Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 6, 2021; 9(19): 4939-4958
Published online Jul 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i19.4939
Published online Jul 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i19.4939
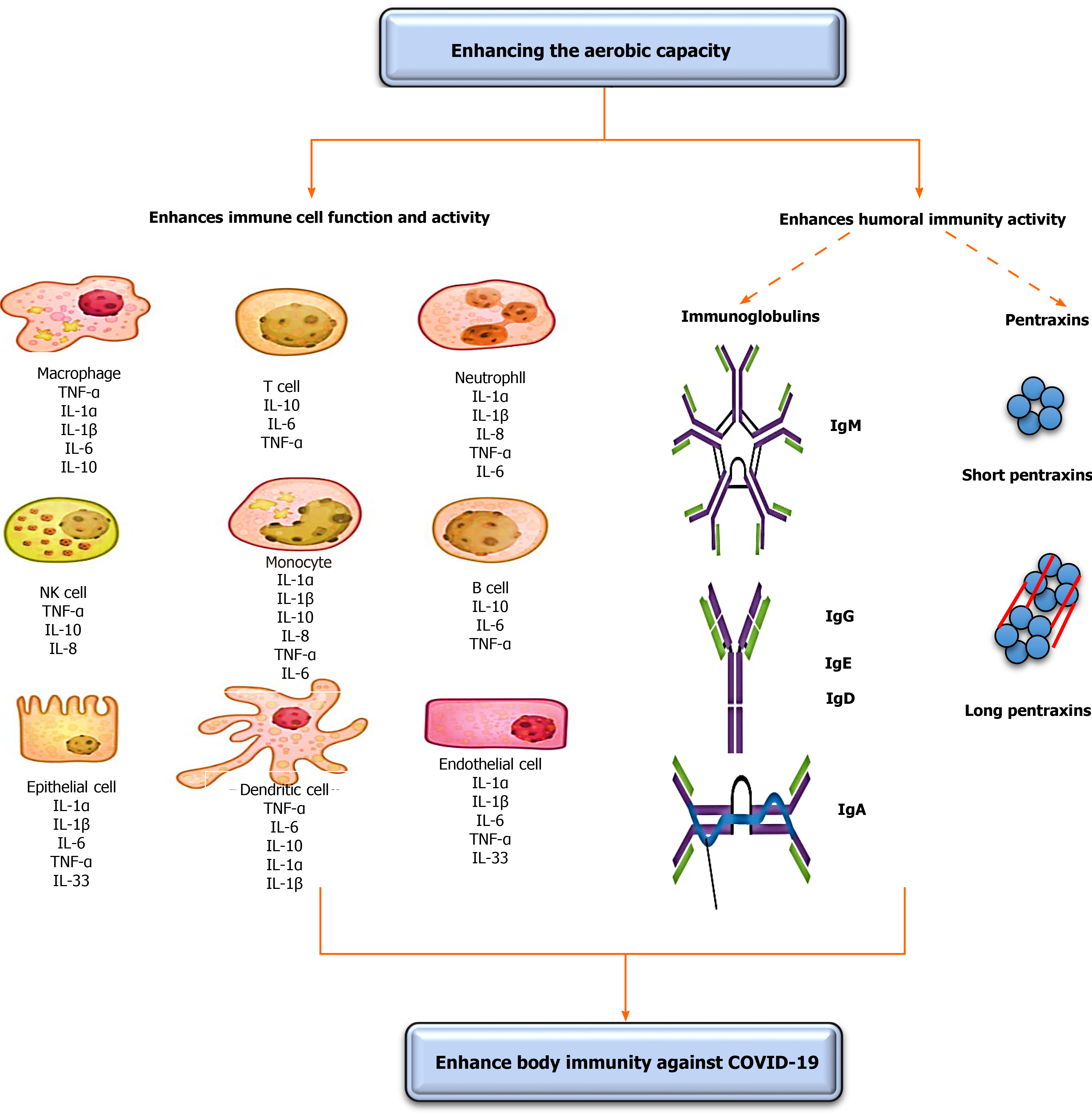
Figure 1 Effect of increasing the aerobic capacity on immunity.
This diagram illustrates possible mechanisms of increasing oxygenation capacity in improving the immunity. These possible mechanisms include increasing the function and activity of immune cells, immunoglobulins, and pentraxins. COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019; Ig: Immunoglobulin; IL: Interleukin; NK: Natural killer; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
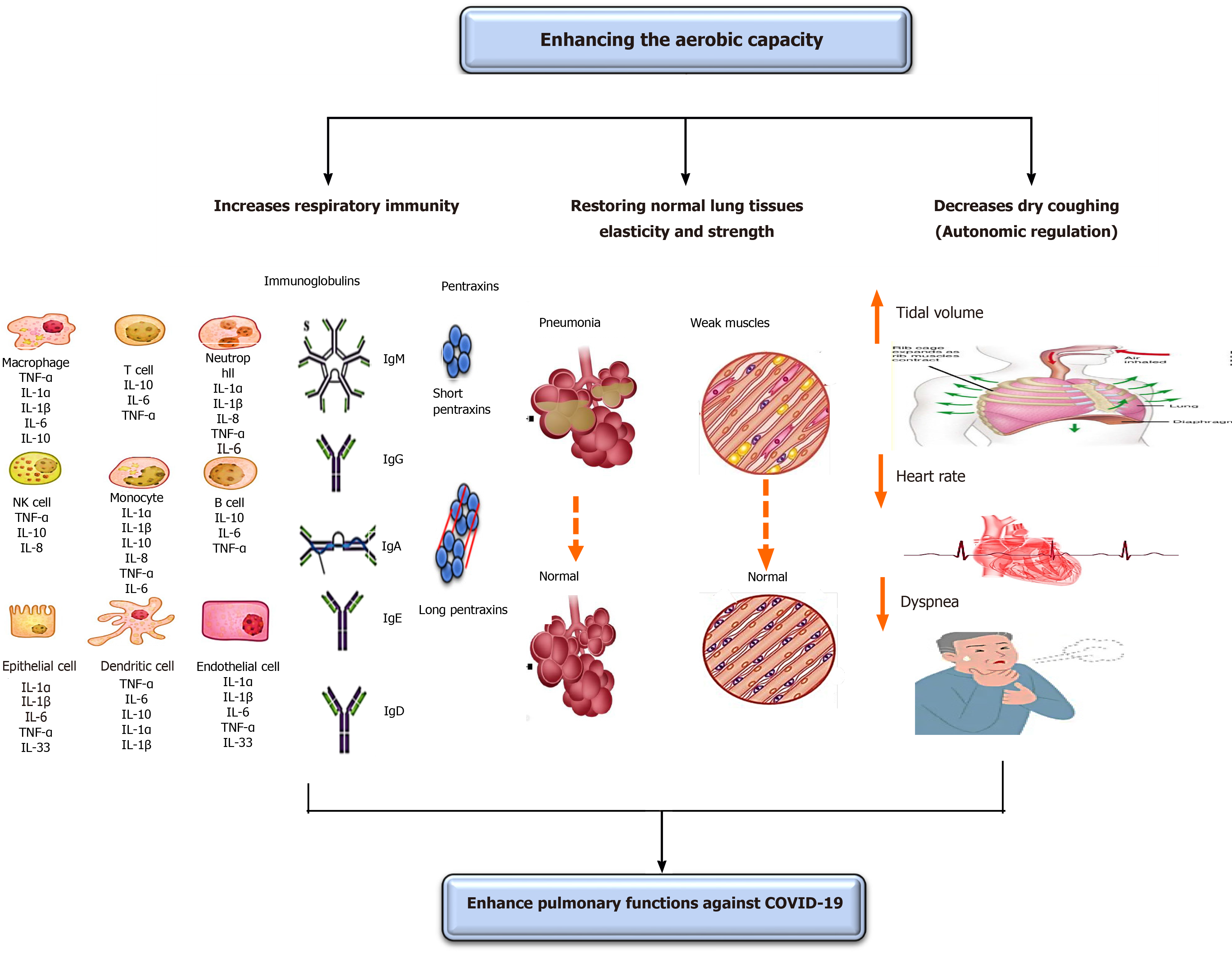
Figure 2 Effect of increasing the aerobic capacity on pulmonary functions.
This diagram illustrates possible mechanisms of increasing oxygenation capacity in improving pulmonary functions. These possible mechanisms include increasing the function of pulmonary immunity, restoring normal lung elasticity and strength, and decreasing coughing through autoimmune regulations. COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019; Ig: Immunoglobulin; IL: Interleukin; NK: Natural killer; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
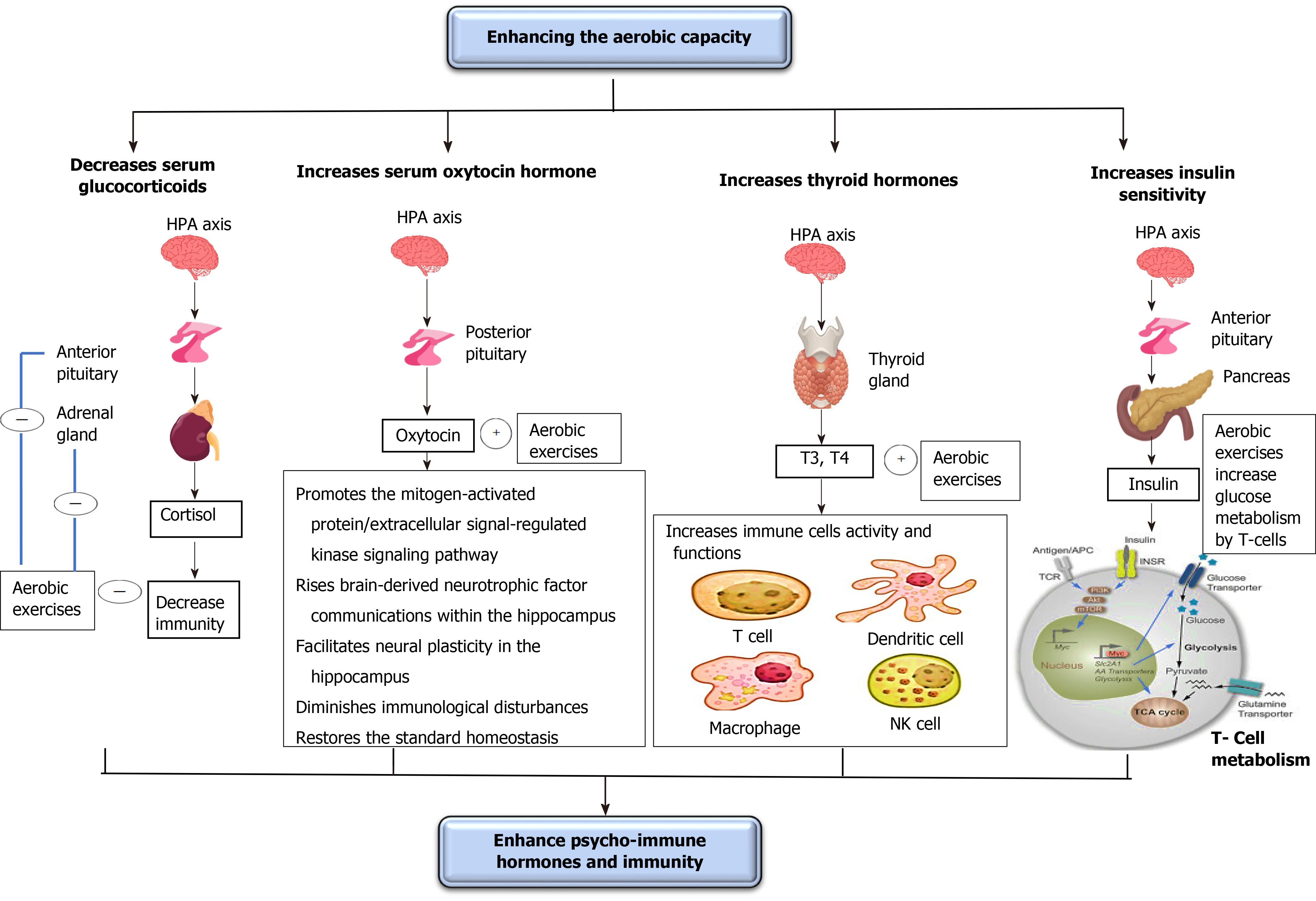
Figure 3 Effect of increasing the aerobic capacity on psycho-immune hormones.
This diagram illustrates the possible mechanisms of increasing oxygenation capacity in improving the psycho-immune hormones and immunity. These possible mechanisms include decreasing serum glucocorticoids and insulin sensitivity and increasing glucocorticoids and oxytocin hormones. HPA: Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal; NK: Natural killer.
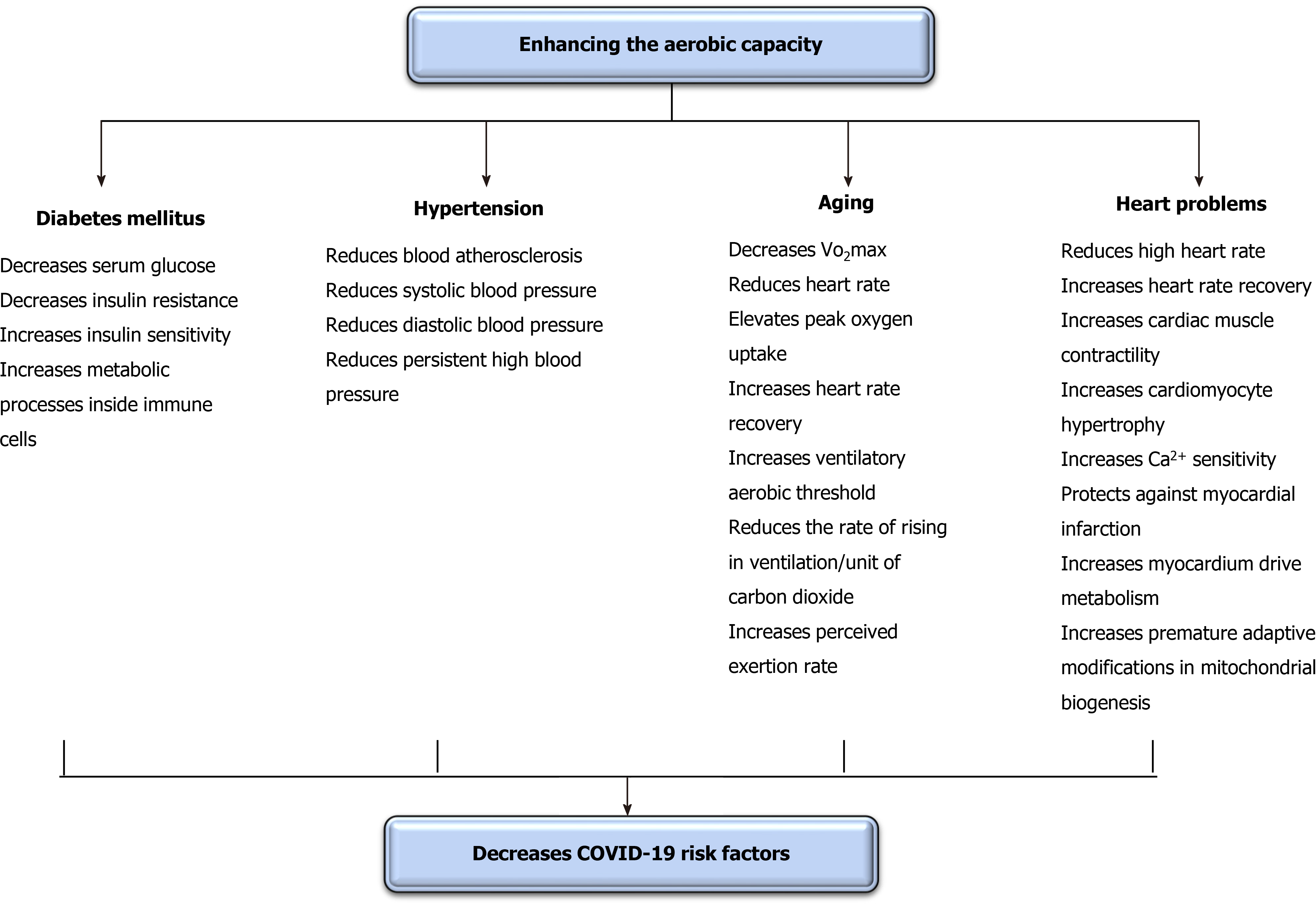
Figure 4 Effect of increasing the aerobic capacity as a defensive role in coronavirus disease 2019.
This diagram illustrates possible mechanisms of increasing oxygenation capacity to decrease the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 risk factors, associated disorders, and death rates. The effects of increasing the oxygenation capacity include its effects in decreasing the incidence of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, aging, and heart problems. COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019.
- Citation: Mohamed A, Alawna M. Enhancing oxygenation of patients with coronavirus disease 2019: Effects on immunity and other health-related conditions . World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(19): 4939-4958
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i19/4939.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i19.4939