Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 6, 2021; 9(28): 8340-8348
Published online Oct 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i28.8340
Published online Oct 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i28.8340
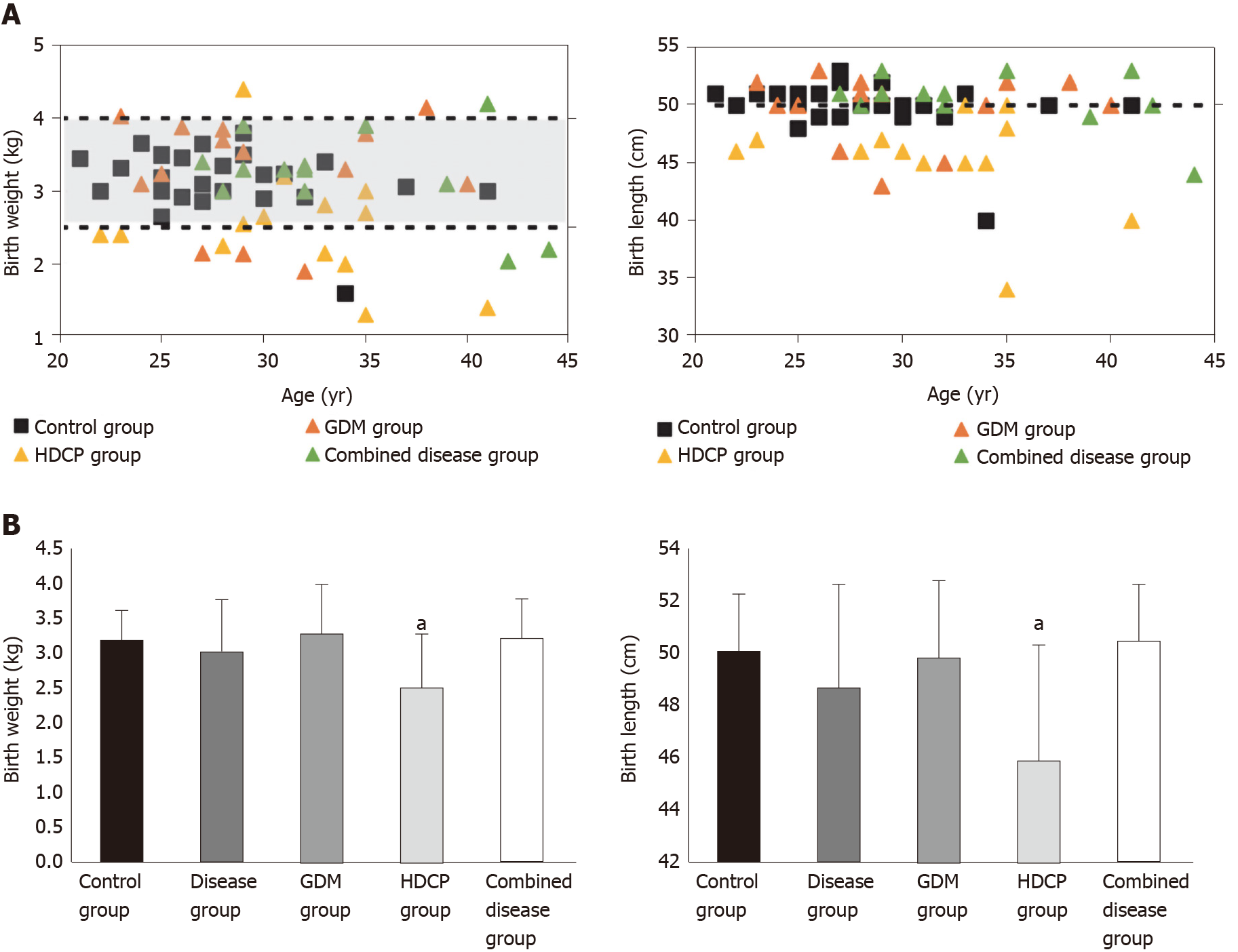
Figure 1 Distribution of birth weight and birth length.
A: Distribution of birth weight and birth length in control group and disease group; B: Birth weight and birth length were shown as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05. Control group: Healthy women who delivered at term without pregnancy complications; Combined disease group: The group with gestational diabetes (GDM) and hypertensive disorder complicating pregnancy (HDCP).
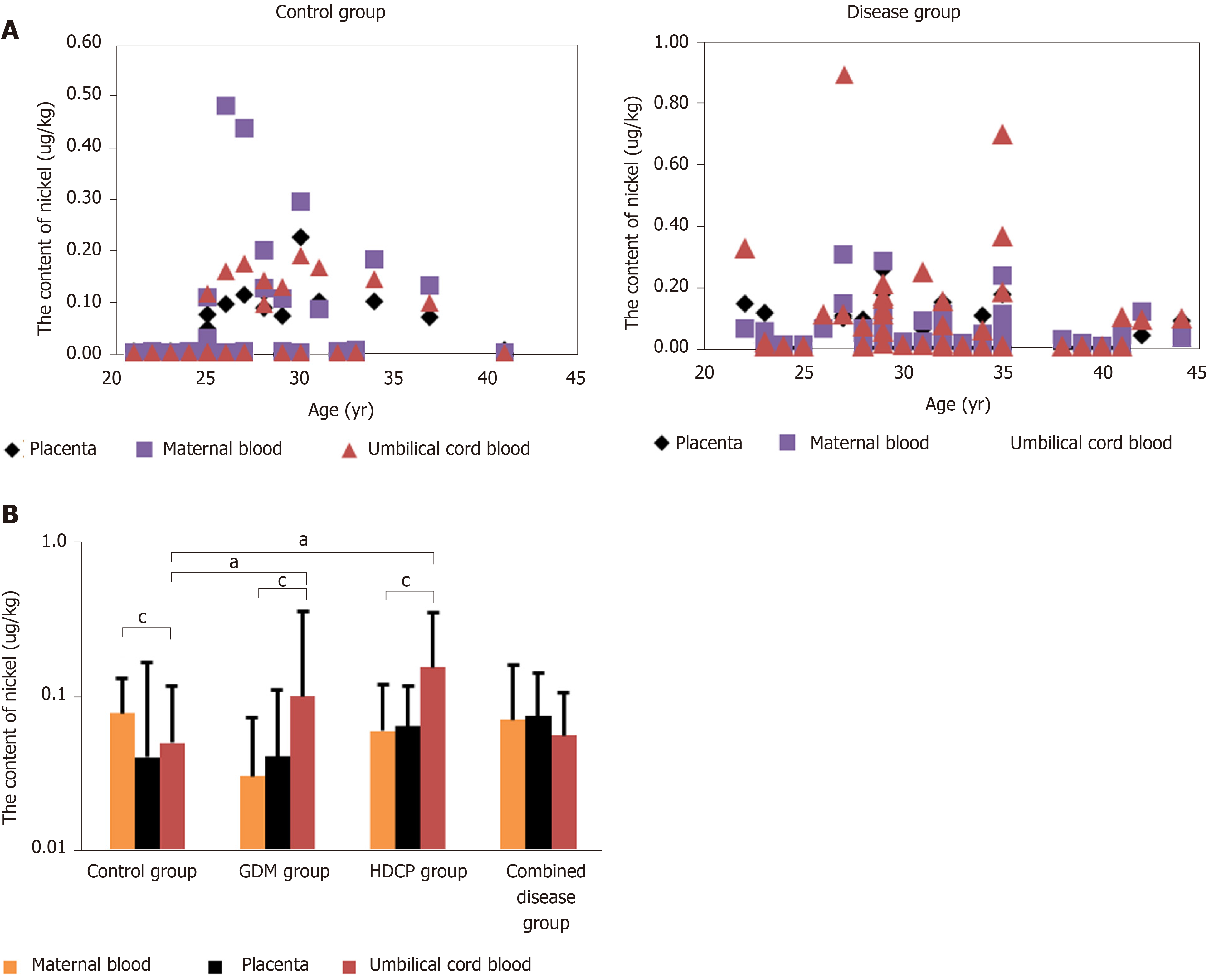
Figure 2 Distribution of nickel content in maternal-fetal system.
A: Nickel (Ni) content in maternal blood, placenta blood and cord blood in control group and disease group; B: The Ni content in maternal-fetal system is shown as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05 vs Ni content in umbilical cord blood in control group; cP < 0.05 vs Ni content in maternal blood in same group. Control group: Healthy women who delivered at term without pregnancy complications; Combined disease group: the group with gestational diabetes (GDM) and hypertensive disorder complicating pregnancy (HDCP).
- Citation: Ding AL, Hu H, Xu FP, Liu LY, Peng J, Dong XD. Pregnancy complications effect on the nickel content in maternal blood, placenta blood and umbilical cord blood during pregnancy. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(28): 8340-8348
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i28/8340.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i28.8340