Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 6, 2021; 9(19): 5245-5251
Published online Jul 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i19.5245
Published online Jul 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i19.5245
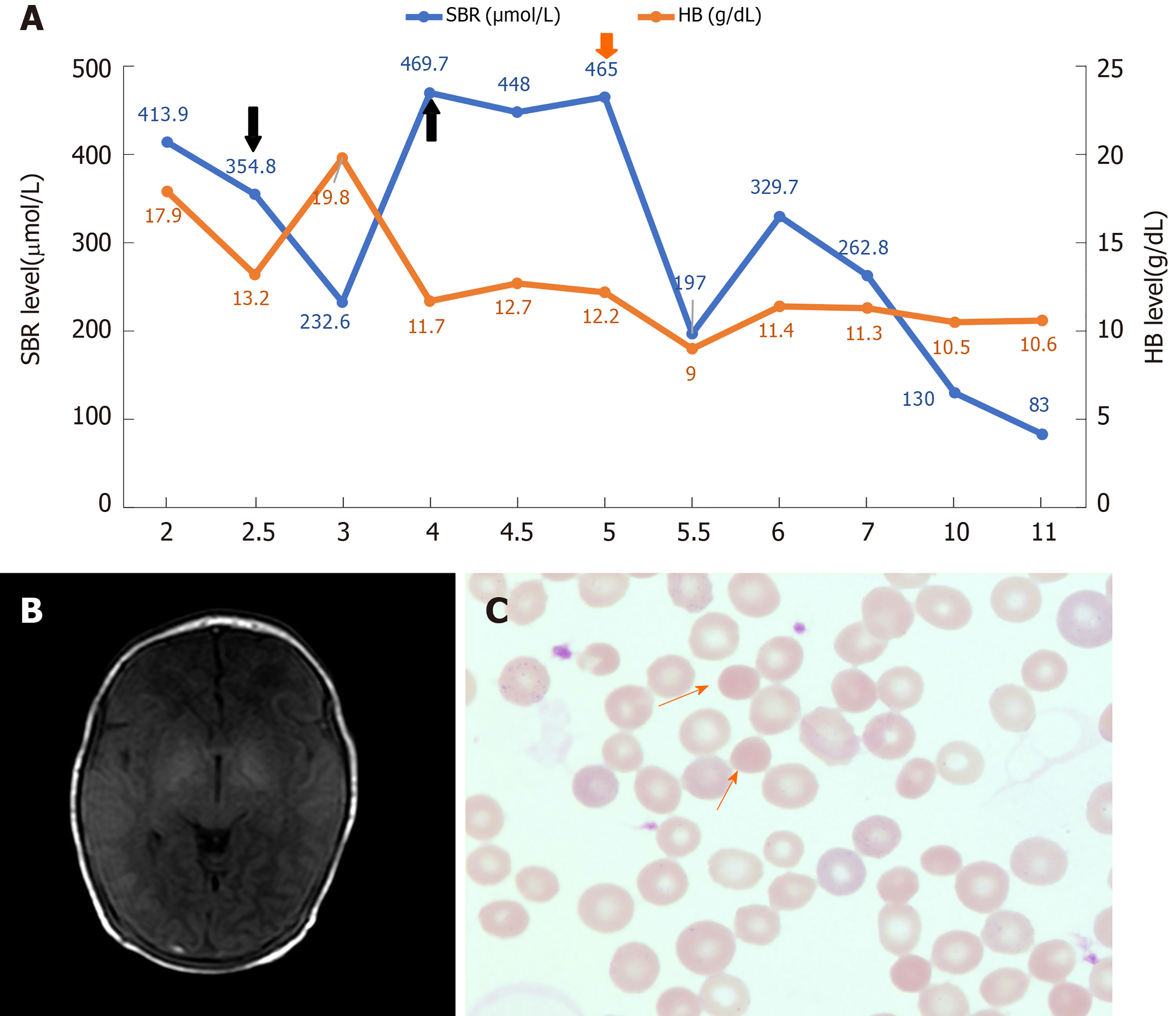
Figure 1 The representative clinical characteristics, imaging findings, and peripheral blood smears results.
A: The dynamic changes of serum bilirubin (SBR) (blue) and hemoglobin (HB) (orange) levels during hospitalization. The treatment of exchange transfusion and plasmapheresis are indicated by the black and red arrow respectively. The number on the X axis represents the number of days after birth; B: The imaging finding of axial T1-weighted brain magnetic resonance imaging sequence done at 1 wk after birth; C: Morphology of erythrocytes in the blood smear (Wright-Giemsa stain; magnification, × 1000). The spherocyte is indicated by the orange arrows.
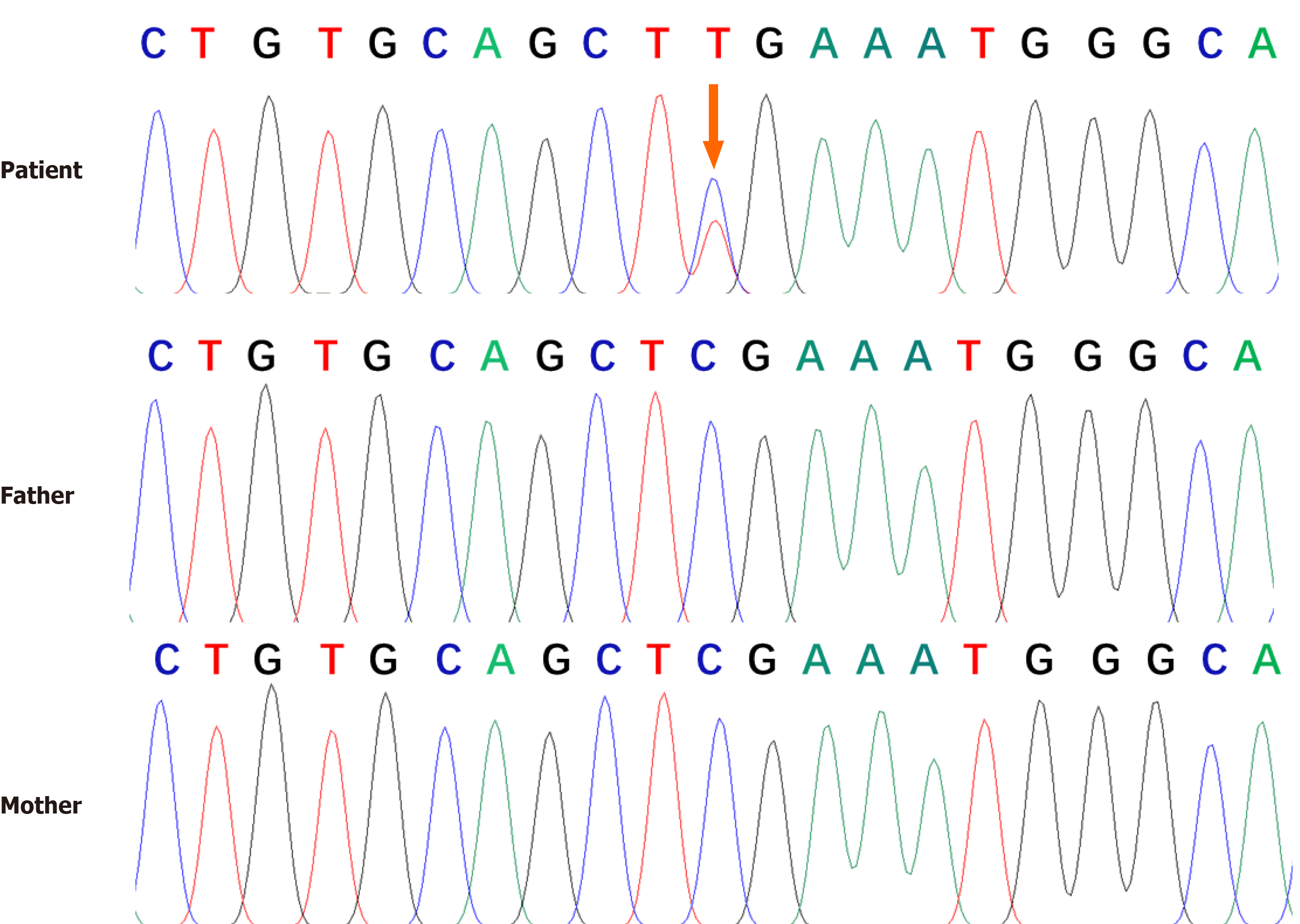
Figure 2 Genomic sequence of the patient.
Genetic analysis revealed a heterozygous null mutation in the patient’s ankyrin gene [c.841C > T (p. Arg281Ter)]. No genetic mutations were found in his parents. The arrows indicated the mutation site.
- Citation: Wang JF, Ma L, Gong XH, Cai C, Sun JJ. Severe hyperbilirubinemia in a neonate with hereditary spherocytosis due to a de novo ankyrin mutation: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(19): 5245-5251
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i19/5245.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i19.5245