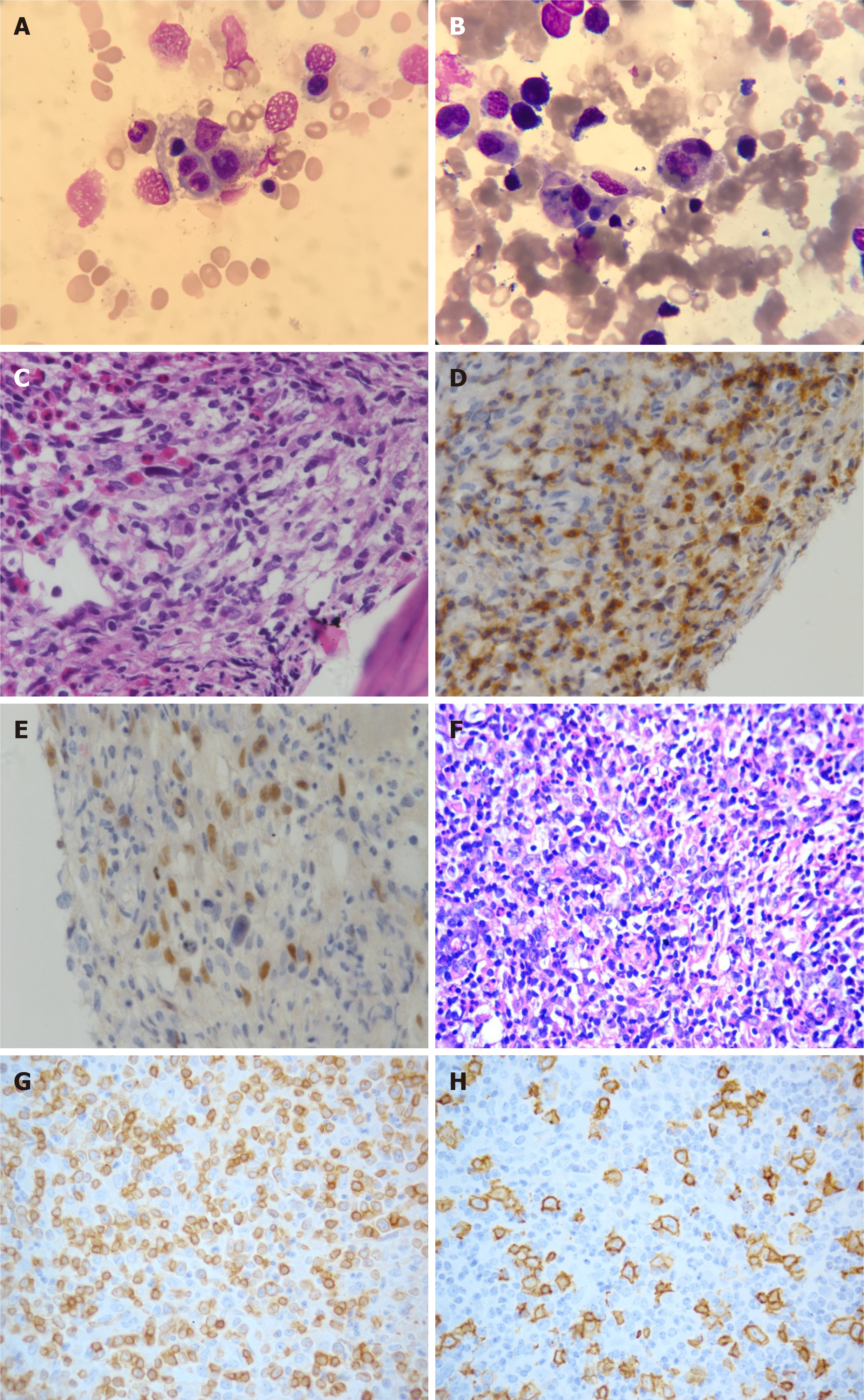
Figure 1 Morphology of bone marrow aspirate smear and biopsy in Case 1.
A and B: Hemophagocytosis (A) and tumor cells (B) (Wright’s stain, × 1000); C: Diffuse small to medium-sized lymphocytes admixed scattered large atypical cells (hematoxylin-eosin stain, × 400); D and E: The tumor cells were positive for CD3 (D) and PAX-5 (E) (immunohistochemistry, IHC × 400); F: Lymph node biopsy sections showed a marked nodular aggregate of medium-sized lymphocytes with scattered large lymphocytes (hematoxylin-eosin stain, × 400); G and H: The tumor cells in lymph nodes were positive for CD3 (G) and CD20 (H) (IHC × 400).
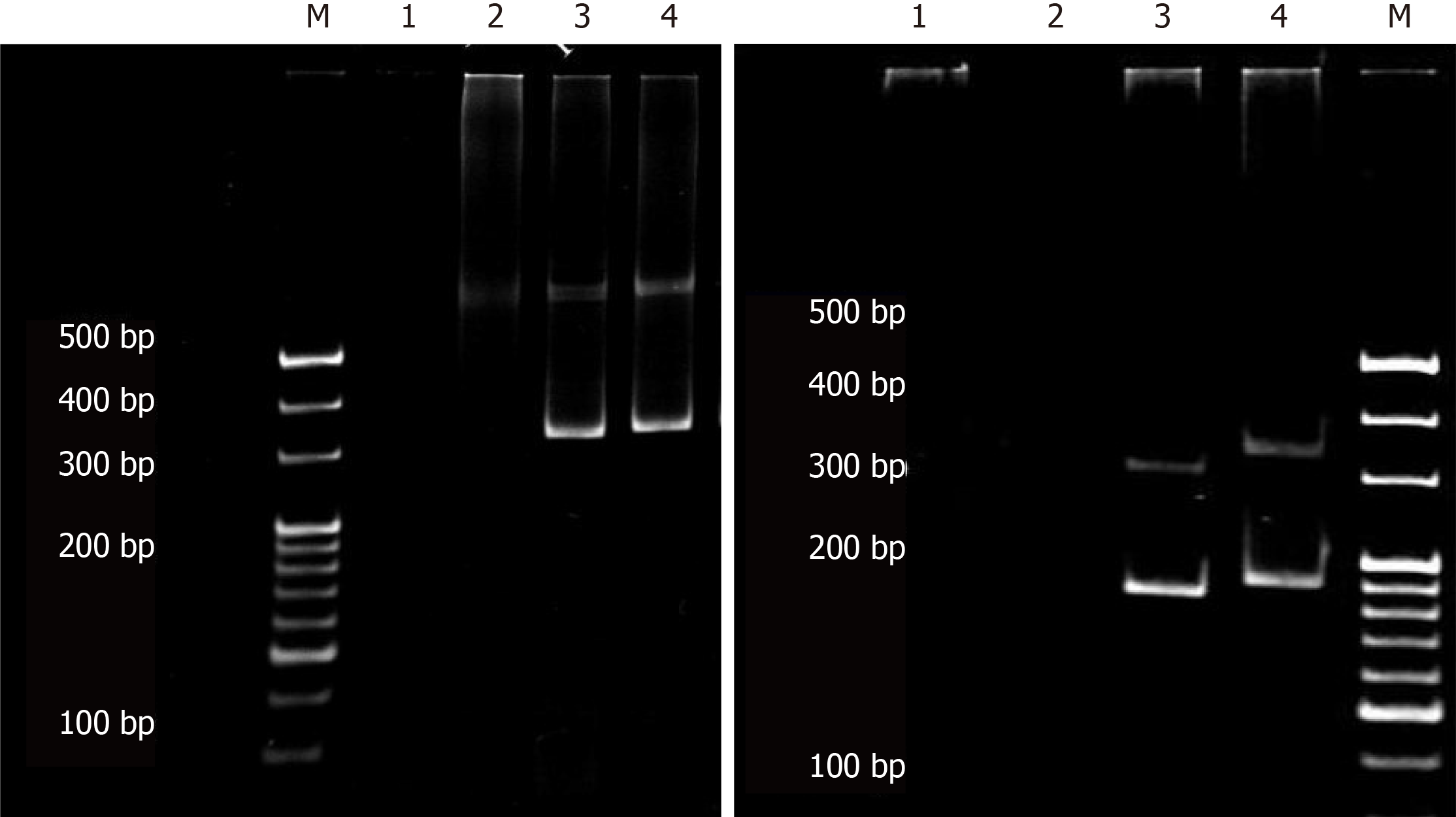
Figure 2 Monoclonal patterns of T-cell receptor and immunoglobulin H rearrangements detection in Case 1.
DNA was extracted from the patient’s lymph node samples and amplified by polymerase chain reaction with primers for the framework 2 portion of the immunoglobulin VH region (left) and the T-cell receptor (TCR) γ chain (right). M: Marker; 1: Water; 2: Negative control; 3: Positive control; 4: Sample.
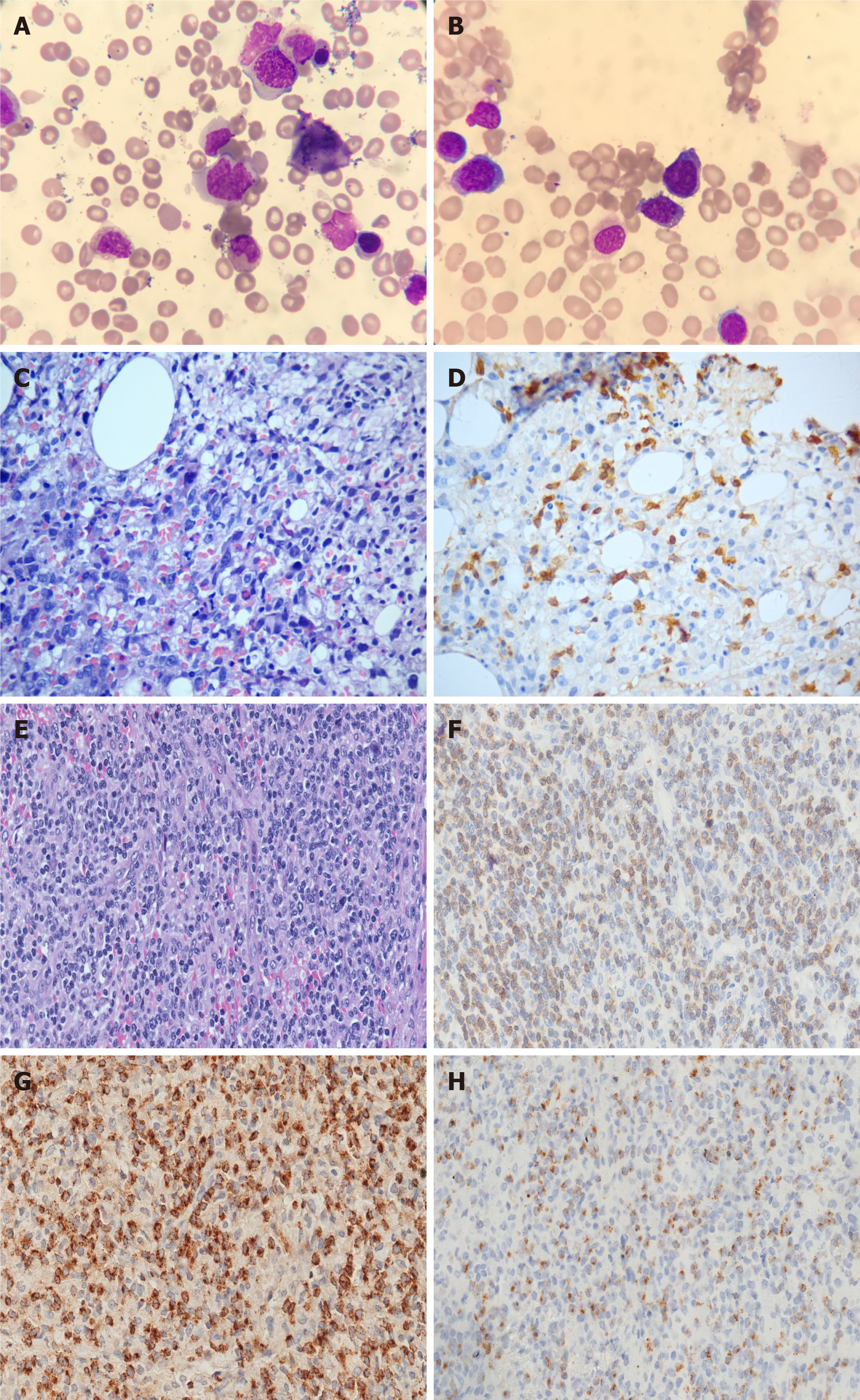
Figure 3 Morphology of bone marrow aspirate smear and biopsy in Case 2.
A and B: Hemophagocytosis (A) and tumor cells (B) (Wright’s stain, × 1000); C: Diffuse medium-sized atypical lymphocytes infiltrated with the effacement of normal architecture (hematoxylin-eosin stain, × 400); D: The tumor cells were positive for PAX-5 (immunohistochemistry, IHC × 400); E: Lymph node biopsy sections showed that nodular tissue architecture was effaced by small- to intermediate-sized lymphocytes (hematoxylin-eosin stain, × 400); F-H: The tumor cells in lymph nodes were positive for CD3 (F), TIA-1 (G) and granzyme B (H) (IHC × 400).
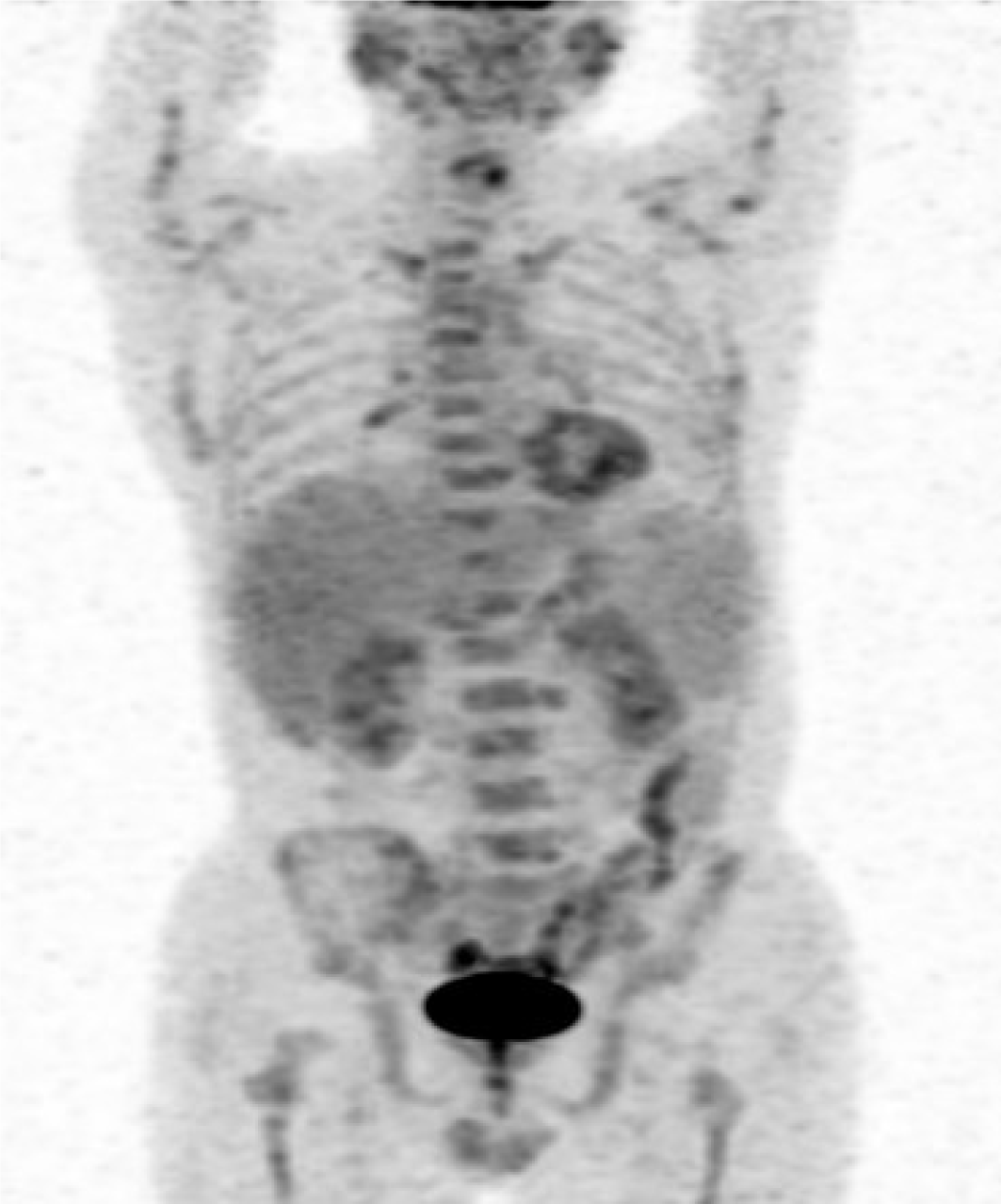
Figure 4 Positron emission tomography-computed tomography scanning in Case 2.
The maximum intensity projection of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography-computed tomography revealed that the spleen was enlarged and 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake was normal. Hypermetabolic lesions were detected in bone marrow, bilateral inguinal and bilateral lung hilar lymphadenopathy.
- Citation: Shen J, Wang JS, Xie JL, Nong L, Chen JN, Wang Z. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis secondary to composite lymphoma: Two case reports. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(30): 9159-9167
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i30/9159.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i30.9159