Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 16, 2021; 9(23): 6879-6885
Published online Aug 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i23.6879
Published online Aug 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i23.6879
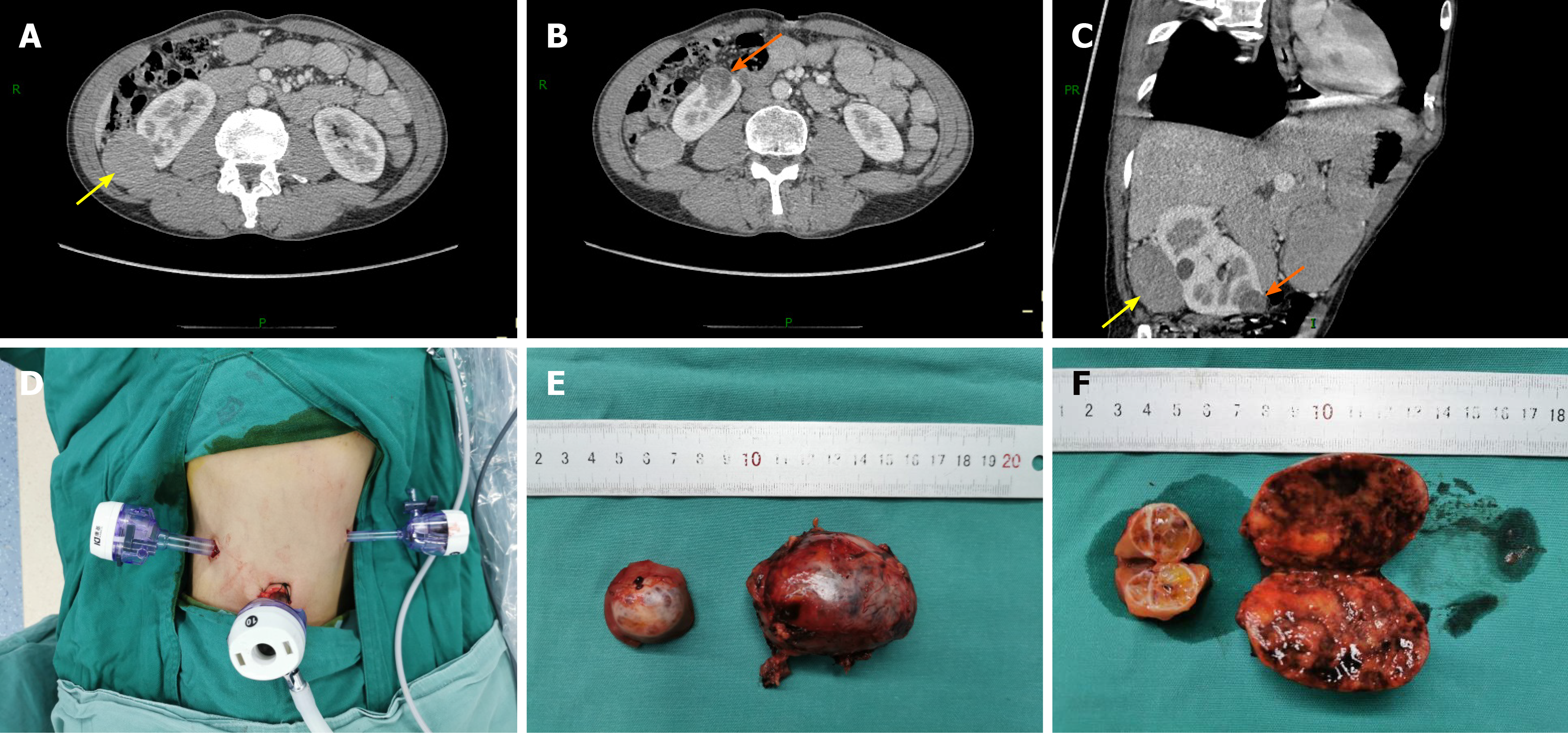
Figure 1 Preoperative contrast-enhanced computed tomography imaging and postoperative surgical specimens.
A and B: Transverse scan; C: Oblique sagittal scan; D: Trocar distribution in the retroperitoneal approach; E: Tumor appearance; F: Cross-section of the tumor specimen. The yellow arrow indicates the large tumor and the orange arrow indicates the small tumor.
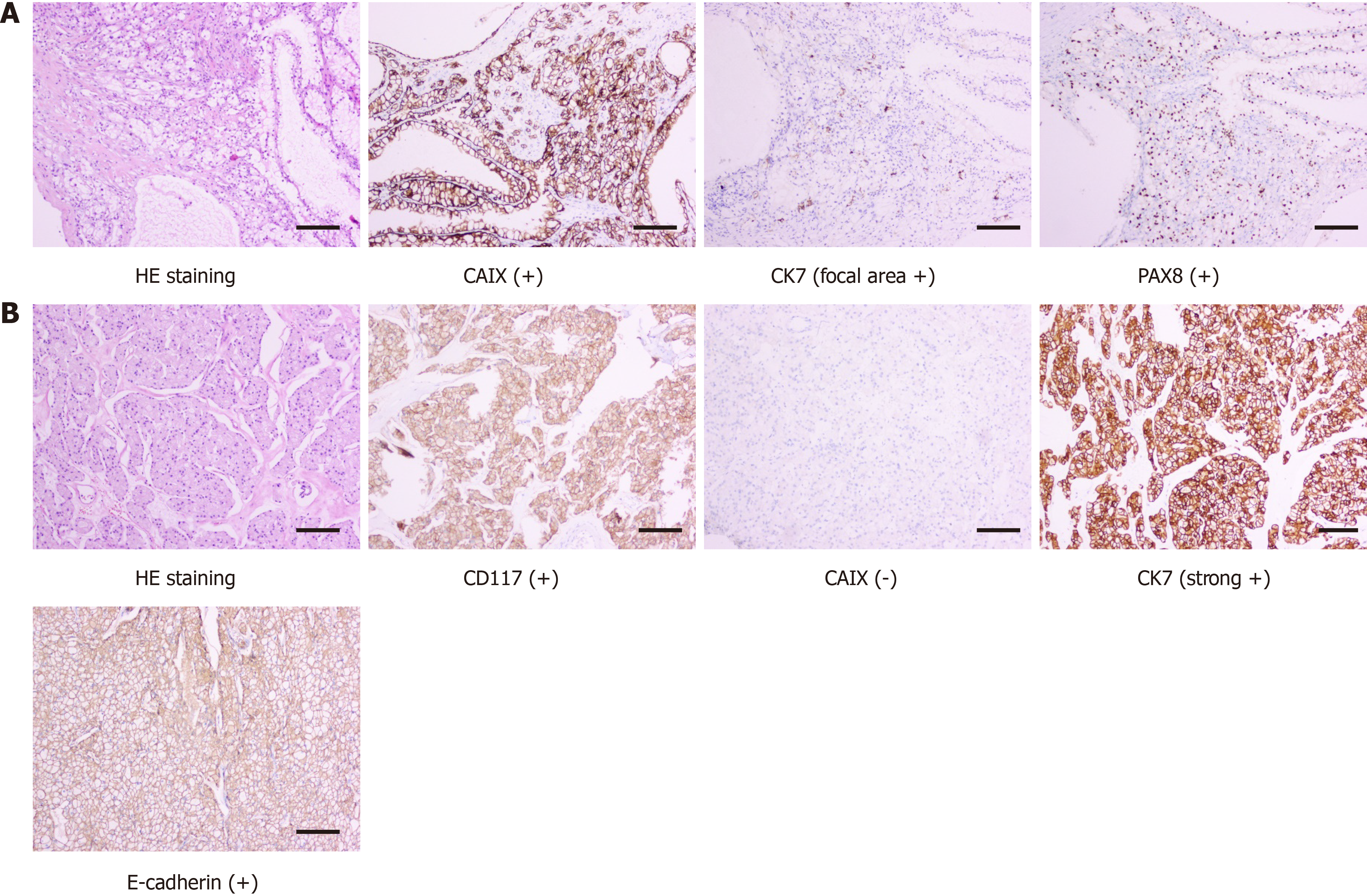
Figure 2 Postoperative pathological diagnosis.
A: Renal clear cell carcinoma (small tumor); B: Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma (large tumor).
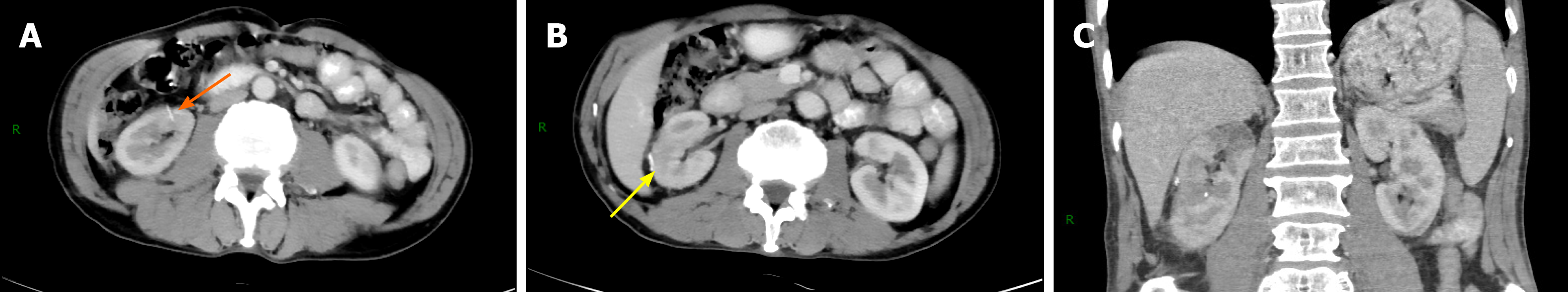
Figure 3 Postoperative contrast-enhanced computed tomography imaging.
A and B: Transverse scan; C: Coronal scan. The yellow arrow indicates the location of the large tumor, and the orange arrow indicates the location of the small tumor after surgery.
- Citation: Xiao YM, Yang SK, Wang Y, Mao D, Duan FL, Zhou SK. Retroperitoneal laparoscopic partial nephrectomy for unilateral synchronous multifocal renal carcinoma with different pathological types: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(23): 6879-6885
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i23/6879.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i23.6879