Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 6, 2021; 9(22): 6393-6402
Published online Aug 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i22.6393
Published online Aug 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i22.6393
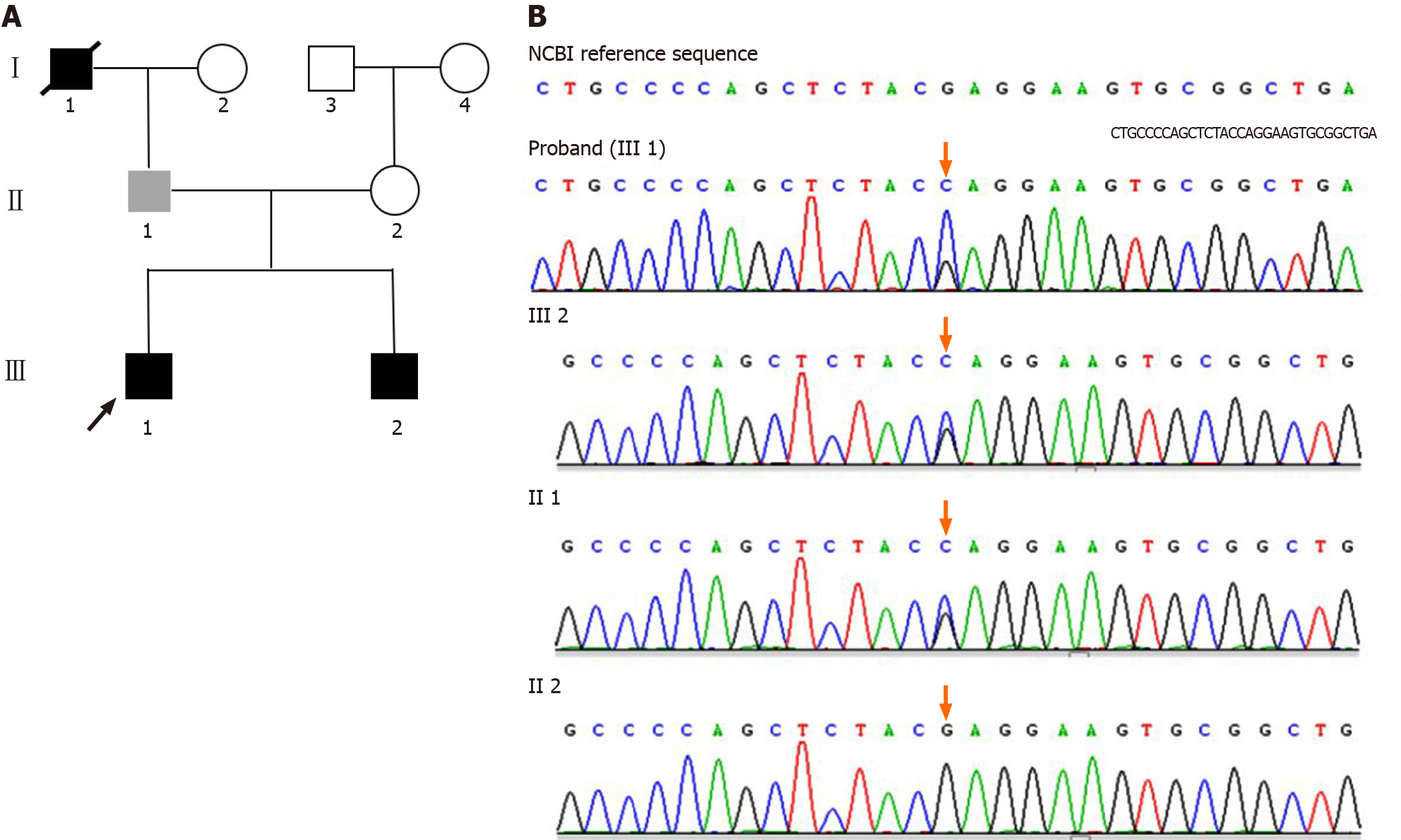
Figure 1 Pedigree of the PAPA family and genetic analysis.
A: Family tree of an autosomal dominant hyponatremia pedigree. Square represents male and circle represents female. Arrow denotes the proband (III-1), black symbols represent the affected individuals (III-1 and III-2). The grey symbol refers to the individual that has the gene mutation without symptoms (II-1). The symbol with diagonal slashes denotes the deceased individual who had the similar symptoms (I-1); B: A missense mutation p.748 G>C (p.E250Q) in PSTPIP1 was found in proband (III-1), III-2, and II-1.
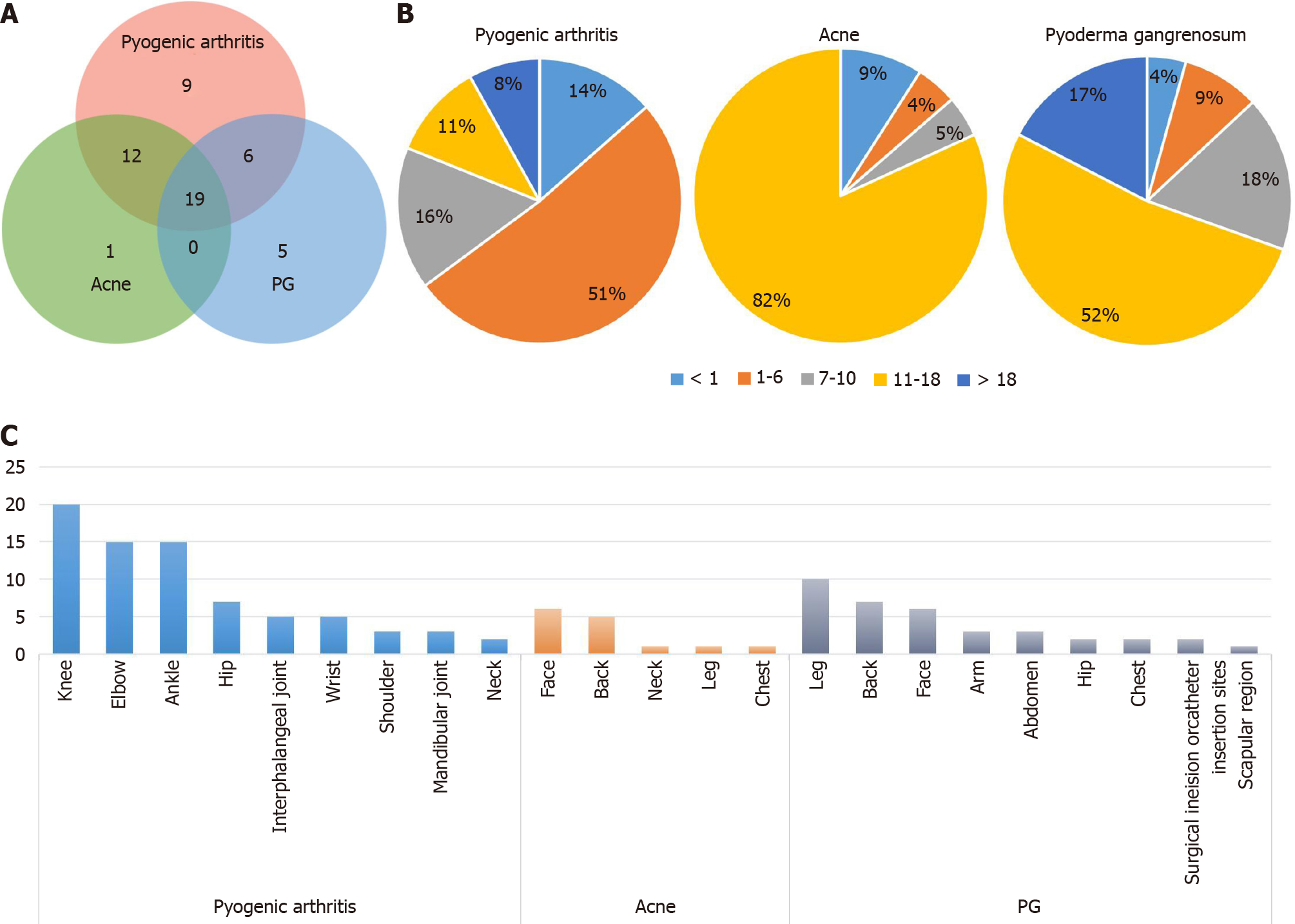
Figure 2 Characteristics of clinical manifestations in pyogenic arthritis, pyoderma gangrenosum, and acne syndrome (data were collected from 52 cases who had detailed description of symptoms).
A: The Venn diagram for the three typical symptoms. Each circle represents a symptom, the area of coincidence represents cases with two or three symptoms; B: The sector diagram for the age of each symptom onset. Pyogenic arthritis always appears in childhood. Skin lesions are more likely to appear from adolescence to adulthood; C: The histogram for the affecting areas of each symptom. Arthritis mainly affects occurs in knee joints, elbow joints, ankle joints, hip joints, and other large joints. Acne always appears on the face and back. Pyogenic granuloma often occurs on the extremities and the back.
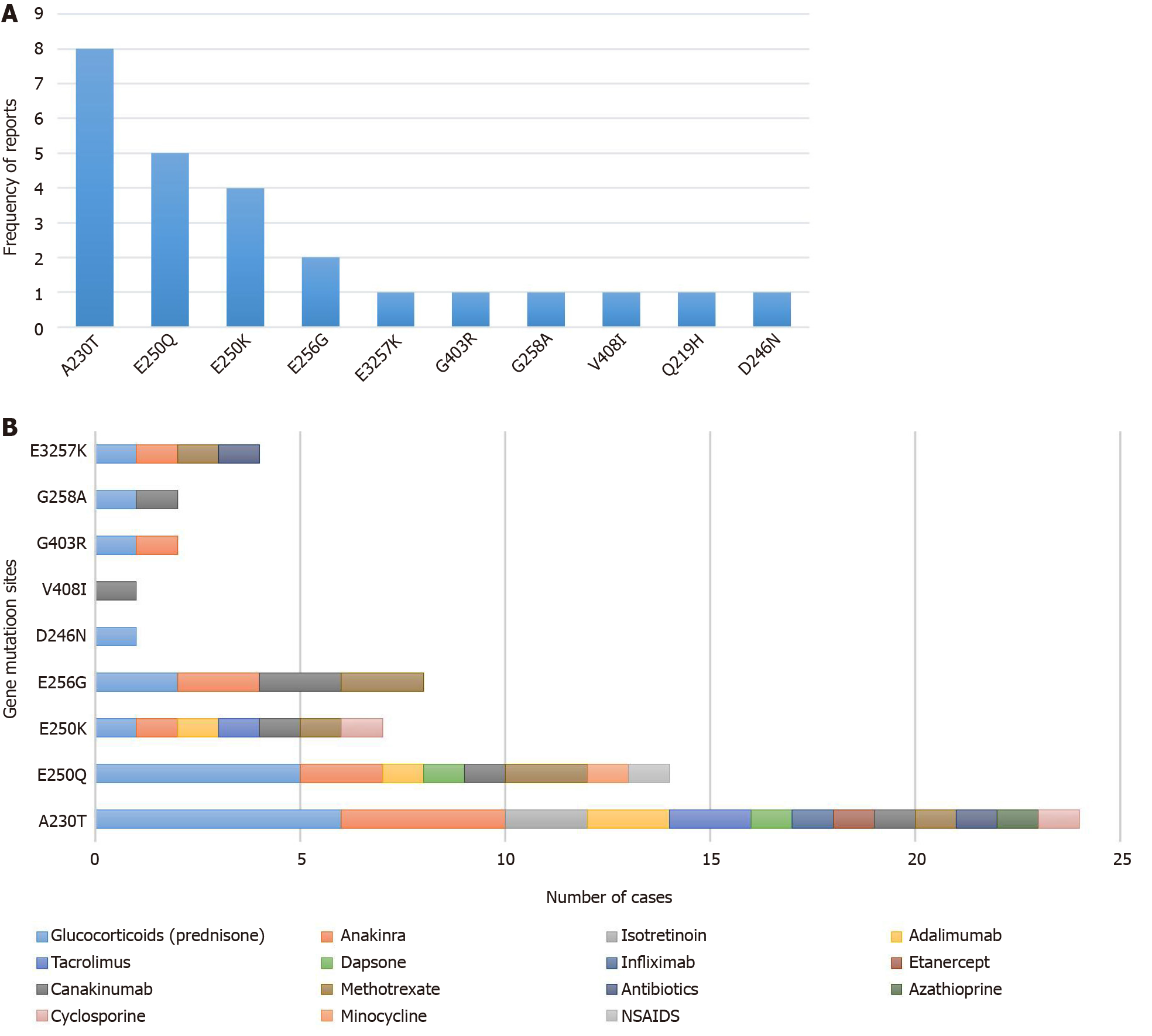
Figure 3 Type of gene mutation and relationship between gene mutation sites and effective drugs.
A: Types of gene mutation. Ten gene mutations of pyogenic arthritis, pyoderma gangrenosum, and acne have been reported worldwide. A230T, E250Q, and E250K are the most common mutations; B: Fifteen drugs with a good efficacy were found, including corticosteroids, azathioprine, sulfasalazine, leflunomide, tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitors, interleukin-1β antagonist, etc. This figure summarizes effective drugs based on their gene mutation sites.
- Citation: Lu LY, Tang XY, Luo GJ, Tang MJ, Liu Y, Yu XJ. Pyogenic arthritis, pyoderma gangrenosum, and acne syndrome in a Chinese family: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(22): 6393-6402
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i22/6393.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i22.6393