Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 6, 2021; 9(22): 6254-6267
Published online Aug 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i22.6254
Published online Aug 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i22.6254
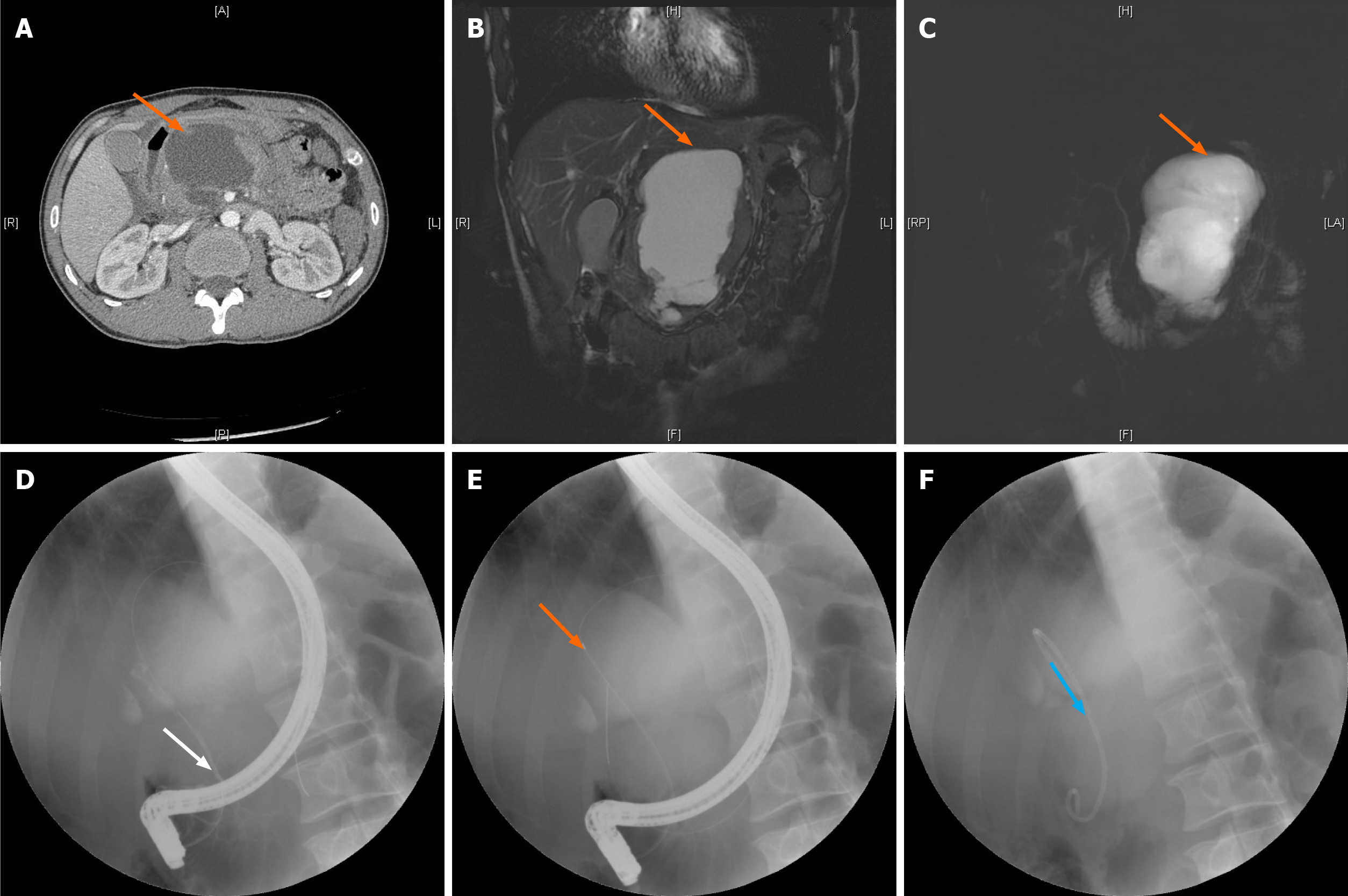
Figure 1 Process of pancreatic duct stenting for pancreatic pseudocysts.
A: Location of the pancreatic pseudocyst shown by computed tomography; B and C: Location of the pancreatic pseudocyst shown by magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (orange arrow) using the T2 weighted image sequence (B) and balanced turbo field echo sequence (C); D: Successful duodenal intubation followed by a guide wire inserted into the pancreatic duct (white arrow); E: Pancreatic duct and cyst shown by imaging (orange arrow); F: Pancreatic duct stenting (blue arrow).
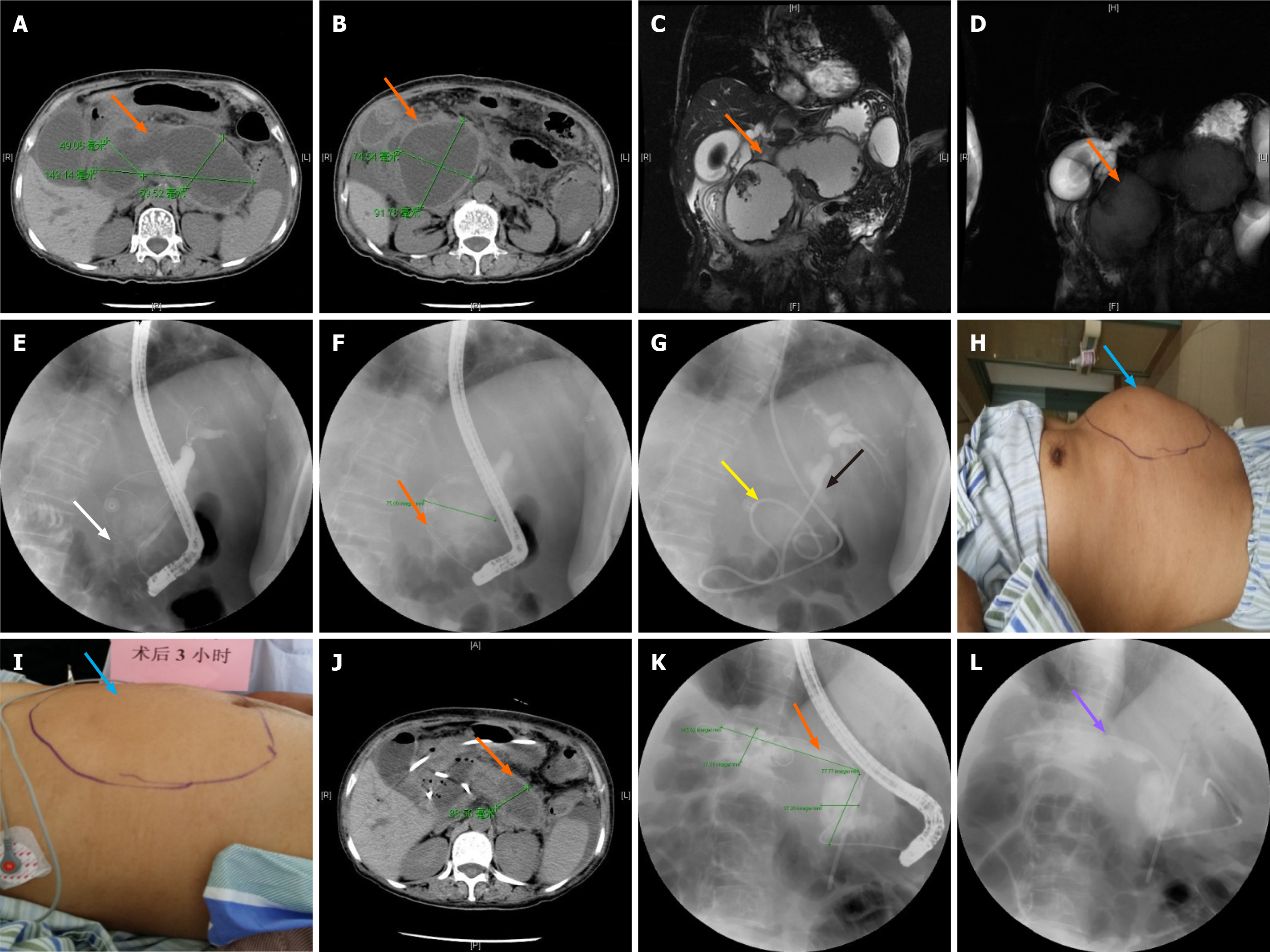
Figure 2 Sequential therapy of pancreatic pseudocysts using the two-step procedure (endoscopic naso-pancreatic drainage combined with endoscopic retrograde pancreatic drainage sequential therapy).
A and B: Location of the pancreatic pseudocyst shown by computed tomography (CT) (orange arrow); C and D: Location of the pancreatic pseudocyst shown by magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (orange arrow) using the T2 weighted image sequence (C) and balanced turbo field echo sequence (D); E: Successful duodenal papilla intubation followed by a guide wire into the pancreatic duct (white arrow); F: Pancreatic pseudocyst shown by imaging of the guide wire into the pancreatic duct (orange arrow); G: Naso-pancreatic duct placed in the pancreatic pseudocyst (yellow arrow is the naso-pancreatic duct, and black arrow is the biliary stent); H: Abdomen of the patient before naso-pancreatic duct placement (blue arrow); I: Changes in the abdomen 3 h after naso-pancreatic duct placement (blue arrow); J: Pancreatic pseudocyst shown by CT 1 wk after naso-pancreatic duct placement (orange arrow); K: Pancreatic pseudocyst shown by guide wire and radiography after removal of the naso-pancreatic duct via endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (orange arrow); L: Placement of the pancreatic duct stent after removal of the naso-pancreatic duct (purple arrow).
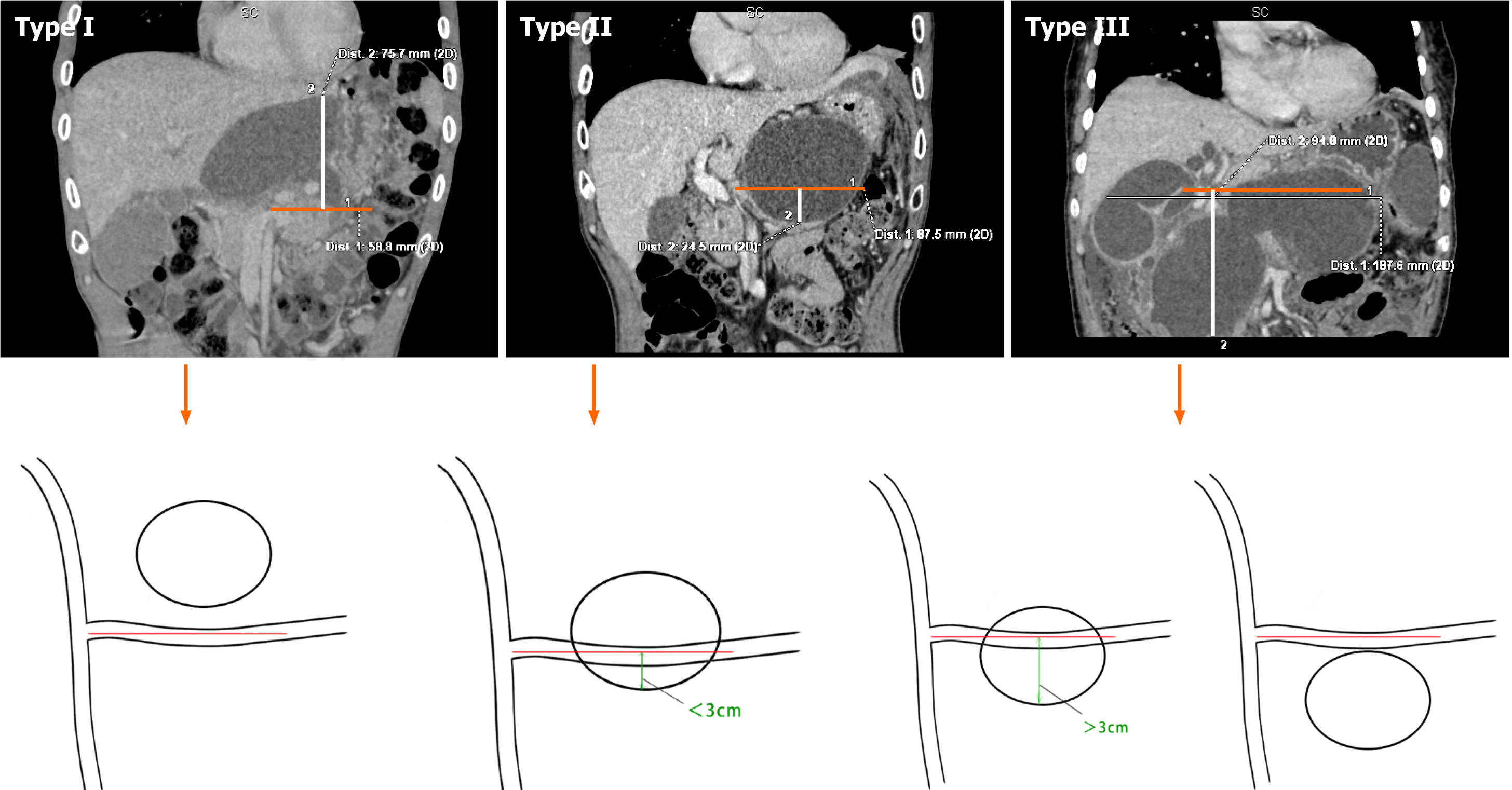
Figure 3 Three cyst types (Xinqiao classification) based on the relationship between the pancreatic pseudocyst and the splenic vein (the orange line on the horizontal axis is the splenic vein plane, and the white line on the vertical axis indicates the distance between the cyst and the splenic vein plane).
Type I: Pancreatic pseudocyst above the splenic vein plane; Type II: Pancreatic pseudocyst located partially above the splenic vein and partially within 3 cm below the splenic vein; Type III: Pancreatic pseudocyst located below the splenic vein (greater than 3 cm or the entire cyst is below the splenic vein).
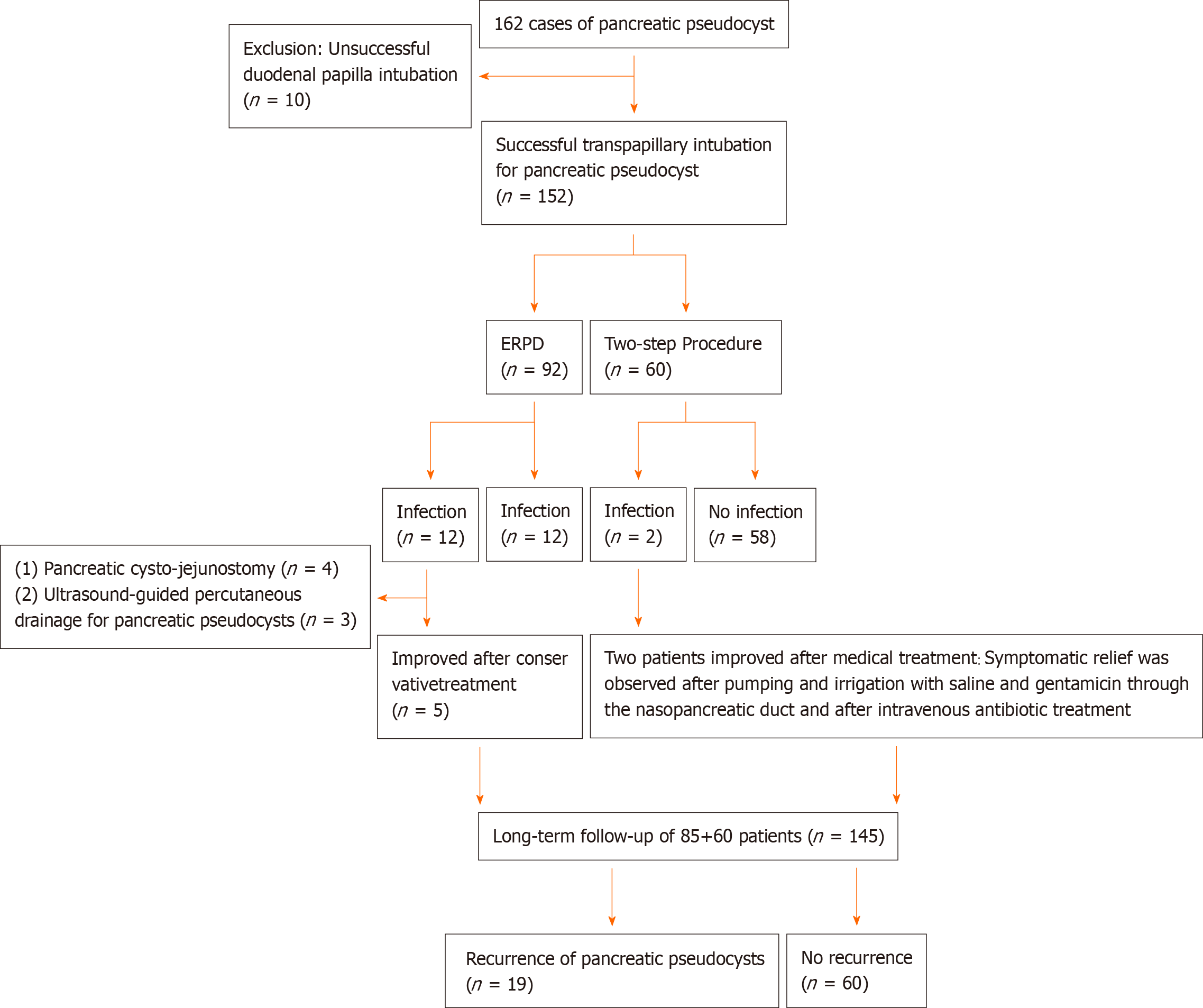
Figure 4 Flow diagram of patient enrollment.
ERPD: Endoscopic retrograde pancreatic drainage.
- Citation: He YG, Li J, Peng XH, Wu J, Xie MX, Tang YC, Zheng L, Huang XB. Sequential therapy with combined trans-papillary endoscopic naso-pancreatic and endoscopic retrograde pancreatic drainage for pancreatic pseudocysts. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(22): 6254-6267
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i22/6254.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i22.6254