Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 6, 2021; 9(22): 6478-6484
Published online Aug 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i22.6478
Published online Aug 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i22.6478
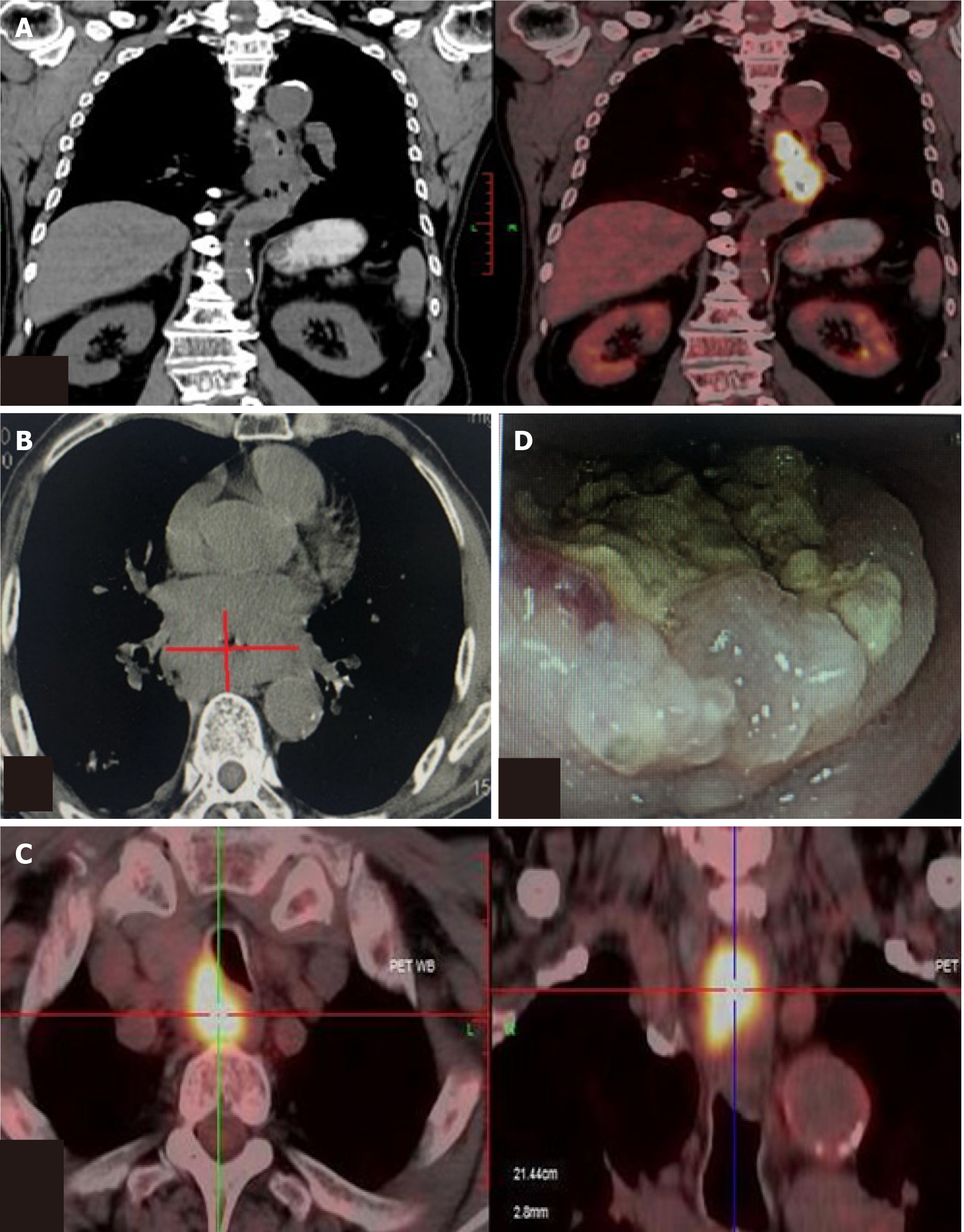
Figure 1 Positron emission tomography-computed tomography, computed tomography and endoscopy demonstrated a tumor sited in the middle and lower esophagus and multiple lymph nodes metastasis.
A: Positron emission tomography-computed tomography showed esophageal carcinoma; B: Computed tomography showed esophageal carcinoma; C: Multiple lymph nodes metastasis; D: Endoscopy outcome.
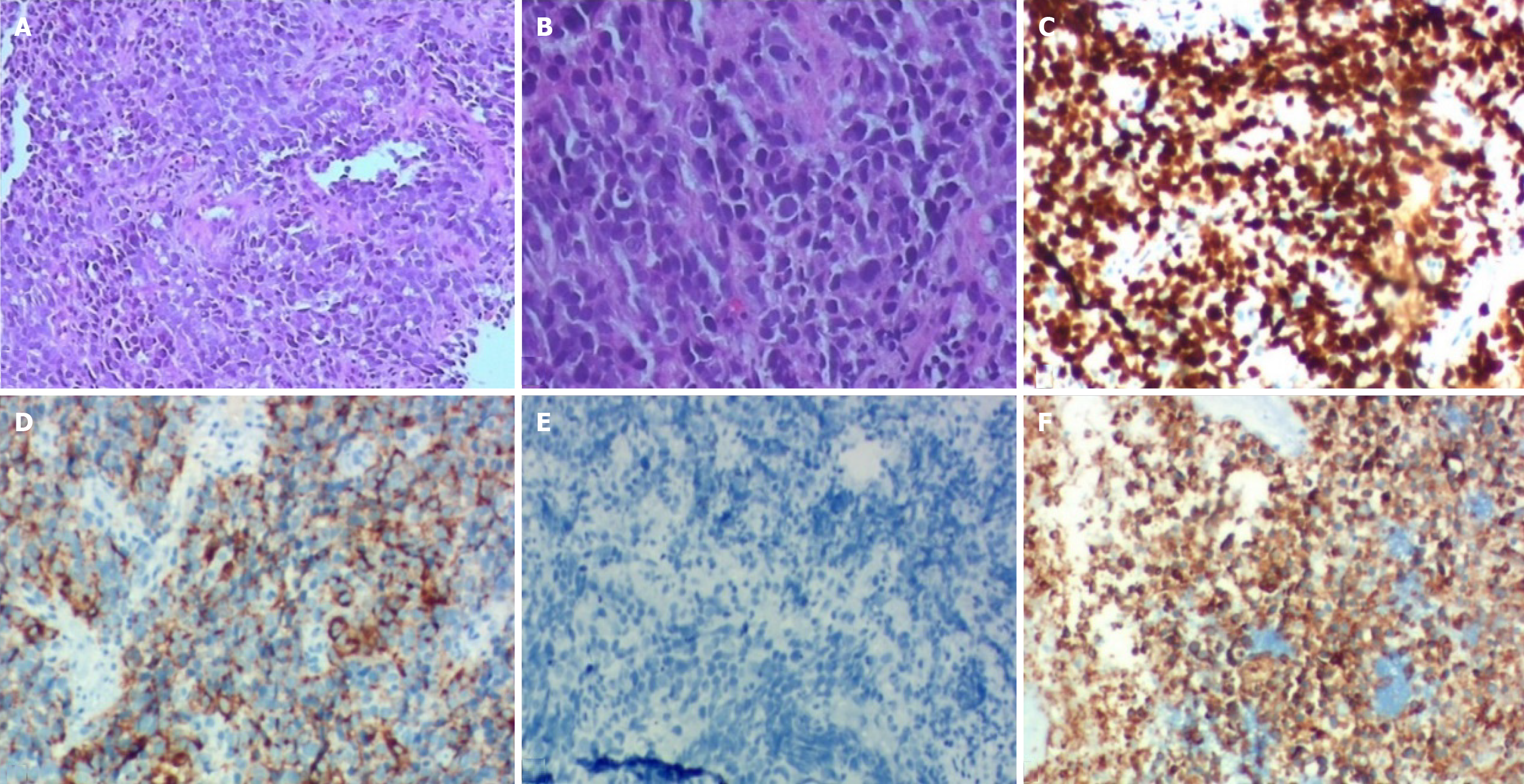
Figure 2 Histopathological and immunohistochemistry examinations.
A: The field of vision was completely filled with tumor cells (hematoxylin-eosin staining, × 10); B: Higher magnification showed small oval and spindle cell shape nuclei, ill-defined cell borders, and inconspicuous nucleoli (hematoxylin-eosin staining, × 200); C: Ki-67 (index > 80%); D: Cg-A-positive; E: p40-positive; F: Syn-positive.
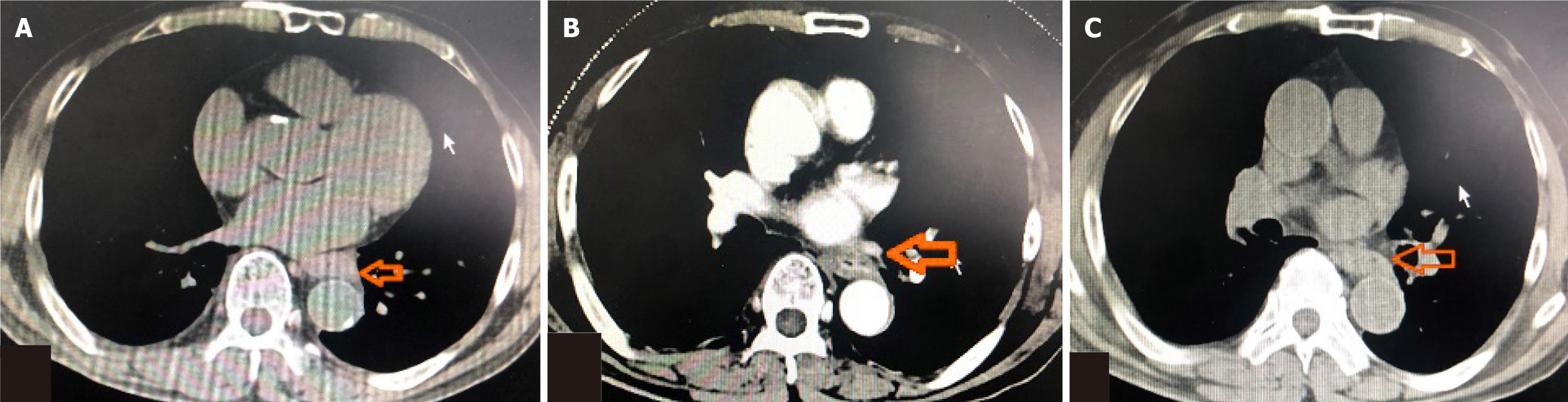
Figure 3 Computed tomography showed the effects of esophageal carcinoma after chemotherapy or immunotherapy.
A: After 4 cycles chemotherapy; B: After 4 cycles immunotherapy; C: After 8 cycles immunotherapy.
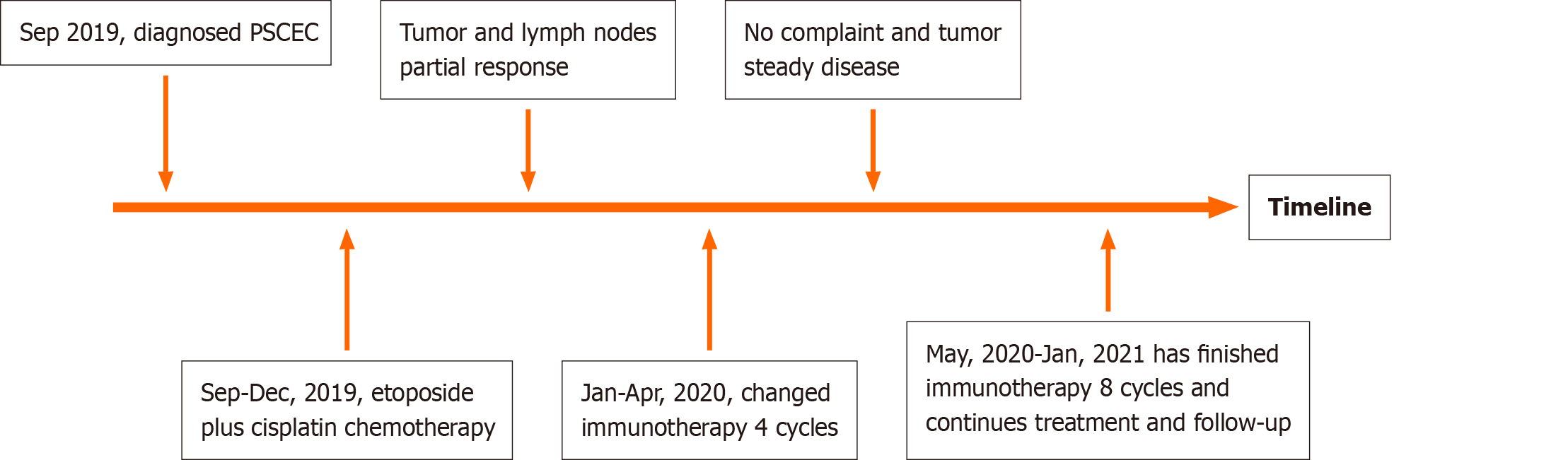
Figure 4 Timeline of the whole medical procedure for this case.
- Citation: Wu YH, Zhang K, Chen HG, Wu WB, Li XJ, Zhang J. Primary small cell esophageal carcinoma, chemotherapy sequential immunotherapy: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(22): 6478-6484
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i22/6478.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i22.6478