Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 6, 2021; 9(16): 4007-4015
Published online Jun 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i16.4007
Published online Jun 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i16.4007
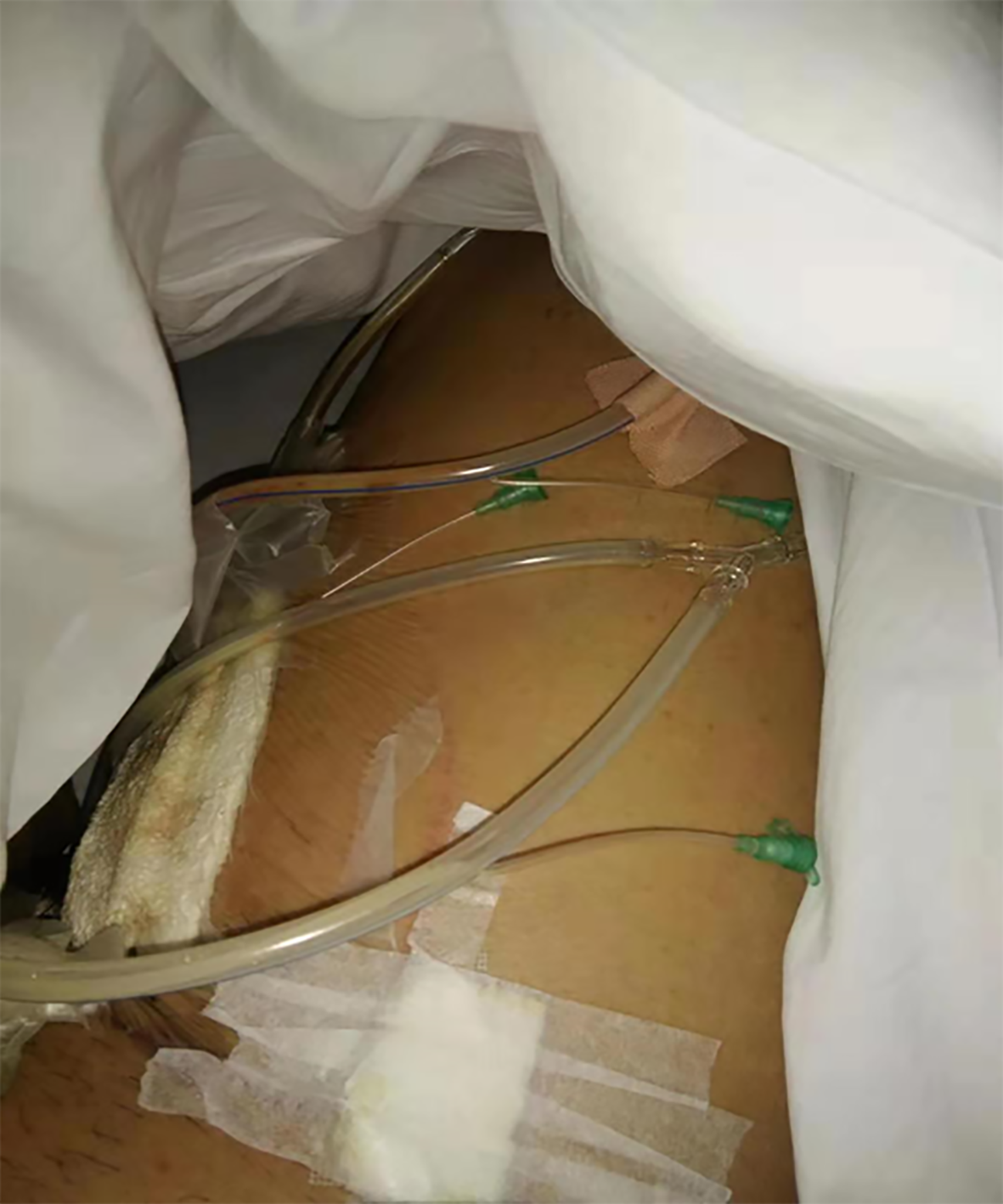
Figure 1 Negative pressure drainage for part of the wound.
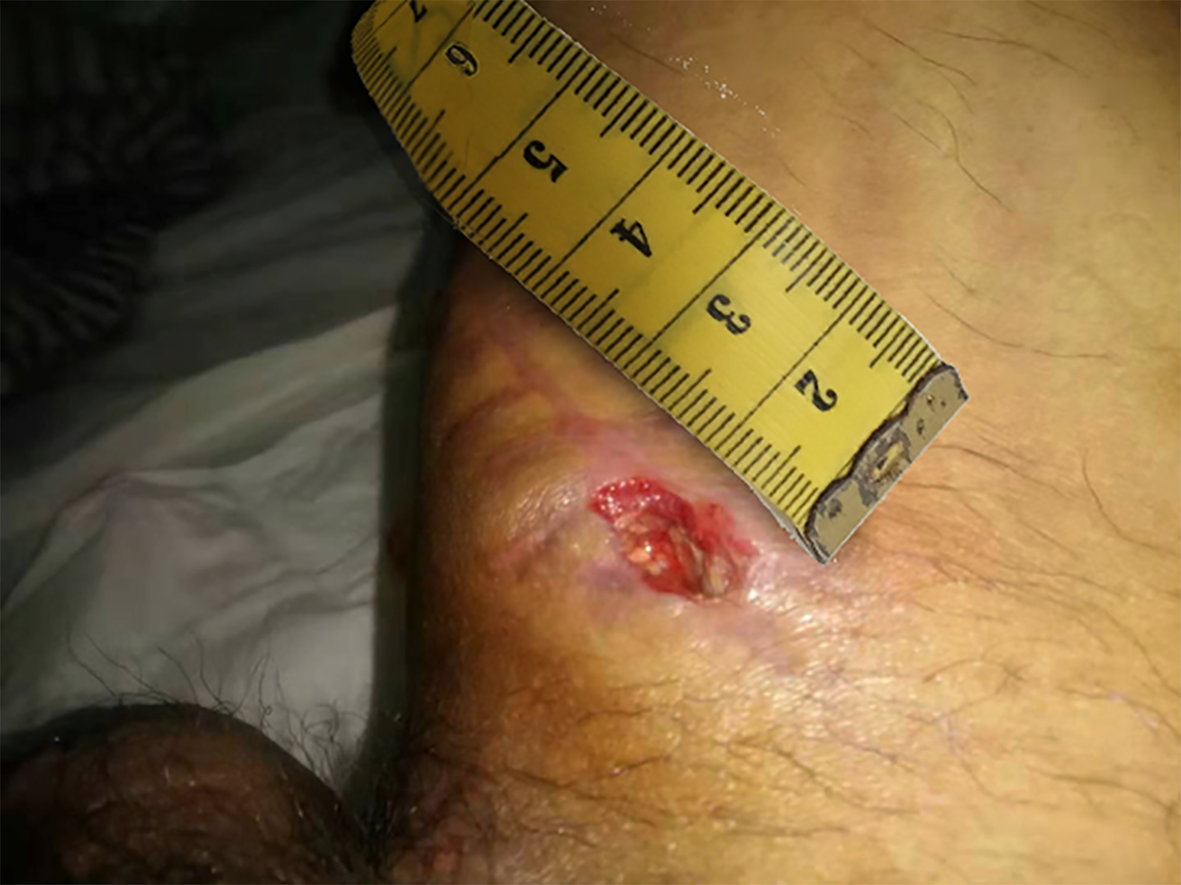
Figure 2 Wound formation after surgical incision rupture.
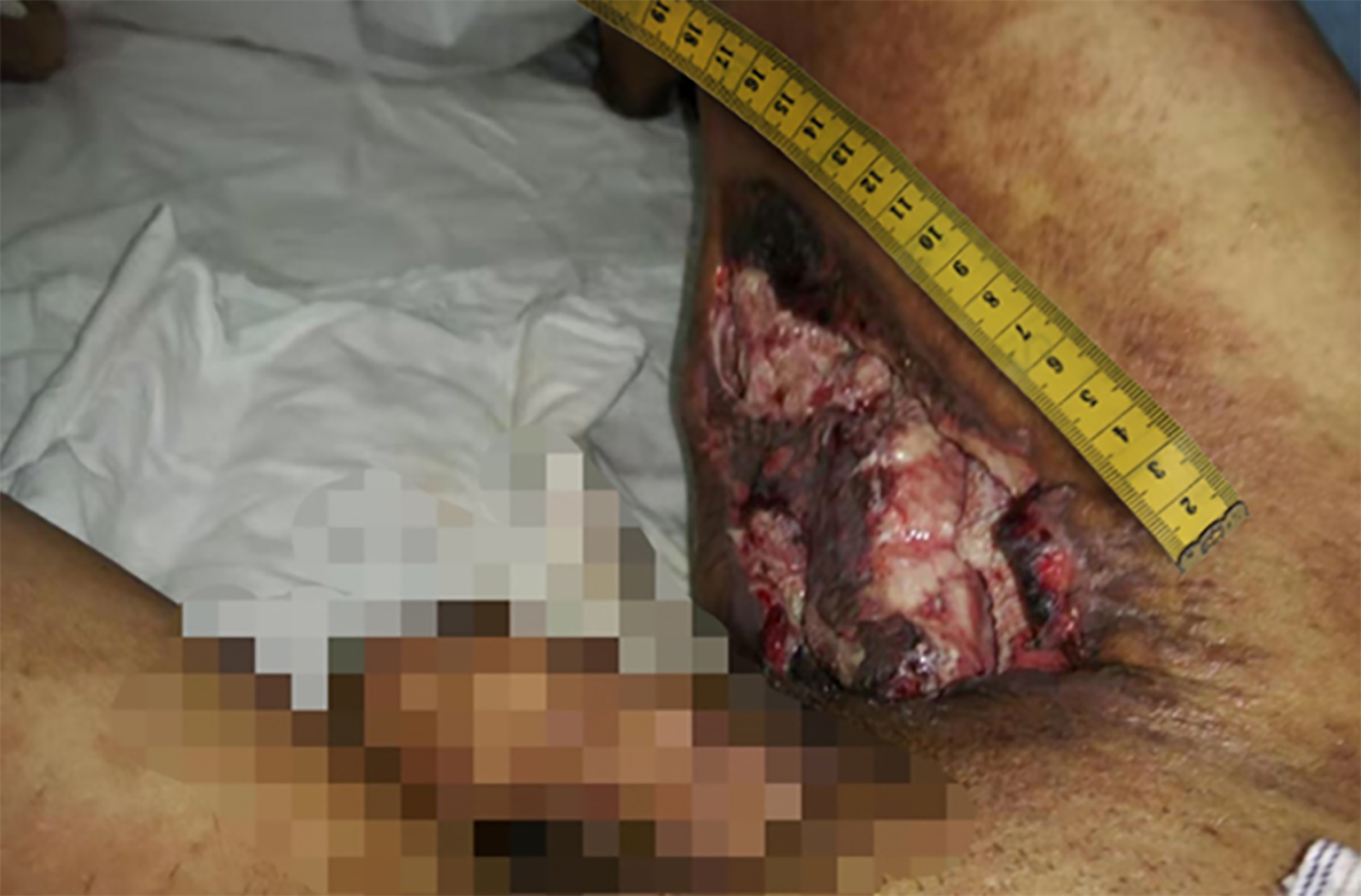
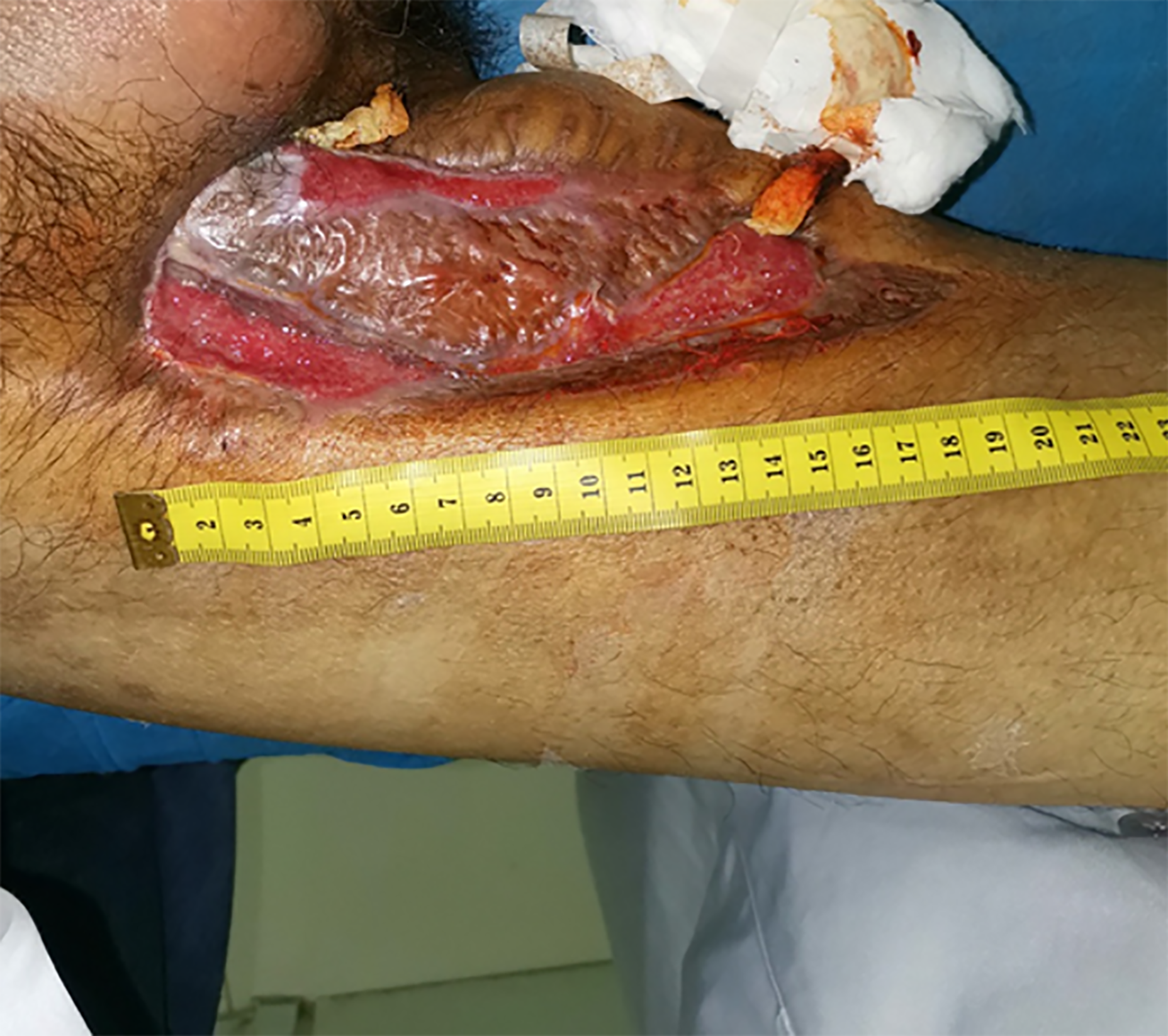
Figure 3 The wound after debridement and dressing change.
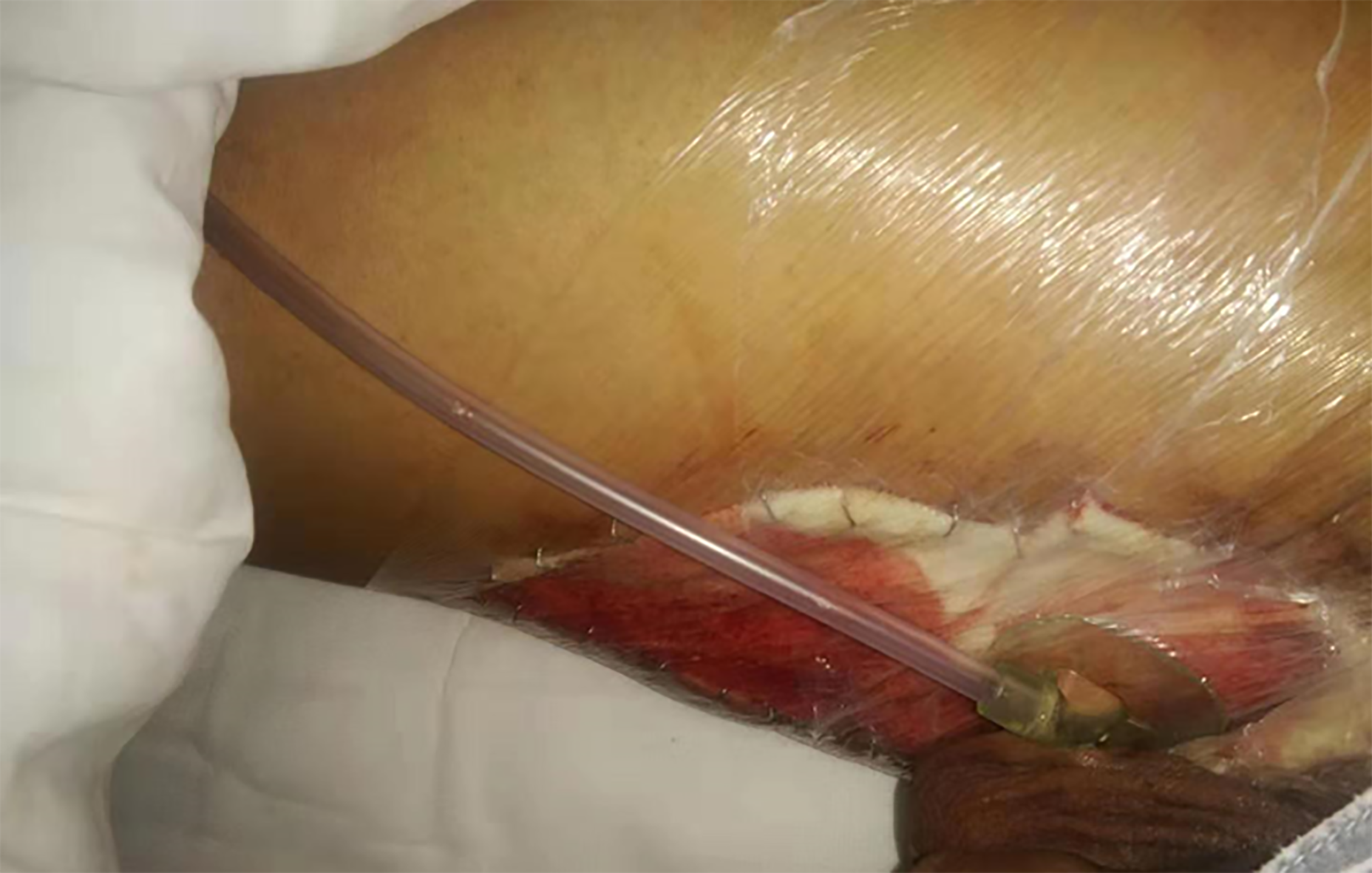
Figure 4 Wound skin grafting and vacuum suction.
Figure 5 Skin lesions and sinus after skin grafting.
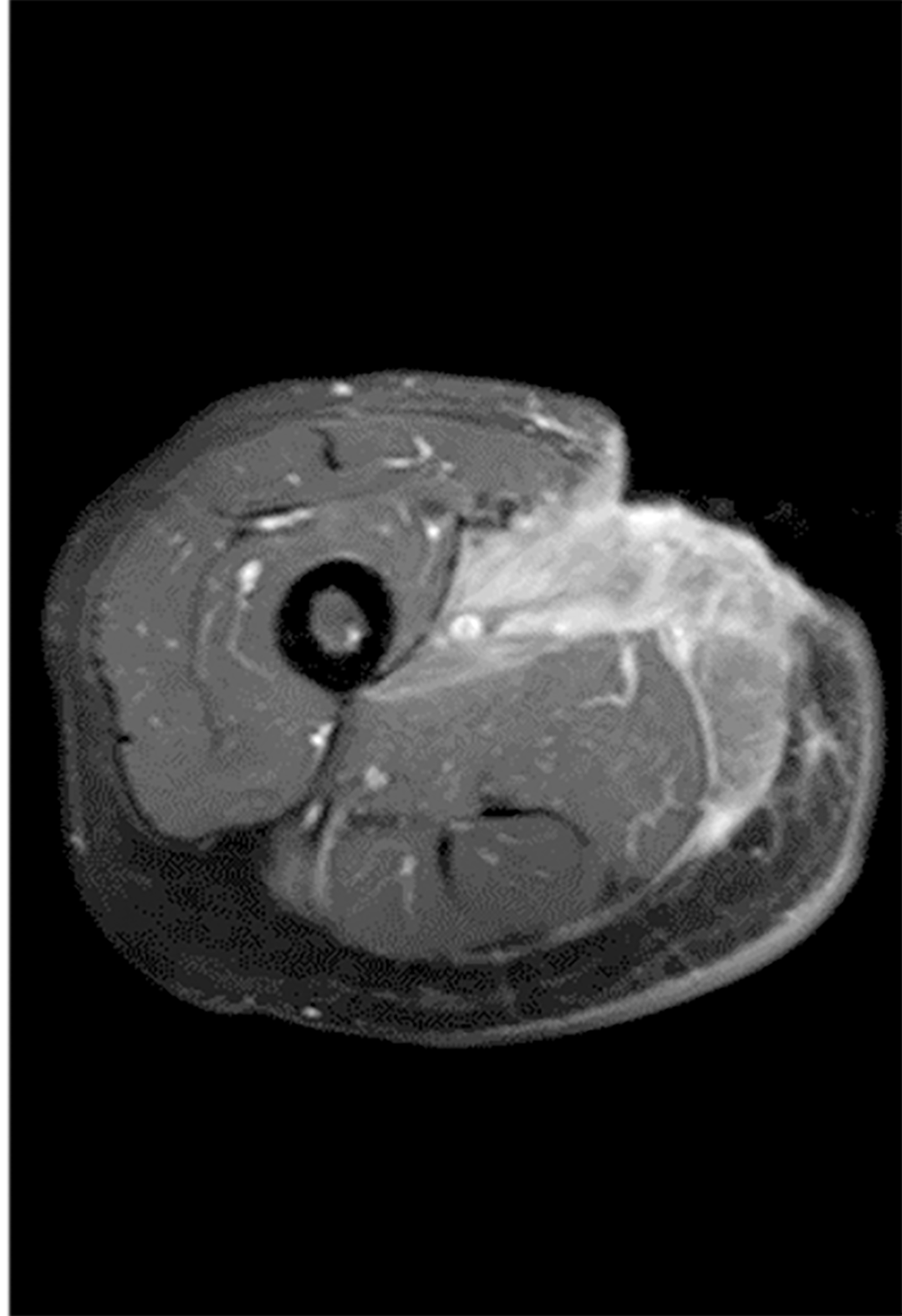
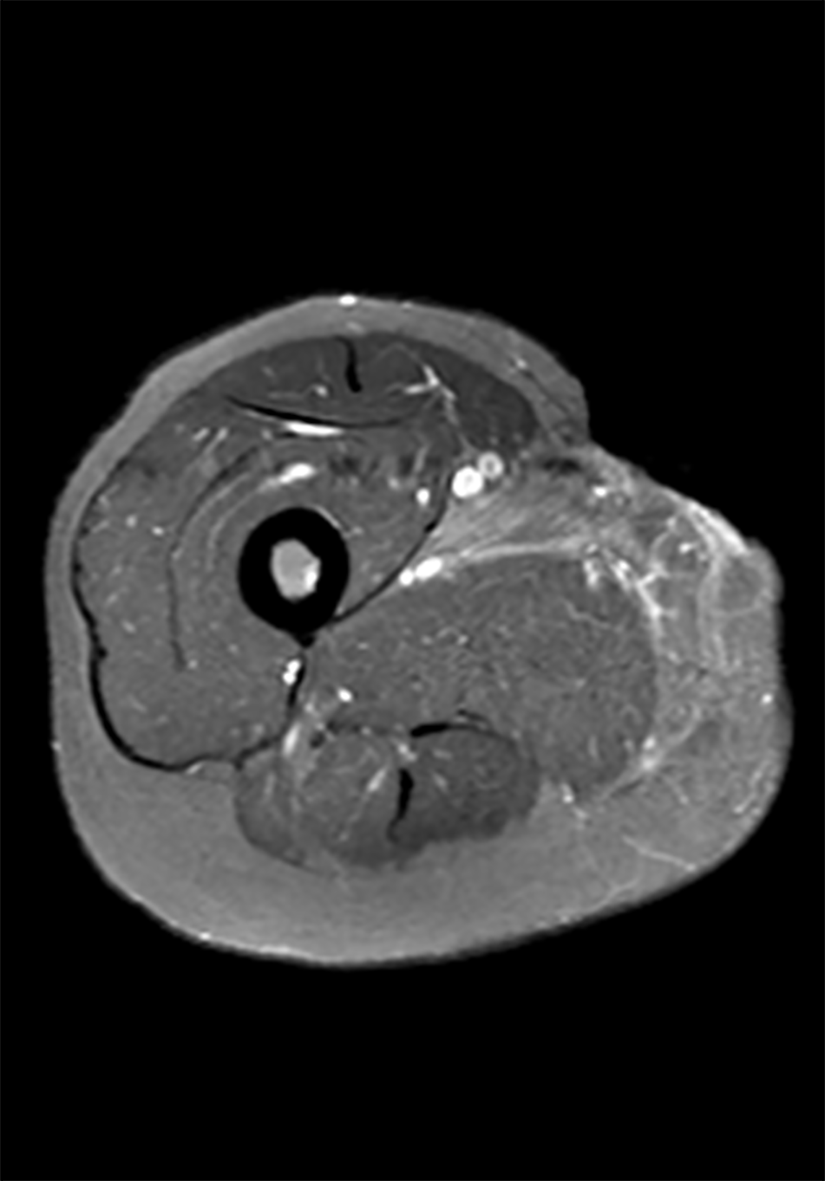
Figure 6 T1-weighted short TI inversion recovery enhancement: Local epidermal tissue defect on the inner right thigh, and strengthening of the medial muscle tissue.
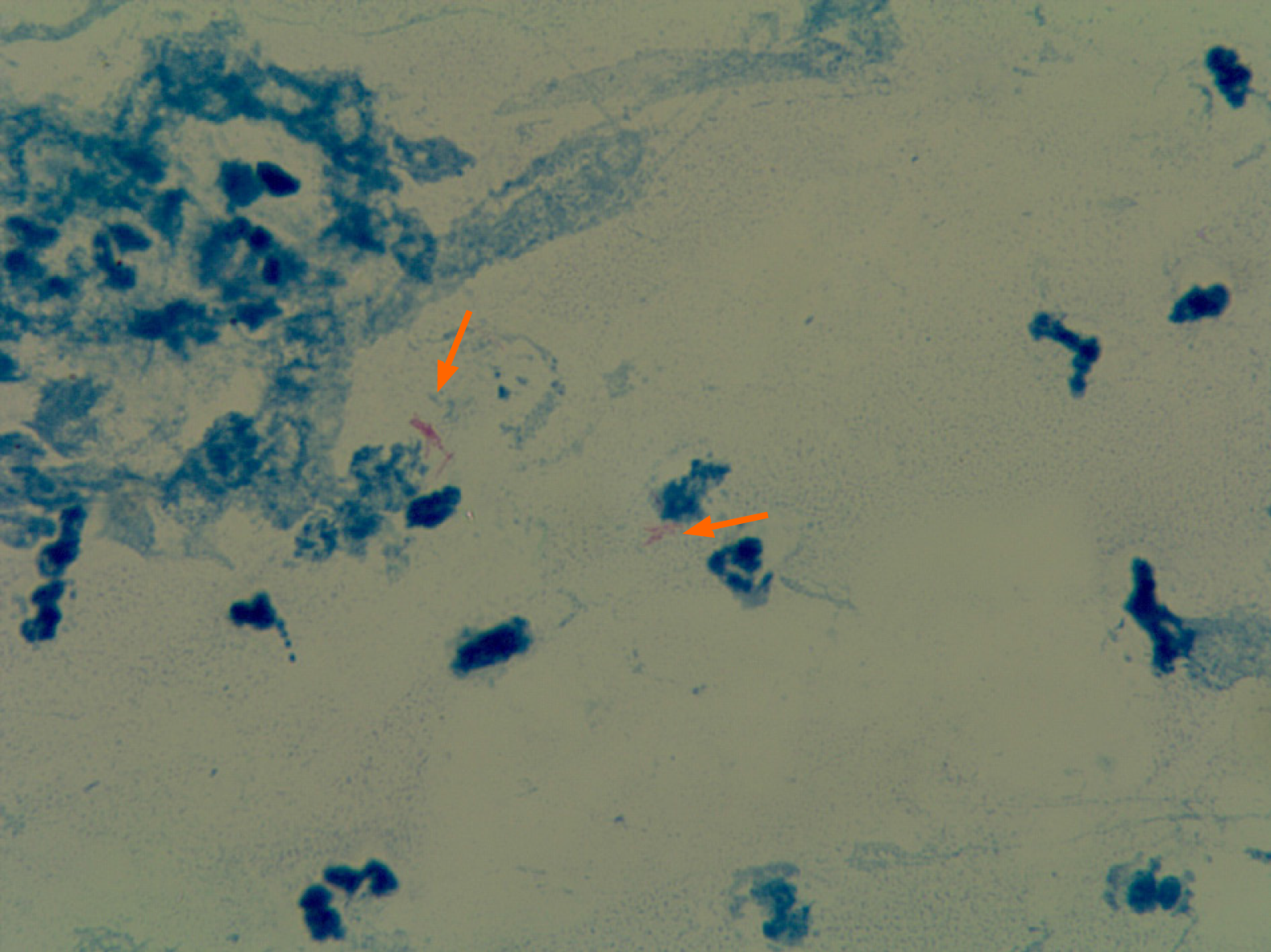
Figure 7 Bacterial culture of pyogenic fluids.
The arrows indicate acid-fast bacilli. Magnification: 100 ×.
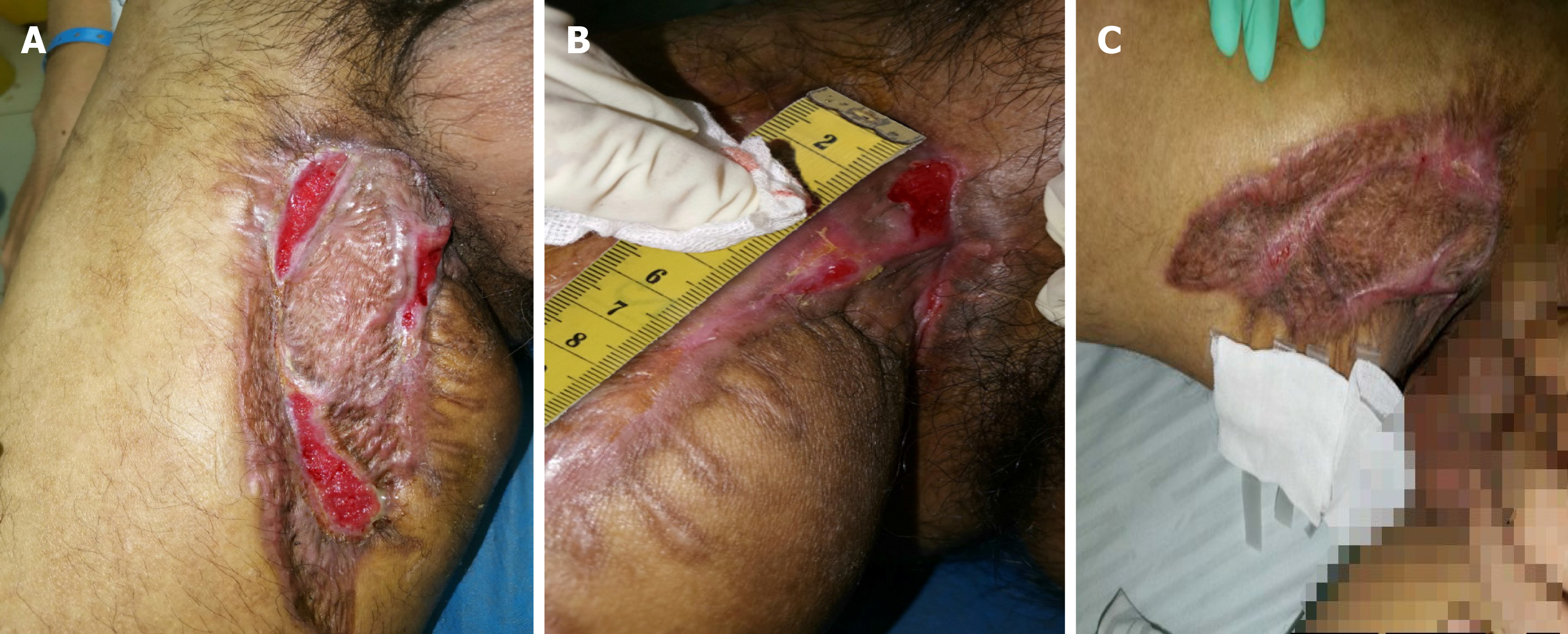
Figure 8 Symptoms of the patient after treatment.
A: Two weeks after the dressing change for part of the wound and anti-tuberculosis treatment; B: One month after the dressing change for part of the wound and anti-tuberculosis treatment; C: Forty-five days after the dressing change for part of the wound and anti-tuberculosis treatment.
Figure 9 T1-weighted short TI inversion recovery enhancement: Extent of lesion enhancement was significantly reduced and the degree of enhancement was reduced.
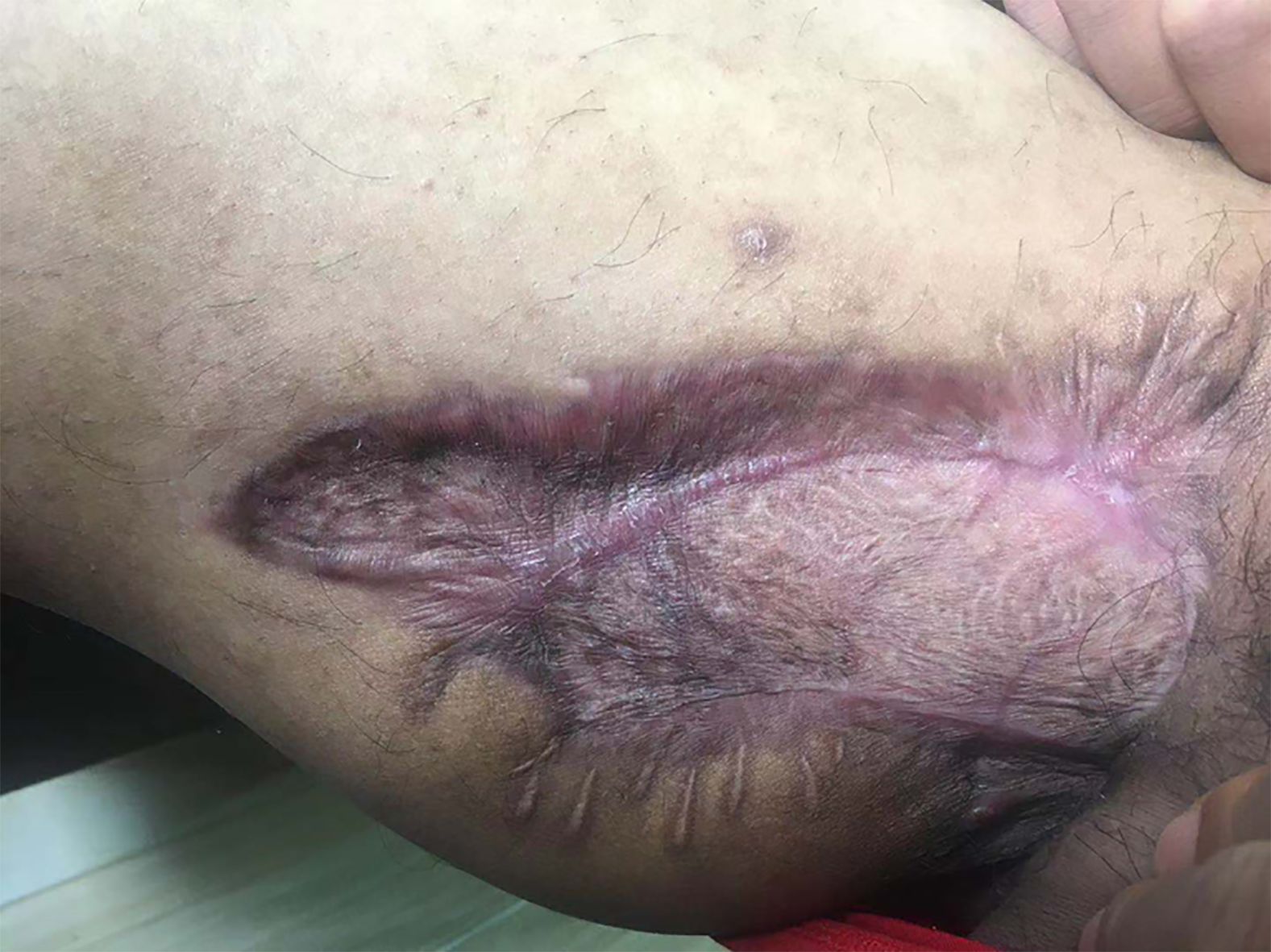
Figure 10 Two months after discharge.
- Citation: Gao LJ, Huang ZH, Jin QY, Zhang GY, Gao MX, Qian JY, Zhu SX, Yu Y. Delayed diagnosis and comprehensive treatment of cutaneous tuberculosis: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(16): 4007-4015
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i16/4007.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i16.4007