Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 26, 2021; 9(12): 2763-2777
Published online Apr 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i12.2763
Published online Apr 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i12.2763
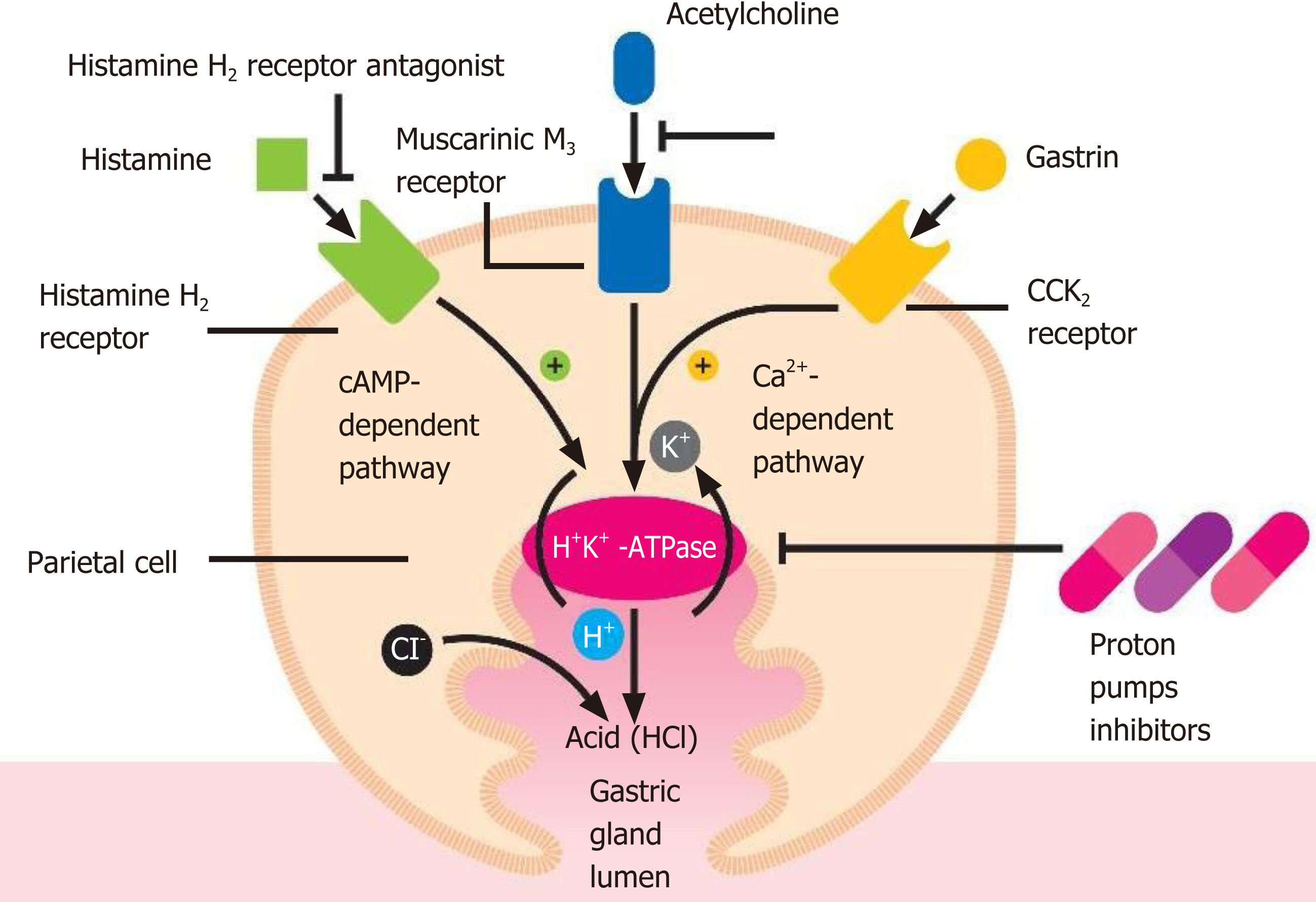
Figure 1 Parietal cell activation by histamine is followed by an intracellular increase in the cAMP-dependent protein kinase cascade (adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate), while gastrin and acetylcholine result in an intracellular increase in the calcium (Ca2+)-dependent cascade, all leading to insertion into the apical membrane and to activation of the H-K-ATPase.
HCl: Hydrochloric acid.
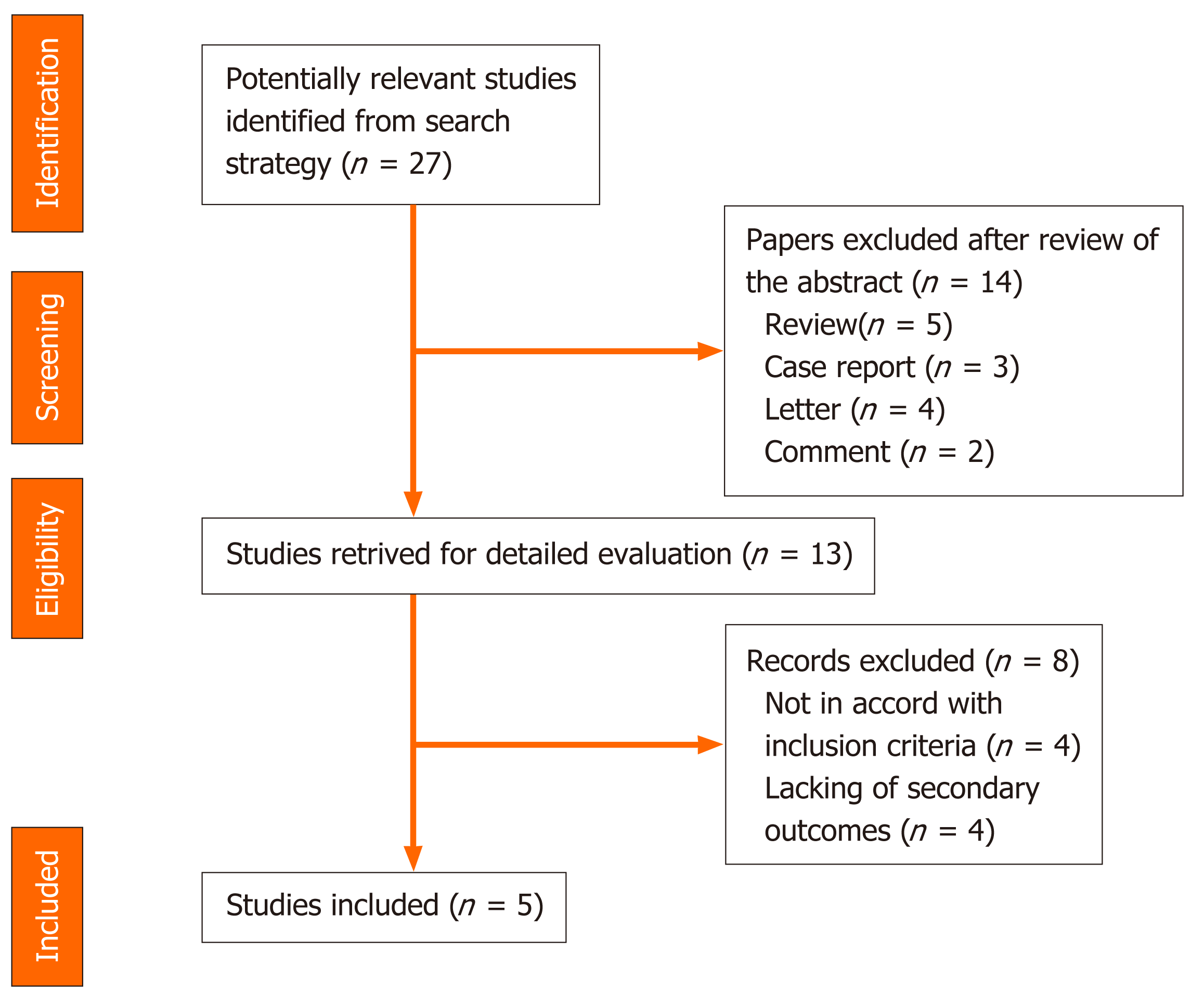
Figure 2 Summary of study identification and selection.
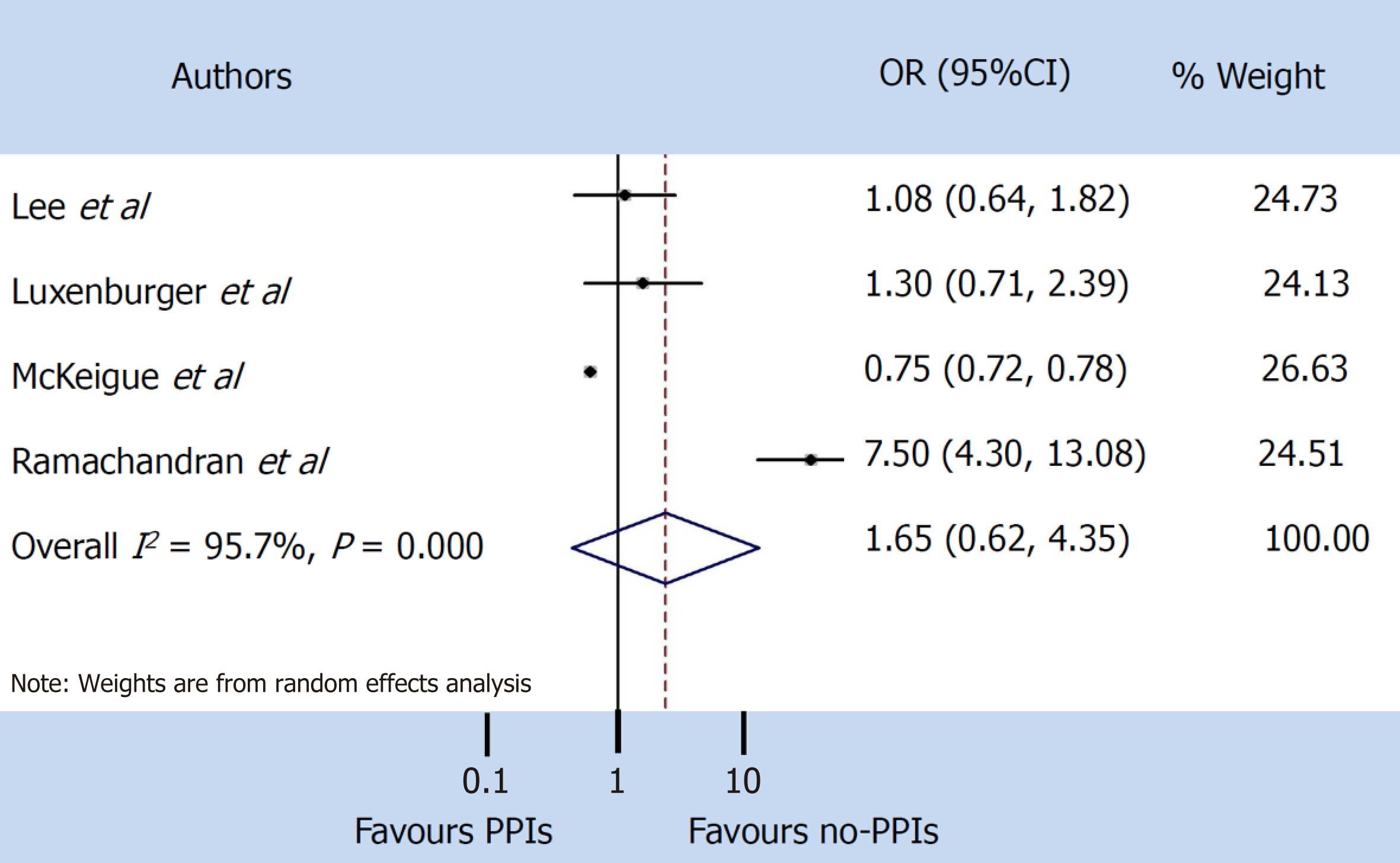
Figure 3 Severe events.
PPIs: Proton pump inhibitors; CI: Confidence interval; OR: Odds ratio.
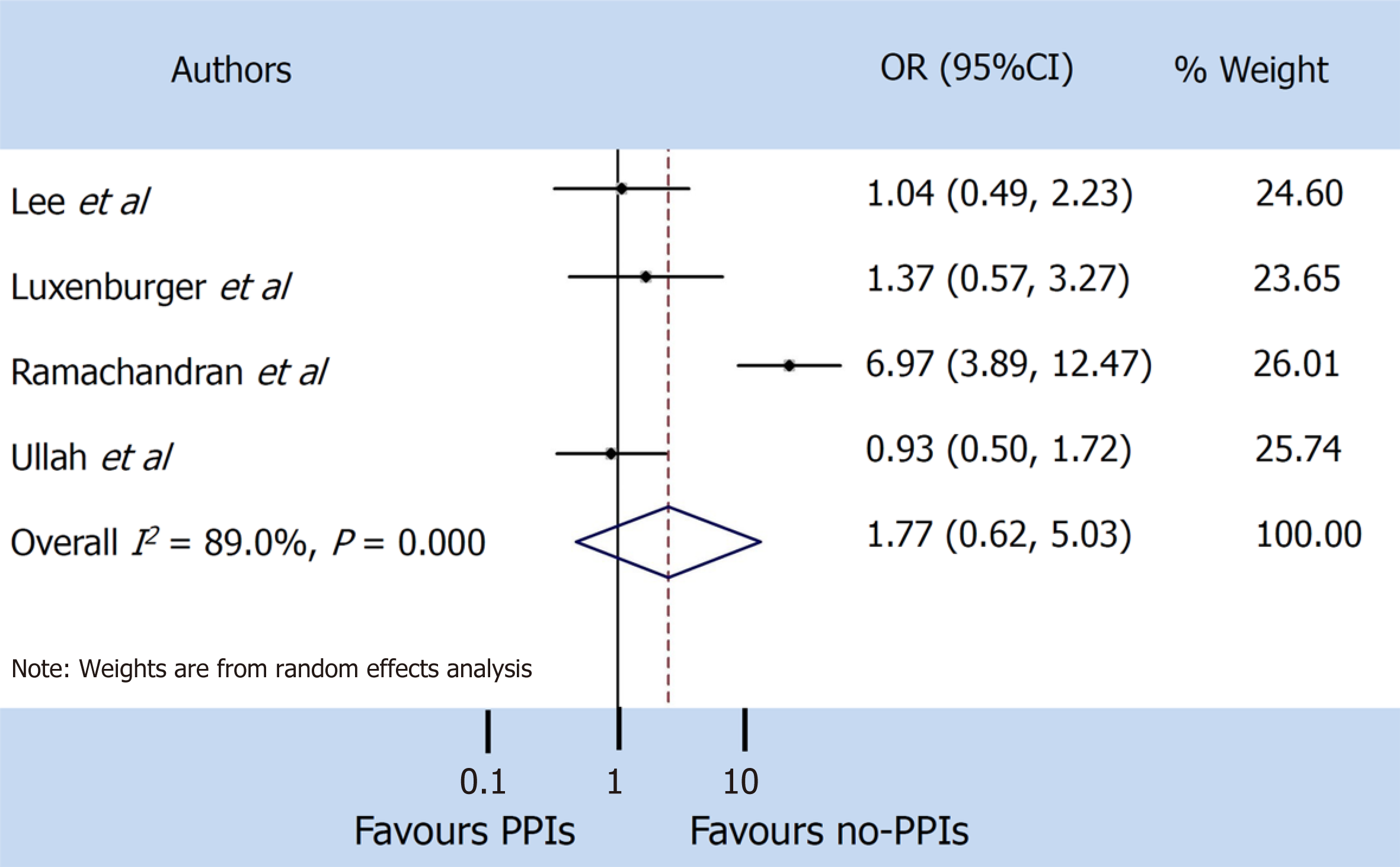
Figure 4 Mortality.
PPIs: Proton pump inhibitors; CI: Confidence interval; OR: Odds ratio.
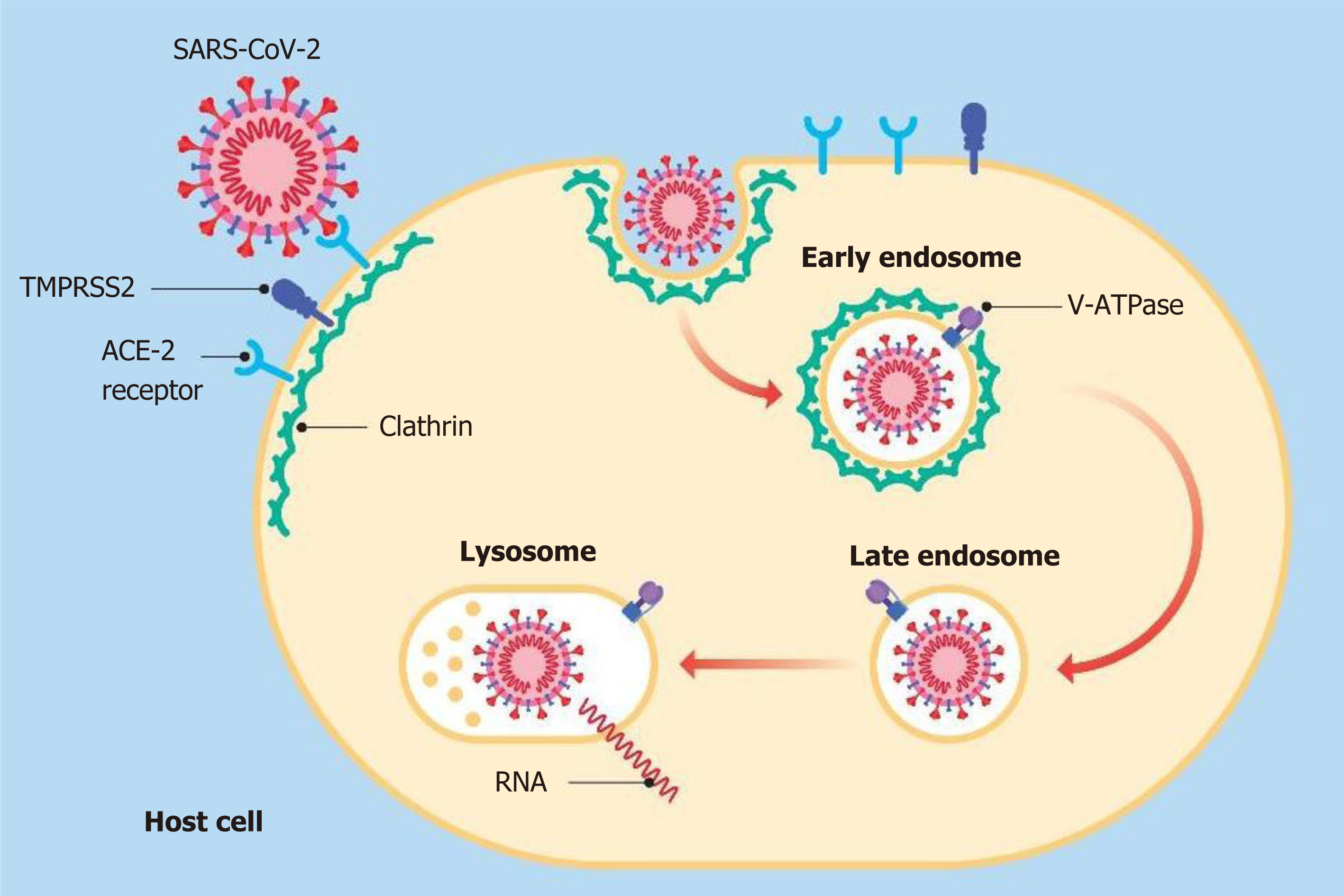
Figure 5 After the virus binds to its respective receptors, a "dimple" forms on the host cell membrane.
This inward fold resulting from the initial endocytosis gives rise to the formation of a clathrin-coated vesicle (early endosome). Later, the vesicle loses this coating (late endosome) and merges with the lysosome for degradation. SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; ACE-2: Angiotensin converting enzyme 2; TMPRSS2: Serine protease transmembrane 2; V-ATPase: Vacuolar ATPase.
- Citation: Zippi M, Fiorino S, Budriesi R, Micucci M, Corazza I, Pica R, de Biase D, Gallo CG, Hong W. Paradoxical relationship between proton pump inhibitors and COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(12): 2763-2777
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i12/2763.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i12.2763