Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 26, 2021; 9(24): 7110-7116
Published online Aug 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i24.7110
Published online Aug 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i24.7110
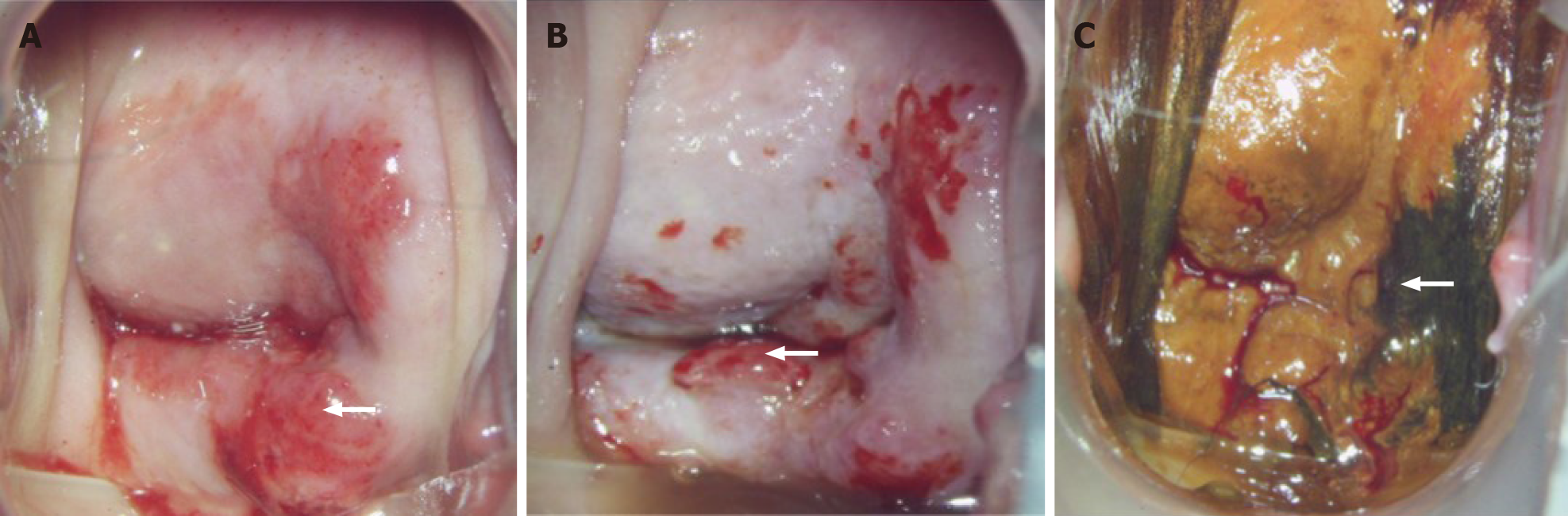
Figure 1 Morphology of cervical lesions.
A: Cervical lesions under colposcopy. White arrow indicates cervical extramedullary plasmacytoma lesions; B: Results of visual inspection with acetic acid. White arrow indicates positive visual inspection with acetic acid for extramedullary plasmacytoma; C: Cervical iodine test results. White arrow indicates negative staining.
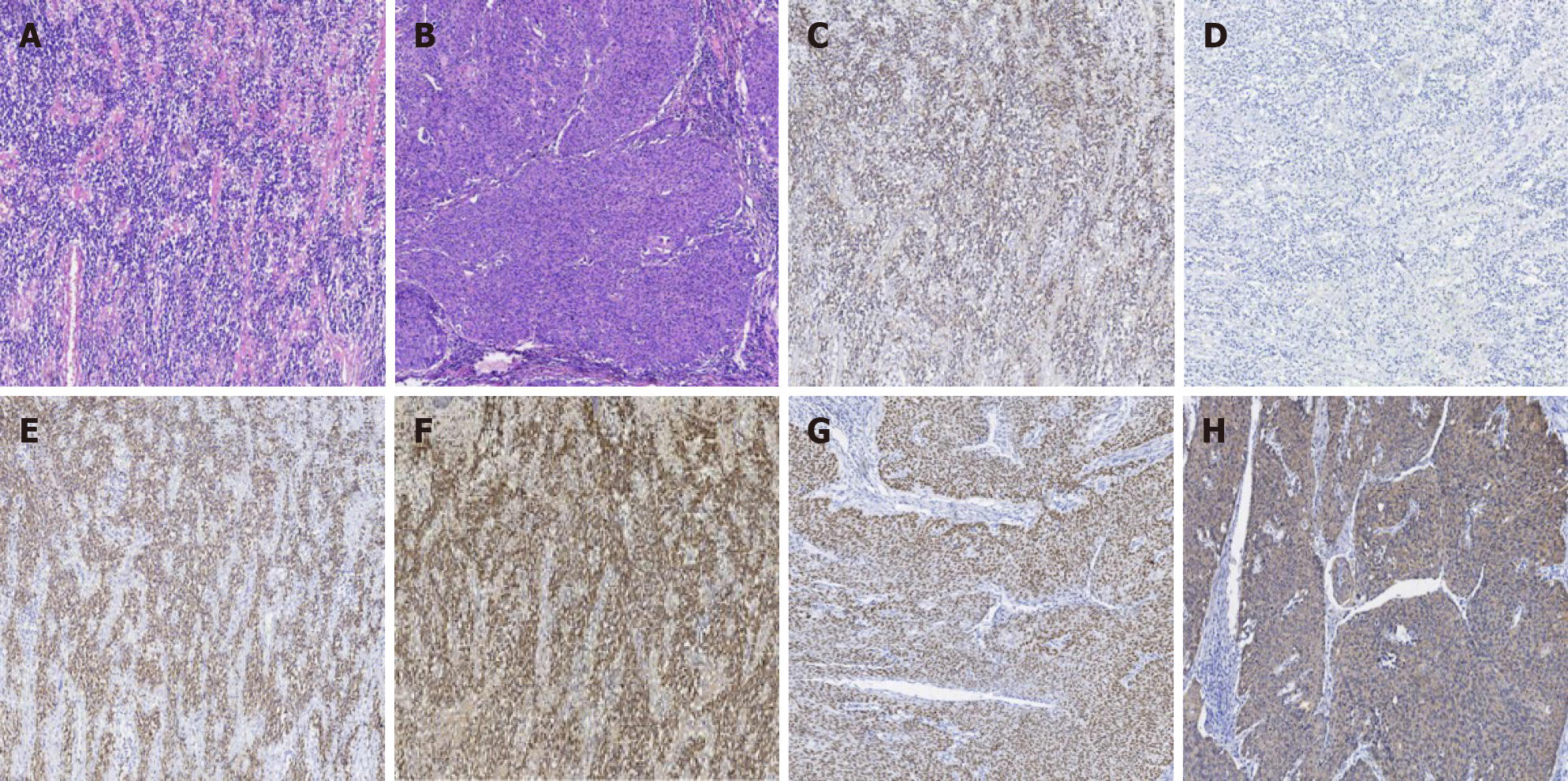
Figure 2 Pathology results of extramedullary plasmacytoma.
A: Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining of extramedullary plasmacytoma. The tumor cells were diffusely distributed. Pathological spindle division and Russell body were observed; B: HE staining of cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Hyperplasia of epithelioid cell nests, infiltrating growth pathological fission, and intercellular Bridges were easily observed; C: Immunohistochemistry staining of Kappa, which was diffusely positive in Plasma tumor cells; D: Immunohistochemistry staining of Lambda, which was diffusely negative in Plasma tumor cells; E: Immunohistochemistry staining of CD38, which was diffusely positive in Plasma tumor cells; F: Immunohistochemistry staining of CD138, which was diffusely positive in Plasma tumor cells; G: Immunohistochemistry staining of p40, which was diffusely positive in cervical squamous cancer cells; H: Immunohistochemistry staining of CK5/6, which was diffusely positive in cervical squamous cancer cells. Magnification: A-H × 40.
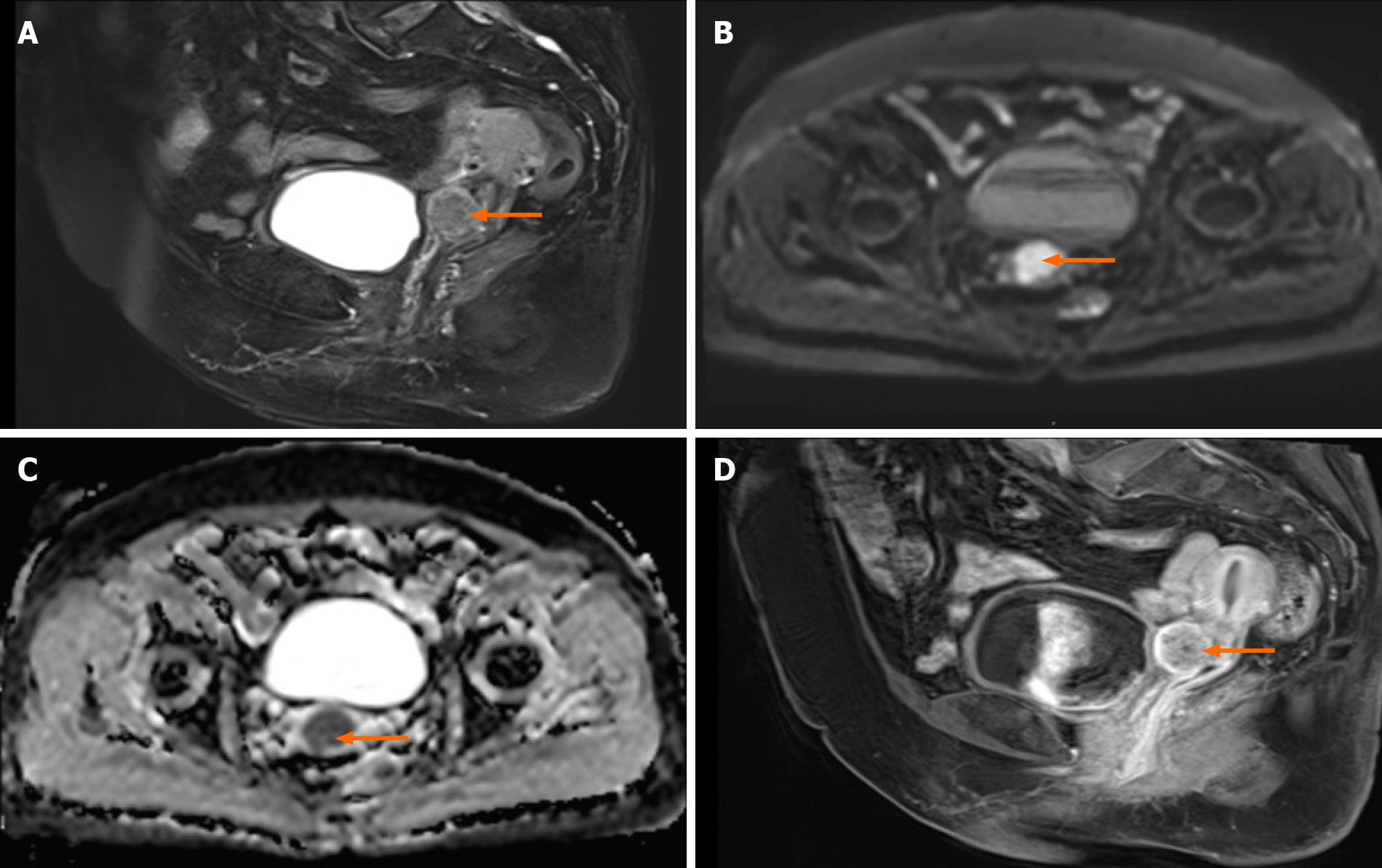
Figure 3 Pelvic enhanced magnetic resonance imaging images.
A: The anterior lip of the cervix showed a slightly high signal on T2WI, with a diameter of about 2.5 cm; B: DWI diffusion was limited and showed high signal; C: Apparent diffusion coefficient value decreased, which was 0.838 × 10-3 mm2/s; D: On contrast-enhanced scan, slight enhancement was observed in the edge. Orange arrows indicate cervical lesions.
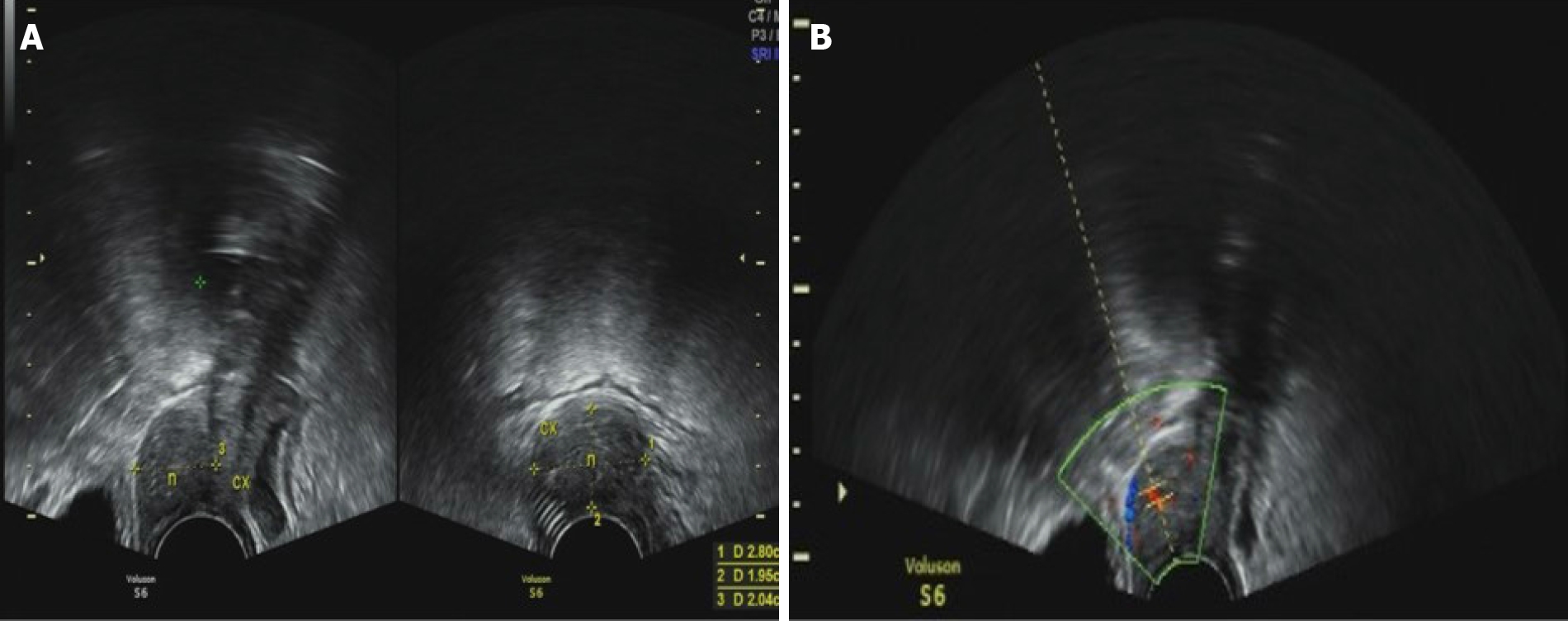
Figure 4 Transvaginal ultrasound images.
A: The thickness of cervix was about 2.8 cm. The thickness of anterior lip was obvious; B: There was a hypoechoic solid nodule with the diameter of 3 cm, with unclear boundary and a dotted blood flow signal. RI: 0.56.cx (cervix), n (nodule).
- Citation: Zhang QY, Li TC, Lin J, He LL, Liu XY. Coexistence of cervical extramedullary plasmacytoma and squamous cell carcinoma: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(24): 7110-7116
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i24/7110.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i24.7110