Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 16, 2021; 9(23): 6886-6899
Published online Aug 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i23.6886
Published online Aug 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i23.6886
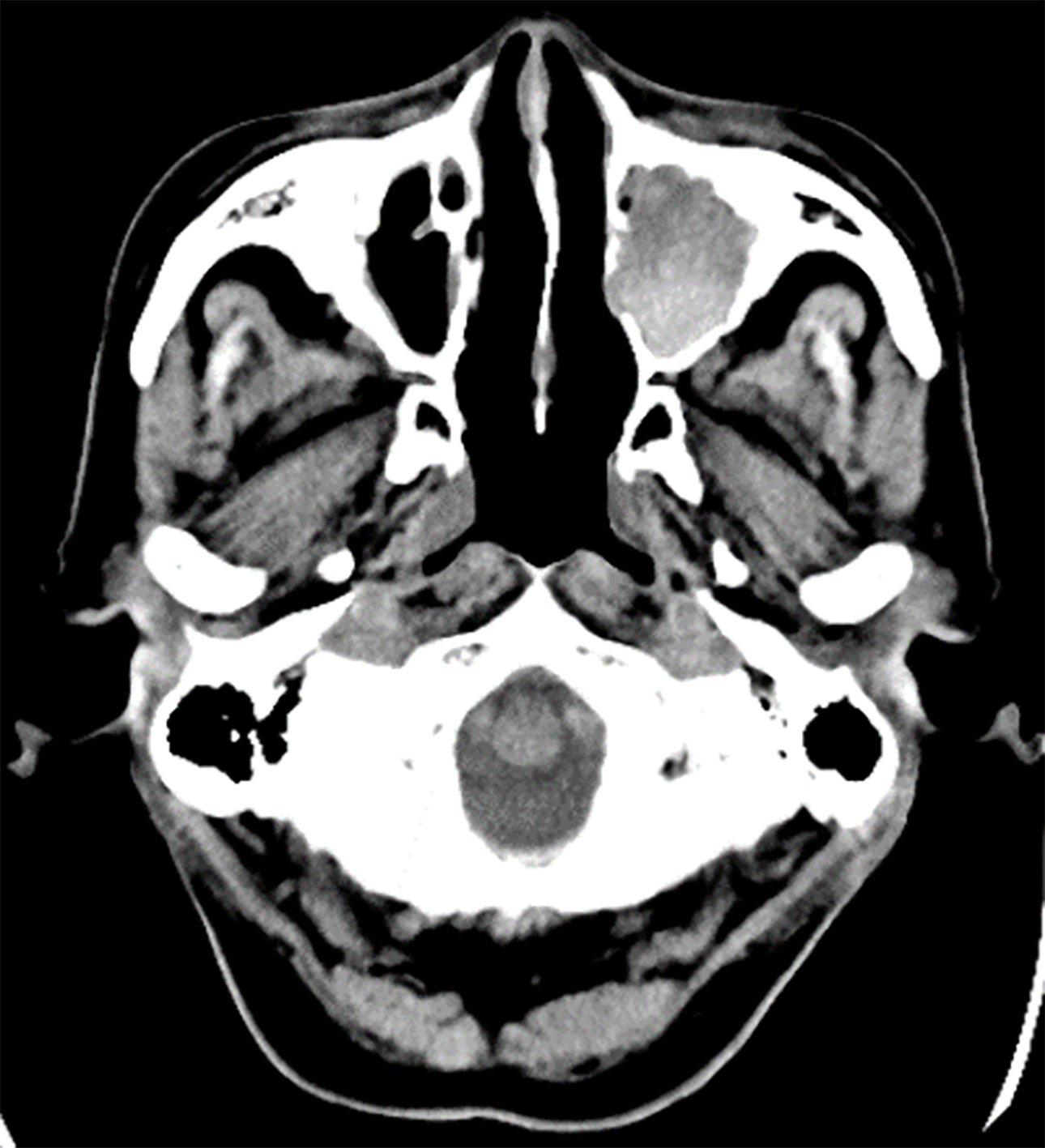
Figure 1 A plain computed tomography scan on day 1.
The 3 cm × 3.1 cm × 3 cm sized left maxillary sinus of the patient was completely filled with mass, and a partially high-density area was confirmed inside.
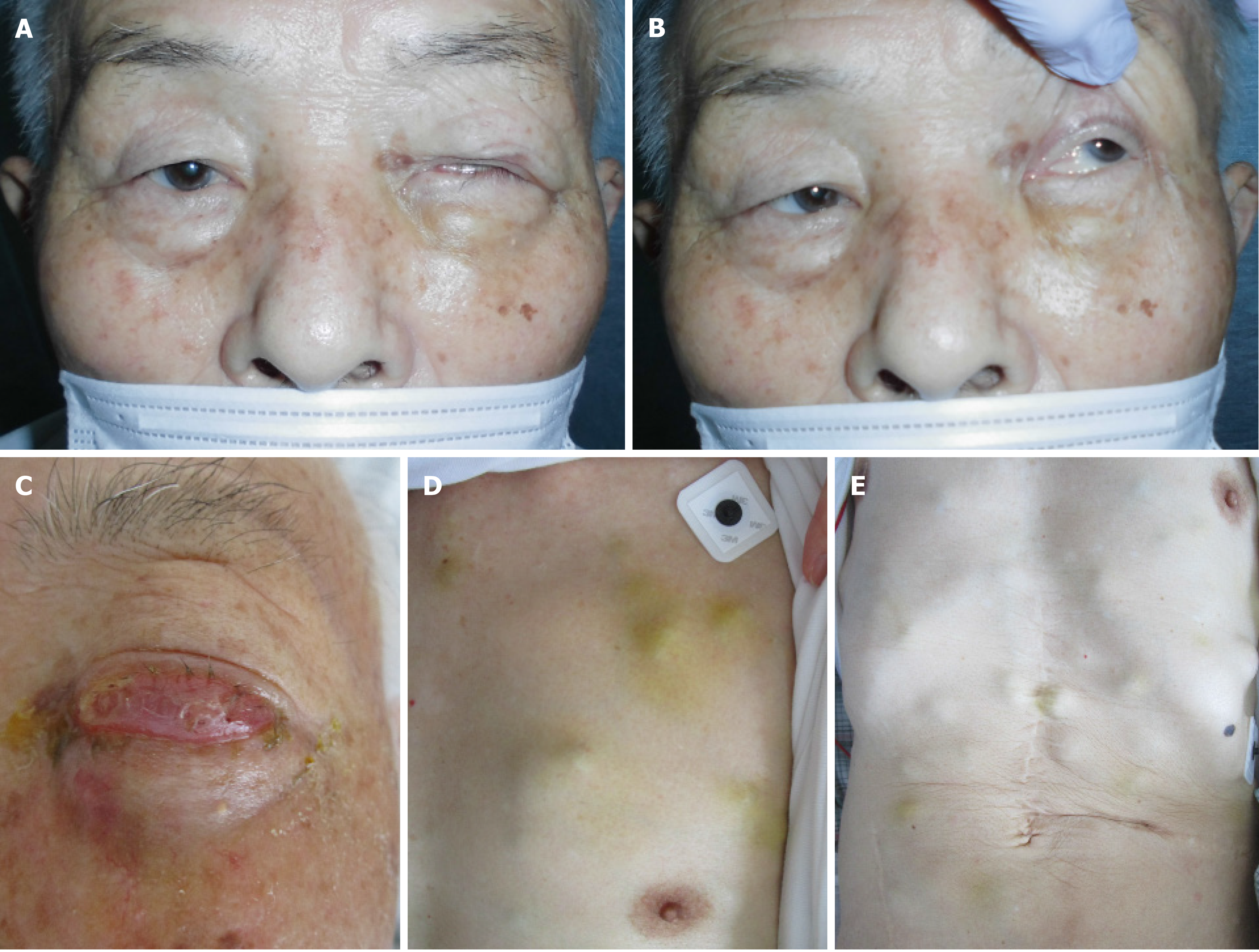
Figure 2 Appearance of the body.
A: Day 31. Left ptosis was confirmed; B: Day 31. When we opened his eyes passively, hyperexophoria of the left eye was confirmed; C: Day 62. Left circumocular swelling was confirmed. At this time, the patient could not open his left eye; D: Day 62. Chest of the patient. Multiple skin tumors were confirmed; E: Day 62. Chest and abdomen of the patient. Multiple skin tumors were confirmed.
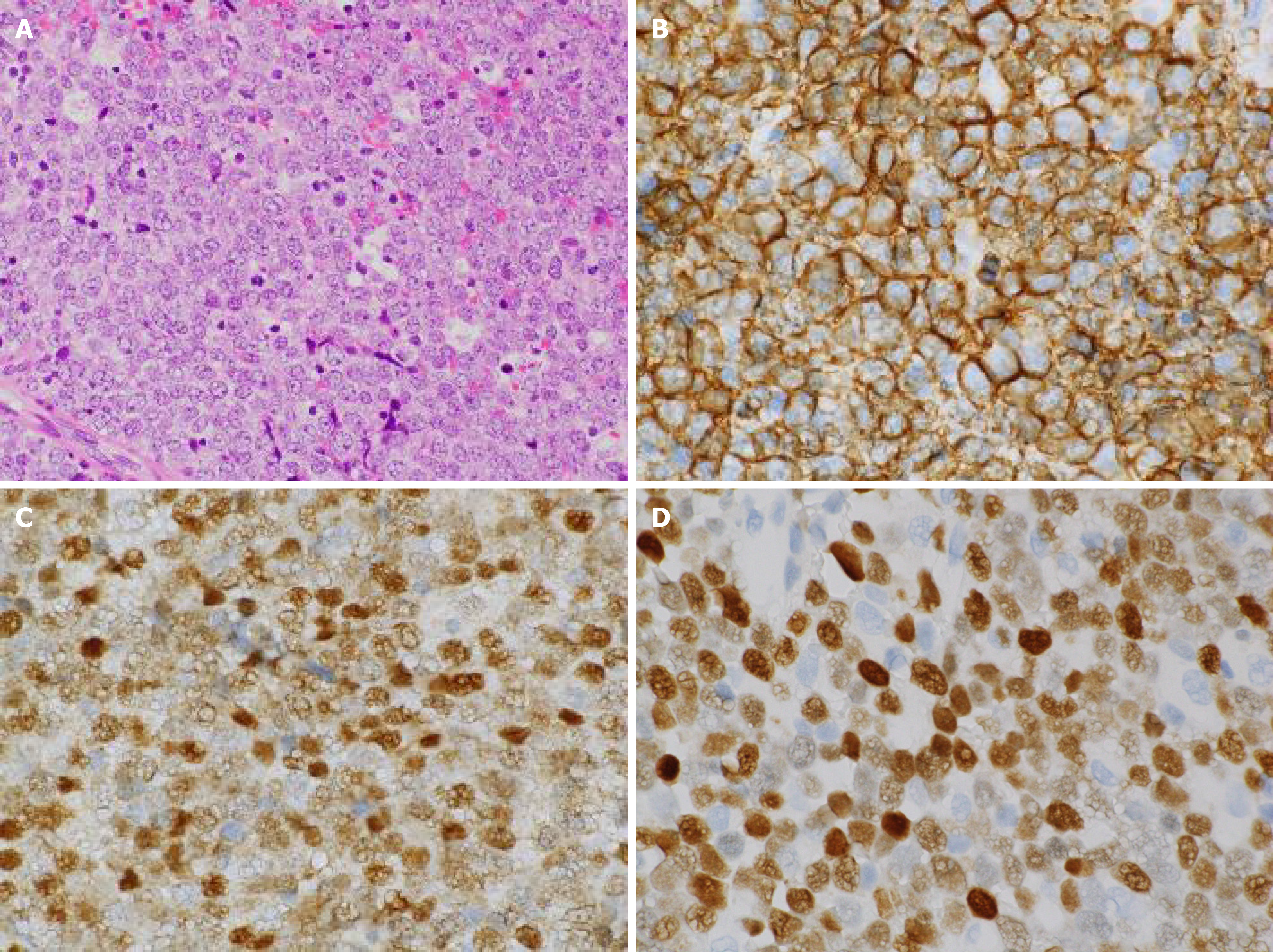
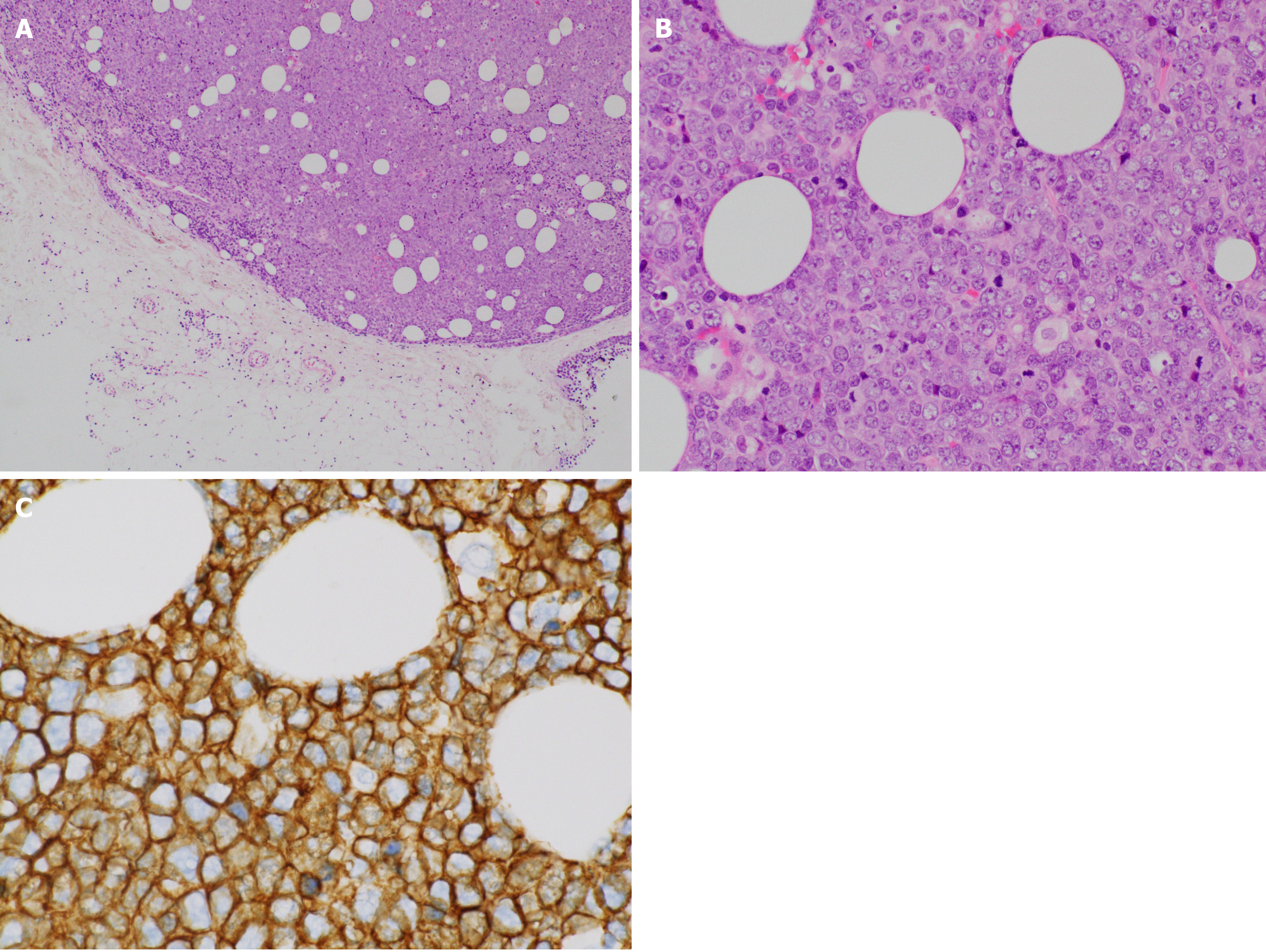
Figure 3 Histopathological images of the biopsy specimen from the left maxillary sinus mass taken on day 50.
A: Aggregates of large atypical lymphocytes with irregular nuclei having uneven chromatin and small to large nucleoli are evident in a necrotic background. Some cells show multilobulated nuclei. Mitosis and apoptotic bodies are conspicuous. Hematoxylin and eosin staining (× 200 magnification); B: Cluster of differentiation 20-positive cells were confirmed through immunohistochemical staining (× 400 magnification); C: Bcl-6-positive cells were confirmed through immunohistochemical staining (× 400 magnification); and D: MUM1-positive cells were confirmed through immunohistochemical staining (× 400 magnification).
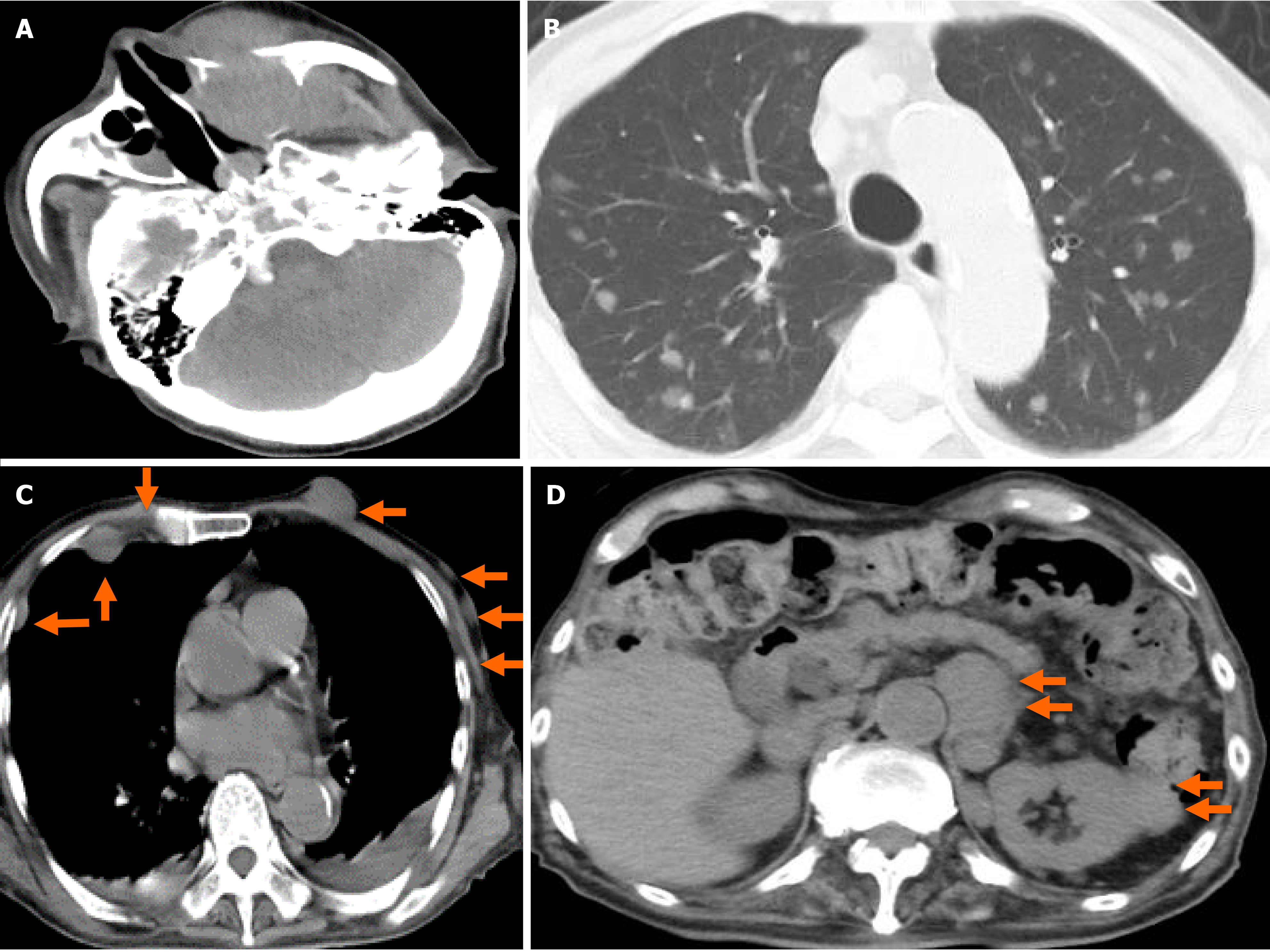
Figure 4 A plain computed tomography scan on day 62.
A: The 4 cm × 3.5 cm × 4 cm sized left maxillary sinus was completely filled with mass, and it was oppressed, involved the orbital base, destroyed the anterior, internal, and external walls, and protuberated outside; B: Chest. Pulmonary window setting. Multiple tumors (0.5-1.5 cm in size) were confirmed in both lungs; C: Chest. Mediastinal window. Multiple subcutaneous tumors and chest wall tumors were confirmed (orange arrows); and D: Abdomen. An abdominal paraaortic lymph node swelling (3 cm in size) and a left kidney nodule (1-2 cm in size) were confirmed (orange arrows).
Figure 5 Histopathological images of the biopsy specimen from skin mass taken on day 70.
A: Aggregates of large atypical lymphocytes with irregular nuclei having uneven chromatin and small to large nucleoli are evident in a necrotic background. Some cells show multilobulated nuclei. Mitosis and apoptotic bodies are conspicuous. Hematoxylin and eosin staining (× 40 magnification); B: Aggregates of large atypical lymphocytes with irregular nuclei having uneven chromatin and small to large nucleoli are evident in a necrotic background. Some cells show multilobulated nuclei. Mitosis and apoptotic bodies are conspicuous. Hematoxylin and eosin staining (× 200 magnification); and C: CD20-positive cells were confirmed through immunohistochemical staining (× 400 magnification).
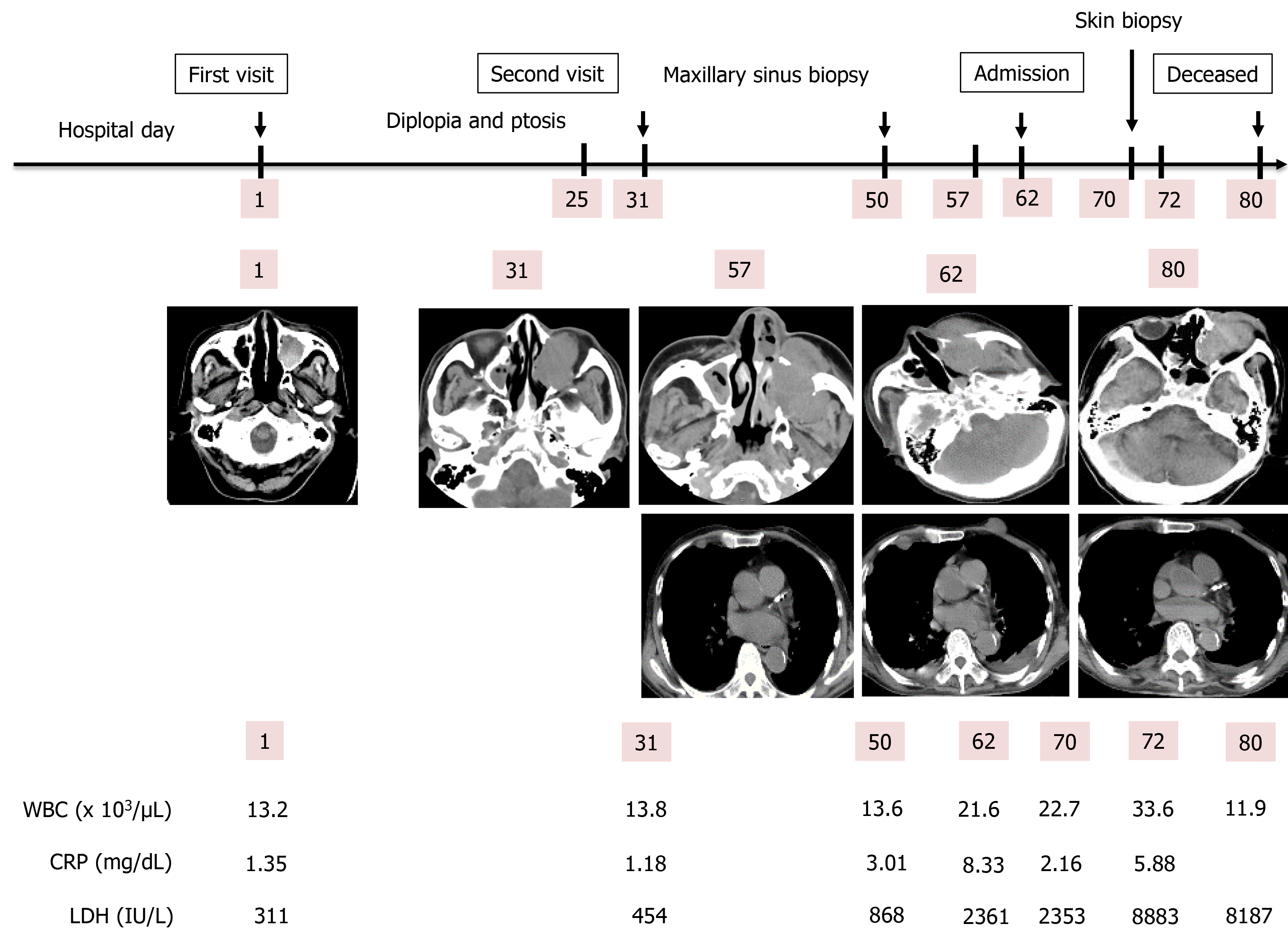
Figure 6 Clinical course of the patient.
The patient initially visited our hospital on day 1. A diplopia occurred on day 31, and a maxillary sinus biopsy was performed on day 50. Afterwards, he was admitted on day 62 due to rapid deterioration of his condition, and a skin biopsy was performed on day 70. He died on day 80. WBC: White blood cell; CRP: C-reactive protein; LDH: Lactate dehydrogenase.
- Citation: Usuda D, Izumida T, Terada N, Sangen R, Higashikawa T, Sekiguchi S, Tanaka R, Suzuki M, Hotchi Y, Shimozawa S, Tokunaga S, Osugi I, Katou R, Ito S, Asako S, Takagi Y, Mishima K, Kondo A, Mizuno K, Takami H, Komatsu T, Oba J, Nomura T, Sugita M, Kasamaki Y. Diffuse large B cell lymphoma originating from the maxillary sinus with skin metastases: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(23): 6886-6899
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i23/6886.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i23.6886