Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 16, 2021; 9(23): 6832-6838
Published online Aug 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i23.6832
Published online Aug 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i23.6832
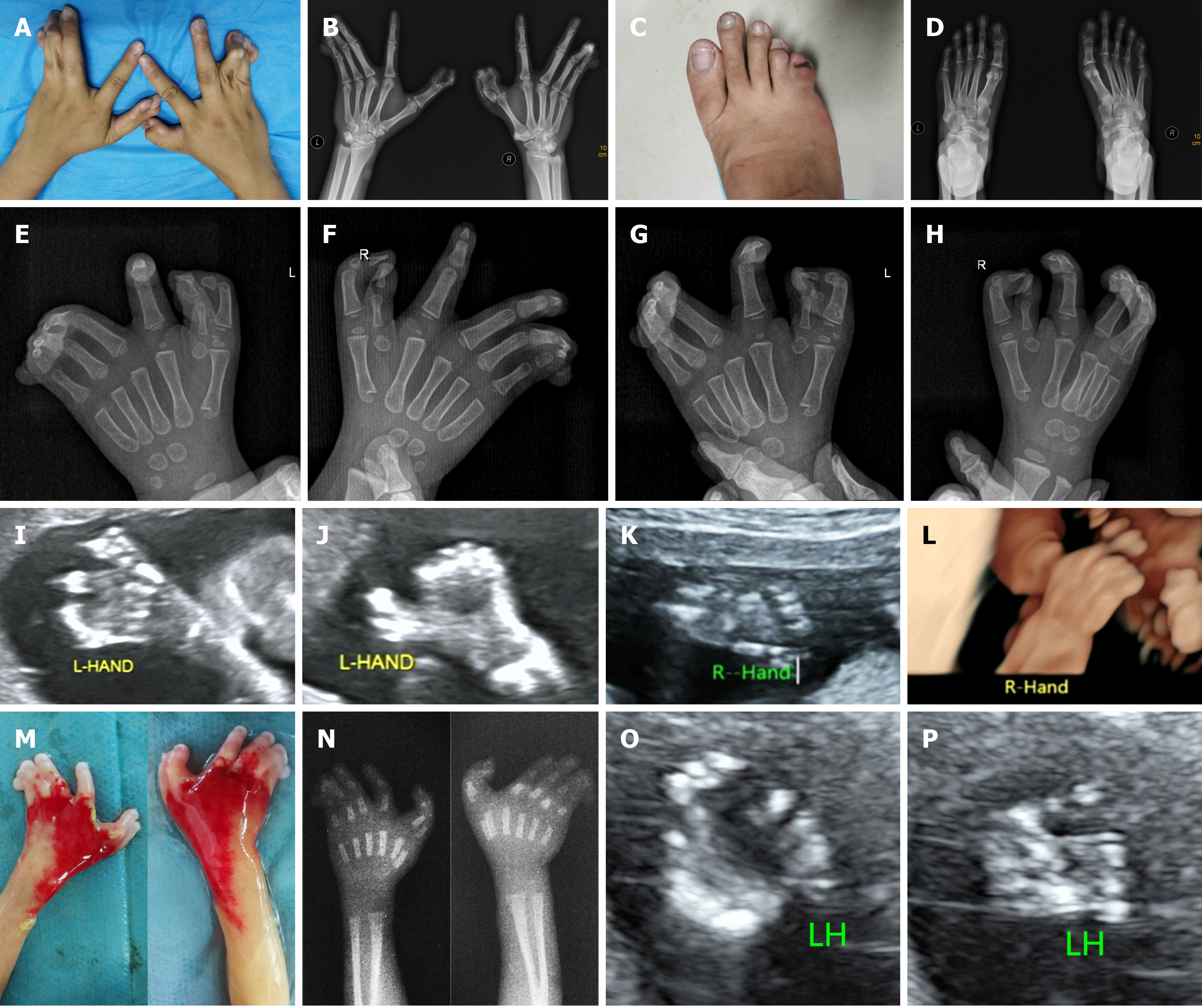
Figure 1 Limb features of patients with triphalangeal thumb-polysyndactyly syndrome.
A and B: Physical and X-ray examinations showed that the mother had triphalangeal thumb, pre- and postaxial polysyndactyly, and cutaneous fusion of the 3rd, 4th, and 5th fingers accompanied by deviant posture of the hands, with unaffected index fingers; C and D: Physical and X-ray examinations showed that the mother’s right foot had postaxial polysyndactyly; E-H: X-ray examination revealed that the son had an abnormality similar to that of his mother; I: Two-dimensional ultrasound showed triphalangeal thumb polysyndactyly; J and K: Two-dimensional ultrasound showed trident-like thumb; L: Three-dimensional ultrasound vividly showed postaxial webbing of the fingers; M: Postnatal autopsy of both hands showed pre- and postaxial polysyndactyly and webbing of the 3rd, 4th, and 5th fingers; N: Postnatal X-ray images of both hands showed triphalangeal thumb polysyndactyly and six metacarpals; O: Prenatal ultrasound image of the left hand showed an echo of an extra digit on the 5th finger side and double thumbs; P: Prenatal ultrasound image of the left hand showed no separation of the 3rd, 4th, and 5th fingers. LH: Left hand; L: Left; R: Right.
- Citation: Zhang SJ, Lin HB, Jiang QX, He SZ, Lyu GR. Prenatal diagnosis of triphalangeal thumb-polysyndactyly syndrome by ultrasonography combined with genetic testing: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(23): 6832-6838
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i23/6832.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i23.6832